
对不同文件中的序列进行组装,输出满足Boltz2批量预测模式需要的序列格式。
进行序列组装的A文件,组装时的固定序列,FASTA格式
进行序列组装的B文件,组装时的遍历序列,FASTA格式
进行序列组装的C文件,组装时的遍历序列,FASTA格式
组装模式,选中表示对B,C文件中的序列进行交叉组装。具体组装逻辑见下述。
组装逻辑:
读取A文件中的所有序列,依次读取B文件及C文件中的相同顺序的一条序列进行组装。如果B文件与C文件中的序列数量不一致,或者其中一个文件为空时,则超出部分的序列单独与A文件序列进行组装。示例如下:
A文件中有两条序列A1/2,B文件中有三条序列B1/2/3,C文件中有5条序列C1/2/3/4/5,输出组合后的序列为:
>A1_A2_B1_C1
A1:A2:B1:C1
>A1_A2_B2_C2
A1:A2:B2:C2
>A1_A2_B3_C3
A1:A2:B3:C3
>A1_A2_C4
A1:A2:C4
>A1_A2_C5
A1:A2:C5
如果选择交叉组装模式,则对B,C文件中的序列进行交叉组装,输出组合后的序列为:
>A1_A2_B1_C1
A1:A2:B1:C1
>A1_A2_B1_C2
A1:A2:B1:C2
>A1_A2_B1_C3
A1:A2:B1:C3
>A1_A2_B1_C4
A1:A2:B1:C4
>A1_A2_B1_C5
A1:A2:B1:C5
>A1_A2_B2_C1
A1:A2:B2:C1
>A1_A2_B2_C2
A1:A2:B2:C2
......
输出组装后的序列文件combined_seqs.fasta。
Assembles sequences from different files and outputs them in the sequence format required for Boltz2 batch prediction mode.
File A used for sequence assembly, fixed sequence during assembly, in FASTA format.
File B used for sequence assembly, traversal sequence during assembly, in FASTA format.
File C used for sequence assembly, traversal sequence during assembly, in FASTA format.
Assembly mode. If selected, sequences from files B and C will be cross-assembled. The specific assembly logic is described below.
Assembly Logic:
Read all sequences from file A. Then, for each sequence in A, read sequences from files B and C in the same order and assemble them together.
If the number of sequences in files B and C are inconsistent, or if one file is empty, the extra sequences will be assembled individually with the sequences from file A.
For example, if file A contains two sequences A1 and A2, file B contains three sequences B1, B2, and B3, and file C contains five sequences C1, C2, C3, C4, and C5, the output assembled sequences will be:
>A1_A2_B1_C1
A1:A2:B1:C1
>A1_A2_B2_C2
A1:A2:B2:C2
>A1_A2_B3_C3
A1:A2:B3:C3
>A1_A2_C4
A1:A2:C4
>A1_A2_C5
A1:A2:C5
If cross-assembly mode is selected, sequences from files B and C will be cross-assembled. The output sequences will be:
>A1_A2_B1_C1
A1:A2:B1:C1
>A1_A2_B1_C2
A1:A2:B1:C2
>A1_A2_B1_C3
A1:A2:B1:C3
>A1_A2_B1_C4
A1:A2:B1:C4
>A1_A2_B1_C5
A1:A2:B1:C5
>A1_A2_B2_C1
A1:A2:B2:C1
>A1_A2_B2_C2
A1:A2:B2:C2
......
The assembled sequence file will be output as combined_seqs.fasta.
对ESM2蛋白质语言模型进行微调,支持分类(二分类)和回归任务。
该模块提供了三种训练方法:
1,基于BioNeMo框架的全参微调
2,序列特征迁移+传统机器学习(ML)预测头
3,序列特征迁移+多层感知机(MLP)预测头
默认会尝试所有训练方法,自动比较训练结果并选择最佳模型。训练完成后可基于训练后的最佳模型进行推理。
| 参数名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Train Method | 训练方法:all (所有方法)、Finetune(基于BioNeMo框架的全参微调)、ml (序列特征迁移+传统机器学习预测头)、mlp (序列特征迁移+多层感知机预测头) |
| Input File | 用于训练的数据文件路径,CSV格式(逗号分隔的文本文件格式) |
| Sequence Column | 数据文件中蛋白序列所在列的列名称,如“sequence” |
| Label Column | 数据文件中标签所在列的列名称,如“label”,标签可以是序列的性质(如:亲和力,稳定性等),也可以是类别(0或1等) |
| Task Type | 任务类型:classification 或 regression |
| Test Size | 训练数据中用于作为测试集的比例,默认值 0.2 |
| Epochs | 训练轮次, 默认10 |
| Batch Size | 训练时的批次大小,默认16 |
| 参数名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Input File | 用于推理的数据文件路径,CSV格式(逗号分隔的文本文件格式) |
| Model Status File | 模型信息JSON文件路径 (训练任务最终输出的result.json文件) |
| Sequence Column | 数据文件中序列所在列的列名称 (如不指定,将从model_info_file中读取与训练时一致的列名称,需要确保推理数据文件中的列名称与训练数据列名称一致) |
| Inference Mode | 推理结果筛选方式:largest(由大到小排序)、smallest(由小到大排序)、closest (按最接近某个数值排序,仅适用于回归任务) |
| Top N | 筛选保留的样本数量,默认值 10000 |
| Target Value | 如果选择closest模式,需要指定的目标值 |
| Target Class | 对于分类任务,只保留特定类别的样本 |
| 指标 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Spearman | Spearman相关性指标,-1至1之间,绝对值越大表示相关性越高,模型效果越好。不同训练方法得到回归模型通过该参数进行排序,选取最优模型。 |
| MAE | 平均绝对误差,数值越小越好 |
分类任务的模型评价指标:
| 指标 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | 准确率,整体预测正确的比例,0-1之间,越大表示模型效果越好 |
| Precision | 精确率,预测为正例的样本中,实际为正的比例,0-1之间,越大表示模型效果越好 |
| Recall | 召回率,实际为正例的样本中,被正确预测的比例,0-1之间,越大表示模型效果越好 |
| F1_score | 精确率与召回率的调和平均值。不同训练方法得到分类模型通过该参数进行排序,选取最优模型。 |
注意:当训练模型失败或指标不符合要求时(如:Spearman为0),不输出该模型及其指标。
This module is designed for fine-tuning the ESM2 protein language model, supporting classification (binary) and regression tasks. It offers three training methods:
By default, all training methods are attempted, and the results are automatically compared to select the best model. After training, inference can be performed using the best-trained model.
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Train Method | Training method: all (all methods), Finetune (full-parameter fine-tuning based on BioNeMo framework), ml (sequence feature transfer with traditional ML prediction head), mlp (sequence feature transfer with MLP prediction head) |
| Input File | Path to the data file used for training, in CSV format (comma-separated text file) |
| Sequence Column | Name of the column containing protein sequences in the data file, e.g., “sequence” |
| Label Column | Name of the column containing labels in the data file, e.g., “label”. Labels can be properties of the sequences (e.g., affinity, stability) or categories (e.g., 0 or 1) |
| Task Type | Task type: classification or regression |
| Test Size | Proportion of training data used as the test set, default is 0.2 |
| Epochs | Number of training epochs, default is 10 |
| Batch Size | Batch size during training, default is 16 |
| Parameter Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Input File | Path to the data file used for inference, in CSV format (comma-separated text file) |
| Model Status File | Path to the JSON file containing model information (result.json file output from the training task) |
| Sequence Column | Name of the column containing sequences in the data file (if not specified, it will be read from the model_info_file to match the column name used during training; ensure column names in the inference data file match those in the training data) |
| Inference Mode | Method for filtering inference results: largest (sorted from largest to smallest), smallest (sorted from smallest to largest), closest (sorted by proximity to a specific value, applicable only to regression tasks) |
| Top N | Number of samples to retain after filtering, default is 10,000 |
| Target Value | If closest mode is selected, specify the target value |
| Target Class | For classification tasks, retain samples of a specific class |
Model Evaluation Metrics for Regression Tasks:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Spearman | Spearman correlation coefficient, ranging from -1 to 1. A higher absolute value indicates stronger correlation and better model performance. Regression models from different training methods are ranked based on this metric to select the optimal model. |
| MAE | Mean Absolute Error. Smaller values indicate better performance. |
Model Evaluation Metrics for Classification Tasks:
| Metric | Description |
|---|---|
| Accuracy | Proportion of correct predictions overall, ranging from 0 to 1. Higher values indicate better model performance. |
| Precision | Proportion of true positives among predicted positives, ranging from 0 to 1. Higher values indicate better performance. |
| Recall | Proportion of true positives correctly identified, ranging from 0 to 1. Higher values indicate better performance. |
| F1_score | Harmonic mean of precision and recall. Classification models from different training methods are ranked based on this metric to select the optimal model. |
Note: If model training fails or evaluation metrics do not meet requirements (e.g., Spearman = 0), the model and its metrics will not be included in the output.
Mutation Score是抗体人源化设计中核心模块,是一个基于结构的自动化评分模块。该模块基于抗体的结构信息以及CDR嫁接后的序列信息,对移植抗体(graft)后的FR区的每个氨基酸在替换前后的变化程度进行量化评分。评分越高,说明CDR嫁接过程中氨基酸的替换对CDR区的构象可能影响较大,需要进行回复突变。模块输出每个氨基酸的打分值,用于抗体人源化设计流程中后续的分组和人源化抗体序列的生成。
抗体Fv区序列文件,FASTA格式。
抗体结构文件,PDB格式。
抗体CDR区Graft后的序列文件,FASTA格式。
指定输出打分文件的名称,CSV格式。
抗体类型:
输出结果文件为score.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | 轻链或重链 |
| UID | 为残基的标准编号(默认为 Kabat) |
| Position | 残基在序列中的位置 |
| Donor Residue | 原始氨基酸 |
| Template Residue | 人源模板的目标氨基酸 |
| score | 回复突变智能评分,Score 越高,认为其回复突变的必要性越高。通常Score>10为高优先级,5-10为中优先级,其他为低优先级 |
Mutation Score is a core module in antibody humanization design, serving as a structure-based automated scoring module. This module quantitatively scores the degree of change for each amino acid in the FR region after grafting CDRs based on the antibody’s structure and the sequence information post-CDR grafting. A higher score indicates that the replacement of amino acids during CDR grafting may have a significant impact on the CDR region’s conformation, suggesting the need for revertant mutations. The module outputs a score for each amino acid, which is used in subsequent grouping and generation of humanized antibody sequences in the antibody humanization design process.
Sequence file of the antibody Fv region in FASTA format.
Antibody structure file in PDB format.
Sequence file of the antibody CDR region after grafting in FASTA format.
Specify the name of the output scoring file in CSV format.
Type of antibody:
The output result file is named score.csv and includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain | Light chain or heavy chain |
| UID | Standard numbering for residues (default is Kabat) |
| Position | Position of the residue in the sequence |
| Donor Residue | Original amino acid |
| Template Residue | Target amino acid from the human template |
| Score | Revertant mutation intelligence score, where a higher score suggests a higher necessity for a revertant mutation. Typically, a Score > 10 is high priority, 5-10 is medium priority, and others are low priority. |
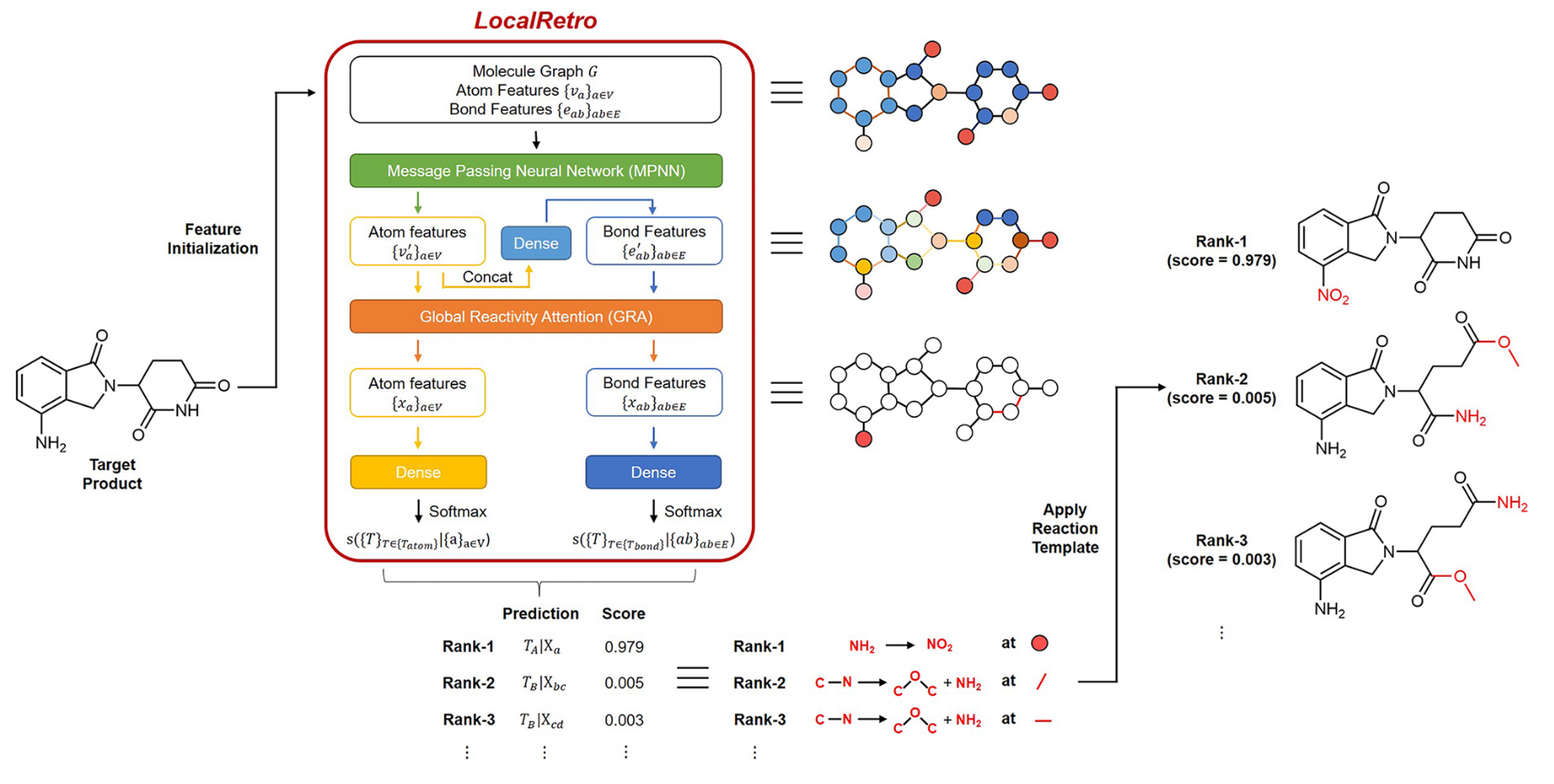
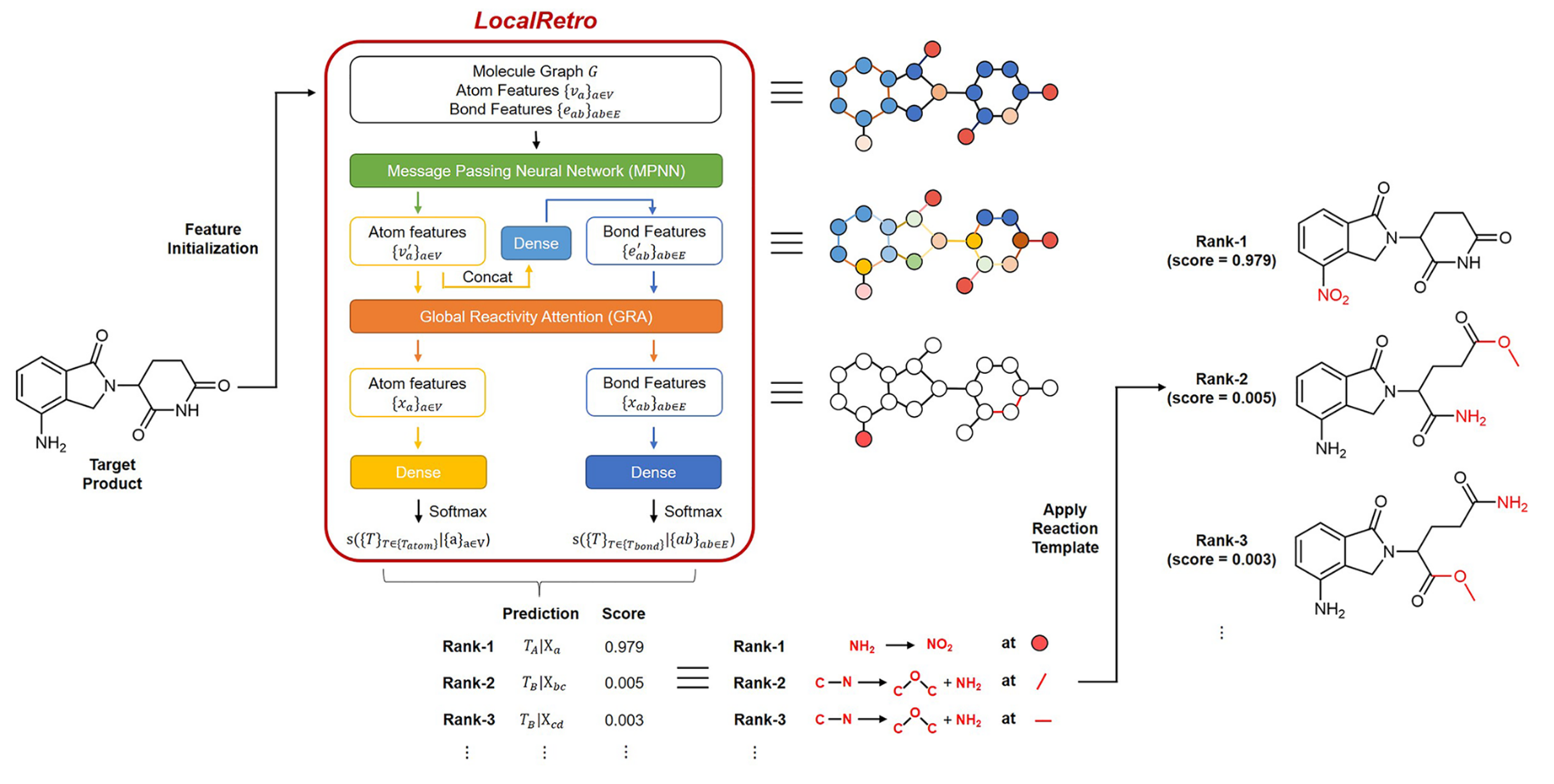
LocalRetro 是局部逆合成预测框架,其动机是化学直觉认为分子变化主要发生在化学反应过程中的局部。这与几乎所有现有的逆合成方法不同,这些方法根据分子的全局结构建议反应物,通常包含与反应没有直接关系的精细细节。这个局部概念产生了涉及原子和键编辑的局部反应模板。由于远程官能团也可以作为次要方面影响整个反应路径,因此进一步细化了所提出的局部编码逆合成模型,以通过全局注意力机制来解释化学反应的非局部效应。模型显示,对于包含 50016 个反应的 USPTO-50K 数据集,top-1 名和 top-5 预测的准确率分别为 89.5% 和 99.2%。在包含 479035 个反应(UTPTO-MIT) 的大型数据集上 top-1 和 top-5 准确率分别为 87.0% 和 97.4%。通过从各种文献中正确预测五种候选药物分子的合成途径,还证明了该模型的实际应用。
输入小分子的SMILES,支持多个批量预测,一行一个,示例:
O=C(Nc4cccc(C(=O)N3CCN(c1ccnc2[nH]ccc12)C3)c4)c5cccc(C(F)(F)F)c5
输出的CSV文件包含以下列:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
Input SMILES |
输入的原始分子SMILES |
Predicted Reactants |
预测反应物的SMILES |
Predicted Site |
预测的反应位点 |
Local Reaction Template |
局部反应模板 |
Score |
预测得分,范围0-1,分数越高,表明该反应发生概率越高 |
注意: 每个输入分子可能产生多个预测反应,因此一个分子会对应多行数据。
LocalRetro, a local retrosynthesis framework, motivated by the chemical intuition that the molecular changes occur mostly locally during the chemical reactions. This differs from nearly all existing retrosynthesis methods that suggest reactants based on the global structures of the molecules, often containing fine details not directly relevant to the reactions. This local concept yields local reaction templates involving the atom and bond edits. Because the remote functional groups can also affect the overall reaction path as a secondary aspect, the proposed locally encoded retrosynthesis model is then further refined to account for the nonlocal effects of chemical reaction through a global attention mechanism. Model shows a promising 89.5 and 99.2% round-trip accuracy at top-1 and top-5 predictions for the USPTO-50K dataset containing 50 016 reactions. LocalRetro was further validated on a large dataset containing 479 035 reactions (UTPTO-MIT) with comparable round-trip top-1 and top-5 accuracy of 87.0 and 97.4%, respectively. The practical application of the model is also demonstrated by correctly predicting the synthesis pathways of five drug candidate molecules from various literature.
SMILES of small molecules, supporting batch prediction of multiple entries, one per line. Demo:
O=C(Nc4cccc(C(=O)N3CCN(c1ccnc2[nH]ccc12)C3)c4)c5cccc(C(F)(F)F)c5
Output CSV file includes:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
Input SMILES |
input SMILES for prediction |
Predicted Reactants |
Predicted reactant in SMILES |
Predicted Site |
Predicted reaction site |
Local Reaction Template |
Template used |
Score |
Predicted score(0~1),and a high score indicating higher the likelihood of the reaction. |
Note: Each input molecule may generate multiple predicted reactions, so one molecule may correspond to multiple lines of data
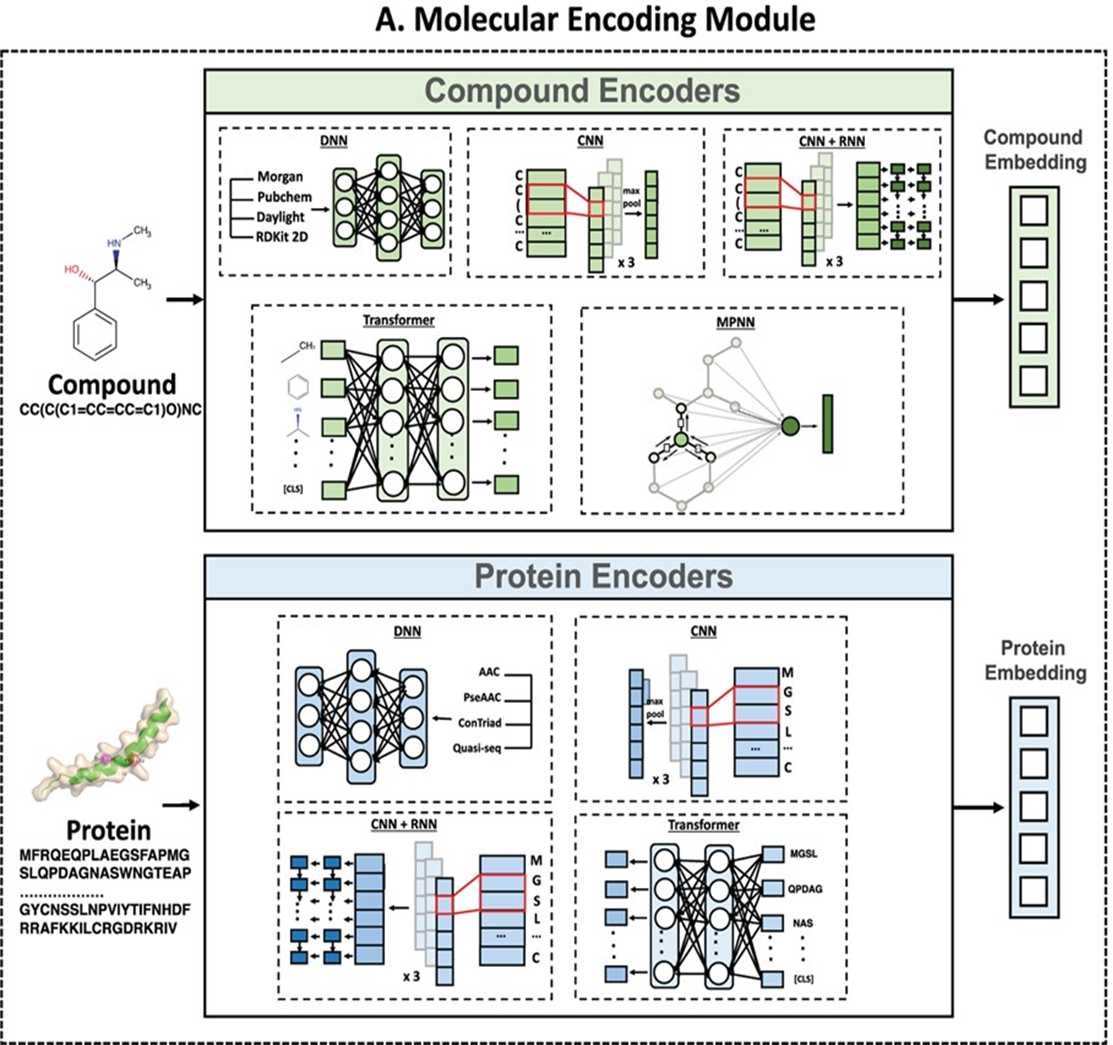
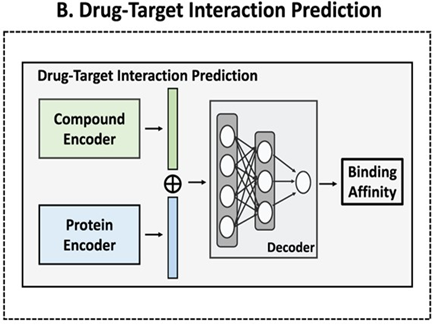
预测小分子与蛋白的亲和力(用pIC50表示)。模块基于DeepPurpose框架实现,采用的预训练模型为MPNN_CNN_BindingDB,是基于BindingDB数据库训练的小分子-蛋白亲和力预测模型。
模型架构如图所示:
模型预测效果在当时是最佳的:
单个或多个蛋白序列,FASTA格式或TXT格式,每个蛋白使用一条序列表示(有多条链时,将单链序列收尾连接放在同一条序列中),txt格式时,每行一个蛋白。
小分子结构文件,TXT格式,支持多个底物分子,使用SMILES表示,每行一个分子,文件内容示例:
OC1=CC=C(C[C@@H](C(O)=O)N)C=C1
CC(O)O
注意:
输入每个小分子都会与每个蛋白计算亲和力,并输出结果。
亲和力预测结果文件名,默认为pred_res.csv
结果文件pred_res.csv,包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SMILES | 小分子结构 |
| Target_ID | 蛋白名称 |
| Target_Sequence | 蛋白序列 |
| Score(pIC50) | 预测的亲和力pIC50数值,越大表示亲和力越高,可与阳性对照分子的预测数值比较。 |
This module predicts the binding affinity between small molecules and proteins, expressed as pIC50. It is implemented based on the DeepPurpose framework, using the pre-trained model MPNN_CNN_BindingDB, which was trained on the BindingDB dataset for small molecule–protein affinity prediction.
The model architecture is shown below:


At the time of its release, the model achieved state-of-the-art performance:

