根据预测的目标推荐使用相应的模块,包括蛋白质结构预测、抗体-抗原复合物结构预测、蛋白-小分子复合物结构预测、完整抗体IgG结构预测、环肽结构预测和RNA结构预测等。推荐使用AlphaFold3 like结构预测模型Protenix、Boltz-1、Chai-1、HelixFold3等,这些模型在常规的蛋白质结构、小分子配体、核酸分子(包括DNA和RNA)的预测精度上与AF3相当。
| 模块/流程名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Structure Prediction (Protenix) | AlphaFold3 like结构预测模型,基于字节跳动AML AI4Science团队的Protenix模型 |
| Structure Prediction (Helixfold3) | AlphaFold3 like结构预测模型,基于百度螺旋桨PaddleHelix团队的HelixFold3模型 |
| Structure Prediction (Chai-1) | AlphaFold3 like结构预测模型,基于Chai Discovery, Inc.公司的Chai-1模型 |
| Structure Prediction (Boltz-1) | AlphaFold3 like结构预测模型,基于MIT麻省理工的Boltz-1模型 |
| Multi-Model Structure Prediction流程 | 集成了3款AF3-like模型(Protenix、Boltz-1、Chai-1),一次调用多个模型进行结构预测 |
| Protein Structure Prediction (AlphaFold2.3.2) | 推荐用于蛋白质结构预测、抗体-抗原复合物结构预测 |
| Protein Structure Prediction (ESMFold) | 推荐用于抗体可变区单体结构预测 |
| Protein Structure Prediction (RaptorX-Single) | 单序列的蛋白质结构预测 |
| Immune Protein Structure Prediction | 免疫蛋白结构预测 |
| Biomolecular Structure Prediction (RFAA) | 蛋白-小分子复合物结构预测 |
| IgG Modeling | 完整抗体IgG结构预测 |
| Cyclic Peptide Structure Prediction | 环肽结构预测 |
| RNA Secondary Structure Prediction | RNA二级结构预测 |
| RNA 3D Structure Prediction | RNA三级结构预测 |
Based on the predicted targets, it is recommended to use the corresponding modules, including protein structure prediction, antibody-antigen complex structure prediction, protein-small molecule complex structure prediction, full antibody IgG structure prediction, cyclic peptide structure prediction, and RNA structure prediction, etc. It is recommended to use structure prediction models like AlphaFold3, such as Protenix, Boltz-1, Chai-1, and HelixFold3. These models achieve prediction accuracy comparable to AF3 for conventional protein structures, small molecule ligands, and nucleic acid molecules (including DNA and RNA).
| Module/Process Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Structure Prediction (Protenix) | An AlphaFold3-like structure prediction model based on the Protenix model developed by ByteDance’s AML AI4Science team. |
| Structure Prediction (HelixFold3) | An AlphaFold3-like structure prediction model based on the HelixFold3 model developed by Baidu’s PaddleHelix team. |
| Structure Prediction (Chai-1) | An AlphaFold3-like structure prediction model based on the Chai-1 model developed by Chai Discovery, Inc. |
| Structure Prediction (Boltz-1) | An AlphaFold3-like structure prediction model based on the Boltz-1 model developed by MIT (Massachusetts Institute of Technology). |
| Multi-Model Structure Prediction Workflow | Combines four AF3-like models (Protenix, Boltz-1, Chai-1, HelixFold3) to perform structure prediction by invoking multiple models simultaneously. |
| Protein Structure Prediction (AlphaFold2.3.2) | Recommended for protein structure prediction, antibody-antigen complex structure prediction |