One or more protein sequences in FASTA or TXT format. Each protein should be represented by a single sequence. For multi-chain proteins, concatenate the chain sequences end-to-end into one line. In TXT format, each line represents one protein.
Small molecule structure file in TXT format, supporting multiple substrate molecules. Molecules are represented using SMILES, with one molecule per line. Example content:
OC1=CC=C(C[C@@H](C(O)=O)N)C=C1
CC(O)O
Note:
Each small molecule will be paired with each protein to compute the binding affinity, and the results will be output accordingly.
The output filename for affinity prediction results. Default is pred_res.csv.
The result file pred_res.csv contains the following fields:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SMILES | Small molecule structure (SMILES format) |
| Target_ID | Protein name |
| Target_Sequence | Protein sequence |
| Score (pIC50) | Predicted binding affinity score (pIC50). A higher value indicates stronger binding, and can be compared with positive control molecules. |
对蛋白、抗体序列进行聚类、可视化。模块使用MMseq2算法对序列进行聚类分析,将多序列分为多个cluster类别,并通过ESM2模型对序列进行embedding,通过可视化模块UMAP对序列embedding进行降维,获取二维可视化信息。
蛋白或抗体序列,FASTA格式
聚类中采用的最小序列一致性数值,范围在0-1之间,默认值为0.5,表示至少具有50% identity的序列才会被聚为一类。
序列类型,选中表示抗体序列,否则为蛋白序列。
序列类型为抗体时的编号规则,支持imgt, chothia, kabat
序列聚类方案,支持2种:full, cdr(仅序列类型为抗体时可用)。‘full’表示使用全长序列进行聚类,‘cdr’表示使用CDR序列进行聚类(具体CDR位置在参数‘CDRs’中设定),默认为‘full’
指定用于聚类的CDR区域,在‘Cluster’参数为cdr时生效。可选区域为(支持多选):CDR1,CDR2,CDR3。默认选择CDR3。
输出cluster_res.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ID | 序列名称 |
| Sequence | 序列 |
| CDR1_AA | CDR1的氨基酸序列,序列为抗体时输出 |
| CDR2_AA | CDR2的氨基酸序列,序列为抗体时输出 |
| CDR3_AA | CDR3的氨基酸序列,序列为抗体时输出 |
| Cluster_ID | 序列所属类别编号,从1开始按顺序编号 |
| Cluster_Size | 序列所属类别包含的序列数目,如:‘5’表示该类别含有5条序列 |
| Cluster_Center | 序列是否为聚类中心,'1’表示是,‘0’表示不是 |
Cluster and visualize protein and antibody sequences. This module uses the MMseqs2 algorithm to perform clustering analysis on sequences, dividing multiple sequences into several cluster categories. It uses the ESM2 model to embed the sequences, and the visualization module UMAP to reduce the dimensionality of the sequence embeddings, obtaining two-dimensional visualization information.
Protein or antibody sequences in FASTA format.
The minimum sequence identity value used in clustering, ranging from 0 to 1. The default value is 0.5, which means sequences must have at least 50% identity to be clustered together.
The type of sequence. Selecting indicates antibody sequences; otherwise, it is protein sequences.
The numbering scheme for antibody sequences, supporting imgt, chothia, kabat.
Sequence clustering scheme, supporting two types: full and cdr (only available for antibody sequences). ‘full’ means using the full-length sequence for clustering, while ‘cdr’ means using CDR sequences for clustering (specific CDR positions are set in the ‘CDRs’ parameter). The default is ‘full’.
Specifies the CDR regions used for clustering, effective when the ‘Cluster’ parameter is set to cdr. Optional regions (supporting multiple selections) are: CDR1, CDR2, CDR3. The default selection is CDR3.
Outputs a result file named cluster_res.csv containing the following information:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Sequence name |
| Sequence | Sequence |
| CDR1_AA | Amino acid sequence of CDR1, output when the sequence is an antibody |
| CDR2_AA | Amino acid sequence of CDR2, output when the sequence is an antibody |
| CDR3_AA | Amino acid sequence of CDR3, output when the sequence is an antibody |
| Cluster_ID | Cluster category number of the sequence, numbered sequentially starting from 1 |
| Cluster_Size | Number of sequences in the cluster category, e.g., ‘5’ means the category contains 5 sequences |
| Cluster_Center | Whether the sequence is a cluster center, ‘1’ indicates yes, ‘0’ indicates no |

该模块是抗体人源化设计流程中分组模块,根据Mutation Score模块输出的回复突变评分表对回复突变进行分组。
更新内容:
抗体CDR区嫁接后序列文件,FASTA格式,由Grafting模块生成
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式
人源化突变评分文件,CSV格式,由Mutation Score模块生成
指定输出的突变序列文件名称,FASTA格式
打分分组的截断值,逗号分割,例如:2,5,10表示将氨基酸突变评分大于10的为一组,5~10的氨基酸为一组,小于2的氨基酸分为一组。
指定输出的回复突变的文件
普通抗体Antibody或者纳米抗体Nanobody
抗体CDR区嫁接后序列文件,FASTA格式,由Grafting模块生成
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式
人源化突变评分文件,CSV格式,由Mutation Score模块生成
指定输出的突变序列文件名称,FASTA格式
打分分组的截断值,逗号分割,例如:2,5,10表示将氨基酸突变评分大于10的为一组,5~10的氨基酸为一组,小于2的氨基酸分为一组。
指定输出的回复突变的文件
普通抗体Antibody或者纳米抗体Nanobody
突变组合的截断值,Mutation Score模块中输出的氨基酸回复突变打分大于截断值的氨基酸参与生成突变组合
高于截断值的突变自动进行回复突变
每条链回复突变打分在Combination Min Cutoff与Combination Max Cutoff之间的选择打分前n个位置进行组合突变
根据不同截断值得到突变分组结果文件mutate_policy.json。
高通量方法HTS Mutate中根据组合突变截断值得到的突变分组结果文件combination_mutate_policy.json,高通量人源化设计流程。
Back mutation grouping in the antibody humanization, which groups the back mutations based on the mutation scoring table generated by the Mutation Score module.
Update Log:
Sequence file of the antibody CDR region after grafting, in FASTA format, generated by the Grafting module.
Sequence file of the antibody, in FASTA format.
Humanization mutation score file, in CSV format, generated by the Mutation Score module.
Specify the name of the output mutation sequence file, in FASTA format.
Cutoff values for scoring grouping, separated by commas. For example, 2,5,10 indicates grouping amino acid mutations with scores greater than 10 in one group, amino acids with scores between 5 and 10 in another group, and amino acids with scores less than 2 in a separate group.
Specify the file for the output of back mutations.
Antibody or Nanobody
Sequence file of the antibody CDR region after grafting, in FASTA format, generated by the Grafting module.
Sequence file of the antibody, in FASTA format.
Humanization mutation score file, in CSV format, generated by the Mutation Score module.
Specify the name of the output mutation sequence file, in FASTA format.
Cutoff values for scoring grouping, separated by commas. For example, 2,5,10 indicates grouping amino acid mutations with scores greater than 10 in one group, amino acids with scores between 5 and 10 in another group, and amino acids with scores less than 2 in a separate group.
Specify the file for the output of back mutations.
Antibody or Nanobody
Cutoff value for mutation combinations. Amino acids with scores (generated from Mutation Score module) greater than the cutoff value are involved in the mutation combinations.
Mutations above the cutoff value automatically undergo reversion mutations.
For each chain, select the top n positions with back mutation scores between the Combination Min Cutoff and the Combination Max Cutoff for combination mutations.
The mutation grouping results file mutate_policy.json is generated based on different cutoff values.
In HTS Mutate, the mutation grouping results file combination_mutate_policy.json is generated based on combination cutoff values.

Humanization Report v2.5是抗体人源化设计报告生成模块,用于生成最终的抗体人源化设计报告以及相应的专利实施例段落。
更新日志:
Grafting模块生成的Graft Policy文件。
Back Mutation Grouping模块生成的Policy文件。
抗体类型,Antibody 标准双链抗体,Nanobody 纳米抗体。
Grafting模块生成的score文件,JSON格式
Mutation模块生成的score文件,CSV格式
Grafting模块生成的Graft Policy文件。
Back Mutation Grouping模块生成的Policy文件。
抗体类型,Antibody 标准双链抗体,Nanobody 纳米抗体。
Grafting模块生成的score文件,JSON格式
Mutation模块生成的score文件,CSV格式
抗体结构RMSD文件,由Antibody RMSD模块生成,CSV格式
从RMSD排序中取前N个RMSD值小的抗体
Absolute Folding Stability模块预测生成的蛋白稳定性文件,CSV格式
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BM.pptx | 回复突变位点汇总文件 |
| batch_registration_template.xlsx | 批量注册模板文件 |
| hotspot_summary.xlsx | 风险位点总结 |
| patent_example_template.docx | 人源化设计序列在相应的专利实施例段落 |
| patent_example_en_template.docx | 英文版人源化设计序列在相应的专利实施例段落 |
| back_mutation_grouping.md | 回复突变分组信息 |
| candidate_score.xlsx | 人源化抗体序列的结构和能量打分汇总 |
| humanized_variants.fasta | 抗体人源化设计序列文件,FASTA格式 |
| Report.docx | 抗体人源化设计报告,包括整个人源化设计过程涉及的序列、分组等信息 |
其中batch_registration_template.xlsx包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein Sequence | 蛋白序列 |
| Molecule Name | 分子名称 |
其中hotspot_summary.xlsx包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ID | 抗体序列名称 |
| Sequence-CDR | CDR序列区域 |
| Deamidation | 脱酰胺位点 |
| Isomerization | 异构化位点 |
| Cleavage | 酶切位点 |
| Hydrolysis | 水解位点 |
| Glycosylation | 糖基化位点 |
| Cys | 半胱氨酸数量 |
| Oxidation | 氧化位点 |
| High risk | 高风险率 |
| High risk sites | 高风险位点 |
The Humanization Report v2.5 is a module for generating reports on antibody humanization design, including the final antibody humanization design report and corresponding paragraphs for patent implementation examples.
Update Log:
The Graft Policy file generated by the Grafting module.
The Policy file generated by the Back Mutation Grouping module.
Antibody type, Antibody or Nanobody
Graft germline score file in JSON format generated by the Grafting module
Mutation score file in csv format generated by the Mutation module
The Graft Policy file generated by the Grafting module.
The Policy file generated by the Back Mutation Grouping module.
Antibody type, Antibody or Nanobody
Graft germline score file in JSON format generated by the Grafting module
Mutation score file in csv format generated by the Mutation module
Antibody structure RMSD file generated by Antibody RMSD module
Select the top N antibodies with the smallest RMSD values from the RMSD ranking
Protein folding stability file generated by Absolute Folding Stability module in CSV format
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BM.pptx | Summary file of back mutation sites |
| batch_registration_template.xlsx | Batch registration template file |
| hotspot_summary.xlsx | Summary of hotspot sites |
| patent_example_template.docx | Humanization design sequences in corresponding patent implementation example paragraphs (Chinese version) |
| patent_example_en_template.docx | Humanization design sequences in corresponding patent implementation example paragraphs (English version) |
| back_mutation_grouping.md | Grouping for back mutations |
| humanized_variants.fasta | Antibody humanization design sequence file in FASTA format |
| Report.docx | Antibody humanization design report, including information on sequences, grouping, etc., involved in the entire humanization design process |
| candidate_score.xlsx | Candidate sequences energy and structure scores |
The batch_registration_template.xlsx file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein Sequence | Protein sequence |
| Molecule Name | Molecule name |
The hotspot_summary.xlsx file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Antibody sequence name |
| Sequence-CDR | CDR sequence region |
| Deamidation | Deamidation site |
| Isomerization | Isomerization site |
| Cleavage | Cleavage site |
| Hydrolysis | Hydrolysis site |
| Glycosylation | Glycosylation site |
| Cys | Number of cysteines |
| Oxidation | Oxidation site |
| High risk | High-risk rate |
| High risk sites | High-risk sites |
合并AF3-like模型(Boltz-2,Protenix,Chai-1)输出的结果。
指定Boltz2结果的打包文件,tar格式,如:Boltz_results.tar。
指定Protenix结果的打包文件,tar格式,如:Protenix_results.tar。
指定Chai-1结果的打包文件,tar格式,如:Chai-1_results.tar。
结构文件合并输出的打包文件名称,默认为merged_results.tar。
打分文件合并输出的打包文件名称,默认为merged_results.csv。
结构文件的合并输出打包文件merged_results.tar,包含输入的所有AF3-like模型预测结果。
打分文件的合并输出打包文件merged_results.csv,包含所有AF3-like模型的打分。
Merge the output results of AF3-like models (Boltz-2, Protenix, Chai-1).
Specify the packaged result file from Boltz-2 in tar format, e.g., Boltz_results.tar.
Specify the packaged result file from Protenix in tar format, e.g., Protenix_results.tar.
Specify the packaged result file from Chai-1 in tar format, e.g., Chai-1_results.tar.
Name of the merged output tar file containing structure files. Defaults to merged_results.tar.
Name of the merged output file containing scores. Defaults to merged_results.csv.
The merged output tar file merged_results.tar contains the structural prediction results from all the input AF3-like models.
The merged score file merged_results.csv includes the scores from all AF3-like models.
合并AF3-like模型打分结果与PPI模块打分结果,并汇总输出。
指定AF3-like多个模型打分的汇总文件,csv格式,如:merged_results.csv。
指定PPI模型Prodigy的结果打分文件,csv格式,如:prodigy_output.csv。
指定PPI模型Graphomer的结果打分文件,csv格式,如:PPI_pred.csv。
打分合并输出的文件名称,默认为score_merge.csv。
打分的合并输出打包文件score_merge.csv,包含所有AF3-like模型的打分及PPI模型打分。
Merge the scoring results from AF3-like models with the PPI module scoring results and generate a consolidated output.
Specify the consolidated score file from multiple AF3-like models in CSV format, e.g., merged_results.csv.
Specify the scoring result file from the PPI model Prodigy in CSV format, e.g., prodigy_output.csv.
Specify the scoring result file from the PPI model Graphomer in CSV format, e.g., PPI_pred.csv.
Name of the merged output score file. Defaults to score_merge.csv.
The merged score output file score_merge.csv includes scoring results from all AF3-like models and PPI models.

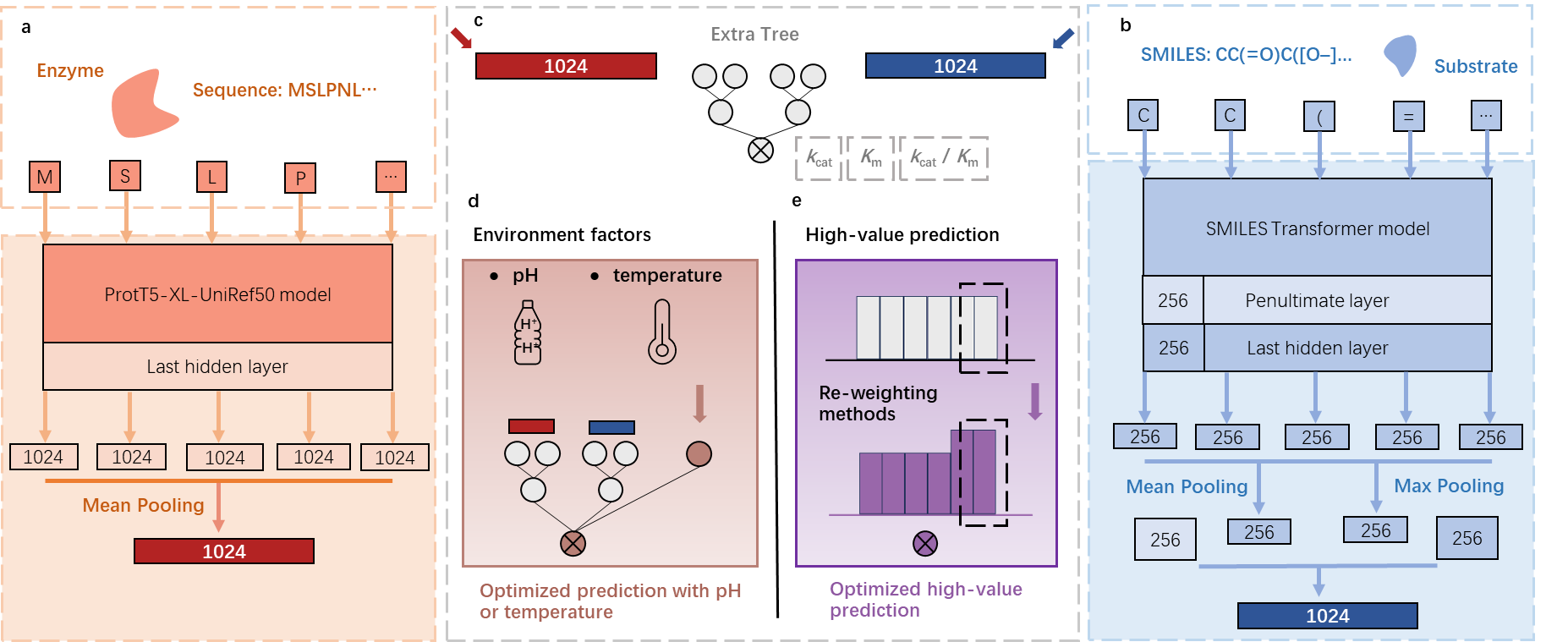
该模块预测酶的动力学参数Kcat与Km。模块基于UniKP框架实现,UniKP是一个用于预测酶动力学参数的计算工具。它结合了蛋白质序列和底物结构信息,利用预训练的语言模型(如 ProtT5-XL-UniRef50)来生成酶的表示,并通过深度学习模型预测酶的动力学参数。
UniKP框架由两个关键组件组成:表示模块和机器学习模块。表示模块使用预训练的语言模型对酶和底物的信息进行编码。具体而言,酶序列中的氨基酸使用ProtT5-XL-UniRef50模型转换为1024维的向量。对于每个蛋白质,应用平均池化方法得到其表示,这被发现是对于蛋白质任务最有效的方法。另一方面,底物结构被转换为简化的分子输入线条记录系统(SMILES)格式,并通过预训练的SMILES转换器进行处理,每个符号生成一个256维的向量。然后,对最后一层和倒数第二层的第一个输出进行平均池化和最大池化,将它们连接起来生成一个1024维的分子表示向量。蛋白质和底物的连接表示向量随后被输入到机器学习模块中(整体架构图如下)。
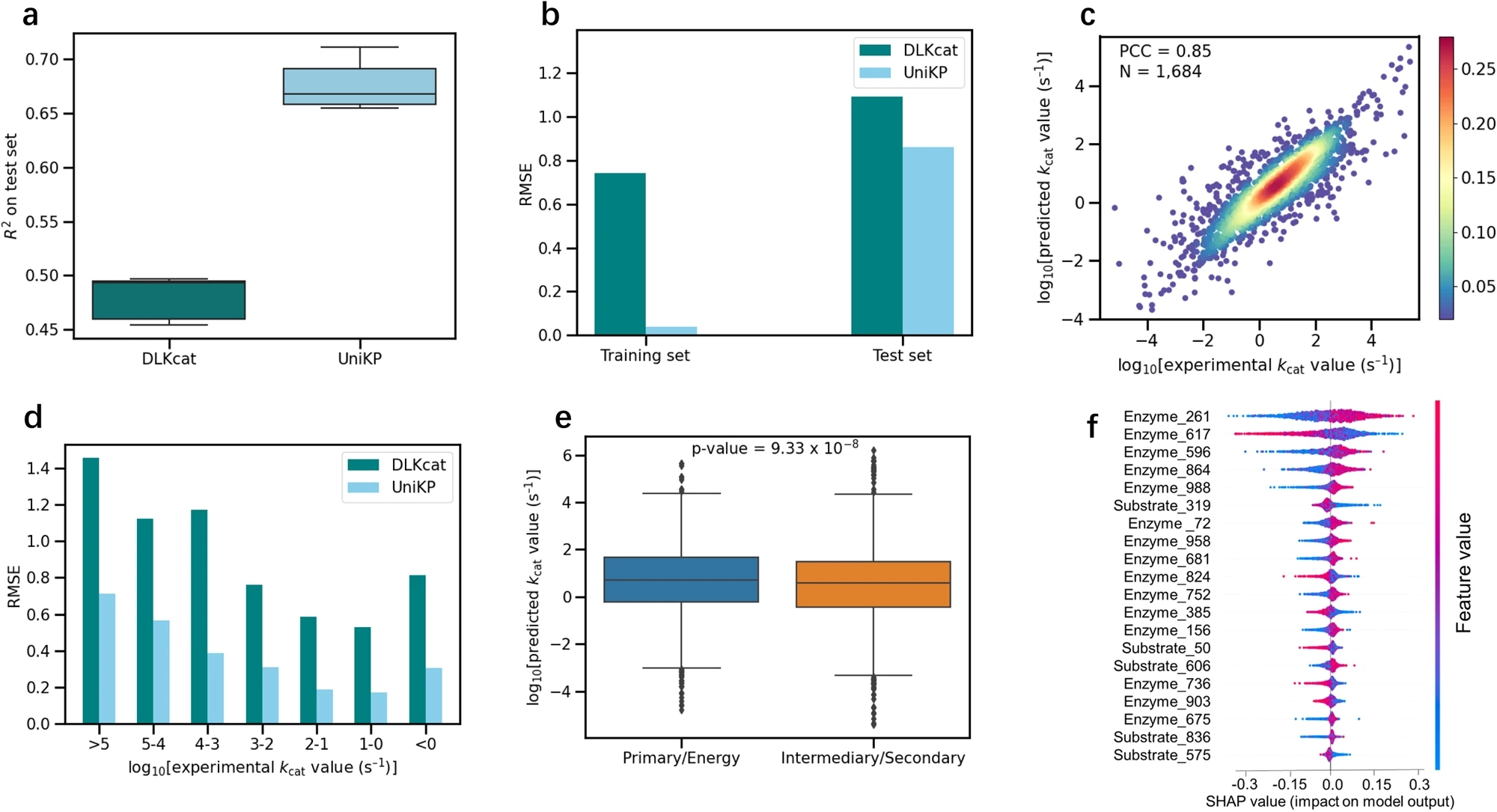
在kcat预测任务中使用DLKcat数据集进行验证。在没有任何额外参数优化的情况下,通过五轮随机分割的测试集上的平均确定系数(R2)值为0.68,比DLKcat提高了20%。此外,这五轮中DLKcat的最高值比UniKP的最低值低16%,进一步证明了UniKP的稳健性。预测值和实验测量值之间的均方根误差(RMSE)在UniKP中也比DLKcat低,无论是在训练集还是测试集中。在测试集中,预测值和实验测量值之间存在着强烈的相关性,相关系数(PCC)为0.85,整个数据集的相关系数为0.99,比DLKcat分别高出14%和11%。
单个或多个酶的序列,fasta格式,每个酶使用一条序列表示(当某个酶有多条链时,将多条单链序列首尾连接作为一条序列)。
底物分子的文件,txt格式,支持多个底物分子,使用SMILES表示,每行一个分子,文件内容示例:
OC1=CC=C(C[C@@H](C(O)=O)N)C=C1
CC(O)O
注意:
1,输入的底物分子数量与酶数量应相同,模块会按文件中的顺序进行酶与底物分子配对。
2,当有多个酶分子时,可只设置一个底物分子,表示每个酶都使用相同的底物分子。
动力学参数预测结果文件名,默认为pred_res.csv
动力学参数结果文件pred_res.csv,包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SeqID | 序列名称 |
| Sequence | 酶序列 |
| SMILES | 底物分子 |
| Kcat(n/s) | 酶的周转数,是酶的动力学参数之一。表示每个酶分子单位时间内能转化底物的最大分子数,单位为个/秒 |
| Km(mM) | 米氏常数,是另一个酶的动力学参数。代表反应速率为最大反应速率一半时的底物浓度,单位为mM |
This module predicts the kinetic parameters Kcat and Km of enzymes. It is implemented based on the UniKP framework, a computational tool designed for enzyme kinetic parameter prediction. UniKP integrates protein sequence and substrate structure information, utilizing pre-trained language models (such as ProtT5-XL-UniRef50) to generate enzyme representations and employs deep learning models to predict enzyme kinetic parameters.
The UniKP framework consists of two key components: the representation module and the machine learning module. The representation module encodes information of enzymes and substrates using pre-trained language models. Specifically, amino acids in enzyme sequences are transformed into 1024-dimensional vectors using the ProtT5-XL-UniRef50 model. For each protein, average pooling is applied to obtain its representation, which has been found to be the most effective method for protein tasks. On the other hand, substrate structures are converted into Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System (SMILES) format and processed by a pre-trained SMILES encoder, generating a 256-dimensional vector for each token. Then, average pooling and max pooling are applied to the first outputs of the last and penultimate layers, concatenated to form a 1024-dimensional molecular representation vector. The concatenated representation vectors of proteins and substrates are then fed into the machine learning module (overall architecture diagram shown below).

The Kcat prediction task was validated using the DLKcat dataset. Without any additional parameter tuning, the average coefficient of determination (R²) on five rounds of random splits of the test set was 0.68, which is a 20% improvement over DLKcat. Furthermore, the highest R² value of DLKcat in these five rounds was 16% lower than the lowest R² value of UniKP, further demonstrating UniKP’s robustness. The root mean square error (RMSE) between predicted and experimental values was also lower in UniKP than in DLKcat for both training and test sets. In the test set, there was a strong correlation between predicted and experimental values, with a Pearson correlation coefficient (PCC) of 0.85, and 0.99 for the entire dataset, which are 14% and 11% higher than DLKcat, respectively.

Sequences of one or more enzymes in FASTA format, with each enzyme represented by a single sequence (for multi-chain enzymes, concatenate the individual chain sequences end-to-end into one sequence).
Substrate molecule file in TXT format. Multiple substrate molecules are supported, represented using SMILES notation, with one molecule per line. Example file content:
OC1=CC=C(C[C@@H](C(O)=O)N)C=C1
CC(O)O
Note:
Filename of the kinetic parameter prediction result file, default is pred_res.csv.
The kinetic parameter result file pred_res.csv contains the following information:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SeqID | Sequence identifier |
| Sequence | Enzyme sequence |
| SMILES | Substrate molecule |
| Kcat (n/s) | Turnover number of the enzyme, one of the kinetic parameters. It represents the maximum number of substrate molecules converted by one enzyme molecule per unit time, in units of per second |
| Km (mM) | Michaelis constant, another kinetic parameter. It represents the substrate concentration at which the reaction rate is half of the maximum, in millimolar (mM) |

DockQ是一种用于评估预测的蛋白-蛋白复合物结构质量的工具和指标,它通过将三个相关但独立的质量测量指标(Fnat、LRMS和iRMS)组合成一个范围在0,1内的单个分数,来评估蛋白质对接模型的质量。DockQ的分数范围为0到1,分数越高表示模型质量越好。根据DockQ的分数,可以将对接模型的质量分为以下几类:
| 分数范围 | 质量分类 |
|---|---|
| 0.00 ≤ DockQ < 0.23 | 错误(Incorrect) |
| 0.23 ≤ DockQ < 0.49 | 可接受质量(Acceptable quality) |
| 0.49 ≤ DockQ < 0.80 | 中等质量(Medium quality) |
| DockQ ≥ 0.80 | 高质量(High quality) |
DockQ的计算公式如下:
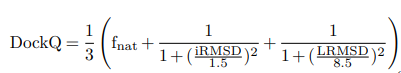
其中:
Fnat:预测复合体在交界面上的作用残基在真实复合体中的比例。
LRMSD:将预测的复合体和真实复合体的两条链中较长的链比对后,较短链的均方根偏差(RMSD)。
iRMSD:度量界面上两个原子相距10 Å内的原子集合的RMSD。
LRMSD与iRMSD是经过缩放后的数值,缩放公式如下:

必填参数,用于DockQ计算的Native复合物结构,PDB格式,一般为实验解析的结构。
必填参数,用于DockQ计算的Model复合物结构,PDB格式,一般为AI模型预测或者分子对接等得到的模拟结构。
可选参数,指定Native结构与Model结构中的链对应关系。相对应的链名之间用逗号分隔,多组链对应时,组间用分号分隔,如:A,E;B,D;C,F表示:
注意:
1,设置该参数时,模块将根据设置的链对应关系来计算DockQ,如不设置该参数,模块会自动匹配所有有界面接触的两条链之间的对应关系,并计算匹配到的所有两条链的DockQ。
2,在特定场景中,计算DockQ时,可能希望合并某些链作为整体来考虑。比如抗原-抗体复合物中,希望将抗体的重、轻链作为一个整体,计算与抗原之间的DockQ值。这种情况,可以在指定mapping参数时,将需要合并的链名写在一起即可,比如C,F;AB,ED 表示:
输出结果文件名称,默认为dockq_res.csv
预测结果文件dockq_res.csv,包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Native_chains | Native结构中用于计算DockQ的链名,多个链名用分号分隔 |
| Model_chains | Model结构中用于计算DockQ的链名,多个链名用分号分隔 |
| DockQ | 计算得到的DockQ数值。DockQ的分数范围为0到1,分数越高表示模型质量越好。 |
| iRMSD | 界面上两个原子相距10 Å内的原子集合的RMSD |
| LRMSD | 将预测的复合体和真实复合体的两条链中较长的链叠合后,较短链的RMSD |
| fnat | 预测复合体在交界面上的作用残基在真实复合体中的比例 |
| fnonnat | 预测复合体在交界面上的作用残基不在真实复合体中的比例 |
| F1 | 预测复合体在交界面上的作用残基是否在真实复合体中,对应的精确率和召回率的调和平均值 |
| clashes | 预测复合体中界面残基存在clash的数量,当两个残基的距离小于2Å时视为clash |
DockQ is a tool and metric used to evaluate the quality of predicted protein-protein complex structures. It combines three related but independent quality assessment metrics—Fnat, LRMS, and iRMS—into a single score ranging from 0 to 1 to assess the accuracy of docking models. A higher DockQ score indicates better model quality. Based on the DockQ score, docking models can be classified as follows:
| Score Range | Quality Category |
|---|---|
| 0.00 ≤ DockQ < 0.23 | Incorrect |
| 0.23 ≤ DockQ < 0.49 | Acceptable quality |
| 0.49 ≤ DockQ < 0.80 | Medium quality |
| DockQ ≥ 0.80 | High quality |
DockQ is computed using the following formula:
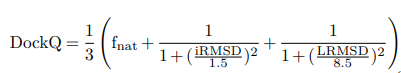
Where:
LRMSD and iRMSD are scaled using the following equations:

Required. The native (reference) structure in PDB format used for DockQ calculation, typically derived from experimental data.
Required. The model structure in PDB format to be evaluated by DockQ, typically generated by AI models or docking simulations.
Optional. Specifies the chain correspondence between the native and model structures. Chain names are separated by commas for each pair, and semicolons are used to separate multiple pairs.
For example: A,E;B,D;C,F means:
Note:
When this parameter is provided, the module uses the specified mapping for DockQ calculation.
If not set, the module will automatically match all chain pairs with interface contacts and calculate DockQ for each matched pair.
In specific scenarios, it may be necessary to consider merged chains as a single unit (e.g., heavy and light chains of an antibody). For such cases, multiple chains can be combined in the mapping, e.g., C,F;AB,ED means:
Output file name for DockQ results. The default is dockq_res.csv.
The result file dockq_res.csv contains the following information:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Native_chains | Chains in the native structure used for DockQ calculation (separated by semicolons) |
| Model_chains | Chains in the model structure used for DockQ calculation (separated by semicolons) |
| DockQ | Computed DockQ score. The DockQ score ranges from 0 to 1, with higher scores indicating better model quality. |
| iRMSD | Interface RMSD of atoms within 10 Å |
| LRMSD | RMSD of the shorter chain after aligning the longer chains |
| fnat | Fraction of native interface contacts |
| fnonnat | Fraction of non-native interface contacts |
| F1 | F1-score combining precision and recall for predicted interface residues |
| clashes | Number of clashes (residue pairs < 2 Å apart) in the predicted complex |
Mirabello C, Wallner B. DockQ v2: improved automatic quality measure for protein multimers, nucleic acids, and small molecules. Bioinformatics. 2024 Oct 1;40(10):btae586; DOI: 10.1101/2024.05.28.596225

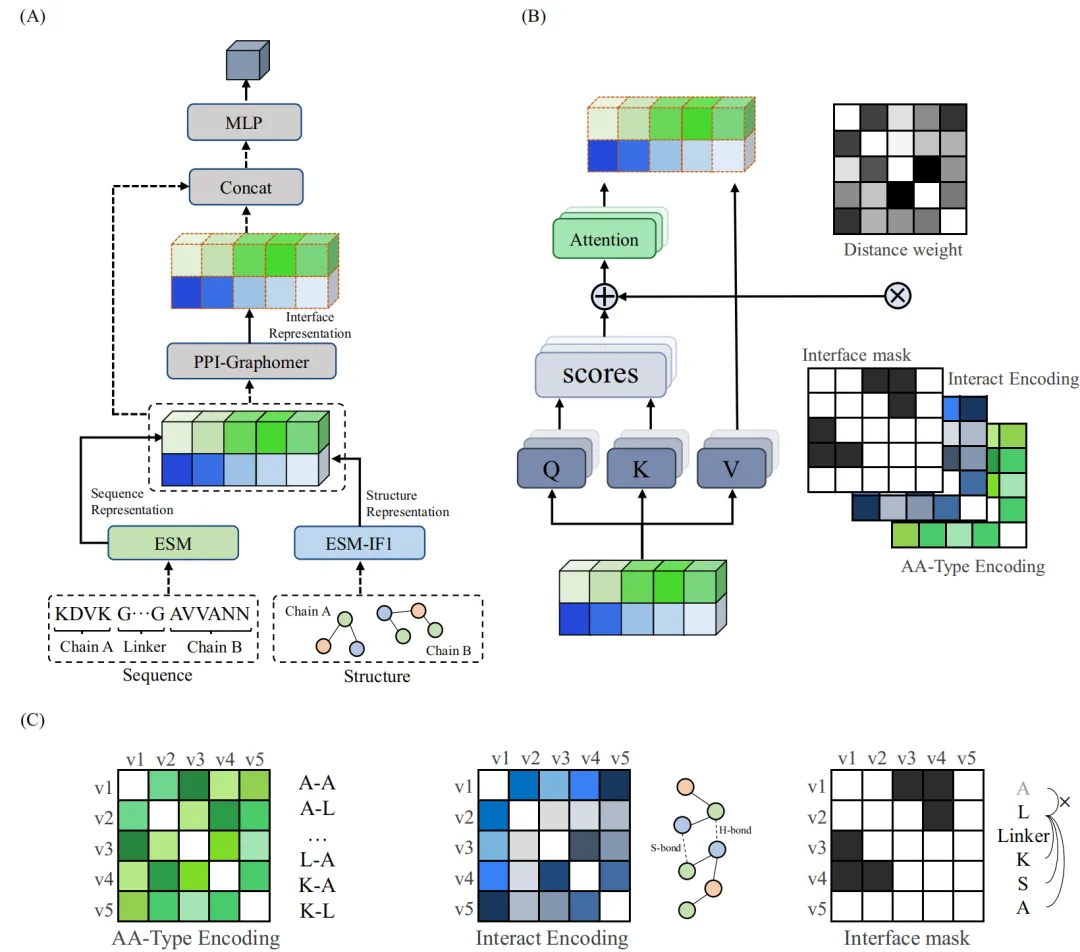
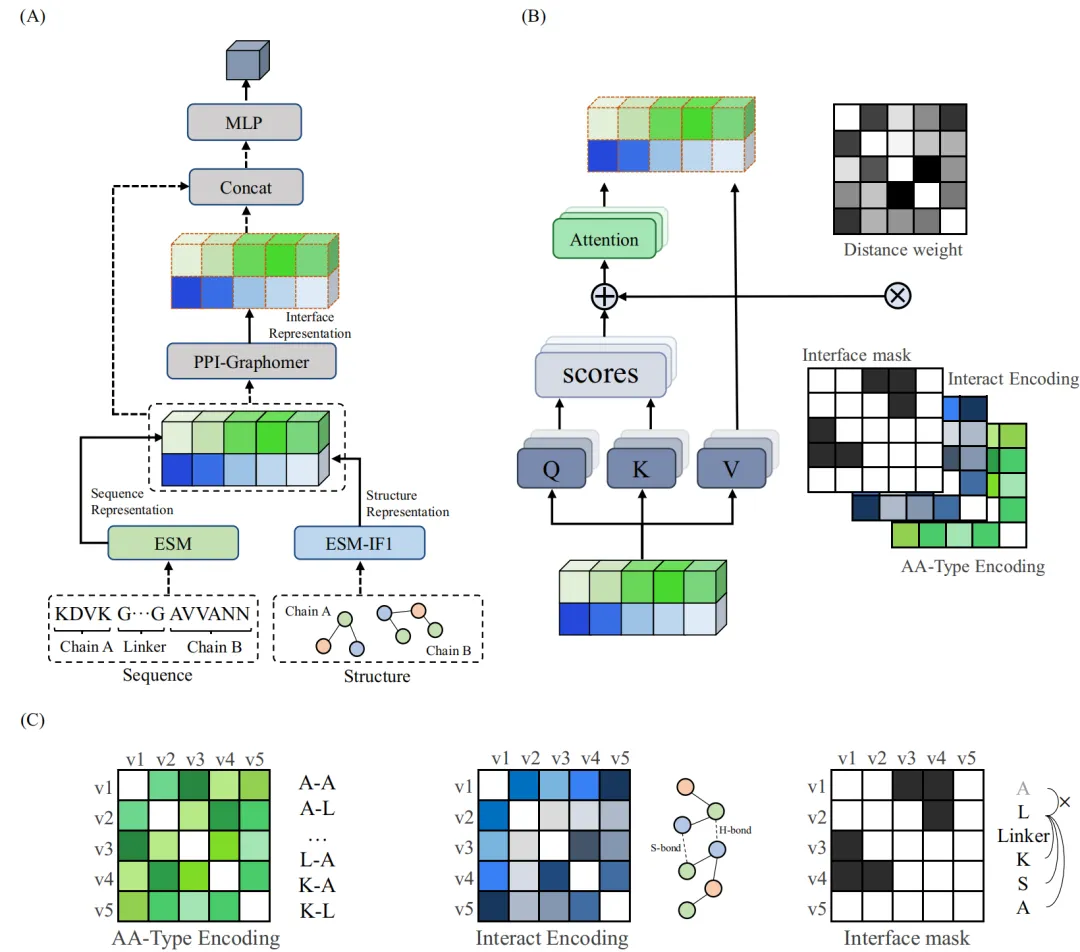
基于PPI-Graphomer模型预测蛋白-蛋白结合亲和力,该模型是一种专门感知界面残基作用的Graph Transformer模型,同时结合了多模态预训练模型,效果显著优于已有主流方法。
模型设计采用:序列 + 结构 + 图神经网络三合一
步骤一:特征提取,蛋白语言模型 + 结构模型协同
步骤二:核心模块,PPI-Graphomer(界面建模利器)
借鉴微软提出的 Graphormer 思想,引入结构感知的图 Transformer 模块,具体包括:
| 编码方式 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 氨基酸对类型编码 AAType(vᵢ,vⱼ) | 区分不同氨基酸组合,推测物理作用趋势 |
| 相互作用力编码 Interact(vᵢ,vⱼ) | 捕捉氢键、盐桥、π堆叠等相互作用数量 |
| 距离权重 Dij + 接口遮罩 | 仅关注跨链、7Å内的残基对,提高关注焦点准确性 |
这些信息被作为注意力偏置项加入到 Transformer 的 Attention 计算中,强化模型对关键界面信息的关注,最终获得接口表征。
步骤三:特征拼接 + 回归预测
使用“跳跃连接式”结构(skip-connection),将界面信息与全局序列结构信息拼接后输入 MLP 预测亲和力(ΔG),输出结果用于与真实值比较回归损失。
模型整体架构示意图如下:
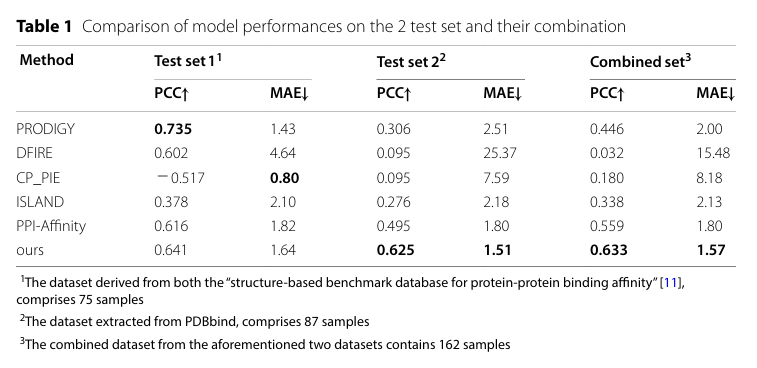
数据集与训练配置如下:
主训练集:PDBbind(共 2376 条蛋白复合物,均转化为ΔG);
测试集:
Affinity Benchmark v1(Test set 1,75 个样本)
PDBbind 精炼子集(Test set 2,87 个样本)
预处理:
移除序列过长(>2000 残基)样本;
使用 BLAST 排除训练集中与测试集相似度>65%的样本,防止数据泄露;
模型参数:
Graphomer 层数:2 层;
Attention 头数:8;
训练轮次:20 epoch;
使用 A40 GPU,推理内存仅需 4GB。
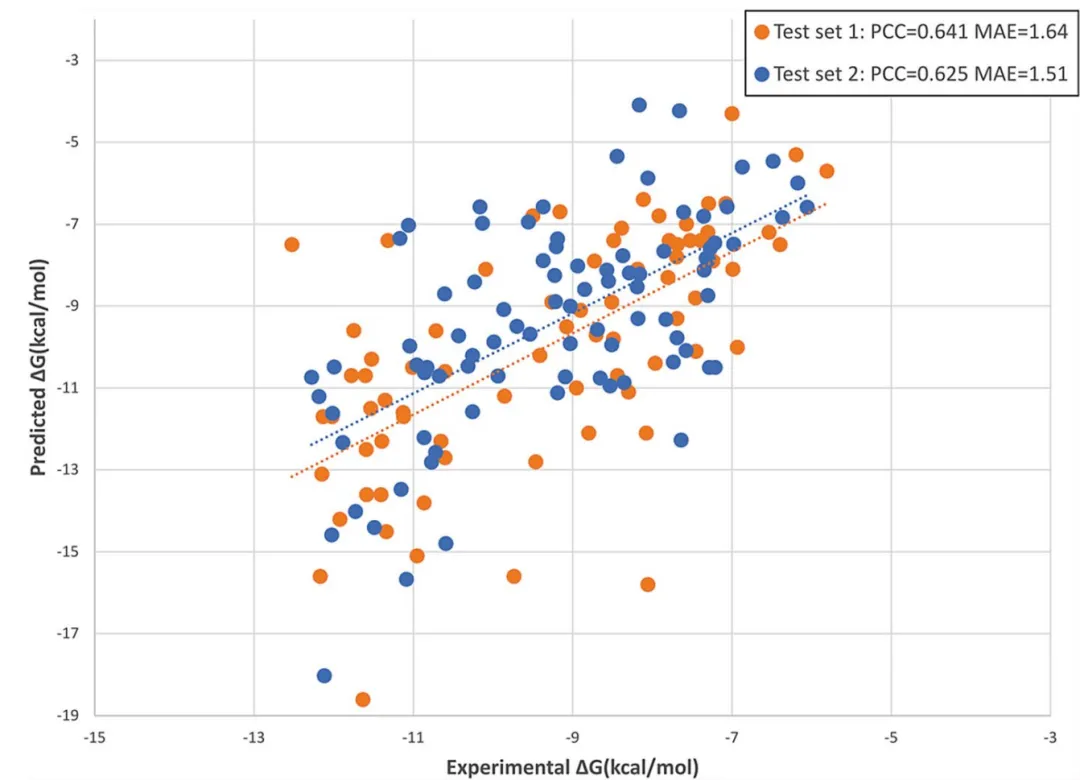
模型预测效果如下:
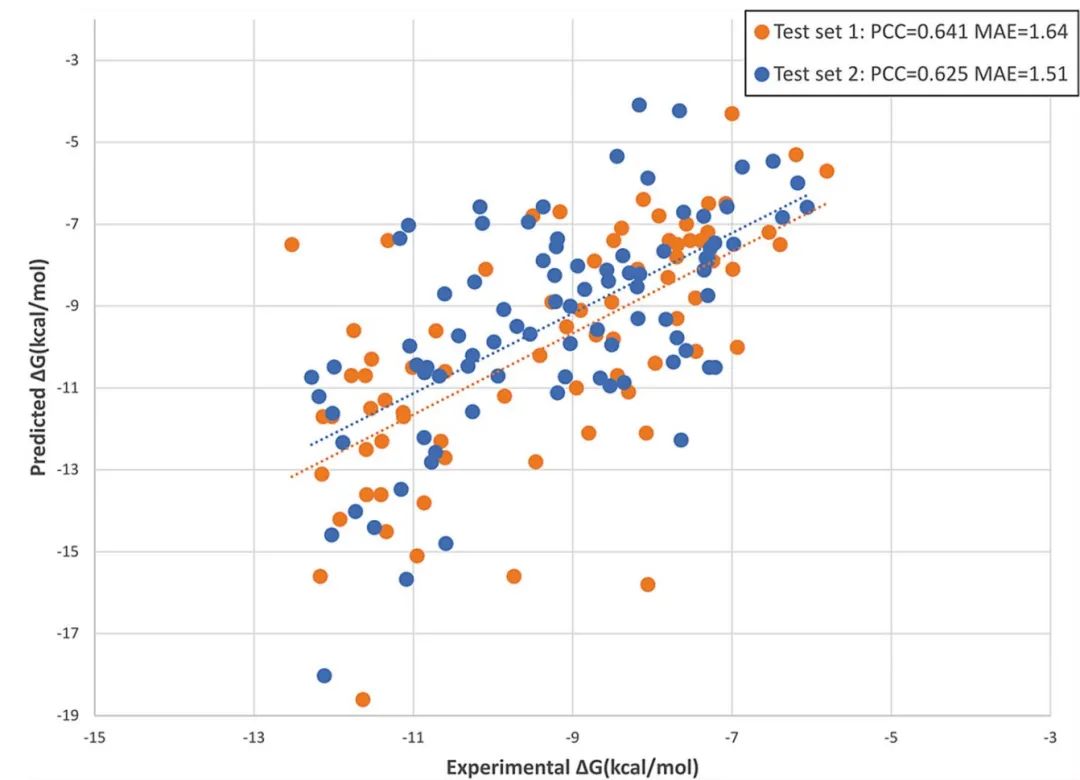
与其他方法的结果比较如下:
蛋白复合物结构,PDB格式。建议PDB体系小于2000AA。
蛋白复合物结构,支持多个复合物结构打包进行批量预测,格式为tar包.tar
亲和力预测的结果文件名,默认为PPI_pred.csv
亲和力预测结果文件PPI_pred.csv,包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 结构名称 |
| Binding_Affinity (kcal/mol) | 预测的亲和力,为Gibbs自由能,单位为kcal/mol。负得越多,亲和力越强。注意:所提供的能量是复合物中所有链之间的亲和力总和。 |
This module predicts protein–protein binding affinity. It is powered by the PPI-Graphomer model, a graph transformer architecture specifically designed to capture interface residue interactions. The model integrates multimodal pretrained features and significantly outperforms existing mainstream approaches.
The model design integrates sequence + structure + graph neural network in a unified framework.
Step 1: Feature Extraction – Coordinated Protein Language and Structure Modeling
Step 2: Core Module – PPI-Graphomer (Interface Modeling Engine)
Inspired by Microsoft’s Graphormer, a structure-aware graph transformer module is introduced. It includes:
| Encoding Type | Description |
|---|---|
Amino Acid Pair Encoding AAType(vᵢ,vⱼ) |
Differentiates amino acid combinations to infer physical interaction trends |
Interaction Force Encoding Interact(vᵢ,vⱼ) |
Captures number of interactions such as hydrogen bonds, salt bridges, and π-stacking |
Distance Weight Dij + Interface Mask |
Focuses only on inter-chain residue pairs within 7Å to enhance attention accuracy |
These encodings are used as attention biases in the transformer’s attention mechanism, reinforcing the model’s focus on key interfacial residues to derive meaningful interface representations.
Step 3: Feature Fusion + Affinity Regression
Using a skip-connection design, the interface features are concatenated with global sequence and structure features and input into an MLP to predict binding affinity (ΔG). The predicted values are compared with ground truth to compute regression loss.
The overall model architecture is illustrated below:
Primary training dataset: PDBbind (2,376 protein complexes, all converted to ΔG);
Test datasets:
Preprocessing:
Model Hyperparameters:
Prediction Performance:
Comparison with Other Methods:
Protein complex structure in PDB format. It is recommended that the PDB system contains fewer than 2000 amino acids.
Protein complex structure, supports multiple complex structure packaging for batch prediction, the format is.tar
Filename for the prediction results. Default is PPI_pred.csv.
The output file PPI_pred.csv contains:
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the structure |
| Binding_Affinity (kcal/mol) | Predicted binding affinity (Gibbs free energy) in kcal/mol.The more negative the value, the stronger the affinity. Note: The provided energy represents the total affinity among all chains within the complex. |
该模块计算蛋白质表面静电和疏水作用相对富集的区域,用于显示出在蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用中其重要作用的区域,这对于预测基于非共价弱相互作用的可逆的聚集现象尤其有用。尤其是,疏水相互作用长期被认为是大分子间吸引相互作用的主要组成部分。对于抗体,静电相互作用牵涉到了自聚集,而偶极-偶极相互作用被认为是导致β-折叠的纤维化的原因。同时,也可以通过WeView界面对蛋白结构进行Patch分析。
v2.1 更新内容
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式
pH值,用于蛋白质子化判断
抗体编号方法,其中 no_use 不使用编号
Hydrophobic cutoff是一个以疏水性氨基酸(通常包括Leu,Ile,Val,Phe,Trp和Met)为基础定义的截断值,用于将表面上疏水性氨基酸的数量与表面面积相比较,从而筛选出可能具有重要生物学功能的区域。一般来说,Patch区域中获得的化学性质信息会根据其表面密度和具有高疏水性氨基酸的数量而有所变化。
Positive Cutoff是一个以阳离子氨基酸为基础定义的截断值,用于将表面上阳离子氨基酸的数量与表面面积相比较,从而筛选出可能具有重要生物学功能的区域。一般来说,positive cutoff方式用于筛选出可能参与离子相互作用的蛋白质表面区域。
Negative Cutoff是一个以阴离子氨基酸为基础定义的截断值,用于将表面上阴离子氨基酸的数量与表面面积相比较,从而筛选出可能具有重要生物学功能的区域。一般来说,negative cutoff方式用于筛选出可能参与离子相互作用的蛋白质表面区域。
SASA Cutoff是一个以溶剂可及表面积为基础定义的截断值,低于截断值的patch残基会被过滤掉。是残基侧链暴露程度的百分比,相对值,范围在0-100之间。
Distance Cutoff是原子距离截断值,低于截断值的才会认为属于同一聚集块。值越小,聚集块patch越小。
Min Distance Cutoff是patch之间的距离截断值,距离小于截断值的归为同一个patch。
输出文件格式,csv或者json
通俗地讲,cutoff代表静电势能或疏水势能的强度阈值,单位是kcal/mol,超过阈值才会被计入面积。阈值越小,则patch越多。
不添加缺失原子(包括氢原子)和结构优化。
使得N-氮端的蛋白残基中性化。
使得C-氮端的蛋白残基中性化。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| patch_list.csv | Patch结果的csv文件。主要关注Area(Å^2)数值,代表patch的大小,越大则越可疑,重点关注100 Å以上的patch。 |
| input_prot.pdb | 质子化后的pdb结构。 |
| patch_list_sum.csv | 统计了三种patch类型(Hyd:疏水中心,Neg:负电中心,Pos:正电中心)在蛋白表面所占面积,重点关注100 Å以上的patch。 |
其中patch_list.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Type | Patch的类型,Hyd:疏水中心,Neg:负电中心,Pos:正电中心 |
| Area(Å^2) | 每个Patch的蛋白质表面区域面积 |
| Residues | 每个Patch的对应的残基 |
其中patch_list_sum.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Type | Patch的类型,Hyd:疏水中心,Neg:负电中心,Pos:正电中心 |
| Total Areas | Patch的蛋白质表面区域总面积 |
| Areas of The Largest | Patch的蛋白质表面区域最大面积 |
| Number of Areas More Than 100 | 超过100 Å以上的patch的数目 |
Protein Patches calculates both electrostatic (excess charge) and hydrophobic surface patches to show regions of significance with respect to protein-protein interactions. This can be particularly useful in the prediction of reversible aggregation, which typically arises from relatively weak non-covalent interactions. In particular, hydrophobic interactions have long been recognized as major contributors in high affinity interactions between macromolecules. In antibodies, electrostatic interactions have been implicated in forming self-associated aggregates [Karshikoff 2006], while dipole-dipole interactions are believed to be the cause of fibrillogenic association of β-sheets. At the same time, protein structures can also be analyzed for patches through the WeView interface.
Electrostatic patches.
The surface electrostatic field is estimated using an exponentially decaying Debye-Hückel field with a screening length of λD=3.5Å.
The map thus obtained is one mostly of excess charge close to the molecular surface.
Significant patches are established by cutting the surface along isocontour lines of absolute field value equal to 40 kcal/mol/C, keeping regions above. Finally, a default minimal patch area of 40Å2 filters out smaller, presumably less relevant, patches.
Hydrophobicity map.
The hydrophobic potential is calculated from the Wildman and Crippen octanol-water partition coefficients f=log P [Wildman 1999]:
where fi is the coefficient of atom i and g(ri) is a Fermi-type distance-dependent weighting function proposed by Heiden et al. [Heiden 1993]:
with rcut=5Å and α=1.5.
Similarly to electrostatic (excess charge) patches, significant hydrophobic patches are established by cutting the surface along isocontour lines, retaining only the portion above a potential threshold value of 0.09 kcal/mol, and filtering for a minimal patch area of 50Å2.
v2.1 updates
Protein structure file in PDB format.
pH value for protein protonation
Antibody Numbering type, no_use indicates no antibody numbering applied.
Hydrophobic Cutoff defined based on hydrophobic amino acids (usually including Leu, Ile, Val, Phe, Trp, and Met) is used to compare the number of hydrophobic amino acids on a surface with the surface area, so as to screen out areas that may have important biological functions. Generally speaking, the chemical property information obtained in the Patch region will vary according to its surface density and the number of highly hydrophobic amino acids.
Positive Cutoff is a cut-off value defined based on cationic amino acids, which is used to compare the number of cationic amino acids on the surface with the surface area to screen out areas that may have important biological functions. Generally speaking, the positive cutoff method is used to screen protein surface regions that may be involved in ion interactions.
Negative Cutoff is a value defined based on anionic amino acids, which is used to compare the number of anionic amino acids on a surface with the surface area, to screen out areas that may have important biological functions. Generally speaking, the negative cutoff method is used to screen the surface regions of proteins that may participate in ion interactions.
SASA Cutoff is a cutoff value defined on the basis of polar surface area, which is used to screen the surface regions of proteins that have enough polar surface areas.
Distance Cutoff is a cutoff value defined on the basis of neighbor atoms, which is used to adjust the size of patches. Lower values result in smaller patches.
Min Distance Cutoff is the cutoff value for neighbor patch point distance (Å). Patches with distances lower than the cutoff value would be merged.
output file format, json or csv
Do no atom addition and optimization.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| patch_list.csv | A CSV file containing patch results. The main focus is on the Area (Å^2) value, which represents the size of the patch. Larger patches are considered more suspicious, with particular attention to patches larger than 100 Å. |
| input_prot.pdb | The protonated PDB structure. |
| patch_list_sum.csv | Summarizes the surface area occupied by three types of patches (Hyd: hydrophobic center, Neg: negative charge center, Pos: positive charge center) on the protein surface. Focus is placed on patches larger than 100 Å. |
Details of patch_list.csv:
The file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | The type of patch: Hyd (hydrophobic center), Neg (negative charge center), Pos (positive charge center). |
| Area (Å^2) | The surface area of each patch on the protein. |
| Residues | The residues corresponding to each patch. |
Details of patch_list_sum.csv:
The file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | The type of patch: Hyd (hydrophobic center), Neg (negative charge center), Pos (positive charge center). |
| Total Areas | The total surface area of patches on the protein. |
| Areas of The Largest | The largest surface area of a patch on the protein. |
| Number of Areas More Than 100 | The number of patches with an area larger than 100 Å. |
WeADApt (Wecomput ADA prediction) 是唯信开发的基于多模融合深度学习架构的免疫原性预测系统(也被熟知为AlphaMHC)。
该方法采用全新的多模融合深度神经网络架构,整合了近10亿条与免疫原性相关的湿实验数据(包括亲和力数据、呈递数据、NGS数据、质谱数据等)进行训练,有机地将多个与免疫原性相关的模型融合,构成一个高效的免疫反应模拟系统,可准确地模拟蛋白、抗体、多肽、疫苗等生物药的免疫原性,并能鉴别潜在的免疫原性的T细胞表位(引起临床人体免疫应答的肽段),实现了从序列到临床免疫原性风险的端到端的预测,并通过了数百条来自FDA、EMA的临床真实免疫原性数据(包括单/多特异性抗体和重组蛋白等)的验证测试。
在同样的42个抗体分子的临床ADA数据集上,WeADApt(v4)预测的相关性超过了知名的商业软件EpiMatrix(R2=0.49 vs R2=0.42)。