| Protein Structure Prediction (ESMFold) | Recommended for antibody variable region monomer structure prediction |
| Protein Structure Prediction (RaptorX-Single) | Single-sequence protein structure prediction |
| Immune Protein Structure Prediction | Immune protein structure prediction |
| Biomolecular Structure Prediction (RFAA) | Protein-small molecule complex structure prediction |
| IgG Modeling | Full antibody IgG structure prediction |
| Cyclic Peptide Structure Prediction | Cyclic peptide structure prediction |
| RNA Secondary Structure Prediction | RNA secondary structure prediction |
| RNA 3D Structure Prediction | RNA tertiary structure prediction |
RMSD (Root Mean Square Deviation) 和 DockQ 都是评估分子结构相似性和对接模型质量的指标,但它们的应用范围和考量因素有所不同。
定义: RMSD 是衡量两个叠加的分子结构之间原子位置平均偏差的量度。它通过计算对应原子(通常是主链原子,如 Cα 原子,或所有重原子)在三维空间中的距离平方的均值,再开平方根得到。
应用场景:
特点:
定义: DockQ 是一个专门用于评估蛋白质-蛋白质对接模型质量的连续性指标,范围在 [0,1] 之间。它结合了多个衡量对接质量的关键因素,以提供一个更全面、更接近 CAPRI (Critical Assessment of PRediction of Interactions) 评估标准的单一分数。
组成部分: DockQ 综合了以下几个关键指标:
计算方式: DockQ 并非简单的线性组合,而是通过对这些组分进行非线性变换和组合得出的,旨在更好地重现 CAPRI 的质量分类(Incorrect, Acceptable, Medium, High)。
应用场景:
特点:
| 特征 | RMSD (Root Mean Square Deviation) | DockQ |
|---|---|---|
| 应用范围 | 广泛用于各种分子结构比较(蛋白质、小分子、构象变化) | 主要用于蛋白质-蛋白质对接模型质量评估 |
| 评估目标 | 衡量两个结构之间原子位置的几何相似性 | 衡量蛋白质-蛋白质对接模型在界面区域的准确性 |
| 考量因素 | 仅考虑原子位置的几何偏差 | 综合考虑界面 RMSD、配体 RMSD 和天然接触分数 |
| 结果形式 | 距离单位(Å),越小越好 | 0-1 之间的连续分数,越大越好 |
| 侧重点 | 全局或局部结构相似性 | 蛋白质相互作用界面的准确性和生物学相关性 |
| 与对接关系 | 可以作为对接评估的一个组成部分(如iRMSD, LRMSD) | 专门为蛋白质对接设计,整合了多个对接相关指标 |
简而言之,RMSD 是一个更通用的几何相似性度量,可以用于各种分子结构比较。而 DockQ 则是一个专门为蛋白质-蛋白质对接模型设计的高度集成的质量评估指标,它更全面地反映了对接的生物学相关性和准确性,因为它综合了界面几何精度和关键相互作用的正确性。在评估蛋白质-蛋白质对接时,DockQ 通常被认为是更优选和更具代表性的指标。
RMSD (Root Mean Square Deviation) and DockQ are both metrics used to evaluate molecular structure similarity and docking model quality, but they differ in their range of applications and considerations.
Definition: RMSD is a measure of the average deviation in atomic positions between two superimposed molecular structures. It is calculated by taking the square root of the mean of the squared distances between corresponding atoms (typically backbone atoms, such as Cα atoms, or all heavy atoms) in three-dimensional space.
Applications:
Characteristics:
Definition: DockQ is a continuous metric specifically designed to evaluate the quality of protein-protein docking models, ranging from [0,1]. It combines multiple key factors for assessing docking quality to provide a more comprehensive score that aligns closely with CAPRI (Critical Assessment of PRediction of Interactions) evaluation standards.
Components: DockQ integrates the following key metrics:
Calculation Method: DockQ is not a simple linear combination but is derived through nonlinear transformations and combinations of these components, aiming to better reproduce CAPRI’s quality classifications (Incorrect, Acceptable, Medium, High).