该版本是截止到2025/04/30的最新主力版本。
相比v4.1进一步提升了预测的特异性,且对不同风险水平的表位的区分度更高,结果对于去免疫原性改造更有指导性。
V4.2版本相对于上个版本v4.1主要有以下改进:
从FDA和EMA的临床试验中收集了200余个已知免疫原性的分子及其ADA的分布,计算模型预测值与真实ADA发生率的相关性,以测试其预测性能。
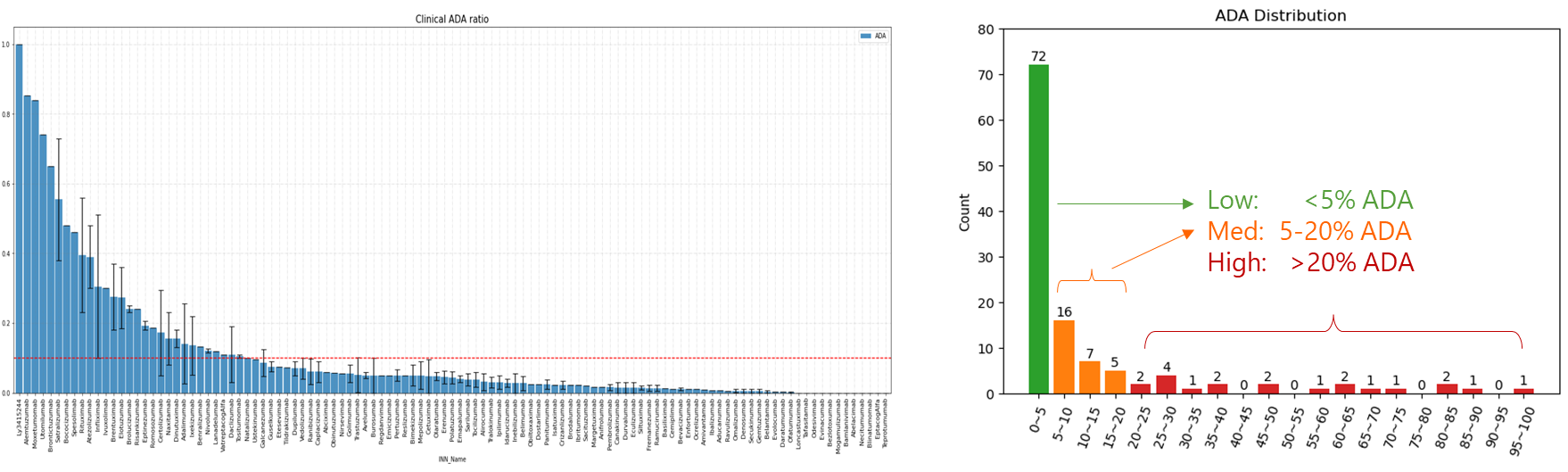
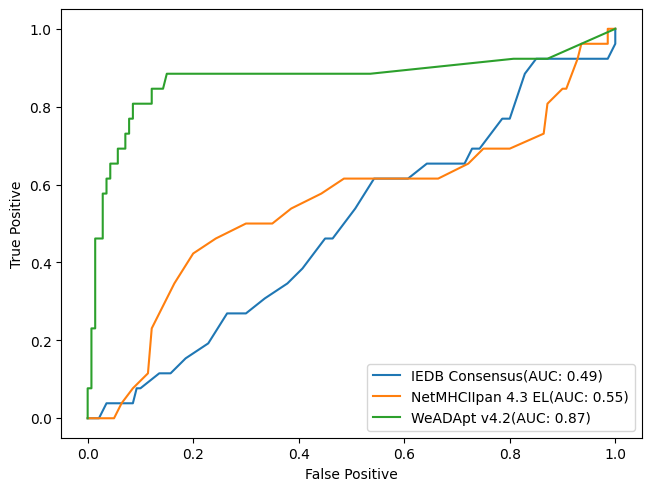
预测的打分(MolScore)与ADA发生率的相关性达到R=0.87(下图)。
在同样的210个分子数据集上,WeADAptV预测的相关性超过了知名免疫原性预测软件IEDB Consensus(R2=0.49)、NetMHCllpan 4.3 EL(R2=0.55)。
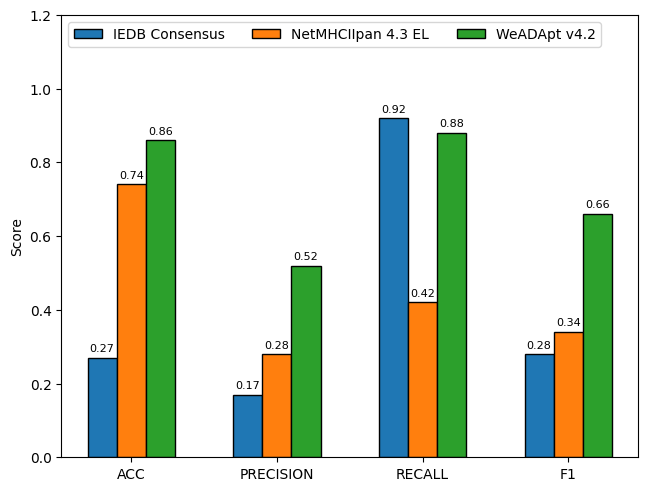
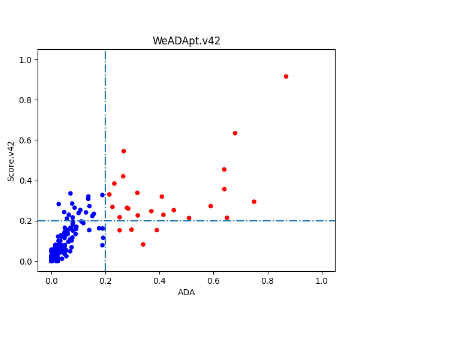
使用唯信收集整理的200多个临床及上市单抗的ADA数据的测试结果如下图所示,预测分数与ADA发生率的Pearson相关性达到R=0.76。
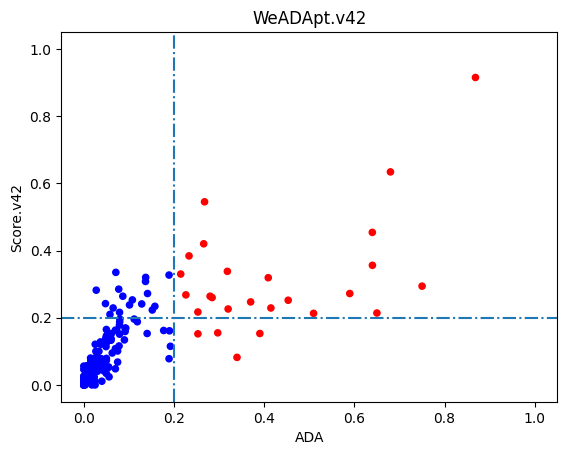
0.2分适合作为单抗的高/低风险的阈值(>20% ADA定义为高风险)。
WeADApt v4被设计为兼容各类的分子形式,不论是对称还是非对称、是否有重复结构域的任意蛋白分子,仅需输入不重复的链即可(重复链全部输入也会自动处理)。
使用唯信收集整理的双抗ADA数据集的测试表现如下图所示,预测分数与ADA发生率的Pearson相关性达到R=0.60。
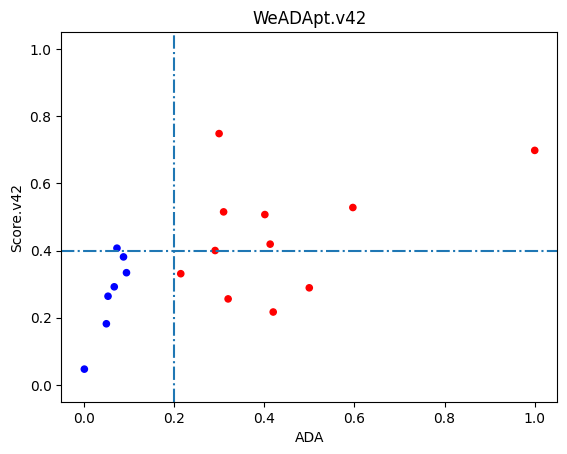
注意区别于v4.1的一点是,由于分布的变化,该版本以0.4的分数作为分界线时,可以较好的区分高、低风险的双抗分子。
本系统仅从序列水平预测产生的影响,因此尤其适合同类靶点分子的相对比较和筛选。
WeADApt (Wecomput ADA Prediction) is an immunogenicity prediction system developed by Wecom, based on a multi-modal fusion deep learning architecture. It is also widely known as AlphaMHC.
This method employs a novel multi-modal fusion deep neural network architecture, trained on nearly 1 billion immunogenicity-related wet-lab experimental data points (including affinity data, presentation data, NGS data, mass spectrometry data, etc.). It organically integrates multiple immunogenicity-related models to form an efficient immune response simulation system. This system accurately simulates the immunogenicity of biologics such as proteins, antibodies, peptides, and vaccines, while identifying potential immunogenic T-cell epitopes (peptides that trigger clinical immune responses in humans). It achieves end-to-end predictions of immunogenicity risks from sequence to clinical outcomes and has been validated against hundreds of real clinical immunogenicity data points (including mono-/multi-specific antibodies and recombinant proteins) from FDA and EMA.
On the same clinical ADA dataset of 42 antibody molecules, the correlation of WeADApt (v4) predictions outperformed the well-known commercial software EpiMatrix (R²=0.49 vs. R²=0.42).

This version is the latest main version as of April 30, 2025.
Compared to v4.1, v4.2 further improves prediction specificity and enhances the discrimination of epitopes with different risk levels, making the results more instructive for de-immunogenicity engineering.
The main improvements of v4.2 compared to the previous version (v4.1) include:
A dataset of over 200 molecules with known immunogenicity and their ADA distributions was collected from FDA and EMA clinical trials. The model’s prediction performance was evaluated by calculating the correlation between the predicted values and the actual ADA incidence rates.

The correlation between the predicted scores (MolScore) and ADA incidence reached R = 0.87 (as shown below).

Using the same dataset of 210 molecules, the WeADAptV prediction demonstrated a higher correlation compared to well-known immunogenicity prediction tools, including IEDB Consensus (R² = 0.49) and NetMHCIIpan 4.3 EL (R² = 0.55).


Using a dataset of over 200 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) with clinical and marketed ADA data collected and curated by Wecom, the test results are shown below. The Pearson correlation between the predicted scores and ADA incidence rates reached R=0.76.

A score of 0.2 is suitable as the threshold for distinguishing between high-risk and low-risk monoclonal antibodies (with >20% ADA incidence defined as high risk).
WeADApt v4 is designed to be compatible with various molecular formats, regardless of symmetry, the presence of repeated domains, or other structural characteristics. Users only need to input the non-redundant chains (redundant chains can also be input, as the system will automatically process them).
The test performance on a bispecific antibody (BsAb) ADA dataset curated by Wecom is shown below. The Pearson correlation between the predicted scores and ADA incidence rates reached R=0.60.

Note: Compared to v4.1, due to distribution changes, this version uses a score of 0.4 as the threshold to better distinguish between high-risk and low-risk bispecific antibodies.
This system predicts immunogenicity solely based on sequence-level information, making it particularly suitable for relative comparisons and screening of molecules targeting similar targets.

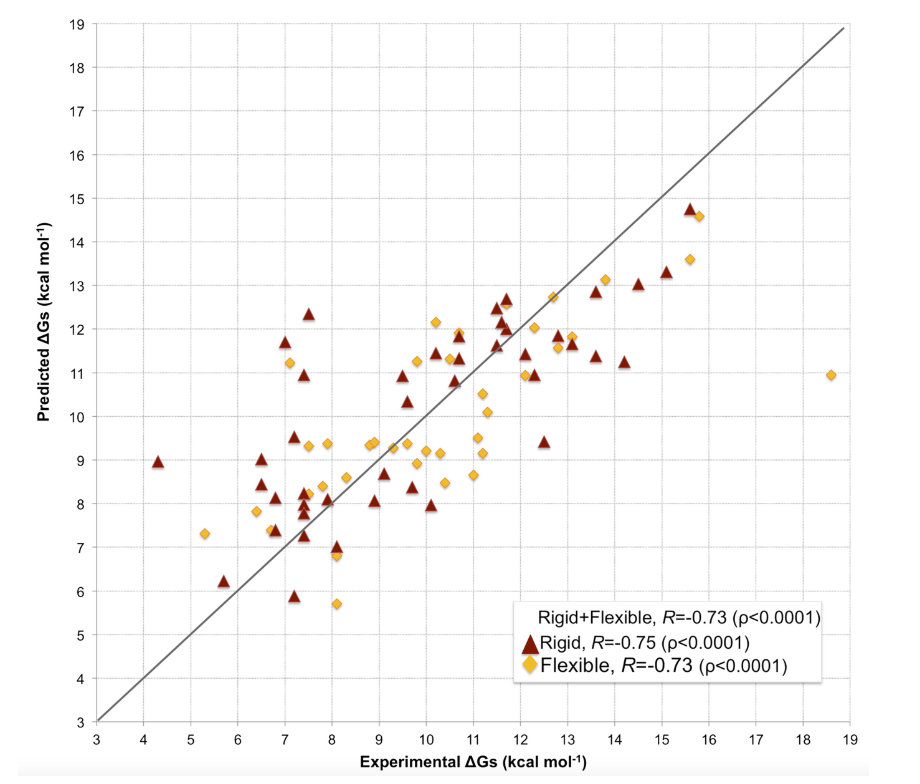
该模块结合界面接触特征与非相互作用表面(NIS)特征,用于预测蛋白-蛋白结合亲和力,并可输出接触界面的残基信息。模块基于PRODIGY模型,该模型通过线性回归利用界面接触点和NIS的物理化学性质来估算结合亲和力,这些性质已被验证对亲和力具有显著影响。
以下为亲和力的计算公式:

公式中的 ICsxxx/yyy 表示在相互作用的两个蛋白之间检测到的界面接触点数,xxx/yyy表示接触残基的类型(带电/极性/非极性等),例如 ICscharged/apolar 表示带电残基与非极性残基之间的接触点数量。若两个残基之间任意重原子的距离小于5.5 Å,则视为发生了接触。
该模型在81个复合物的数据集上进行了验证,预测亲和力与实验值之间的皮尔逊相关系数为0.73(p < 0.0001),均方根误差(RMSE)为1.89 kcal/mol。
蛋白复合物的结构文件,格式支持 .pdb 或 .cif。支持多个复合物结构打包进行批量预测,压缩格式支持 .tar、.tar.gz 或 .zip。
用于将结构中的多个链组合为组,组内链作为整体,仅计算组与组之间的结合亲和力。组合格式为:组内链名用逗号分隔,组与组之间用分号分隔。
示例:H,L;A 表示将链 H 和 L 作为一组,链 A 作为另一组,计算这两组之间的亲和力。
注意:
输出链间接触界面的残基对信息。
预测结果文件名,默认值为 prodigy_output.csv。
接触界面残基对的结果文件名,默认值为 contacts.txt。
预测结果文件 prodigy_output.csv 包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 结构名称 |
| Binding_Affinity (kcal/mol) | 预测的结合亲和力,单位为 kcal/mol,值越小越好,负得越多表示结合越强 |
| Dissociation_Constant (25.0˚C) | 根据公式 ΔG = RTlnKd 计算出的25°C下的解离常数 |
| Intermolecular Contacts | 接触残基对总数 |
| Charged_Charged Contacts | 带电残基-带电残基的接触对数 |
| Charged_Polar Contacts | 带电残基-极性残基的接触对数 |
| Charged_Apolar Contacts | 带电残基-非极性残基的接触对数 |
| Polar_Polar Contacts | 极性残基-极性残基的接触对数 |
| Apolar_Polar Contacts | 非极性残基-极性残基的接触对数 |
| Apolar_Apolar Contacts | 非极性残基-非极性残基的接触对数 |
| Percentage of Apolar NIS | 非极性非相互作用表面的百分比 |
| Percentage of Charged NIS | 带电非相互作用表面的百分比 |
可选接触界面结果文件 Contacts.txt,每行记录一个接触残基对,包含残基名称、编号及所在链名。
若启用批量模式,在设置contacts参数后,将给出打包文件:
Contacts.tar.gz:接触残基对结果This module predicts protein-protein binding affinity by combining interfacial contact features with non-interacting surface characteristics. It also provides residue-level information for the contact interface. The module is based on the PRODIGY model, which applies linear regression using properties of interfacial contacts and non-interacting surfaces (NIS), both of which have been shown to influence binding affinity.
The binding affinity is calculated using the following formula:

ICsxxx/yyy represent the number of interfacial contact points found between interacting protein 1 and interacting protein 2, categorized by the polarity/charge of the interacting residues (e.g., ICscharged/apolar indicates the number of interfacial contact points between charged and apolar residues). Two residues are considered to be in contact if any of their heavy atoms are within 5.5 Å of each other.
The model’s prediction accuracy was evaluated using a dataset of 81 complexes. The Pearson correlation coefficient between predicted and experimental binding affinities is 0.73 (p < 0.0001), with a root-mean-square error (RMSE) of 1.89 kcal/mol⁻¹.
The protein complex structure in PDB or CIF format. Multiple complex structures can be packaged together for batch prediction. Supported package formats: .tar, .tar.gz, or .zip.
Allows grouping of multiple chains in the structure. Chains in the same group are treated as a single unit, and binding affinity is only calculated between groups. Use chain IDs to define groups: separate chains in the same group with commas, and separate groups with semicolon.
Example: H,L;A means chains H and L are treated as one group, and chain A as another group. The binding affinity is then calculated between these two groups.
Note:
Outputs residue pairs at the inter-chain contact interface.
Filename for the binding affinity prediction result. Default: prodigy_output.csv
Filename for the contact interface residue pairs. Default: contacts.txt
The binding affinity prediction result is saved in prodigy_output.csv, which includes the following columns:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Structure name |
| Binding_Affinity (kcal/mol) | Predicted binding affinity in kcal/mol. The smaller the value, the better. The more negative it is, the stronger the binding. |
| Dissociation_Constant (25.0˚C) | Dissociation constant at 25°C, calculated using: ΔG = RTlnKd |
| Intermolecular Contacts | Total number of interfacial residue pairs |
| Charged_Charged Contacts | Number of contacts between charged residues |
| Charged_Polar Contacts | Number of contacts between charged and polar residues |
| Charged_Apolar Contacts | Number of contacts between charged and apolar residues |
| Polar_Polar Contacts | Number of contacts between polar residues |
| Apolar_Polar Contacts | Number of contacts between apolar and polar residues |
| Apolar_Apolar Contacts | Number of contacts between apolar residues |
| Percentage of Apolar NIS | Percentage of apolar non-interacting surface |
| Percentage of Charged NIS | Percentage of charged non-interacting surface |
The optional contact interface file Contacts.txt lists one contacting residue pair per line, including residue names, numbers, and chain IDs.
In batch mode:
Contacts.tar.gz
该模块是抗体人源化设计流程中分组模块,根据Mutation Score模块输出的回复突变评分表对回复突变进行分组,并返回突变后的序列。
更新内容:
抗体CDR区嫁接后序列文件,FASTA格式,由Grafting模块生成
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式
人源化突变评分文件,CSV格式,由Mutation Score模块生成
指定输出的突变序列文件名称,FASTA格式
打分分组的截断值,逗号分割,例如:2,5,10表示将氨基酸突变评分大于10的为一组,5~10的氨基酸为一组,小于2的氨基酸分为一组。
指定输出的回复突变的文件
普通抗体Antibody或者纳米抗体Nanobody
突变组合的截断值,Mutation Score模块中输出的氨基酸回复突变打分大于截断值的氨基酸参与生成突变组合
高于截断值的突变自动进行回复突变
每条链回复突变打分在Combination Min Cutoff与Combination Max Cutoff之间的选择打分前n个位置进行组合突变
根据不同截断值得到突变分组结果文件mutate_policy.json。
根据组合突变截断值得到的突变分组结果文件combination_mutate_policy.json,高通量人源化设计流程。
Back mutation grouping in the antibody humanization, which groups the back mutations based on the mutation scoring table generated by the Mutation Score module.
Sequence file of the antibody CDR region after grafting, in FASTA format, generated by the Grafting module.
Sequence file of the antibody, in FASTA format.
Humanization mutation score file, in CSV format, generated by the Mutation Score module.
Specify the name of the output mutation sequence file, in FASTA format.
Cutoff values for scoring grouping, separated by commas. For example, 2,5,10 indicates grouping amino acid mutations with scores greater than 10 in one group, amino acids with scores between 5 and 10 in another group, and amino acids with scores less than 2 in a separate group.
Specify the file for the output of back mutations.
Antibody or Nanobody
Cutoff value for mutation combinations. Amino acids with scores (generated from Mutation Score module) greater than the cutoff value are involved in the mutation combinations.
Mutations above the cutoff value automatically undergo reversion mutations.
For each chain, select the top n positions with back mutation scores between the Combination Min Cutoff and the Combination Max Cutoff for combination mutations.
The mutation grouping results file mutate_policy.json is generated based on different cutoff values.
The mutation grouping results file combination_mutate_policy.json is generated based on combination cutoff values.

该模块具有两方面的功能:
1,用于预测肽段(长度不超过10个氨基酸)被18种基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)切割的效率。
2,基于指定的目标切割谱(如:仅被MMP13切割),生成相应的多肽底物。
模块基于CleaveNet模型实现,CleaveNet是一种基于深度学习的蛋白酶底物设计工具,通过整合预测与生成技术,实现了从“虚拟筛选”到“智能设计”的转变。
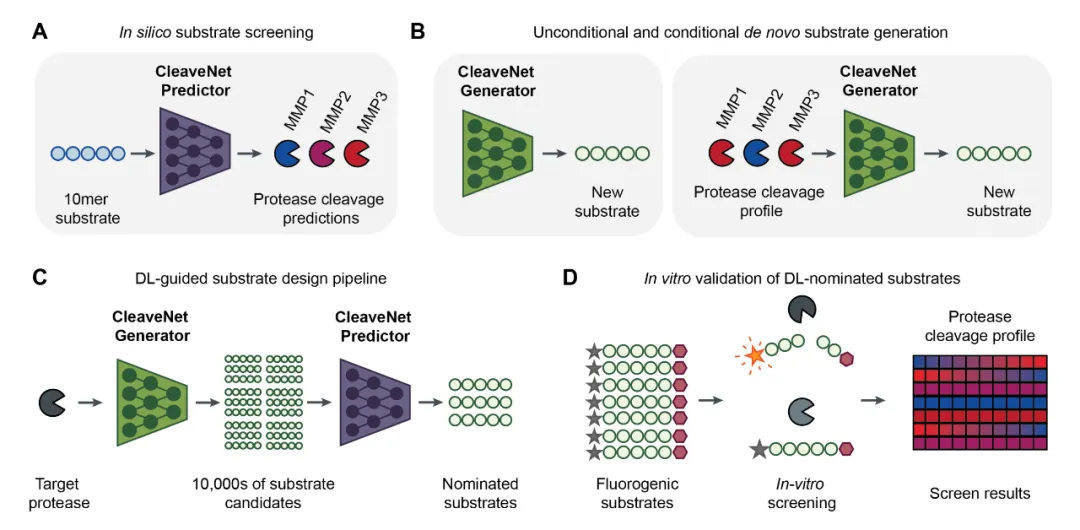
CleaveNet包含两个核心模块:
预测模块
生成模块
这一端到端的设计流程显著提高了底物设计的效率和精准性,为蛋白酶研究提供了一种全新的计算驱动方法。
实验验证
为评估CleaveNet的实际应用能力,研究团队以MMP13(一种与癌症转移、伤口愈合和骨关节炎相关的胶原酶)为目标,设计并合成了95条肽段底物,并通过荧光共振能量转移(FRET)技术验证其切割效率。实验结果表明:
这些结果验证了CleaveNet在设计高效且特异性底物方面的能力,同时也展示了其揭示未知底物偏好的潜力。
必填参数,多肽序列,txt或fasta格式,支持多条(txt格式时,每行放置一条多肽)。注意:多肽长度不能超过10个残基,超过长度的多肽序列会自动被过滤掉。
txt格式实例如下:
LRVFL
FMPLNFTASG
LGPYAMTSRG
AARFKKFATE
可选参数,预测得到的MMPs酶切概率结果文件名称,默认为“pred_cleavage.csv”。
可选参数,指定需要生成的多肽数量,默认为50。
可选参数,指定多肽生成的酶切条件,CSV文件格式。包含每种MMP酶的酶切概率Z-score值,值越大表示酶切的可能性越高,值可为负,一般阈值为2.5,大于该阈值时,表示极大可能被酶切。模型会根据设置的各种MMPs酶的酶切概率Z-score值进行多肽生成。注意:18种MMPs的Z-score数值都必须设定,不能缺少任意一种。
文件内容实例如下:
MMP1,MMP10,MMP11,MMP12,MMP13,MMP14,MMP15,MMP16,MMP17,MMP19,MMP2,MMP20,MMP24,MMP25,MMP3,MMP7,MMP8,MMP9
2.0,1.2,2.2,2.9,3.3,4.1,2.2,3.1,2.2,1.91,3.6,2.83,2.7,0.2,1.8,2.1,0.61,4.2
以上内容为一组条件,也支持多组条件同时输入,每行一组条件即可。每组条件都会生成指定数量的多肽。多组条件示例如下:
MMP1,MMP10,MMP11,MMP12,MMP13,MMP14,MMP15,MMP16,MMP17,MMP19,MMP2,MMP20,MMP24,MMP25,MMP3,MMP7,MMP8,MMP9
2.0,1.2,2.2,2.9,3.3,4.1,2.2,3.1,2.2,1.91,3.6,2.83,2.7,0.2,1.8,2.1,0.61,4.2
3.33,2.5,3.6,2.7,2.9,5.2,3.4,4.2,2.7,2.0,3.5,2.6,4.0,3.1,3.5,0.61,2.1,2.9
可选参数,指定生成的温度条件,用于控制生成多肽序列的多样性,默认为1.0,越大表示多样性越高。如果希望多样性低一些,推荐0.7,如果希望多样性再高一些,推荐1.2~1.5。
可选参数,指定序列输出文件名称,fasta或txt格式,默认为“gen_seqs.fasta”。
预测得到的MMPs酶切概率结果文件,默认为pred_cleavage.csv。包含如下内容:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SEQ | 多肽序列 |
| MMP1,MMP2,MMP3,… | 各种MMPs蛋白酶对多肽酶切能力强弱的Z-score数值,数值越大表示酶切的可能性越高,目前的阈值为2.5,大于该阈值时,表示极大可能被酶切。 |
生成的序列文件,默认为“gen_seqs.fasta”。
This module has two functions:
Predicting the cleavage efficiency of peptides (≤10 amino acids) by 18 matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs).
Generating corresponding peptide substrates based on a specified cleavage profile (e.g., only cleaved by MMP13).
Built on the CleaveNet model, a deep - learning - based protease substrate design tool, it integrates prediction and generation, shifting from “virtual screening” to “intelligent design”.
CleaveNet has two core modules:
Prediction Module
Trained on a large - scale mRNA - displayed peptide library using a Transformer architecture.
Predicts peptide cleavage efficiency by 18 MMPs, with a test - set Pearson correlation of 0.80, outperforming traditional binary - classification models.
Reproduces known cleavage motifs and reveals new substrate preferences (e.g., methionine at P4), enhancing understanding of protease specificity.
Generation Module
Uses conditional generation. Users can set target cleavage profiles (e.g., “high MMP13 activity, low other MMP activities”) via conditional tags.
Adjusts generation direction with attention mechanisms. Generated 6 - mer peptides have 89% novelty, surpassing training data limits.
Is about 5.5 times more efficient than traditional virtual screening, supporting complex designs like “dual - protease logic gate” substrates.
This end - to - end design process improves substrate design efficiency and accuracy, offering a new computation - driven method for protease research.
Experimental Validation
To assess CleaveNet’s practicality, the team targeted MMP13 (a collagenase linked to cancer metastasis, wound healing, and osteoarthritis). They designed and synthesized 95 peptide substrates, validating cleavage efficiency via fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). Results showed:
All CleaveNet - designed MMP13 substrates were efficiently cleaved. One (DL73) had 39% higher efficiency than the best training - set substrate (p<0.01).
Three substrates (e.g., DL41) were absolutely specific to MMP13, and five (e.g., DL48) had both high activity and selectivity, addressing traditional method gaps.
Analysis of generated sequences revealed leucine preference at P2 and aspartic acid’s role at P3’, offering new insights into MMP13’s specificity mechanism.
These results confirm CleaveNet’s ability to design efficient, specific substrates and its potential to uncover unknown substrate preferences.
Required parameter, peptide sequence, in txt or fasta format, supporting multiple sequences (when in txt format, place each peptide on a separate line). Note: The length of the peptide cannot exceed 10 residues.
An example in txt format is as follows:
LRVFL
FMPLNFTASG
LGPYAMTSRG
AARFKKFATE
Optional parameter, the file name of the predicted MMPs cleavage probability results, default is “pred_cleavage.csv”。
Optional parameter, specify the number of peptides to be generated, default is 50.
Optional parameter, specify the cleavage conditions for peptide generation in CSV file format. It includes the Z-score values of cleavage probabilities for each type of MMP enzyme. A higher value indicates a higher likelihood of cleavage. The value can be negative. The general threshold is 2.5. When the value is above this threshold, it indicates a very high probability of being cleaved. The model will generate peptides based on the set Z-score values of cleavage probabilities for various MMPs enzymes. Note: The Z-score values for all 18 types of MMPs must be set, and none can be missing.
An example of the file content is as follows:
MMP1,MMP10,MMP11,MMP12,MMP13,MMP14,MMP15,MMP16,MMP17,MMP19,MMP2,MMP20,MMP24,MMP25,MMP3,MMP7,MMP8,MMP9
2.0,1.2,2.2,2.9,3.3,4.1,2.2,3.1,2.2,1.91,3.6,2.83,2.7,0.2,1.8,2.1,0.61,4.2
The above content is a set of conditions, and multiple sets of conditions can also be input simultaneously. Just place each set of conditions on a separate line. Peptides of the specified quantity will be generated for each set of conditions. An example of multiple sets of conditions is as follows:
MMP1,MMP10,MMP11,MMP12,MMP13,MMP14,MMP15,MMP16,MMP17,MMP19,MMP2,MMP20,MMP24,MMP25,MMP3,MMP7,MMP8,MMP9
2.0,1.2,2.2,2.9,3.3,4.1,2.2,3.1,2.2,1.91,3.6,2.83,2.7,0.2,1.8,2.1,0.61,4.2
3.33,2.5,3.6,2.7,2.9,5.2,3.4,4.2,2.7,2.0,3.5,2.6,4.0,3.1,3.5,0.61,2.1,2.9
Optional parameter, specify the temperature condition for controlling the diversity of the generated peptide sequences. The default value is 1.0. A higher value indicates higher diversity. If you want lower diversity, it is recommended to use 0.7. If you want higher diversity, it is recommended to use a value between 1.2 and 1.5.
Optional parameter, specify the output file name for the sequences in fasta or txt format. The default is “gen_seqs.fasta”.
The predicted MMPs cleavage probability results file, default is pred_cleavage.csv. It contains the following content:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SEQ | Peptide sequence |
| MMP1, MMP2, MMP3, … | Z-score values representing the strength of cleavage by various MMPs proteases. A higher value indicates a higher likelihood of cleavage. The current threshold is 2.5. If the value is above this threshold, it indicates a very high probability of being cleaved. |
The generated sequence file, default is “gen_seqs.fasta”.

该模块用于分析和可视化蛋白质表面的静电特性,这对分子识别、蛋白质溶解性、粘度和抗体的可开发性等过程至关重要。它主要通过定义“Patch”来识别和量化蛋白质表面的静电势,这些Patch是具有统一正或负电势值的连接区域。
主要功能和特点:
蛋白结构文件,PDB格式。
分子表面的类型:sas或者ses。以下是两个选项的解释:
探针半径,单位为纳米(默认:0.14)。
Patch面积(area )阈值,单位为Ų。如果 Size Cutoff = 0,则不过滤任何 patch,即所有 patch 都会被保留。
pH 值。
输出Patch文件名称
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| patches.csv | 识别出的蛋白质表面静电Patch的信息。 |
| apbs.pqr | APBS计算静电势的输入文件。PQR文件类似于PDB文件,但包含了每个原子的电荷和半径信息。 |
| apbs.pqr.dx | 通过APBS计算得到的静电势分布数据。DX文件是网格格式,描述了蛋白质周围空间的静电势值。 |
| apbs.pdb | APBS计算静电势的PDB文件 |
其中patches.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| nr | 代表Patch的编号。这是每个识别出的静电Patch的唯一标识符,用于区分不同的Patch。 |
| type | 表示Patch的类型,通常为“positive”或“negative”,指示Patch的电荷性质是正电还是负电。 |
| npoints | Patch中包含的表面点的数量。这些点构成了Patch在蛋白质表面上的区域。 |
| area | Patch的面积,单位为Ų。这表示Patch在蛋白质表面上覆盖的物理面积。 |
| value | Patch的总静电势值,通常为Patch内所有点的静电势值的总和或平均值。这反映了Patch的整体静电强度。 |
| residue | Patch中的氨基酸残基,通常是Patch所在区域的一个代表性残基。这个残基可能是Patch中电荷最集中的位置或最显著的氨基酸。其他的氨基酸编号与apbs.pdb对应。 |
This module is designed for analyzing and visualizing the electrostatic properties of protein surfaces, which are critical for processes such as molecular recognition, protein solubility, viscosity, and antibody developability. It primarily identifies and quantifies the electrostatic potential on protein surfaces by defining “patches,” which are connected regions with uniform positive or negative potential values.
Key Features:
Electrostatic Potential Calculation:
This tool uses APBS (Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver) to compute electrostatic potentials. Additionally, it can accept user-provided potential maps or mappings based on hydrophobicity scales.
Molecular Surface Generation:
The tool generates molecular surfaces and maps the calculated electrostatic potentials onto these surfaces. The surface can then be visualized using color coding to indicate positive and negative regions.
Patch Identification:
It identifies and quantifies different positive and negative electrostatic patches on the protein surface, which are crucial for understanding protein-protein interactions and antibody development.
The protein structure file in PDB format.
The type of molecular surface: SAS or SES. Below are explanations for the two options:
The radius of the probe, measured in nanometers (default: 0.14).
Patch area threshold (area), measured in Ų. If Size Cutoff = 0, no patch will be filtered, meaning all patches will be retained.
The pH value.
The name of the output file for identified patches.
The output includes the following files:
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
patches.csv |
Information about the identified electrostatic patches on the protein surface. |
apbs.pqr |
Input file for APBS electrostatic potential calculations. PQR files are similar to PDB files but include charge and radius information for each atom. |
apbs.pqr.dx |
Electrostatic potential distribution data calculated by APBS. DX files are grid-format files describing the electrostatic potential values in the space surrounding the protein. |
apbs.pdb |
PDB file with electrostatic potential information calculated by APBS. |
The patches.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| nr | Patch number. This is a unique identifier for each identified electrostatic patch. |
| type | Patch type, typically “positive” or “negative,” indicating whether the patch is positively or negatively charged. |
| npoints | The number of surface points in the patch, which defines the region of the patch on the protein surface. |
| area | The area of the patch in Ų, representing the physical coverage of the patch on the protein surface. |
| value | The total electrostatic potential value of the patch, usually the sum or average of all potential values within the patch. This indicates the overall electrostatic intensity of the patch. |
| residue | Representative amino acid residue within the patch, typically the residue with the highest charge concentration or the most prominent residue in the patch. Other residue numbers correspond to the apbs.pdb file. |

该模块计算蛋白质表面静电和疏水作用相对富集的区域,用于显示出在蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用中其重要作用的区域,这对于预测基于非共价弱相互作用的可逆的聚集现象尤其有用。尤其是,疏水相互作用长期被认为是大分子间吸引相互作用的主要组成部分。对于抗体,静电相互作用牵涉到了自聚集,而偶极-偶极相互作用被认为是导致β-折叠的纤维化的原因。同时,也可以通过WeView界面对蛋白结构进行Patch分析。
V2 更新内容
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式
Hydrophobic cutoff是一个以疏水性氨基酸(通常包括Leu,Ile,Val,Phe,Trp和Met)为基础定义的截断值,用于将表面上疏水性氨基酸的数量与表面面积相比较,从而筛选出可能具有重要生物学功能的区域。一般来说,Patch区域中获得的化学性质信息会根据其表面密度和具有高疏水性氨基酸的数量而有所变化。
Positive Cutoff是一个以阳离子氨基酸为基础定义的截断值,用于将表面上阳离子氨基酸的数量与表面面积相比较,从而筛选出可能具有重要生物学功能的区域。一般来说,positive cutoff方式用于筛选出可能参与离子相互作用的蛋白质表面区域。
Negative Cutoff是一个以阴离子氨基酸为基础定义的截断值,用于将表面上阴离子氨基酸的数量与表面面积相比较,从而筛选出可能具有重要生物学功能的区域。一般来说,negative cutoff方式用于筛选出可能参与离子相互作用的蛋白质表面区域。
SASA Cutoff是一个以溶剂可及表面积为基础定义的截断值,低于截断值的patch会被过滤掉。
Distance Cutoff是原子距离截断值,低于截断值的才会认为属于同一聚集块。值越小,聚集块patch越小。
Min Distance Cutoff是patch之间的距离截断值,距离小于截断值的归为同一个patch。
输出文件格式,csv或者json
通俗地讲,cutoff代表静电势能或疏水势能的强度阈值,单位是kcal/mol,超过阈值才会被计入面积。阈值越小,则patch越多。
不添加缺失原子(包括氢原子)和结构优化。
使得N-氮端的蛋白残基中性化。
使得C-氮端的蛋白残基中性化。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| patch_list.csv | Patch结果的csv文件。主要关注Area(Å^2)数值,代表patch的大小,越大则越可疑,重点关注100 Å以上的patch。 |
| input_prot.pdb | 质子化后的pdb结构。 |
| patch_list_sum.csv | 统计了三种patch类型(Hyd:疏水中心,Neg:负电中心,Pos:正电中心)在蛋白表面所占面积,重点关注100 Å以上的patch。 |
其中patch_list.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Type | Patch的类型,Hyd:疏水中心,Neg:负电中心,Pos:正电中心 |
| Area(Å^2) | 每个Patch的蛋白质表面区域面积 |
| Residues | 每个Patch的对应的残基 |
其中patch_list_sum.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Type | Patch的类型,Hyd:疏水中心,Neg:负电中心,Pos:正电中心 |
| Total Areas | Patch的蛋白质表面区域总面积 |
| Areas of The Largest | Patch的蛋白质表面区域最大面积 |
| Number of Areas More Than 100 | 超过100 Å以上的patch的数目 |
Protein Patches calculates both electrostatic (excess charge) and hydrophobic surface patches to show regions of significance with respect to protein-protein interactions. This can be particularly useful in the prediction of reversible aggregation, which typically arises from relatively weak non-covalent interactions. In particular, hydrophobic interactions have long been recognized as major contributors in high affinity interactions between macromolecules. In antibodies, electrostatic interactions have been implicated in forming self-associated aggregates [Karshikoff 2006], while dipole-dipole interactions are believed to be the cause of fibrillogenic association of β-sheets. At the same time, protein structures can also be analyzed for patches through the WeView interface.
Electrostatic patches.
The surface electrostatic field is estimated using an exponentially decaying Debye-Hückel field with a screening length of λD=3.5Å.
The map thus obtained is one mostly of excess charge close to the molecular surface.
Significant patches are established by cutting the surface along isocontour lines of absolute field value equal to 40 kcal/mol/C, keeping regions above. Finally, a default minimal patch area of 40Å2 filters out smaller, presumably less relevant, patches.
Hydrophobicity map.
The hydrophobic potential is calculated from the Wildman and Crippen octanol-water partition coefficients f=log P [Wildman 1999]:
where fi is the coefficient of atom i and g(ri) is a Fermi-type distance-dependent weighting function proposed by Heiden et al. [Heiden 1993]:
with rcut=5Å and α=1.5.
Similarly to electrostatic (excess charge) patches, significant hydrophobic patches are established by cutting the surface along isocontour lines, retaining only the portion above a potential threshold value of 0.09 kcal/mol, and filtering for a minimal patch area of 50Å2.
V2 updates
Protein structure file in PDB format.
Hydrophobic Cutoff defined based on hydrophobic amino acids (usually including Leu, Ile, Val, Phe, Trp, and Met) is used to compare the number of hydrophobic amino acids on a surface with the surface area, so as to screen out areas that may have important biological functions. Generally speaking, the chemical property information obtained in the Patch region will vary according to its surface density and the number of highly hydrophobic amino acids.
Positive Cutoff is a cut-off value defined based on cationic amino acids, which is used to compare the number of cationic amino acids on the surface with the surface area to screen out areas that may have important biological functions. Generally speaking, the positive cutoff method is used to screen protein surface regions that may be involved in ion interactions.
Negative Cutoff is a value defined based on anionic amino acids, which is used to compare the number of anionic amino acids on a surface with the surface area, to screen out areas that may have important biological functions. Generally speaking, the negative cutoff method is used to screen the surface regions of proteins that may participate in ion interactions.
SASA Cutoff is a cutoff value defined on the basis of polar surface area, which is used to screen the surface regions of proteins that have enough polar surface areas.
Distance Cutoff is a cutoff value defined on the basis of neighbor atoms, which is used to adjust the size of patches. Lower values result in smaller patches.
Min Distance Cutoff is the cutoff value for neighbor patch point distance (Å). Patches with distances lower than the cutoff value would be merged.
output file format, json or csv
Do no atom addition and optimization.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| patch_list.csv | A CSV file containing patch results. The main focus is on the Area (Å^2) value, which represents the size of the patch. Larger patches are considered more suspicious, with particular attention to patches larger than 100 Å. |
| input_prot.pdb | The protonated PDB structure. |
| patch_list_sum.csv | Summarizes the surface area occupied by three types of patches (Hyd: hydrophobic center, Neg: negative charge center, Pos: positive charge center) on the protein surface. Focus is placed on patches larger than 100 Å. |
Details of patch_list.csv:
The file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | The type of patch: Hyd (hydrophobic center), Neg (negative charge center), Pos (positive charge center). |
| Area (Å^2) | The surface area of each patch on the protein. |
| Residues | The residues corresponding to each patch. |
Details of patch_list_sum.csv:
The file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Type | The type of patch: Hyd (hydrophobic center), Neg (negative charge center), Pos (positive charge center). |
| Total Areas | The total surface area of patches on the protein. |
| Areas of The Largest | The largest surface area of a patch on the protein. |
| Number of Areas More Than 100 | The number of patches with an area larger than 100 Å. |

该模块是一种用于分子对接模拟工具,主要用于预测分子之间的结合模式和相互作用,得到分子对接的能量和结合亲和力等信息。它还可以计算和比较多个分子之间的结合能力,用于药物分子的筛选、设计和优化。AutoDock-GPU是AutoDock4.2.6的OpenCL和Cuda加速版本,其利用可并行的LGA,从而通过在多个计算单元上并行处理配体-受体结合构象。
支持自行上传小分子文件(Private Ligand Library)或者选择公共分子虚筛库(Public Ligand Library)。
对接模式为刚性配体对接(rigid)或者柔性配体对接(flex),
刚性配体对接:配体自身保持刚性,经平移、旋转,在口袋内寻找合适的结合取向。
柔性配体对接:配体在固定某些非关键部位的键长、键角的前提下允许其构象发生一定程度的变化。
受体结构文件,PDB格式
配体结构文件,支持SDF、PDB、MOL格式。只会计算前100的分子。
对接口袋中心的三维坐标(XYZ),空格分割。例如:0 0 0。
对接口袋长方体盒子的大小,必须是整数,空格分割,例如 24 22 32。
每个分子保留的最大结合模式数量
虚拟筛选中保留打分排名前n个分子。
未结合状态模型选择:
保留非标准氨基酸,格式为[链名]:[残基名称]-[残基编号],如A:UNL-311。不能包含特殊离子的小分子结构。
配体结构文件,支持SDF、PDB、MOL格式。只会计算前10,000的分子。
其余参数与**Private Ligand Library (Comp<100)**模式一致。
提供17个公共分子虚筛库用于分子对接,包括:
其他参数与Private Ligand Library模式相同,公共库只允许刚性对接。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| TopNScores.csv | 分子对接得到的打分csv文件。输出小分子最多为10,000。 |
| complex_001.pdb | 展示配体与受体的复合物构象文件。 |
| output_ligand_topn.sdf | 筛选后配体的SDF文件。根据指定的topN数生成,最多为10,000。 |
| output_complex_topn.tar.bz2 | 小分子与受体对接后的复合物构象PDB文件压缩包,最多生成前1000小分子的复合物结构。 |
| TopNScores_Molecule_Info.csv | 当Private Ligand Library模式,该csv中不仅有打分信息,还有配体原有信息。 |
其中TopNScores.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 对接小分子名称 |
| Bingding Energy (AutoDock GPU) | 对接打分结果 |
| Cluster RMSD | 指一个配体构象相对于同一聚类(cluster)中的中心构象(通常是最低能量构象)的均方根偏差(RMSD)。RMSD 截断值为2.0 Å。 |
| Reference RMSD | 指对接得到的配体构象与 参考构象(通常是实验解析的晶体结构或用户指定的标准结构)之间的 RMSD。 |
其中TopNScores_Molecule_Info.csv包含TopNScores.csv的信息和SDF格式小分子原有信息。
This module is a molecular docking simulation tool primarily used for predicting molecular binding modes and interactions. It provides information on docking energy and binding affinity. Additionally, it allows for the calculation and comparison of binding abilities among multiple molecules, facilitating the screening, design, and optimization of drug molecules.
AutoDock-GPU is the OpenCL and CUDA-accelerated version of AutoDock 4.2.6, utilizing parallelizable LGA (Lamarckian Genetic Algorithm) to process ligand-receptor binding conformations in parallel across multiple computing units.
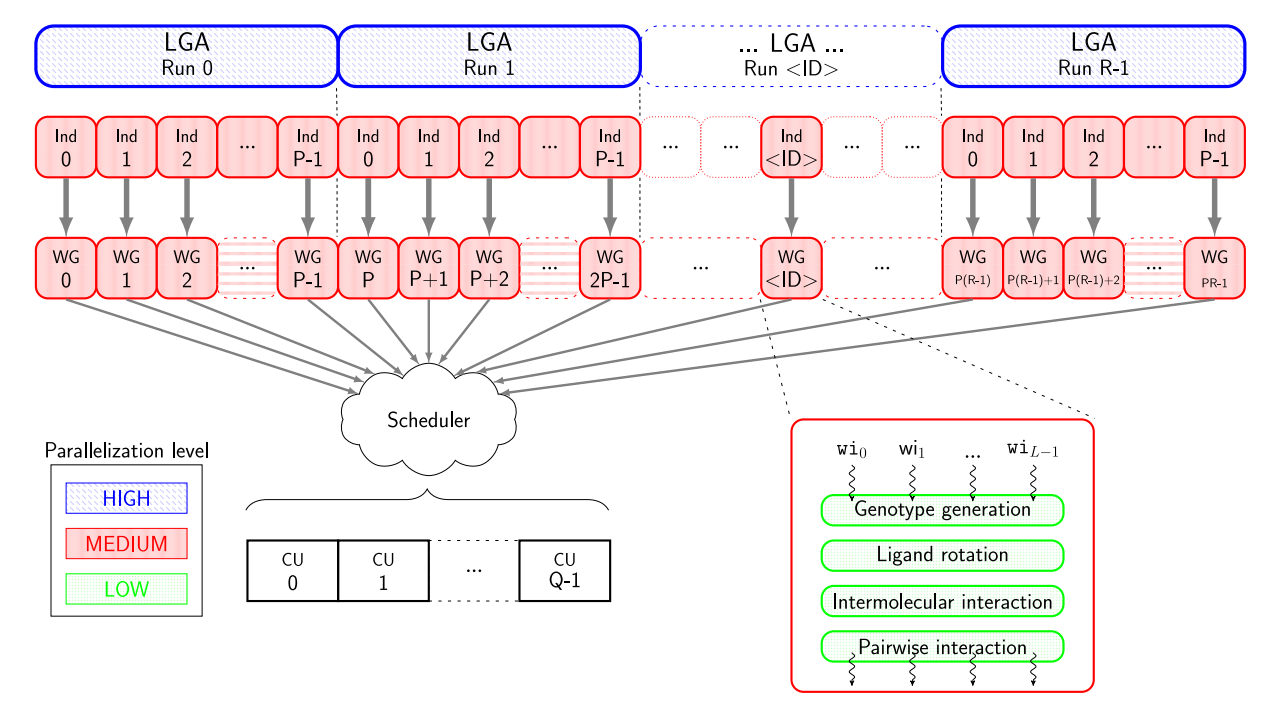
It supports private ligand file uploads (Private Ligand Library) or the selection of public virtual screening libraries (Public Ligand Library).
Docking mode can be either rigid docking or flexible docking:
100 molecules will be processed.0 0 024 22 32Defines the unbound state model:
[Chain Name]:[Residue Name]-[Residue Number], e.g., A:UNL-311.10,000 molecules will be processed.🔹 Other parameters are identical to those in Private Ligand Library (Comp <100) mode.
Provides 17 public virtual screening libraries for molecular docking, including:
🔹 Other parameters are identical to Private Ligand Library, but only rigid docking is allowed.
The docking results include:
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| TopNScores.csv | CSV file containing docking scores for up to 10,000 molecules. |
| complex_001.pdb | Ligand-receptor complex conformation file. |
| output_ligand_topn.sdf | Top-N selected ligands in SDF format (max 10,000). |
| output_complex_topn.tar.bz2 | Compressed file of the top 1,000 ligand-receptor complex structures in PDB format. |
| TopNScores_Molecule_Info.csv | If using the Private Ligand Library mode, this CSV includes both docking scores and original ligand information. |
📌 TopNScores.csv Fields:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the docked molecule. |
| Binding Energy (AutoDock GPU) | Docking score. |
| Cluster RMSD | RMSD relative to the cluster center (default cutoff: 2.0 Å). |
| Reference RMSD | RMSD relative to the reference structure (e.g., crystal structure). |
The TopNScores_Molecule_Info.csv file contains the information from TopNScores.csv along with the original data of small molecules in SDF format.
.png)
RFantibody 是目前最先进的抗体从头生成方法,通过人工智能(AI)技术实现抗体的从头(de novo)设计,包括单域抗体(VHH)和单链抗体片段(scFv),能够精准结合用户指定的目标表位,并已通过湿实验验证其功能。
RFantibody基于蛋白质结构预测模型RoseTTAFold2(RF2)和蛋白质生成模型RFdiffusion,通过对原始RFdiffusion进行微调,开发出专用于抗体设计的RFdiffusion版本。其核心原理如下:
抗体结构特性利用:RFdiffusion在蛋白质数据库(PDB)中的抗体结构数据(约8100个抗体结构)上进行微调,重点训练抗体特有的互补决定区(CDR)loop 区域,同时保持框架结构接近用户指定的优化框架。训练过程中,通过逐步添加噪声(Cα 坐标加入三维高斯噪声,残基方向加入 SO(3) 布朗运动),网络学习预测去噪后的结构。
表位靶向设计:通过引入"热点"(Hotspot)特征,用户可指定目标蛋白上的表位,网络通过CDR loop与表位的相互作用进行设计。训练时,抗体框架以全局坐标无关的方式提供(通过二维距离和二面角矩阵表示),允许网络自由设计CDR Loop构象及抗体与目标的刚体定位。
序列设计与验证:结构设计后,使用ProteinMPNN生成CDR loop区序列,优化与目标表位的相互作用。设计的抗体通过微调后的RF2进行结构预测和自一致性验证,筛选高潜力候选分子。
支持 VHH 和 scFv 设计:RFdiffusion 不仅支持单域抗体(VHH)的设计,还可应用于单链抗体片段(scFv)的设计。scFv 设计涉及重链和轻链的所有六个 CDR 的设计。
通过上述方法,RFantibody能够生成多样化的抗体结构,显著区别于训练数据集,同时实现与目标表位的高度形状互补性和功能性结合。
RFantibody项目针对多个疾病相关表位进行了VHH和scFv设计,并通过表面等离子共振(SPR)、冷冻电镜(cryo-EM)、中和实验等手段验证了设计的有效性。以下是具体实验结果及分析:
1, 单域抗体(VHH)设计与实验验证
实验选择了多个疾病相关靶点,包括流感血凝素(HA)、呼吸道合胞病毒(RSV)位点I和III、SARS-CoV-2受体结合域(RBD)、艰难梭菌毒素B(TcdB)和IL-7Rα。以下为关键结果:
结合亲和力(KD):
中和活性(EC50):
结构准确性(cryo-EM):
亲和力成熟(OrthoRep):
2, 单链抗体片段(scFv)设计与实验验证
进一步扩展至scFv设计,涉及重链和轻链六个CDR的设计,采用结构导向的组合库策略以提高成功率。实验靶点包括TcdB的Frizzled-7表位和Phox2b/HLA-C*07:02复合物。
结合亲和力(KD):
结构准确性(cryo-EM):
3, 实验结果分析
4, 总结
RFantibody通过微调RFdiffusion网络,实现了从头设计VHH和scFv的目标,能够靶向多种疾病相关表位。实验结果显示设计的抗体具有较高的结构准确性(RMSD低至0.9 Å)和功能性(KD低至72 nM,EC50为460 nM)。cryo-EM验证了设计的原子级精度,而亲和力成熟和组合库策略进一步提升了成功率。
用于抗体设计的抗体-抗原复合物结构,PDB格式。如果指定了该参数,后续的Antigen,Antibody参数不用再指定。如果不指定该参数,则需要分别输入Antigen与Antibody的结构。
注意:
1,当前只支持单链抗原,如存在多链时会提示错误,可以使用蛋白编辑工具去掉抗原多余的链,保留单链抗原即可。
2,抗体编号方式只支持Chothia,会自动转成Chothia编号。
指定抗原的结构文件,PDB格式。
说明:抗原结构通常需要截短以减少计算开销,建议保留表位周围约 10Å 的区域即可。
指定抗体的结构文件,PDB格式。
指定设计的抗体数量,默认为20。
分别指定需要设计的抗体重、轻链CDR区的长度范围。格式为:起始长度-终止长度(如:5-13),或单一长度(如:7)。
说明:这些参数定义了每个CDR区的允许长度范围,如果设置的是起始长度-终止长度(如:5-13),模型将从中均匀采样长度。如果设置的是单一长度(如:7),则该CDR将以指定长度进行设计。如果不指定某个CDR的长度范围(如:不设置H-CDR1的长度),则该CDR将保持原始结构和序列不被设计。
对于VHH设计,仅需指定H-CDR1, H-CDR2, H-CDR3;对于scFv设计,可指定所有六个CDR。长度选择可参考自然抗体的CDR 长度分布,推荐较短的H-CDR3(如:5-13),以降低设计难度。
指定抗原上的结合位点残基,用于定义抗体结合的表位。格式为:逗号分隔的残基列表,格式为 305,456
经过抗体设计后,得到的抗体-抗原复合物结构,并根据质量评估指标进行排序。包括:
结构文件:按结构质量排序的PDB格式抗体-抗原复合物结构的打包文件 de_novo_antibody.tar及最优的设计结果rank_1.pdb
结构评分:CSV格式的评估指标表格 cdr_sequences.csv,包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Design_ID | 预测结构的文件名 |
| CDR_H1/H2/H3/L1/L2/L3 | 设计后得到的CDR序列 |
| ipAE | 界面预测对齐误差 (the predicted interaction alignment error),衡量抗体与抗原结合界面的结构预测置信度,该指标反映了抗体-抗原复合物界面的结构稳定性和预测准确性,数值越小表示结合界面预测越可靠,推荐选择ipAE<10的设计进行实验验证 |
| pLDDT | 预测局部距离差异测试,衡量整体结构预测的质量和可靠性,该指标反映了抗体结构本身的稳定性和折叠质量,数值范围为 0-1.0,数值越接近1.0表示结构预测越可靠,推荐选择pLDDT > 0.8的设计进行实验验证 |
输出示例
Design_ID,CDR_H3,ipAE,pLDDT
rank_1,IAYTPGAPLF,8.91,0.92
rank_2,VAPSKTDALF,9.29,0.92
抗体设计与从头设计结合子类似,但处于较早的开发阶段。在此,我们分享如何最好地利用此流程来设计可在实验中起作用的抗体的建议和经验。我们预计随着更多抗体设计活动的开展和最佳实践的形成,其中一些建议会发生变化。以下几个部分借鉴了 RFdiffusion README 中的相关内容,由于两者方法相似,这些建议也同样适用。
并非靶蛋白上的每个位点都是抗体设计的良好候选。一个有吸引力的结合候选位点应具有 >~3 个疏水残基,以便结合子与之相互作用。结合带电荷的极性位点仍然非常困难。结合靠近聚糖的位点也很困难,因为它们通常在结合时变得有序,这将带来能量损失。结合非结构化环历来很困难。然而,论文(https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06953-1)概述了一种利用 RFdiffusion 结合非结构化肽的策略。由于这些肽与非结构化环有许多共同点,此策略理论上也适用于抗体。但需注意,根据环的柔韧性,在结合过程中使环有序化将付出能量代价。
当您开始查看纳米抗体输出时,您可能会注意到许多以侧向对接方式结合。这不是一个错误,而是模型在自然纳米抗体对接上训练的结果,这些对接通常以这种侧向对接方式结合并产生一些框架介导的接触。您也许可以调整您的热点和 CDR 长度以获得更像抗体的对接,但我们建议,如果您想要一个抗体样对接,那么您应该使用抗体框架进行设计。
RFdiffusion 和 RF2 的运行时间按 O(N^2) 缩放,其中 N 是系统中残基的数量。因此,截短大靶点是一个非常好的主意,这样您的计算就不会不必要地昂贵。RFantibody 流程中的所有步骤都设计为允许截短靶点。截短靶点是一门艺术。对于某些靶点,例如多结构域细胞外膜,自然的截短点是两个结构域由柔性接头连接的地方。对于其他蛋白质,例如病毒刺突蛋白,这个截短点不那么明显。通常,您希望保留二级结构并引入尽可能少的链断裂。您还应该尝试在目标位点的两侧留下 ~10Å 的靶蛋白。
热点是我们集成到模型中的一个功能,用于控制抗体将与之相互作用的靶点上的位点。在训练期间,如果靶点残基与最近的 5 个抗体 CDR 残基的平均 Cβ 距离小于 8 埃,我们将其归类为热点。用户可以精确控制在靶点上识别出的热点中,实际提供给模型的比例(0-100%),其余热点则被遮蔽,以此来引导抗体与靶点的相互作用。我们发现 RFantibody 对热点的精确选择比普通的 RFdiffusion 更敏感。RFdiffusion 在给出错误的热点集时倾向于生成长螺旋,而 RFantibody 在给出错误的热点集时通常只会生成一个未对接的抗体。在生成数千个设计之前进行几次试运行是一个非常好的主意,以确保您提供的热点数量会产生您喜欢的结果。
对于我们在手稿中报告的一些靶点活动,我们能够从 95 个设计中识别出 VHH 结合子。然而,在更一般的情况下,我们预计需要进行 10k 范围的设计活动才能识别出命中。这在很大程度上是由于缺乏可靠的过滤指标。所有数据,无论是阳性还是阴性,对优化和评估过滤器都至关重要。因此,如果您开展设计活动并愿意与更广泛的社区共享数据,这将极大地促进开发更可靠的过滤器、提高成功率并降低设计成本。
我们用于设计活动的环范围在 RFdiffusion 示例文件中提供。我们通过查看每个环的自然发生长度频率并尝试用我们的范围覆盖大部分密度来确定这些范围。我们还尝试选择相对较短的 H3 环,因为我们认为这些环更容易设计和预测,同时仍能提供足够的长度以有效结合。在某些靶点上,拥有长的 H3 可能很有用,例如当靶向蛋白质中的疏水口袋时。在这些情况下,H3 范围应超出我们在示例中提供的范围。
我们建议以下最低过滤标准:
缺乏有效的过滤器是 RFantibody 流程目前的主要限制。RF2版本在某些情况下可能显示结合子比非结合子有弱富集,但需要更多数据才能令人信服地得出这个结论。新出现的结构预测模型(如 AF3)为 RF2 提供了一个有前景的替代方案,我们正在评估这些模型对我们设计活动的预测能力。
RFantibody is the most advanced de novo antibody generation method currently available. Through artificial intelligence (AI) technology, it achieves de novo design of antibodies, including single-domain antibodies (VHH) and single-chain antibody fragments (scFv), capable of precisely binding to user-specified target epitopes, with functionality validated through wet lab experiments.
RFantibody is based on the protein structure prediction model RoseTTAFold2 (RF2) and the protein generation model RFdiffusion. By fine-tuning the original RFdiffusion, a specialized version for antibody design has been developed. Its core principles are as follows:
Utilization of Antibody Structural Features: RFdiffusion is fine-tuned on antibody structural data (approximately 8,100 antibody structures) from the Protein Data Bank (PDB), focusing on training the antibody-specific complementarity-determining region (CDR) loops while maintaining framework structures close to user-specified optimized frameworks. During training, noise is gradually added (3D Gaussian noise to Cα coordinates, SO(3) Brownian motion to residue orientations), and the network learns to predict the denoised structure.
Epitope-Targeted Design: By introducing “Hotspot” features, users can specify epitopes on target proteins, and the network designs through interactions between CDR loops and the epitope. During training, the antibody framework is provided in a globally coordinate-independent manner (represented by 2D distance and dihedral angle matrices), allowing the network to freely design CDR loop conformations and rigid-body positioning of the antibody relative to the target.
Sequence Design and Validation: After structural design, ProteinMPNN is used to generate sequences for CDR loop regions, optimizing interactions with the target epitope. The designed antibodies are validated through structure prediction and self-consistency verification using the fine-tuned RF2, screening for high-potential candidates.
Support for VHH and scFv Design: RFdiffusion supports not only the design of single-domain antibodies (VHH) but also single-chain antibody fragments (scFv). scFv design involves designing all six CDRs of the heavy and light chains.
Through these methods, RFantibody can generate diverse antibody structures that significantly differ from the training dataset while achieving high shape complementarity and functional binding to target epitopes.
Experimental Validation
The RFantibody project has conducted VHH and scFv designs targeting multiple disease-related epitopes and validated their effectiveness through surface plasmon resonance (SPR), cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM), neutralization assays, and other methods. The following are specific experimental results and analyses:
1, Single-Domain Antibody (VHH) Design and Experimental Validation
Experiments selected multiple disease-related targets, including influenza hemagglutinin (HA), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) sites I and III, SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD), Clostridioides difficile toxin B (TcdB), and IL-7Rα. Key results include:
Binding Affinity (KD):
Neutralization Activity (EC50):
Structural Accuracy (cryo-EM):
Affinity Maturation (OrthoRep):
2, Single-Chain Antibody Fragment (scFv) Design and Experimental Validation
Further expansion to scFv design involved designing six CDRs of heavy and light chains, adopting a structure-guided combinatorial library strategy to increase success rates. Experimental targets included the Frizzled-7 epitope of TcdB and the Phox2b/HLA-C*07:02 complex.
Binding Affinity (KD):
Structural Accuracy (cryo-EM):
3, Analysis of Experimental Results
4, Summary
RFantibody, through fine-tuning the RFdiffusion network, has achieved the goal of de novo designing VHHs and scFvs capable of targeting various disease-related epitopes. Experimental results show that the designed antibodies have high structural accuracy (RMSD as low as 0.9 Å) and functionality (KD as low as 72 nM, EC50 of 460 nM). Cryo-EM validated the atomic-level precision of the designs, while affinity maturation and combinatorial library strategies further improved success rates.
The structure of the antibody-antigen complex used for antibody design, in PDB format. If this parameter is specified, the subsequent Antigen and Antibody parameters do not need to be specified. If this parameter is not specified, the structures of Antigen and Antibody need to be input separately.
The structure file of the antigen, in PDB format.
Note: The antigen structure usually needs to be truncated to reduce computational cost. It is recommended to retain only the region within approximately 10 Å around the epitope.
The structure file of the antibody, in PDB format.
The number of antibodies to be designed, with a default value of 20.
Specify the length range of the CDR regions in the heavy and light chains to be designed. The format is: start length-end length (e.g., 5-13), or a single length (e.g., 7).
Note: These parameters define the allowed length range for each CDR region. If a range is specified (e.g., 5-13), the model will uniformly sample lengths within this range. If a single length is specified (e.g., 7), the CDR will be designed with the given length. If the length range of a CDR is not specified (e.g., H-CDR1 is not set), that CDR will retain its original structure and sequence without being designed.
For VHH design, only H-CDR1, H-CDR2, and H-CDR3 need to be specified; for scFv design, all six CDRs can be specified. The length selection can refer to the natural distribution of CDR lengths in antibodies. It is recommended to use a shorter H-CDR3 (e.g., 5-13) to reduce design complexity.
Specify the binding site residues on the antigen to define the epitope for antibody binding. The format is: a comma-separated list of residues, e.g., 305,456.
Note: Binding site residues help the model focus on specific epitopes. It is recommended to select more than three hydrophobic residues within the epitope and avoid areas with excessive polarity or glycosylation.
After antibody design, the antibody-antigen complex structures are obtained and sorted based on quality assessment metrics. These include:
Structure Files: The packed file of antibody - antigen complex structures in PDB format sorted by structural quality is de_novo_antibody.tar, and the optimal design result rank_1.pdb.
Structure Scores: A CSV file cdr_sequences.csv containing the assessment metrics, with the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Design_ID | The filename of the predicted structure |
| CDR_H1/H2/H3/L1/L2/L3 | Designed sequence of CDRs |
| ipAE | Predicted interaction alignment error, which measures the confidence of the structural prediction at the antibody-antigen binding interface. This metric reflects the stability and accuracy of the antibody-antigen complex interface. Lower values indicate more reliable predictions. Designs with ipAE < 10 are recommended for experimental validation. |
| pLDDT | Predicted Local Distance Difference Test, which measures the overall quality and reliability of the structural prediction. This metric reflects the stability and folding quality of the antibody structure itself. The value ranges from 0 to 1.0, with values closer to 1.0 indicating more reliable structural predictions. Designs with pLDDT > 0.8 are recommended for experimental validation. |
Example
Design_ID,CDR_H3,ipAE,pLDDT
rank_1,IAYTPGAPLF,8.91,0.92
rank_2,VAPSKTDALF,9.29,0.92
Designing antibodies is similar to designing de novo binders but is in an earlier stage of development. Here we share advice and learnings on how best to use this pipeline to design antibodies which will work experimentally. We expect some of this advice to change as more antibody design campaigns are performed and best-practices crystallize. Several of these sections are adapted from the analogous section of the RFdiffusion README as these two methods share many similarities and the advice applies to both.
Not every site on a target protein is a good candidate for antibody design. For a site to be an attractive candidate for binding it should have >~3 hydrophobic residues for the binder to interact with. Binding to charged polar sites is still quite hard. Binding to sites with glycans close to them is also hard since they often become ordered upon binding and you will take an energetic hit for that. Binding to unstructured loops has historically been hard but this paper (https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06953-1) outlines a strategy to use RFdiffusion to bind unstructured peptides which share much in common unstructured loops, using this strategy should work with antibodies but depending on the flexibility of the loop, you will pay an energetic price for ordering the loop during binding.
When you begin looking at your nanobody outputs, you may notice that many are binding in a side-on dock. This is not a bug and is a result of the model being trained on natural nanobody docks which often bind in this side-on docking style and make some framework-mediated contacts. You may be able to tune your hotspots and CDR lengths to get a more antibody-like dock, but we recommend that if you desire an antibody-like dock, then you should design with an antibody framework.
RFdiffusion and RF2 scale in runtime as O(N^2) where N is the number of residues in your system. As such, it is a very good idea to truncate large targets so that your computations are not unnecessarily expensive. All steps in the RFantibody pipeline are designed to allow for a truncated target. Truncating a target is an art. For some targets, such as multidomain extracellular membranes, a natural truncation point is where two domains are joined by a flexible linker. For other proteins, such as virus spike proteins, this truncation point is less obvious. Generally you want to preserve secondary structure and introduce as few chain breaks as possible. You should also try to leave ~10A of target protein on each side of your intended target site.
Hotspots are a feature that we integrated into the model to allow for the control of the site on the target which the antibody will interact with. During training, we classify a target residue as a hotspot if it has an average Cβ distance to the closest 5 antibody CDR residues of less than 8 Angstroms. Of all of the hotspots which are identified on the target 0-100% of these hotspots are actually provided to the model and the rest are masked. We find that RFantibody is more sensitive to exactly which hotspots are selected than vanilla RFdiffusion is. Where RFdiffusion tends to generative long helices when given a bad set of hotspots, RFantibody will generally just generate an undocked antibody if a bad set of hotspots is given. It is a very good idea to run a few pilot runs before generating thousands of designs to make sure the number of hotspots you are providing will give results you like.
For some of the target campaigns that we report on in our manuscript, we were able to identify VHH binders from a set of 95 designs. In the more general case, however, we expect that design campaigns in the 10k range will be required to identify hits. This is in large part due to the lack of a reliable filtering metric. All data, both positive and negative, is useful for tuning and evaluating filters so if you run a design campaign and wish to share your data with the broader community that would be extremely helpful for moving toward a more reliable filter, higher success rates, and cheaper design campaigns.
The loop ranges that we used for our design campaigns are provided in the RFdiffusion example files. We determined these ranges by looking at the frequency of naturally occuring lengths for each loop and trying to cover most of the density with our range. We also tried to choose relatively short H3 loops, as we figured these would be easier to design and predict while still giving us enough length to bind effectively. There are some targets where having a long H3 may be useful, for instance when targeting a hydrophobic pocket in a protein. In these cases, the H3 range should be increased beyond what we provide in the examples.
We recommend the following minimal filtering critieria:
The lack of an effective filter is the main limitation of the RFantibody pipeline at the moment. The version of RF2 that we provide may show weak enrichment of binders over non-binders in some cases but more data is needed to make this conclusion convincingly. Newly available structure prediction models such as AF3 present a promising alternative to RF2 and we are in the process of evaluating these models for predictivity on our design campaigns.