Applications:
Characteristics:
| Feature | RMSD (Root Mean Square Deviation) | DockQ |
|---|---|---|
| Scope of Application | Widely used for various molecular structure comparisons (proteins, small molecules, conformational changes) | Primarily used for evaluating the quality of protein-protein docking models |
| Evaluation Target | Measures geometric similarity of atomic positions between two structures | Measures the accuracy of the interface region in protein-protein docking models |
| Considered Factors | Considers only geometric deviations of atomic positions | Integrates interface RMSD, ligand RMSD, and fraction of native contacts |
| Result Format | Distance unit (Å), smaller is better | Continuous score between 0-1, higher is better |
| Focus | Global or local structural similarity | Accuracy and biological relevance of protein interaction interfaces |
| Relation to Docking | Can be a component of docking evaluation (e.g., iRMSD, LRMSD) | Specifically designed for protein docking, integrating multiple docking-related metrics |
In short, RMSD is a more general metric for geometric similarity, applicable to various molecular structure comparisons. DockQ, on the other hand, is a highly integrated quality assessment metric specifically designed for protein-protein docking models, providing a more comprehensive reflection of the biological relevance and accuracy of docking by integrating interface geometric precision and the correctness of key interactions. In evaluating protein-protein docking, DockQ is often considered a more preferred and representative metric.
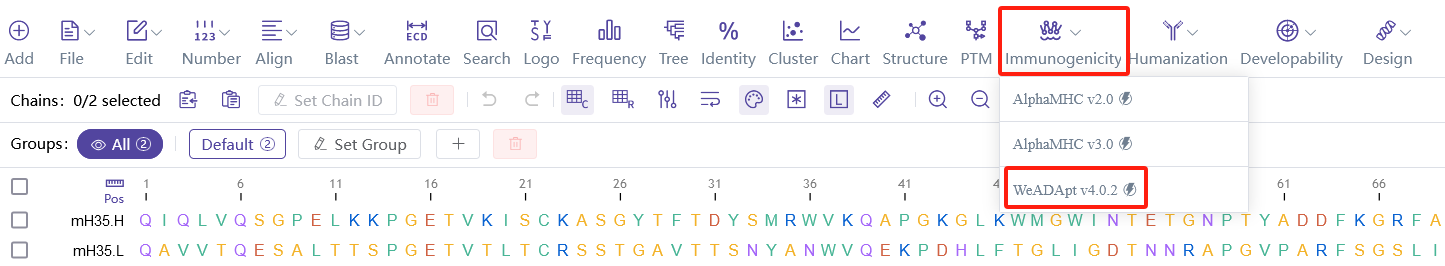
免疫原性预测已经历多个版本迭代,目前应用版本为:WeADApt v4.1.0, AlphaMHC v3.0 beta, AlphaMHC v2.0。
同时也可以从WeSeq中提交预测:WeSeq->Immunogenicity,界面更友好(推荐v4)。
Immunogenicity prediction has undergone multiple iterations, and the currently applied versions are:
You can also submit predictions from WeSeq: WeSeq->Immunogenicity, which offers a more user-friendly interface (supports v2/v3/v4).
热稳定性与蛋白的折叠自由能正相关,可能影响表达、纯度、PK等,优化方式包括基于物理的能量计算和ML/AI模型。
优化抗体稳定性,可使用Antibody Stability Optimization v3.1或Antibody Stability Optimization v3.0 plus MD或。
抗体稳定性优化流程介绍文档
优化蛋白稳定性,可使用Protein Stability Optimization v3.1或Protein Stability Optimization v3.0 plus MD。
蛋白稳定性优化流程介绍文档
预测蛋白质的绝对稳定性,可使用Absolute Folding Stability。
蛋白绝对稳定性预测介绍文档
预测蛋白稳定性相对结合自由能,可使用Protein FEP。
基于ThermoMPNN模型预测蛋白质单点突变的稳定性变化,可使用Mutation Energy of Stability (ThermoMPNN)。
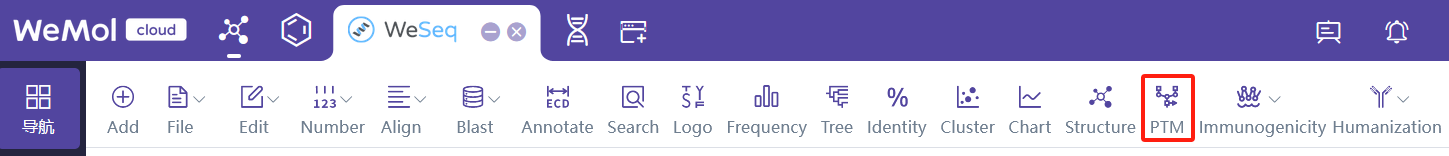
基于序列预测蛋白中潜在的PTM位点,可使用PTM Hotspot by Sequence。建议在WeSeq中进行分析:WeSeq->PTM。
基于结构预测蛋白中潜在的PTM位点,可使用PTM Hotspot by Structure。
基于ESMIF逆折叠模型,预测能提升结构稳定性的单点或多点突变,可使用Structure Evolution。
Thermal stability is positively correlated with the folding free energy of proteins, which may affect expression, purity, pharmacokinetics (PK), etc. Optimization methods include physics-based energy calculations and ML/AI models.