对MD体系进行溶剂化操作,添加水盒子和离子。
输入的受体拓扑文件,可由GMX Receptor Parameterization模块生成。
输入的受体结构文件,可由GMX Receptor Parameterization模块生成。
输入的受体参数(压缩)文件,可由GMX Receptor Parameterization模块生成。
输入的配体结构(压缩)文件,可由GMX Ligand Parameterization模块生成。
输入的配体参数(压缩)文件,可由GMX Ligand Parameterization模块生成。
需要添加的离子,支持钠离子NA,钾离子K,氯离子CL,钙离子CA,镁离子MG,锌离子ZN,同时添加多个使用英文冒号:分割,如NA:K:MG
需要添加的离子数目,添加多种离子时,和Ions参数对应,使用英文冒号:分割,如15:20:30
说明:Number of Ions与Concentration of Ions,选择其中一种输入,不要同时输入
需要添加的离子浓度,单位为mol/L,添加多种离子时,和Ions参数对应,使用英文冒号:分割,如0.15:0.3:0.1
说明:Number of Ions与Concentration of Ions,选择其中一种输入,不要同时输入
输出的体系总的拓扑文件
输出的体系总的结构文件
输出的体系参数的(压缩)文件
距离限制,仅当Disre不为no时生效,格式如下所示:
[AtomIndex1] [AtomIndex2] [Type] [Index] [Type] [Low] [Up1] [Up2] [Factor]
其中,AtomIndex1和AtomIndex2为在system.gro的原子编号;Type为施加约束类型,通常设置为1,Type类型见表1;Index是计算顺序;Low、Up1、Up2为原子间限制距离,Low到Up1区间的原子距离是不受限制的,但是不能超过Up2,单位为nm;Factor为因子,将Factor乘以“Disre Force Constant”即为限制力的大小,单位为kJ/mol/nm2。
例如:
10 16 1 0 1 0.0 0.3 0.4 1.0
10 46 1 1 1 0.0 0.3 0.4 1.0
16 22 1 2 1 0.0 0.3 0.4 2.5
表1:GROMACS中三种约束类型对原子对进行限制
| Type Code | 约束类型 | 作用情况 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Complex NMR distance restraints | 当Disre Type为ensemble时,即非键相互作用设置为1 |
| 6 | Simple harmonic restraints | 当Disre Type为simple时,即分子内成键相互作用设定,可设为6或者10. |
| 10 | Piecewise linear/harmonic restraints | 当Disre Type为simple时,即分子内成键相互作用设定,可设为6或者10 |
角度限制是两对原子间角度的限制,仅当Disre不为no时生效,格式如下所示:
[AtomIndex1] [AtomIndex2] [AtomIndex3] [AtomIndex4] [Type] [Theta0] [Force Constant] [Multiplicity]
其中,AtomIndex1-AtomIndex2是第一对原子编号;AtomIndex3-AtomIndex4为第二对原子编号;Type在这里无用,定义为1即可;Theta0为约束的角度,单位为deg;Force Constant为约束力常数,单位为kJ/mol;Multiplicity为多重度。
例如
2642 2643 2635 2652 1 67.0 1500 1
二面角限制,仅当Disre不为no时生效,格式如下所示:
[AtomIndex1] [AtomIndex2] [AtomIndex3] [AtomIndex4] [Type] [Label] [Phi] [dPhi] [KFactor] [Power]
其中,AtomIndex1-AtomIndex4为组成二面角的原子编号;Type为约束类型函数,总是为1;Label无效;Phi为参考角,dPhi为超出参考角的角度值,单位为deg;KFactor为因子,将KFactor乘以“Disre Force Constant”即为限制力的大小,单位为 kJ/mol/rad2;Power无效。
例如:
2642 2643 2635 2652 1 67.0 1500 1
约束势函数如下所示:
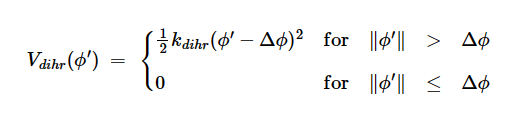
其中,Φ’为参考角Phi,ΔΦ为超出参考角的值dPhi,K_dihr为限制力的大小KFactor。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| system.gro | 体系的分子坐标文件 |
| system_itp.tar.gz | 体系平衡模拟时固定原子位置所施加的力 |
| system.top | 体系的拓扑文件 |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25. DOI: 10.1016/j.softx.2015.06.001
通过序列比对在人类生殖系数据库中搜索与目标抗体序列最接近的同源模板,输出对应的模板序列以及序列一致性信息。
抗体的序列(纯序列信息,非FASTA格式文件)。
抗体编号类型:kabat、chothia、imgt。
输出同源性最高的n条序列。
抗体的序列文件,FASTA格式。
抗体编号类型:kabat、chothia、imgt。
输出同源性最高的n条序列。
| 输出参数 | 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Hits Sequence | hits.fasta | 包含同源性最高的n条序列的序列文件 |
| Result | result.json | 包含找到的Germline模板以及序列的一致性信息 |
抗体常用的germline模板:
临床后期及已上市抗体的germline配对分布情况(统计自Adimab数据集):
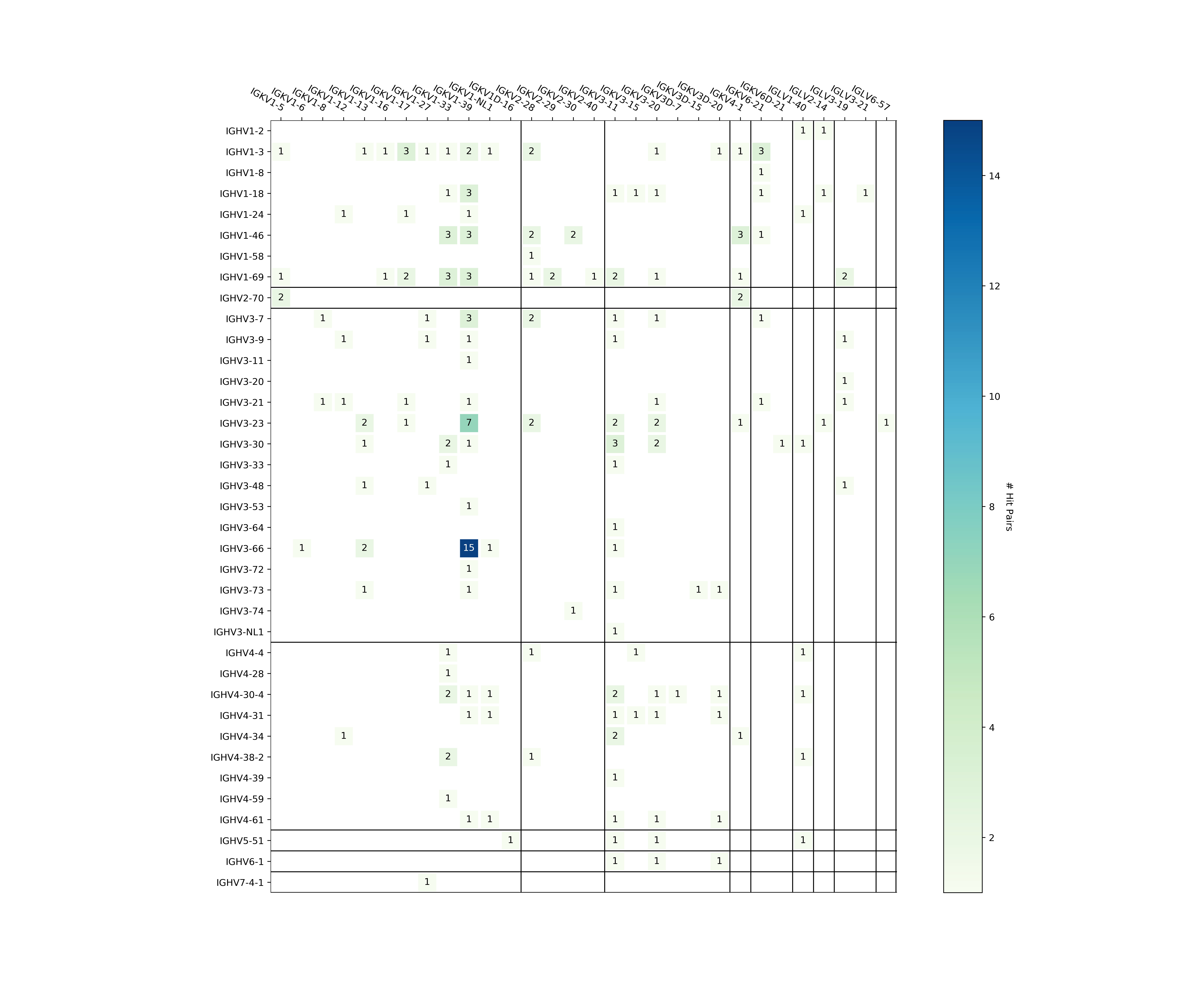
This module performs sequence alignment to search for the closest homologous template in the human germline database for a given target antibody sequence. It outputs the corresponding template sequence along with sequence similarity information.
The antibody sequence (pure sequence information, not in FASTA format).
Type of antibody numbering: kabat, chothia, imgt.
Number of top hits to output.
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
Type of antibody numbering: kabat, chothia, imgt.
Number of top hits to output.
| Output Parameter | Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hits Sequence | hits.fasta | File containing the top n sequences with the highest homology |
| Result | result.json | File containing the found Germline template and sequence similarity information |
Commonly used germline templates for antibodies:

Distribution of germline pairing for late-stage and marketed antibodies (statistics from the Adimab dataset):




Grafting模块是移植抗体的CDR到特定的框架区模板上,通常用于人源化设计。版本:v2.4
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式
抗体编号规则:kabat,imgt,chothia
指定输出抗体graft后的序列文件名称,FASTA格式
指定输出graft策略文件,JSON格式
指定输出抗体FR区序列比对同源性打分文件
指定轻链或重链使用特定germline模板,也可都指定,写法如下:
seq_name1:germline_name1,seq_name2:germline_name2
其中链名来自于流程第一步输入的fasta文件。
例1:以下语句为链"Infliximab.H"指定了模板"IGHV3-7*01":
Infliximab.H:IGHV3-7*01
例2:以下语句为两条链分别指定了模板:
Infliximab.H:IGHV3-7*01,Infliximab.L:IGKV1-39*01
指定参考模板序列,FASTA格式
指定输出FR区序列比对结果文件,FASTA格式
指定输出命中序列的数目
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| germline_hits.fasta | 输出FR区序列比对结果文件 |
| germline_score.json | 输出抗体FR区序列比对同源性打分文件 |
| grafted.fasta | 输出抗体graft后的序列文件名称 |
| graft_policy.json | 输出graft策略文件 |
The Grafting module is used to graft the CDRs of an antibody onto a specific framework region template, typically used for humanization design. Version: v2.4
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
Antibody numbering rule: kabat, imgt, chothia.
Specify the output file name for the grafted antibody sequence in FASTA format.
Specify the output grafting strategy file in JSON format.
Specify the output file for the homology scores of the antibody FR region sequences.
Specify the specific germline template to be used for the light chain or heavy chain, or both, in the format:
seq_name1:germline_name1,seq_name2:germline_name2
Where the chain names come from the FASTA file input in the first step of the process.
Example 1: The following statement specifies the template “IGHV3-7*01” for the chain “Infliximab.H”:
Infliximab.H:IGHV3-7*01
Example 2: The following statement specifies templates for two chains separately:
Infliximab.H:IGHV3-7*01,Infliximab.L:IGKV1-39*01
Specify the reference template sequence in FASTA format.
Specify the output file for the FR region sequence alignment results in FASTA format.
Specify the number of sequences to output.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| germline_hits.fasta | Output file for FR region sequence alignment results |
| germline_score.json | Output file for homology scores of the antibody FR region sequences |
| grafted.fasta | Output file name for the grafted antibody sequence |
| graft_policy.json | Output file for the grafting strategy |

该模块基于Pythia模型实现,该模型是一种针对零样本 ∆∆G 预测量身定制的自监督图神经网络。
蛋白质突变效应预测是解码分子进化机制、优化蛋白质工程改造的关键物理量。然而,传统预测方法面临两大挑战:一是基于物理力场的计算方法(如自由能微扰)计算复杂度高,难以满足大规模筛选需求;二是依赖于实验数据的监督学习方法易受训练集偏差影响,泛化能力受限。
为了应对这些问题,研究团队提出了Pythia框架,它结合了图神经网络与注意力机制,能够直接从蛋白质的三维结构中学习氨基酸之间的相互作用。通过这种“零监督”预训练策略,Pythia突破了传统方法对标记数据的依赖,成功捕捉了蛋白质折叠过程中隐藏的物理化学约束规律。
Pythia的模型架构采用了将蛋白质局部结构转化为k近邻图的方式,每个氨基酸作为节点,通过欧几里得距离连接其32个最近的氨基酸。节点的特征包括氨基酸类型以及主链的二面角,边的特征则涉及主链原子之间的距离、序列位置和链信息。通过消息传递神经网络(MPNN)架构,Pythia可以高效地更新每个氨基酸节点的信息,并对突变的稳定性变化进行准确预测。
与传统的基于物理力场的方法相比,Pythia能够在单核计算中实现每分钟预测约50,000个突变,速度提升了5个数量级。其在标准测试集S2648上的Spearman相关系数为0.616,Pearson相关系数为0.598,表现优于现有的所有对比模型。这一进展为大规模蛋白质序列空间扫描提供了强大的计算支持,能够处理多达2600万个高质量蛋白质结构数据,显著加深了我们对蛋白质序列空间的理解。
在实验验证中,Pythia表现出了比传统能量函数方法高出一倍的成功率,充分证明了其在实际应用中的可靠性。同时,Pythia的可解释性也为蛋白质工程提供了宝贵的生物学见解,使其更易于应用于复杂的蛋白质工程任务。
模型架构:Pythia将蛋白质局部结构转换为k近邻图,其中每个氨基酸作为一个节点,并通过欧几里得距离连接其32个最近的氨基酸。节点的特征包括氨基酸类型和主链的二面角(φ、ψ、ω),边的特征包括主链原子之间的距离、序列位置和链信息。
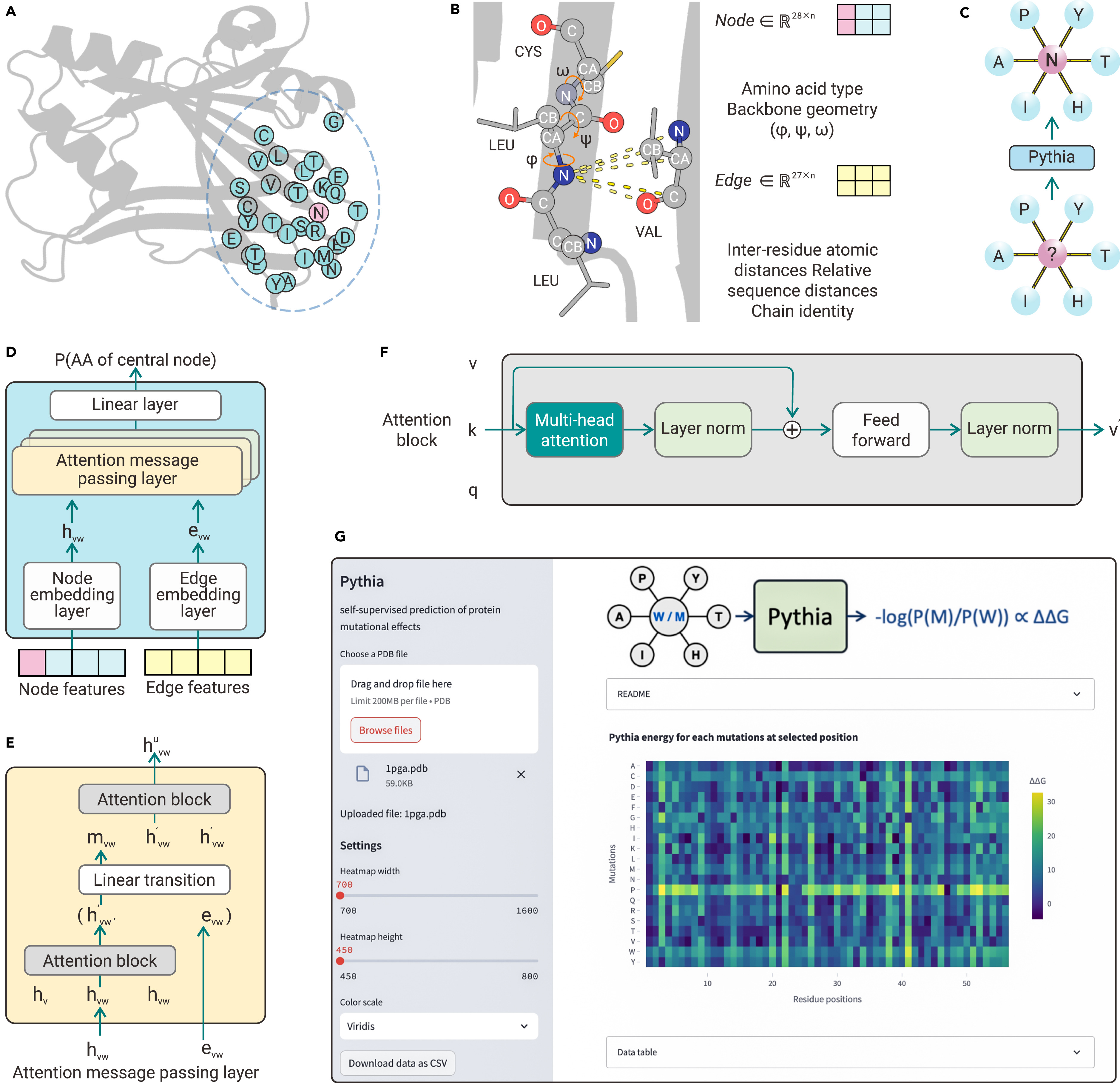
训练目标:Pythia的训练目标是预测中心节点的自然氨基酸类型,使用来自节点和边的信息。
消息传递神经网络(MPNN):Pythia采用消息传递神经网络(MPNN)架构,具体为带有注意力机制的消息传递层(AMPL)。在每个AMPL层中,顶点表示通过注意力块更新,然后与边表示连接以派生消息表示,最终通过另一个注意力块进一步细化节点表示。
损失函数:通过估计特定位置处每个氨基酸的概率来实现ΔΔG的预测。
在与其他自监督预训练模型和基于力场的方法的比较基准中,Pythia以极高的相关性超越其他同类算法,同时以最少的参数运行,使得计算速度显着加快,高达105倍。Pythia的功效通过其在预测柠檬烯环氧水解酶 (LEH) 的热稳定突变中的应用得到证实,实验成功率显着提高。
S2648数据集上的性能:Pythia在S2648数据集上的Spearman相关系数为0.616,Pearson相关系数为0.598,优于所有测试的模型。
S669数据集上的性能:在S669数据集上,Pythia的Spearman相关系数为0.66,在所有评估的方法中表现最佳。
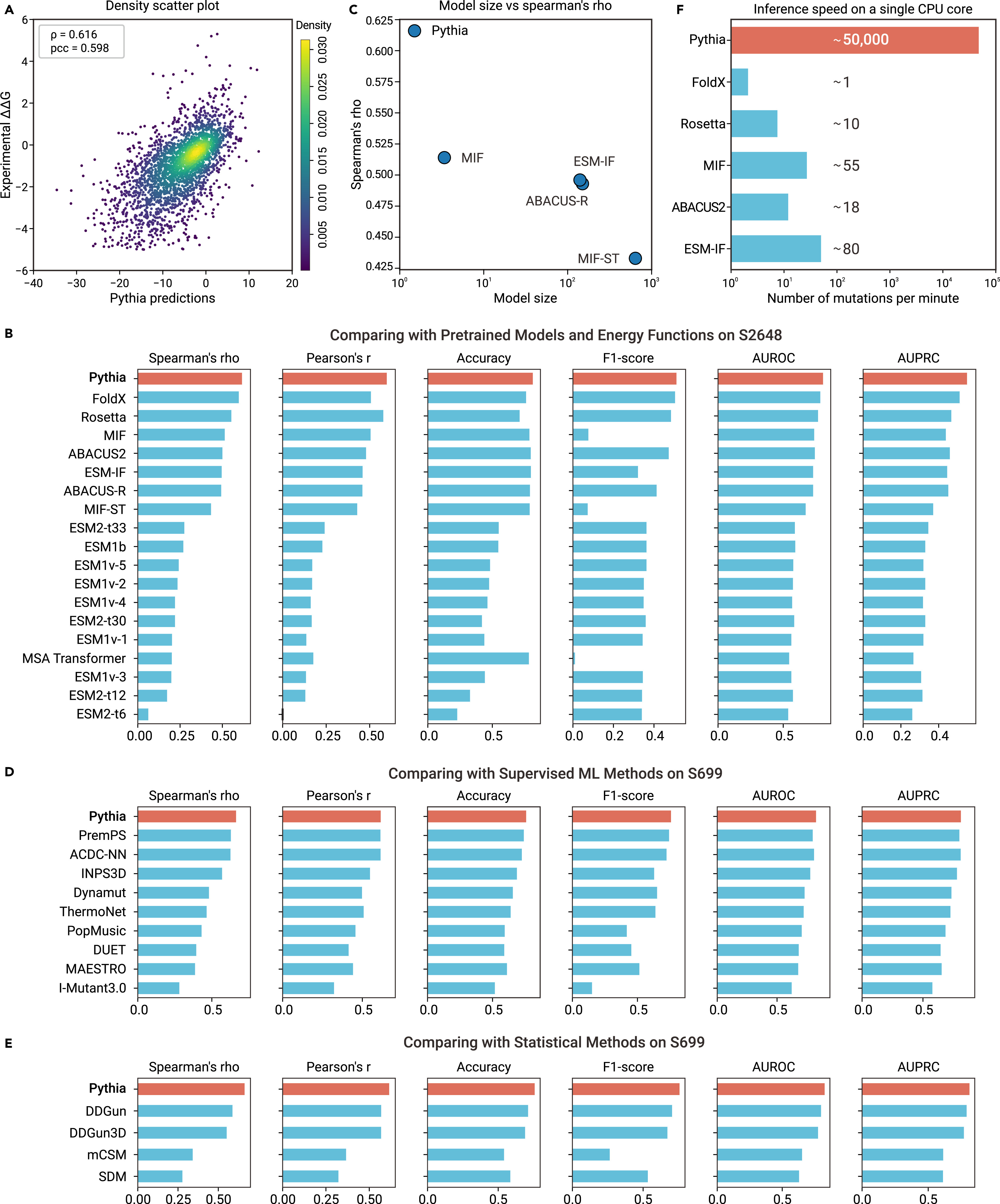
大规模数据集上的性能:在一个包含约100万个突变的百万级数据集上,Pythia的Spearman相关系数为0.602,Pearson相关系数为0.633,AUROC为0.83,AUPRC为0.88。
计算速度:Pythia的计算速度比传统的力场方法快105倍,能够在20秒内完成S2648数据集的计算,单核速度约为50,000个突变/分钟。
蛋白结构文件,PDB格式。不支持含有非标准氨基酸的蛋白。
指定要突变扫描的链名,可多链,用英文逗号分隔,如:A,B,默认为空,表示全部链都扫描。
输出文件名称,默认mutation_energy.csv。
特定格式化的输出文件名称,默认mutation_energy_fmt.csv。
指定输出能量最优的前N个突变对应的序列,默认为100。
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列,默认为mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列,复合物中各链之间用分号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式),默认为mutant_seqs_complex.fasta。
备注:当前24GB的GPU显存支持计算的残基数量在2000个左右。
输出mutation_energy.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | 链名称,如:'A’表示A链 |
| Mutation | 单点突变信息,如:'G1A’表示该链中,残基位置编号为1的残基甘氨酸G,突变为丙氨酸A,残基位置编号从1开始按顺序编号(非PDB文件中的残基序号) |
| Energy | 突变对应的能量变化,负值表示突变使得体系能量降低,体系变得更稳定。负得越多表示稳定性提升越多 |
输出mutation_energy_fmt.csv结果文件,包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | PDB结构中的链名称 |
| WT | PDB结构中的初始AA |
| Pos | AA位置编号,从1开始 |
| Consensus | 该位置出现能量最优的AA |
| L,A,G,V… | 该位置每种AA对应的能量变化值,变化值为负时,表示更稳定,负得越多,越稳定 |
输出结果对应的热图mutation_energy_[chain].png
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列,复合物中各链之间用冒号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式)mutant_seqs_complex.fasta。
This module is implemented based on the Pythia model, which is a self-supervised graph neural network specifically designed for zero-shot ∆∆G prediction.
Predicting the effects of protein mutations is a key factor in decoding molecular evolution mechanisms and optimizing protein engineering modifications. However, traditional prediction methods face two major challenges: first, computational methods based on physical force fields (such as free energy perturbation) have high computational complexity, making them unsuitable for large-scale screening; second, supervised learning methods that rely on experimental data are susceptible to training set biases, limiting their generalization ability.
To address these issues, the research team proposed the Pythia framework, which combines graph neural networks with attention mechanisms to learn interactions between amino acids directly from the three-dimensional structure of proteins. Through this “zero-supervision” pre-training strategy, Pythia overcomes the traditional methods’ dependence on labeled data and successfully captures the hidden physicochemical constraints in the protein folding process.
The architecture of Pythia converts the local structure of proteins into k-nearest neighbor graphs, where each amino acid acts as a node connected to its 32 nearest amino acids based on Euclidean distance. Node features include amino acid type and backbone dihedral angles, while edge features involve distances between backbone atoms, sequence positions, and chain information. Using a message-passing neural network (MPNN) architecture, Pythia efficiently updates information for each amino acid node and accurately predicts changes in mutation stability.
Compared to traditional physical force field-based methods, Pythia can predict approximately 50,000 mutations per minute on a single-core processor, achieving a speed increase of five orders of magnitude. On the standard test set S2648, it achieves a Spearman correlation coefficient of 0.616 and a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.598, outperforming all existing comparative models. This advancement provides powerful computational support for large-scale scanning of protein sequence space, capable of handling up to 26 million high-quality protein structure data points, significantly deepening our understanding of protein sequence space.
In experimental validation, Pythia demonstrated a success rate twice as high as traditional energy function methods, fully proving its reliability in practical applications. Additionally, Pythia’s interpretability offers valuable biological insights for protein engineering, making it more applicable to complex protein engineering tasks.
Model Architecture: Pythia transforms the local structure of proteins into a k-nearest neighbor graph, where each amino acid is represented as a node, connected to its 32 nearest amino acids by Euclidean distance. The features of the nodes include the amino acid type and the backbone dihedrals (φ, ψ, ω), while the features of the edges include the distances between backbone atoms, sequence positions, and chain information.

Training Objective: The training objective of Pythia is to predict the natural amino acid type of the central node, using information from both nodes and edges.
Message Passing Neural Network (MPNN): Pythia employs a message passing neural network (MPNN) architecture, specifically an Attention-based Message Passing Layer (AMPL). In each AMPL layer, the vertices are updated through an attention block, and then connected to edge representations to derive message representations, which are further refined through another attention block.
Loss Function: The prediction of ΔΔG is achieved by estimating the probability of each amino acid at specific positions.
In benchmark comparisons with other self-supervised pre-training models and force-field-based methods, Pythia outperforms other similar algorithms with high correlation while operating with minimal parameters, significantly accelerating computational speed by up to 105 times. The effectiveness of Pythia is demonstrated through its application in predicting thermally stable mutations of limonene epoxide hydrolase (LEH), with a notable increase in experimental success rates.
Performance on the S2648 Dataset: Pythia achieves a Spearman correlation coefficient of 0.616 and a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.598 on the S2648 dataset, outperforming all tested models.
Performance on the S669 Dataset: On the S669 dataset, Pythia achieves a Spearman correlation coefficient of 0.66, performing the best among all evaluated methods.
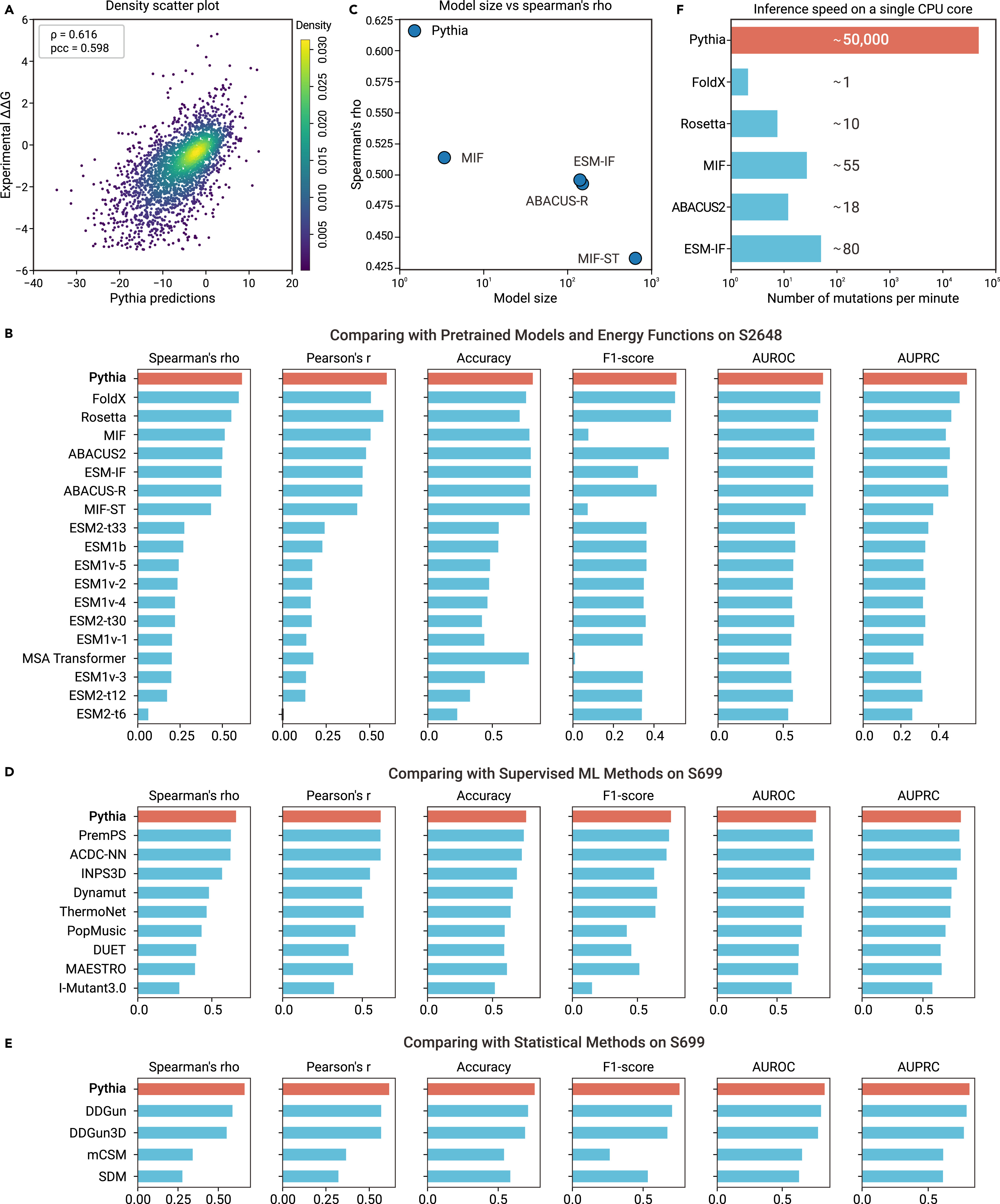
Performance on Large-scale Datasets: On a large dataset containing approximately 1 million mutations, Pythia achieves a Spearman correlation coefficient of 0.602, a Pearson correlation coefficient of 0.633, an AUROC of 0.83, and an AUPRC of 0.88.
Computational Speed: Pythia is 105 times faster than traditional force-field methods, capable of completing calculations on the S2648 dataset in 20 seconds, with a single-core speed of approximately 50,000 mutations per minute.
Protein structure file in PDB format. Proteins containing non-standard amino acids are not supported.
Specify the chain names to be scanned for mutations. Multiple chains can be listed, separated by commas, e.g., A,B. The default is empty, which means all chains will be scanned.
Output file name, mutation_energy.csv is the default.
Formatted output file name, mutation_energy_fmt.csv is the default.
Specify the sequences corresponding to the top N mutations with the optimal energy. The default value is 100.
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN.
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN. The chains within the complexes are separated by semicolons (;) (for batch mode structure prediction by Boltz2).
Outputs a mutation_energy.csv file containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain | Chain name, e.g., ‘A’ represents chain A |
| Mutation | Single point mutation information, e.g., ‘G1A’ indicates that in this chain, the residue at position 1, Glycine (G), is mutated to Alanine (A), with residue positions numbered sequentially starting from 1 (not the residue numbering in the PDB file) |
| Energy | The energy change associated with the mutation; negative values indicate that the mutation lowers the system’s energy, making it more stable. The more negative the value, the greater the increase in stability. |
The heatmap output mutation_energy_[chain].png
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN. mutant_seqs.fasta
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN. The chains within the complexes are separated by : (for batch mode structure prediction by Boltz2). mutant_seqs_complex.fasta

Mutation Energy of Binding (Pythia-PPI)模块基于Pythia-PPI模型实现,该模型基于深度学习,结合了多任务学习和自蒸馏策略,以克服实验数据稀缺的瓶颈,并提高预测准确性。Pythia-PPI由两个模块组成:预训练的结构图编码器模块和ΔΔG预测模块。该模型使用k-最近邻(k-NN)图将蛋白质或蛋白质-蛋白质复合物的局部结构转换为图表示,每个氨基酸作为一个节点,与其32个最近的氨基酸基于C-alpha原子的欧几里得距离建立连接。输入的结构图编码器结合了氨基酸类型的一热编码,以及使用正弦和余弦函数表示的主链二面角(φ、ψ和ω)作为节点特征。边特征则考虑了五个主链原子(C-alpha、C、N、O和C-beta)之间的距离,以及序列位置和链信息。通过结构图编码器,节点和边输入特征被转换为嵌入,这些嵌入与预训练模块中的氨基酸概率相结合,形成ΔΔG预测模块的输入向量。Pythia-PPI采用迁移学习和多任务学习相结合的方法,共享结构编码器层以预测突变对PPI结合亲和力和蛋白质稳定性的影响。
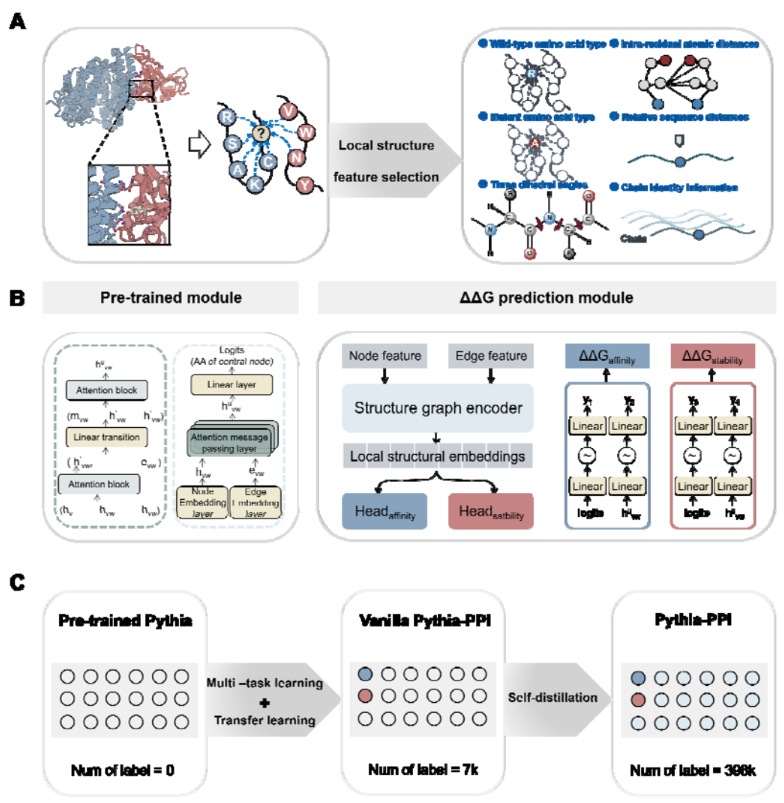
使用了SKEMPI数据集进行基准测试,并与其他方法进行了比较。结果显示,Pythia-PPI在SKEMPI数据集上的皮尔逊相关系数从0.6447提高到0.7850,在病毒-受体数据集上的皮尔逊相关系数从0.3654提高到0.6051。这些结果表明Pythia-PPI是一个分析蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用适应性景观的有力工具。
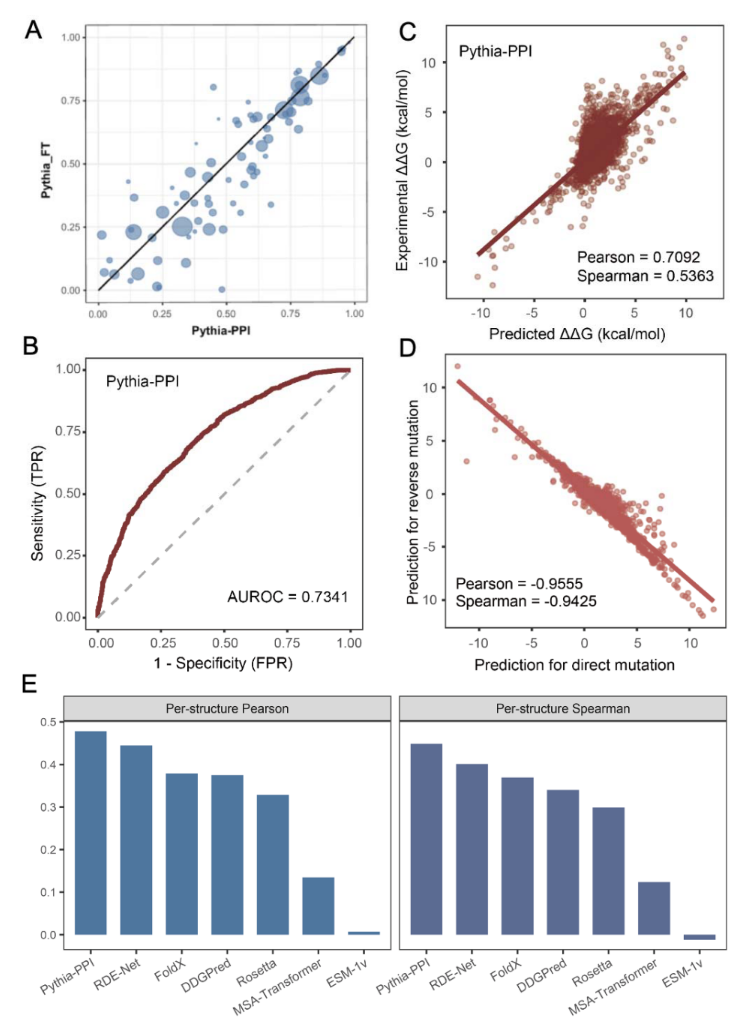
蛋白复合物结构文件,PDB格式。不支持含有非标准氨基酸的蛋白。
指定要突变扫描的链名,可多链,用英文逗号分隔,如:A,B,默认为空,表示全部链都扫描。
输出文件名称,默认mutation_ddg.csv。
特定格式化输出的结果文件名称,默认mutation_ddg_fmt.csv。
指定输出能量最优的前N个突变对应的序列,默认为100。
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列,默认为mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列,复合物中各链之间用分号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式),默认为mutant_seqs_complex.fasta。
备注:当前24GB的GPU显存支持计算的残基数量在1500个左右。
输出mutation_ddg.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | 链名称,如:'A’表示A链 |
| Mutation | 单点突变信息,如:'G1A’表示该链中,残基位置编号为1的残基甘氨酸G,突变为丙氨酸A,残基位置编号从1开始按顺序编号(非PDB文件中的残基序号) |
| ddG_Pred | 突变对应的结合自由能ddG变化,负值表示突变使得亲和力变高,负得越多表示亲和力提升越多 |
输出mutation_ddg_fmt.csv结果文件,包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | PDB结构中的链名称 |
| WT | PDB结构中的初始AA |
| Pos | AA位置编号,从1开始 |
| Consensus | 该位置出现能量最优的AA |
| L,A,G,V… | 该位置每种AA对应的能量变化值,变化值为负时,表示更稳定,负得越多,越稳定 |
输出结果对应的热图mutation_ddg_[chain].png
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列mutant_seqs_complex.fasta,复合物中各链之间用冒号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式)。
The Mutation Energy of Binding (Pythia-PPI) module is implemented based on the Pythia-PPI model, which utilizes deep learning and combines multi-task learning with a self-distillation strategy to overcome the bottleneck of scarce experimental data and improve prediction accuracy. Pythia-PPI consists of two modules: a pre-trained structural graph encoder module and a ΔΔG prediction module. The model uses a k-nearest neighbors (k-NN) graph to convert the local structure of proteins or protein-protein complexes into a graph representation, where each amino acid is represented as a node, connected to its 32 nearest amino acids based on the Euclidean distance of C-alpha atoms. The input structural graph encoder combines one-hot encoding of amino acid types with backbone dihedrals (φ, ψ, and ω) represented using sine and cosine functions as node features. Edge features take into account the distances between five backbone atoms (C-alpha, C, N, O, and C-beta), as well as sequence positions and chain information. Through the structural graph encoder, the input features for nodes and edges are transformed into embeddings, which are combined with amino acid probabilities from the pre-trained module to form the input vector for the ΔΔG prediction module. Pythia-PPI employs a combination of transfer learning and multi-task learning, sharing structural encoder layers to predict the effects of mutations on PPI binding affinity and protein stability.