To optimize antibody stability, you can use Antibody Stability Optimization v3.0 or Antibody Stability Optimization v3.0 plus MD.
Antibody Stability Optimization Process Introduction Document
To optimize protein stability, you can use Protein Stability Optimization v3.0 or Protein Stability Optimization v3.0 plus MD.
Protein Stability Optimization Process Introduction Document
To predict the absolute stability of proteins, you can use Absolute Folding Stability.
Absolute Folding Stability Prediction Introduction Document
To predict the relative binding free energy of protein stability, you can use Protein FEP.
To predict the stability changes of protein single-point mutations based on the ThermoMPNN model, you can use Mutation Energy of Stability (ThermoMPNN).
To predict potential PTM sites in proteins based on sequence, you can use PTM Hotspot by Sequence. It is recommended to perform the analysis in WeSeq: WeSeq -> PTM.

To predict potential PTM sites in proteins based on structure, you can use PTM Hotspot by Structure.
可开发性包括蛋白表面patch分析、理化性质计算(含pI)、TAP原则、PTM(基于序列)、基于结构的异构化预测、断裂位点预测等。
成药性一键综合评价
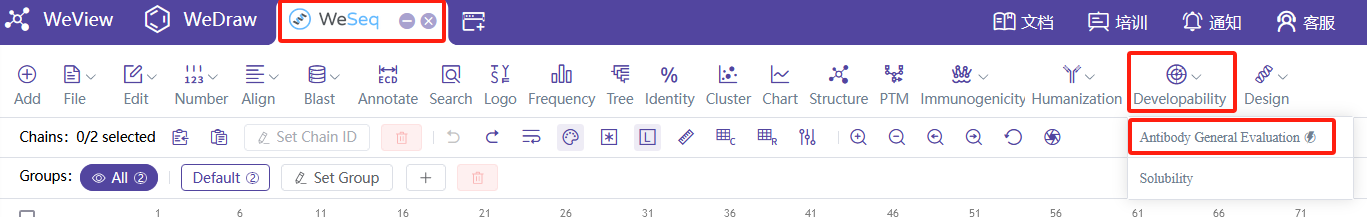
进行成药性一键综合评价,可以使用抗体可开发性预测流程,Antibody Developability Properties v4或Antibody Developability Properties v3。
同时,也可以在WeSeq中进行抗体可开发性预测分析,WeSeq->Developability->Antibody General Evaluation。
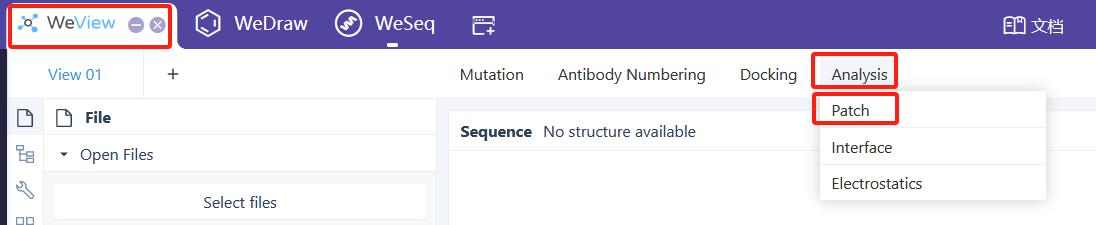
Patch分析
建议从WeView中运行:WeView->Analysis->Patch。Patch分析介绍文档
PTM预测
基于序列的PTM预测,建议直接在WeSeq运行:WeSeq->PTM。PTM预测介绍文档
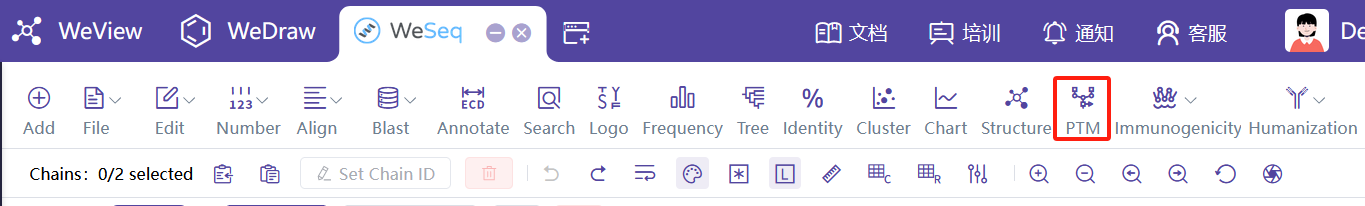
基于结构的PTM预测,可以直接在模块中运行PTM Hotspot by Structure。
抗体成药性预测(TAP)
溶解度预测
聚集度预测
Developability includes protein surface patch analysis, physicochemical property calculations (including pI), TAP principles, PTM (based on sequence), structure-based isomerization prediction, cleavage site prediction, etc.
For a comprehensive evaluation of druggability, you can use the antibody developability prediction workflows, Antibody Developability Properties v4 or Antibody Developability Properties v3.
Additionally, you can perform antibody developability prediction analysis in WeSeq: WeSeq -> Developability -> Antibody General Evaluation.

It is recommended to run from WeView: WeView -> Analysis -> Patch. Patch Analysis Introduction Document

For sequence-based PTM prediction, it is recommended to run directly in WeSeq: WeSeq -> PTM. PTM Prediction Introduction Document

For structure-based PTM prediction, you can run directly in the module PTM Hotspot by Structure.
序列分析包括序列编号、多序列比对、测序数据分析、频率分析、序列突变等。
序列编号
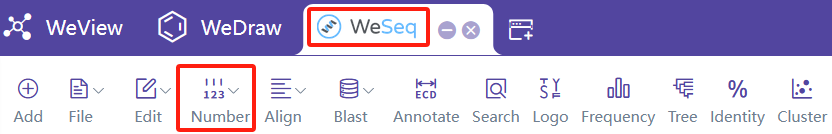
进行抗体序列编号,建议在WeSeq中运行:WeSeq->Number。序列编号介绍文档
多序列比对
进行多序列比对,建议在WeSeq中运行:WeSeq->Align。多序列比对介绍文档

测序数据分析
进行测序数据分析,可以使用NGS Analysis。NGS Analysis介绍文档
频率分析
进行频率分析,建议在WeSeq运行,WeSeq->Frequency。频率分析介绍文档

序列突变
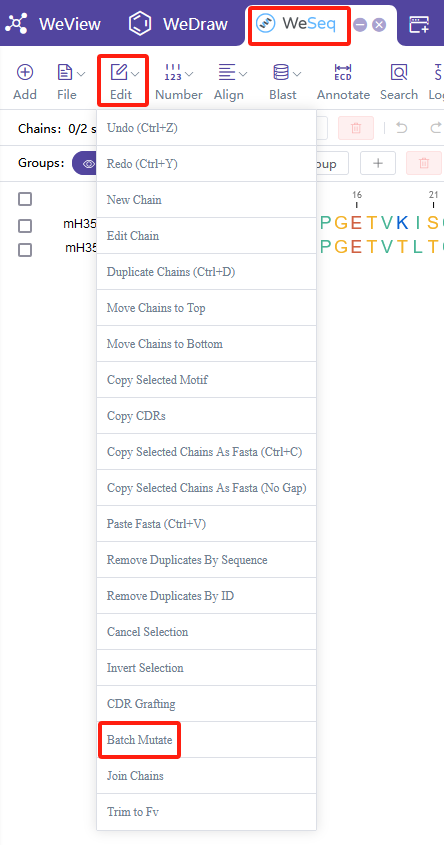
进行序列突变,建议在WeSeq中操作:WeSeq->Edit->Batch Mutate。或者使用Sequence Mutation模块。
Sequence analysis includes sequence numbering, multiple sequence alignment, sequencing data analysis, frequency analysis, and sequence mutations.
For antibody sequence numbering, it is recommended to run in WeSeq: WeSeq -> Number. Sequence Numbering Introduction Document
For multiple sequence alignment, it is recommended to run in WeSeq: WeSeq -> Align. Multiple Sequence Alignment Introduction Document
For sequencing data analysis, you can use NGS Analysis. NGS Analysis Introduction Document
For frequency analysis, it is recommended to run in WeSeq: WeSeq -> Frequency. Frequency Analysis Introduction Document
For sequence mutation, it is recommended to operate in WeSeq: WeSeq -> Edit -> Batch Mutate. Alternatively, you can use the Sequence Mutation module.
专利分析包括专利抗体CDR序列搜索、专利序列提取、专利图片OCR。专利分析介绍文档
进行专利抗体CDR序列搜索,可以应用Patent BLAST。
从专利文本文件或专利序列图片OCR提取专利序列,可以应用Patent Sequence Listing。
Patent analysis includes searching for antibody CDR sequences in patents, extracting patent sequences, and performing OCR on patent images. Patent Analysis Introduction Document
To search for antibody CDR sequences in patents, you can use Patent CDR BLAST.
To extract sequences from patent text files or perform OCR on patent sequence images, you can use Patent Sequence Listing.
从头结构生成
进行蛋白结构从头生成,可以应用Protein Design (RFDiffusion)。RFDiffusion介绍文档
基于主链结构设计序列(逆折叠)
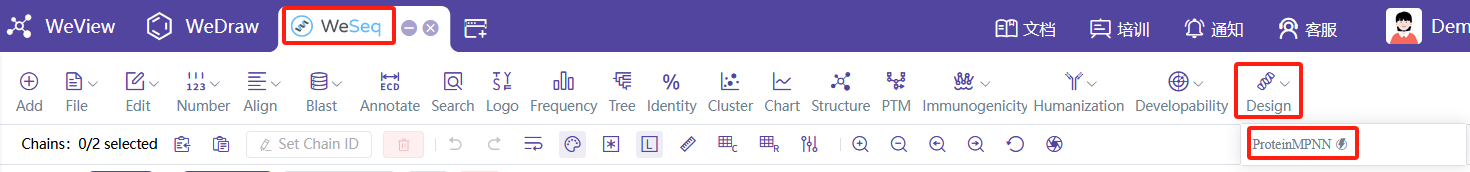
ProteinMPNN,建议从WeSeq中运行:WeSeq->Design->ProteinMPNN。ProteinMPNN介绍文档
ABACUS-R,可以使用Protein Design (ABACUS-R)。
RFDesign,可以使用Protein Design (RFDesign)。RFDesign介绍文档。
ESMIF逆折叠模型,可使用Structure Evolution。
To perform de novo protein structure generation, you can use Protein Design (RFDiffusion). RFDiffusion Introduction Document
ProteinMPNN
ABACUS-R
RFDesign
ESMIF Inverse Folding Model
RFAntibody
是基于RFAntibody(抗体微调版RFdiffusion)的抗体从头设计。Antibody Design (RFAntibody)。
MEAN模型
基于MEAN模型实现的抗体设计,该模型采用多通道等变图注意力网络,可用于设计CDR的一维序列和三维结构。Antibody Design (MEAN)。
DiffAb模型
基于扩散概率模型和等价神经网络的抗体设计,可针对特定抗原结构生成抗体,也可基于抗体-抗原复合物结构进行抗体结构和序列的优化。Antibody Design (DiffAb)。
RFAntibody
RFAntibody is an antibody de novo design method based on the fine-tuned version of RFdiffusion. Antibody Design (RFAntibody).
MEAN Model
The MEAN model enables antibody design using a multi-channel equivariant graph attention network, which can be used to design both the one-dimensional sequence and three-dimensional structure of CDRs. Antibody Design (MEAN).
DiffAb Model
The DiffAb model utilizes diffusion probabilistic models and equivariant neural networks for antibody design. It can generate antibodies specific to a given antigen structure and optimize antibody structure and sequence based on antibody-antigen complex structures. Antibody Design (DiffAb).
多肽分析包括线性肽/环肽结构预测、多肽对接筛选、线性肽/环肽设计、信号肽预测。
Peptide analysis includes linear/cyclic peptide structure prediction, peptide docking screening, linear/cyclic peptide design, and signal peptide prediction.
包括密码子优化、CDS优化、UTR优化等。
Including codon optimization, CDS optimization, UTR optimization, etc.
靶点鉴定包括疾病相关靶点提取以及小分子靶点预测模块。靶点鉴定介绍文档
Target identification includes disease-related target extraction and small molecule target prediction modules. Target Identification Introduction Document
小分子生成是从头设计全新分子的过程,可以基于多种AI架构生成类药分子,也可以基于靶点,骨架、活性分子生成衍生物或者相似分子。分子生成介绍文档
Small molecular generation is the process of designing entirely new molecules from scratch. It can generate drug-like molecules based on various AI architectures, or generate derivatives or similar molecules based on targets, scaffolds, or active molecules. Molecular Generation Introduction Document
虚拟筛选根据配体或受体结构,对小分子化合物进行筛选,预测可能的活性分子,大大提高化合物药物发现进程,缩减药物发现费用。
Virtual screening is a computational technique used to identify potential active compounds by screening large libraries of small molecules. This process can significantly accelerate drug discovery and reduce costs.
Property Filtering
Structure Search
3D Shape Search
Structure Clustering
分子性质包括小分子的理化性质以及药代动力学(ADMET)性质。
Molecular properties include the physicochemical properties and pharmacokinetic (ADMET) properties of small molecules.
分子对接是研究相互作用的重要工具,包括蛋白-小分子,蛋白-蛋白对接。
蛋白-小分子对接
AutoDock-GPU,建议从WeView中运行:WeView->Docking。基于GPU加速的AutoDock的分子对接工具。AutoDock-GPU对接介绍文档
Molecular Docking (SMINA),基于Autodock Vina分支SMINA的分子对接工具。SMINA对接介绍文档
Molecular Docking (DOCK),基于Dock6的分子对接工具。DOCK对接介绍文档
Molecular Docking (DiffDock),基于扩散生成模型的对接工具。DiffDock对接介绍文档
蛋白-蛋白/核酸对接
Molecular docking is an important tool for studying interactions, including protein-small molecule and protein-protein docking.
Protein-Small Molecule Docking
AutoDock-GPU, recommended to run from WeView: WeView->Docking. A GPU-accelerated molecular docking tool based on AutoDock. AutoDock-GPU Docking Documentation

Molecular Docking (SMINA), a molecular docking tool based on the AutoDock Vina branch SMINA. SMINA Docking Documentation
Molecular Docking (DOCK), a molecular docking tool based on Dock6. DOCK Docking Documentation
Molecular Docking (DiffDock), a docking tool based on diffusion generative models. DiffDock Docking Documentation
Protein-Protein/Nucleic Acid Docking
分子格式转换工具,包括不同格式文件转换、氨基酸字母格式转换等。
Molecular format conversion tools, including conversion of different format files, amino acid letter format conversion, etc.
对PDB结构文件进行处理,包括去除杂质、补全确实原子或残基、加氢、修改链名或残基编号等。
| 模块/流程名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Structure Preparation | 首选,支持提取链,去除杂质,补全缺失原子、残基,以及蛋白氨基酸残基的质子化判断以及加氢等操作 |
| Structure Minimization | 结构优化模块,支持氢原子优化、氨基酸侧链优化、整体优化三种方式 |
| PDB ReNumbering | 针对蛋白PDB文件中残基重新编号的工具模块,指定残基开始编号序号,同时支持抗体kabat,imgt以及chothia的重编号 |
| PDB Mutation | 用于突变PDB格式的蛋白质结构并返回突变后的结构 |
Processing of PDB structure files includes removing impurities, completing missing atoms or residues, adding hydrogen atoms, modifying chain names or residue numbers, etc.
| Module/Process Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Structure Preparation | Preferred option, supports chain extraction, impurity removal, completion of missing atoms and residues, and operations like protonation judgment and hydrogen addition for protein amino acid residues |
| Structure Minimization | Structure optimization module, supports three methods: hydrogen atom optimization, amino acid side chain optimization, and overall optimization |
| PDB ReNumbering | Tool module for renumbering residues in protein PDB files, specifying the starting number for residues, and supporting renumbering according to Kabat, IMGT, and Chothia schemes |
| PDB Mutation | Used for mutating protein structures in PDB format and returning the mutated structure |
Introduction to Simulated Structure Processing Documentation
轨迹分析对分子动力学模拟后产生的轨迹进行结构分析,观察研究对象在模拟过程中的动态变化。
| 模块/流程名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| MD Trajectory | 可根据起始帧数、结束帧数以及间隔帧数对平衡模拟进行轨迹提取,并将其转换为GRO或者PDB格式文件 |
| MD RMS | 体系结构稳定性分析模块,包括RMSD、RMSF的计算 |
| MD Hbond | 轨迹氢键分析工具 |
| MD Distance | 轨迹距离分析工具,输出指定原子、残基之间动态距离变化 |
| MD Clustering | 轨迹聚类分析工具 |
| MD PCA | 轨迹主成分分析工具 |
| MD Gyration | 回旋半径分析工具 |
| MD SASA | 计算指定组别的溶剂可及表面积 |
Trajectory analysis involves structural analysis of the trajectories generated from molecular dynamics simulations to observe the dynamic changes of the study object during the simulation process.
| Module/Workflow Name | Description |
|---|---|
| MD Trajectory | Extracts trajectories from equilibrium simulations based on start frame, end frame, and interval frame, and converts them to GRO or PDB format files |
| MD RMS | System structure stability analysis module, including calculations of RMSD and RMSF |
| MD Hbond | Trajectory hydrogen bond analysis tool |
| MD Distance | Trajectory distance analysis tool, outputs dynamic distance changes between specified atoms or residues |
| MD Clustering | Trajectory clustering analysis tool |
| MD PCA | Trajectory principal component analysis tool |
| MD Gyration | Radius of gyration analysis tool |
| MD SASA | Calculates the solvent accessible surface area of specified groups |
结合自由能计算是预测分子间结合强弱的重要方法。
| 模块/流程名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA | 计算受体与配体之间的结合自由能,并且提供能量分解数据等数据 |
| Alanine Scan (MMPBSA) | 计算丙氨酸突变后的结合自由能,并且提供能量分解数据 |
| MMPBSA of One Protein/DNA Structure | 计算一帧蛋白-蛋白复合物/蛋白-核酸复合物结构的结合自由能流程 |
| MMPBSA of One Protein-Ligand Structure | 计算一帧蛋白-小分子结构的结合自由能流程 |
| PPI Binding Energy (Graphomer) | 蛋白-蛋白复合物结合能模块,基于图transformer模型预测蛋白-蛋白结合亲和力 |
| PPI Binding Energy & Contacts | 蛋白-蛋白复合物结合能与相互作用分析模块,基于界面接触特征预测蛋白-蛋白结合亲和力 |
Combining free energy calculations is a crucial method for predicting the strength of molecular interactions.
| Module/Workflow Name | Description |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA | Calculates the binding free energy between receptor and ligand, and provides energy decomposition data |
| Alanine Scan (MMPBSA) | Calculates the binding free energy after alanine mutation, and provides energy decomposition data |
| MMPBSA of One Protein/DNA Structure | Workflow for calculating the binding free energy of a single protein-protein or protein-nucleic acid complex structure |
| MMPBSA of One Protein-Ligand Structure | Workflow for calculating the binding free energy of a single protein-small molecule structure |