Benchmarking was conducted using the SKEMPI dataset and compared with other methods. The results show that Pythia-PPI improved the Pearson correlation coefficient from 0.6447 to 0.7850 on the SKEMPI dataset, and from 0.3654 to 0.6051 on the virus-receptor dataset. These results indicate that Pythia-PPI is a powerful tool for analyzing the adaptive landscape of protein-protein interactions.
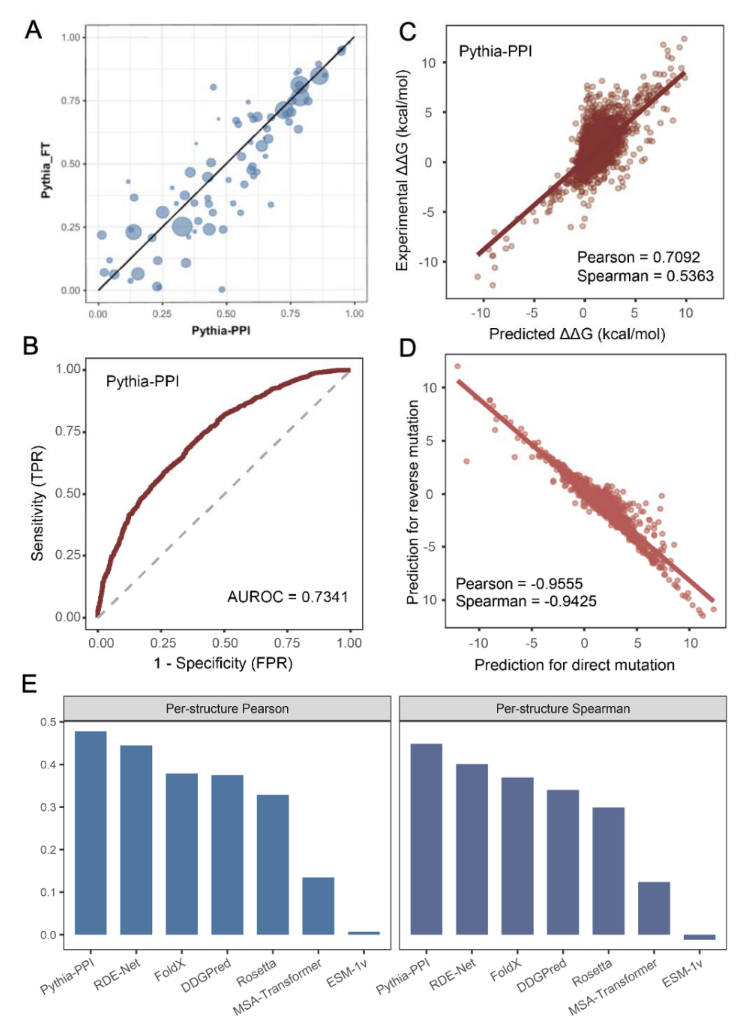
Protein complex structure file in PDB format. Proteins containing non-standard amino acids are not supported.
Specify the chain names to be scanned for mutations. Multiple chains can be listed, separated by commas, e.g., A,B. The default is empty, which means all chains will be scanned.
Output file name, mutation_ddg.csv is the default.
Formatted output file name, mutation_ddg_fmt.csv is the default.
Specify the sequences corresponding to the top N mutations with the optimal energy. The default value is 100.
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN.
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN. The chains within the complexes are separated by semicolons (;) (for batch mode structure prediction by Boltz2).
Outputs a mutation_ddg.csv file containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain | Chain name, e.g., ‘A’ represents chain A |
| Mutation | Single point mutation information, e.g., ‘G1A’ indicates that in this chain, the residue at position 1, Glycine (G), is mutated to Alanine (A), with residue positions numbered sequentially starting from 1 (not the residue numbering in the PDB file) |
| ddG_Pred | The change in binding free energy (ddG) corresponding to the mutation; negative values indicate that the mutation increases affinity, with more negative values indicating a greater increase in affinity. |
Outputs a mutation_ddg_fmt.csv file containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain | Chain name in the PDB structure |
| WT | Initial AA in the PDB structure |
| Pos | Position index of the AA, start from 1 |
| Consensus | The AA with the most affinity value at that position |
| L, A, G, V… | The ddg of each AA at that position. Negative values indicate that the mutation increases affinity, with more negative values indicating a greater increase in affinity. |
The heatmap output mutation_ddg_[chain].png
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN mutant_seqs.fasta.
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN mutant_seqs_complex.fasta. The chains within the complex are separated by colons(:) (for batch mode of Boltz2 structure prediction) .
Antibody (Off-) Target Prediction模块对输入的抗体进行潜在靶点预测,基于丰富的抗体-抗原相互作用数据库,寻找与输入抗体在序列及结构上高度相似的一系列抗体。基于相似性原理(相似抗体可能具有相似靶点),这些高度相似的抗体对应的抗原靶点可能是输入抗体的潜在靶点。当前抗体-抗原相互作用数据库包含16万对抗原-抗体复合物,主要来源于文献、专利等开源数据。
待预测靶点的抗体结构文件,PDB格式或CIF格式。推荐使用AF3-like相关的结构预测模块进行抗体结构预测,如:Protenix
搜索模式,支持4种模式(默认为模式3):
保留打分排名最高的前N个结果,默认为50。
物种信息过滤:
输出结果的文件名,默认为“hits.csv”
检索结果文件默认为hits.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Query | 查询抗体结构名称 |
| Target | 数据库的抗体结构名称 |
| Antigen Name | 预测的靶点名称 |
| Description | 对数据库结构的描述 |
| Antigen Organism Label | 靶点的来源物种 |
| Comprehensive Score | 潜在靶点的综合打分,数值在0-1.0之间,越接近1.0,表示成为抗体靶点的可能性越大,默认基于该打分对潜在靶点进行排序。该打分综合了多种结构比对与复合物评价指标。 |
| Alignment TMScore \ Query TMScore \ Target TMScore | TM-score (Template Modeling Score) 是一种结构比对指标,用于衡量两个蛋白质三维结构的相似性,与 RMSD相比,TM-score 更加稳定,对结构长度不敏感,能更准确地反映蛋白质结构的全局相似性。其取值范围在0到1之间,TM-score > 0.5 表示显著相似。其中,Query TMScore指使用查询抗体结构进行长度归一化;Target TMScore指使用数据库抗体结构进行长度归一化;Alignment TMScore指使用查询抗体和数据库抗体的序列匹配区的结构进行长度归一化。 |
| RMSD | 查询抗体与数据库抗体的骨架结构中alpha碳原子C𝛂位置差异的均方根偏差。 |
| RMSD_score | 基于结构比对叠合后的主链C𝛂原子的位置差异RMSD值,进行归一化获得,计算公式为:RMSD_score = exp(-RMSD/3.8),将其归一化到0-1.0之间,其中3.8为经验参数。 |
| DockQ | 衡量抗体与潜在靶点之间的虚拟结合参数,其值在0-1.0之间,越大表示抗体越能与潜在靶点结合。 |
The Antibody (Off-) Target Prediction module predicts potential targets for the input antibody. Based on a rich database of antibody-antigen interactions, it identifies a series of antibodies that are highly similar to the input antibody in both sequence and structure. Following the principle of similarity (similar antibodies may have similar targets), the antigen targets corresponding to these highly similar antibodies could be potential targets for the input antibody. The current antibody-antigen interaction database contains 160,000 antigen-antibody complexes, primarily sourced from open-source data such as literature and patents.
Antibody structure file for the target to be predicted, in PDB or CIF format.
Search Modes, supporting 4 modes (default is Mode 3):
Retain the top N results with the highest scores, with the default being 50.
Species Information Filtering:
The name of output file, default is “hits.csv”.
The search result file hits.csv contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Query | Name of the query antibody structure |
| Target | Name of the antibody structure in the database |
| Antigen Name | Name of the predicted target |
| Description | Description of the structure in the database |
| Antigen Organism Label | Source organism of the target |
| Comprehensive Score | The comprehensive scoring of potential targets ranges from 0 to 1.0. The closer the score is to 1.0, the higher the likelihood of it being an antibody target. By default, target hits are ranked based on this score. This score integrates various structural alignment and complex evaluation metrics |
| Alignment TMScore \ Query TMScore \ Target TMScore | TM-score (Template Modeling Score) is a structural alignment metric used to measure the similarity between two protein 3D structures. Compared to RMSD, TM-score is more stable and less sensitive to structural length, providing a more accurate reflection of the global similarity of protein structures. It ranges from 0 to 1, with TM-score > 0.5 indicating significant similarity. Query TMScore refers to length normalization using the query antibody structure; Target TMScore refers to length normalization using the database antibody structure; Alignment TMScore refers to length normalization using the sequence-matched regions of the query and database antibodies. |
| RMSD | Query the root mean square deviation (RMSD) of the alpha carbon atom C𝛂 positions between the antibody and the database antibody’s backbone structures. |
| RMSD_score | The RMSD value of the backbone C𝛂 atoms’ position differences after structural alignment is normalized to obtain the score. The calculation formula is: RMSD_score = exp(-RMSD/3.8), which normalizes the score to the range of 0-1.0, where 3.8 is an empirical parameter. |
| DockQ | A virtual binding parameter that measures the interaction between an antibody and a potential target, with values ranging from 0 to 1.0. The higher the value, the greater the likelihood of the antibody binding to the potential target. |
LigandMPNN是一种基于深度学习的蛋白质序列设计方法,专门用于模拟蛋白质与非蛋白质组分(如小分子、核苷酸和金属)之间的相互作用。它是 ProteinMPNN的升级版,能够在蛋白质设计中加入非蛋白质的组分,从而提升对非蛋白-蛋白相互作用的理解。
主要特点和优势:
全面建模:LigandMPNN结合了蛋白质图、配体图和蛋白质-配体图三种图结构,全面建模蛋白质与非蛋白质组分的相互作用。
高性能:在恢复与小分子、核苷酸和金属相互作用的原生背景序列方面,LigandMPNN的表现优于传统方法如Rosetta和ProteinMPNN。
侧链预测:除了生成蛋白质序列,LigandMPNN还能生成侧链构象,允许对结合相互作用进行更详尽的评估。
LigandMPNN 在酶设计、小分子结合剂开发以及生物传感器的设计中具有广阔的应用前景。其高效性和准确性使其成为蛋白质工程领域的重要工具。
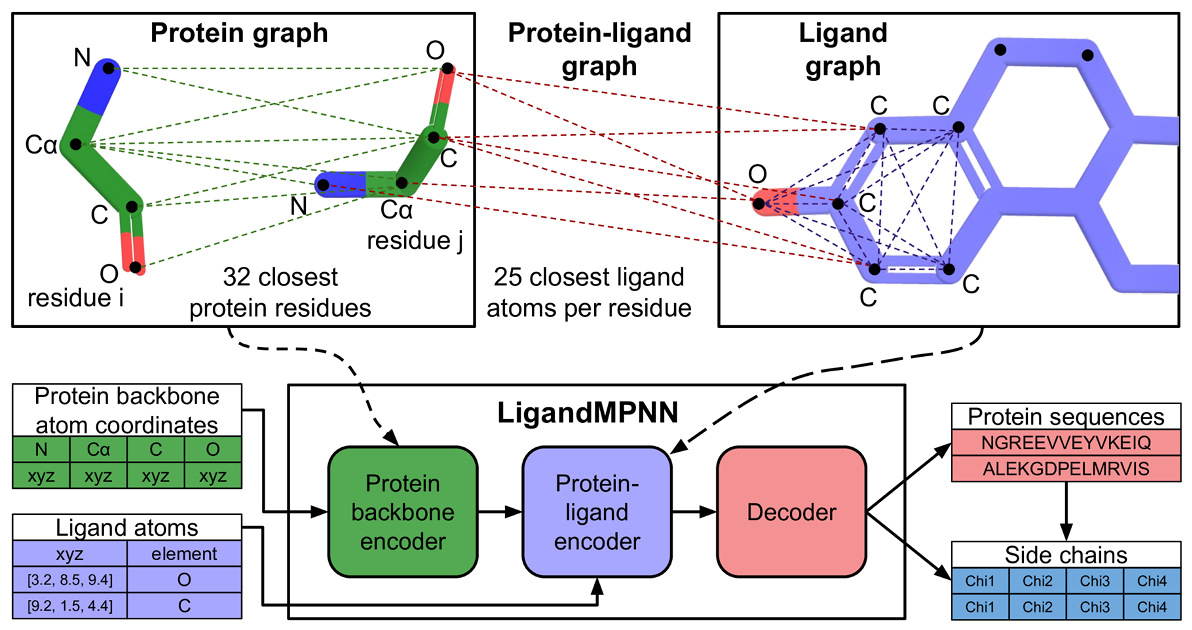
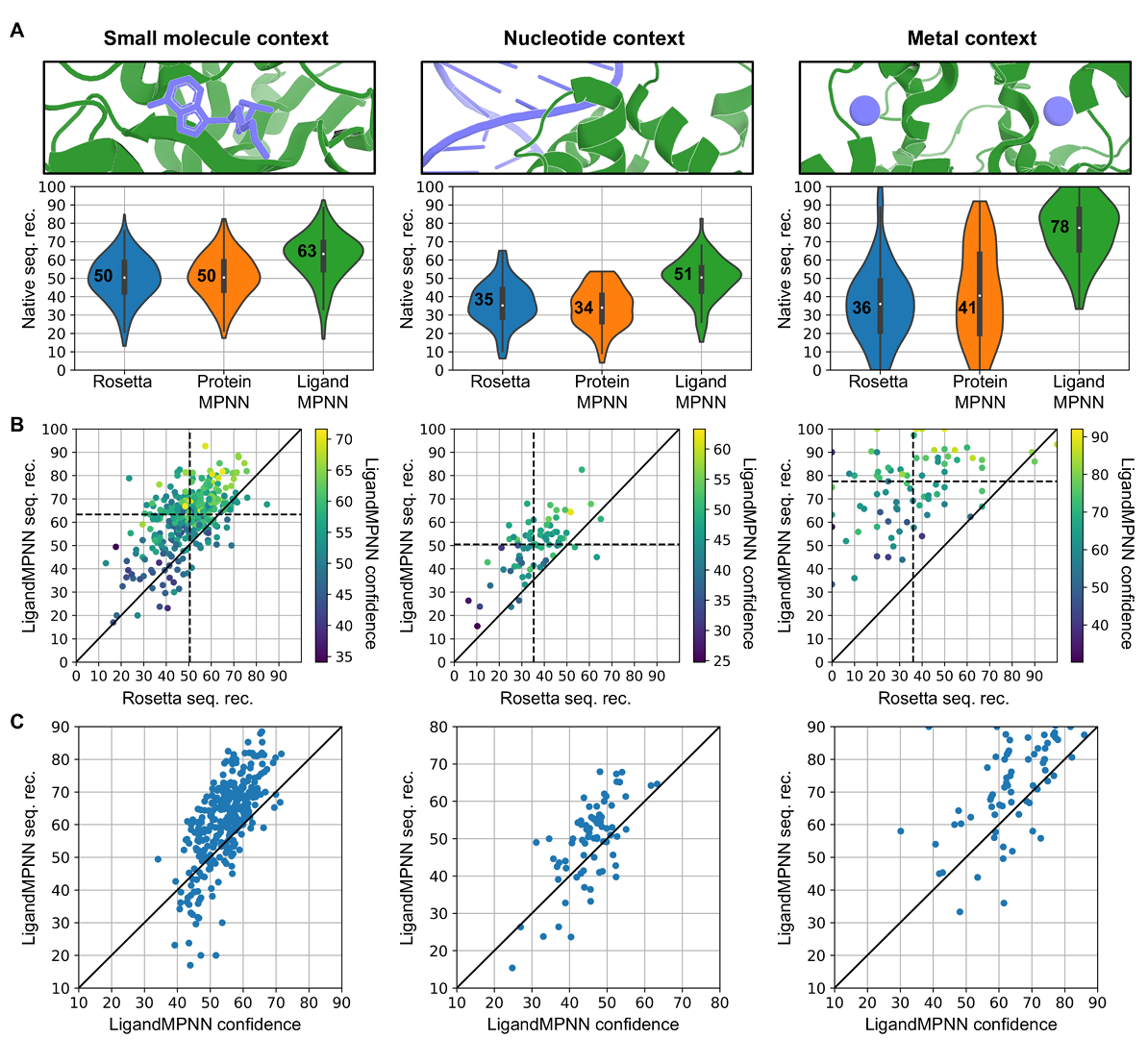
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式。
指定需要设计的链,多条链用空格分割,例如:A,B。
输出设计的序列数目。
氨基酸采样温度,T=0.0表示取argmax,T>>1.0表示随机采样。建议的取值为0.1、0.15、0.2、0.25、0.3。较高的值会导致更多的多样性。
设计残基模式:
可选参数,设置氨基酸序号,对设置的氨基酸根据Position Type选项进行固定或设计。当参数Chain设置为A,C时,此参数如果设置为1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 23 25, 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 40意味着对链A中的残基1 2 3…25和链C中的残基10 11 12…40进行固定或设计。
注意:同一条链的氨基酸序号用空格分隔,不同链的氨基酸用逗号分隔。根据原始 PDB 编号设计的,并且支持插入代码。
指定在生成的结果序列中不许出现的氨基酸种类。
可选参数,可指定设计时参考的模式。具体含义如下:
–homomer:基于同源多聚体进行序列设计;
–pack_side_chains:对设计的序列生成侧链结构。
最终设计的序列文件result.fasta,里面包含最终设计的序列。
其中序列名称:
指定参数--pack_side_chains时,输出设计后的结构打包文件packed_side_chains.tar.gz,包含最终设计的序列对应的复合物结构PDB文件。
LigandMPNN is a deep learning-based protein sequence design method specifically designed to simulate interactions between proteins and non-protein components (such as small molecules, nucleotides, and metals). It is an upgraded version of ProteinMPNN and can incorporate non-protein components into protein design, thereby enhancing the understanding of non-protein-protein interactions.
Key Features and Advantages:
LigandMPNN has broad application prospects in enzyme design, small molecule binder development, and biosensor design. Its efficiency and accuracy make it an important tool in the field of protein engineering.


Protein structure file in PDB format.
Specify the chain to be designed, multiple chains are separated by spaces, for example: A,B.
Output the number of sequences designed.
Residue Design Mode:
Optional parameter to set the amino acid sequence number for fixing or designing amino acids based on the Position Type option. When the parameter Chain is set to A C, if this parameter is set to 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 23 25, 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 40, it means that residues 1 2 3…25 in chain A and residues 10 11 12…40 in chain C are fixed or designed.
Note: Amino acid sequence numbers of the same chain are separated by spaces, while amino acids from different chains are separated by commas. The position is designed according to the original PDB numbering and also supports insertion codes.
Amino acid sampling temperature, T=0.0 means argmax, T>>1.0 means random sampling. The suggested values are 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, 0.3. Higher values result in more diversity.
Optional parameter specifying the types of amino acids that are not allowed to appear in the generated sequence.
Optional parameter specifying the reference mode for design. Specific meanings are as follows:
–homomer: Sequence design based on homologous oligomers;
–pack_side_chains:Generate side chain structures for the designed sequence。
The output file is result.fasta and contains the final design sequence.
Where the sequence name:
When the parameter --pack_side_chains is specified, the output is a packed structure file named packed_side_chains.tar.gz, which includes the PDB file of the final designed sequence’s corresponding complex structure.

基于TemBERTure开发的Thermostability Prediction是一个用于预测蛋白质热稳定性的深度学习工具,专注于氨基酸序列分析。它包括两个模型:TemBERTureCLS和TemBERTureTm。TemBERTureCLS是一个分类模型,用于预测蛋白质序列的热类别,即判断其是嗜热的还是非嗜热的。TemBERTureTm是一个回归模型,用于根据蛋白质序列预测其熔点温度(Tm)。这两个模型都基于protBERT-BFD语言模型,该模型在大量蛋白质序列数据集上进行了预训练。通过基于适配器的方法进行高效微调,使得TemBERTure能够在不需要广泛重新训练的情况下,稳健地适应特定任务。
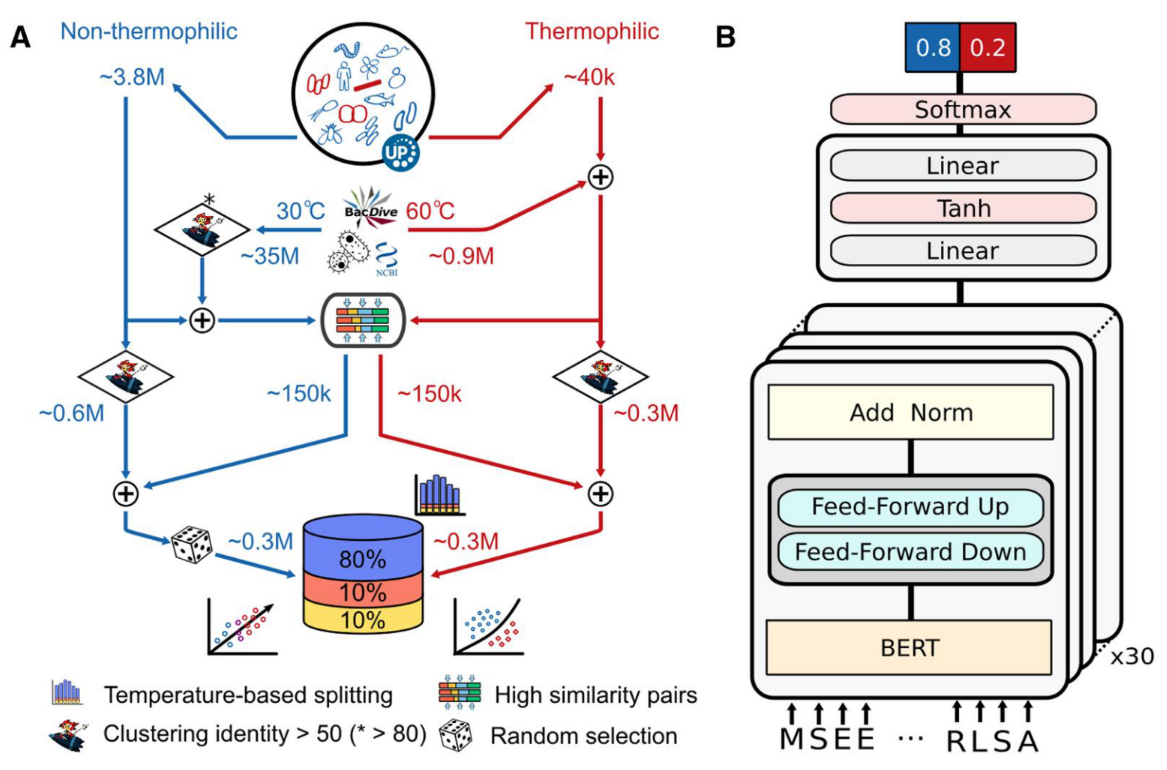
TemBERTureCLS与其他常用模型的预测结果比较
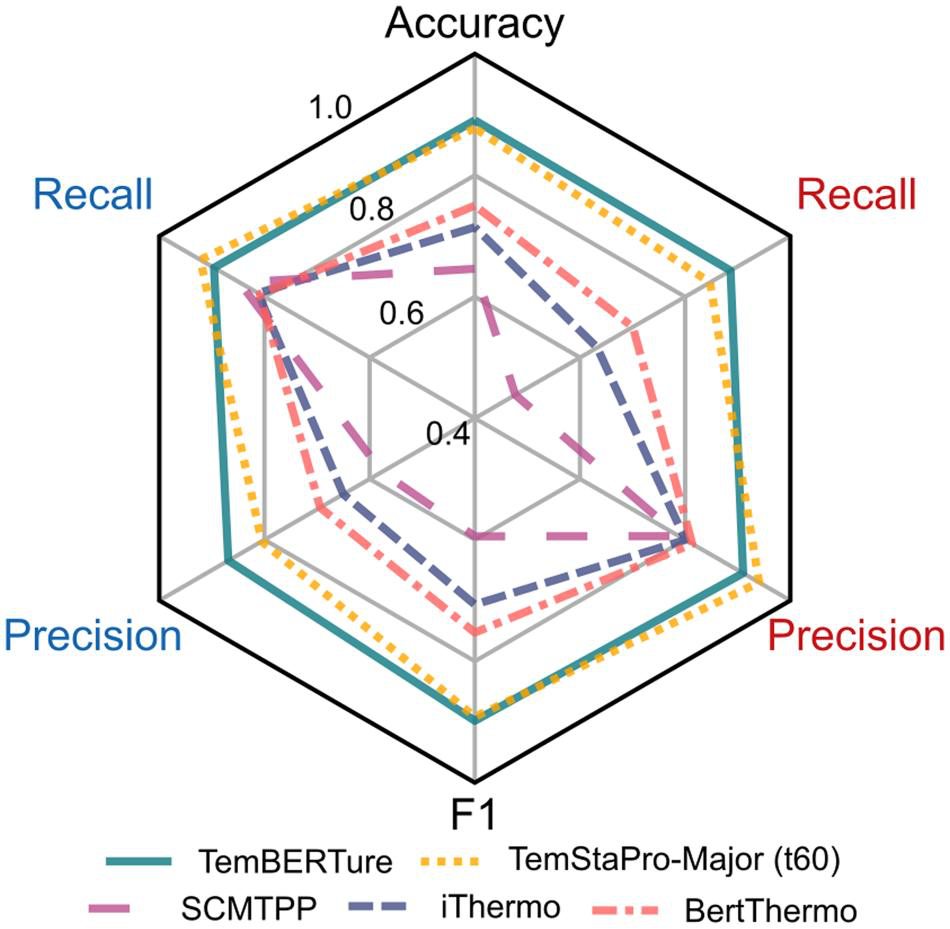
TemBERTureTm与其他常用模型的预测结果比较
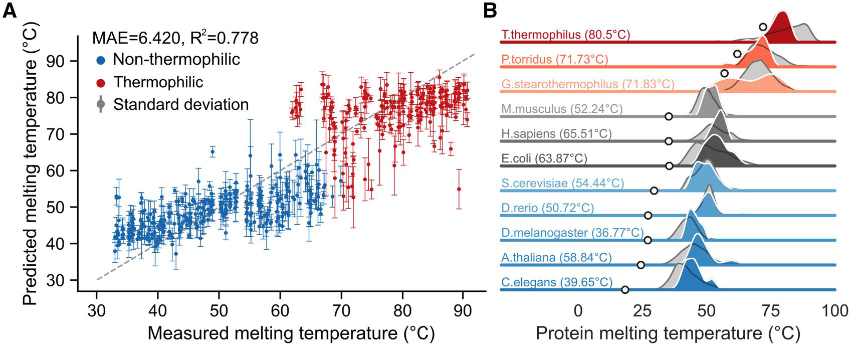
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式
默认输出结果文件为predicted_Tm.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ID | 序列ID |
| Tm | 预测得到的蛋白Melting Temperature ™ 值 |
| Thermostability Type | 预测得到的蛋白热稳定性类别,有两种:Thermophilic与Non-thermophilic |
| Thermophilicity Prediction Score | 预测得到的蛋白嗜热性概率评分,数值在0-1.0之间,越大表示蛋白嗜热的概率越高 |
Thermostability Prediction, developed based on TemBERTure, is a deep learning tool designed to predict protein thermostability, focusing on amino acid sequence analysis. It includes two models: TemBERTureCLS and TemBERTureTm. TemBERTureCLS is a classification model used to predict the thermal category of a protein sequence, determining whether it is thermophilic or non-thermophilic. TemBERTureTm is a regression model used to predict the melting temperature ™ of a protein based on its sequence. Both models are based on the protBERT-BFD language model, which has been pre-trained on a large dataset of protein sequences. By using an adapter-based fine-tuning approach, TemBERTure can efficiently and robustly adapt to specific tasks without the need for extensive retraining.
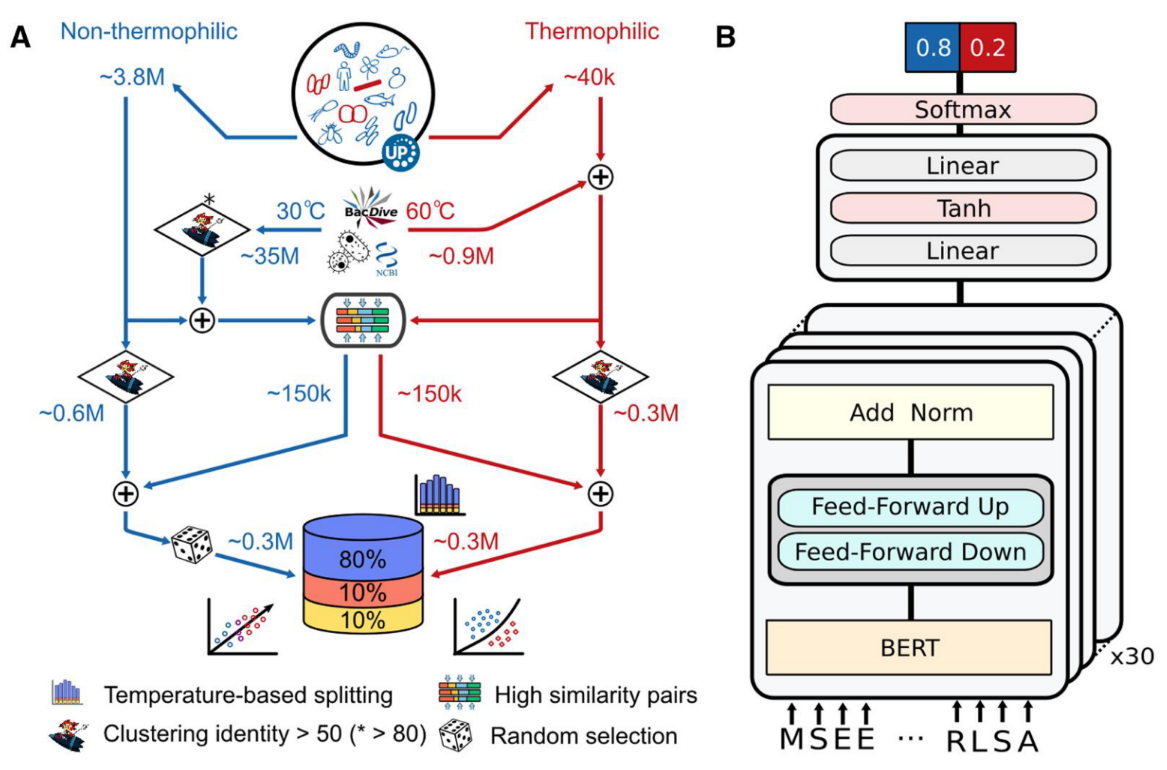
Comparison of TemBERTureCLS with other common models’ prediction results
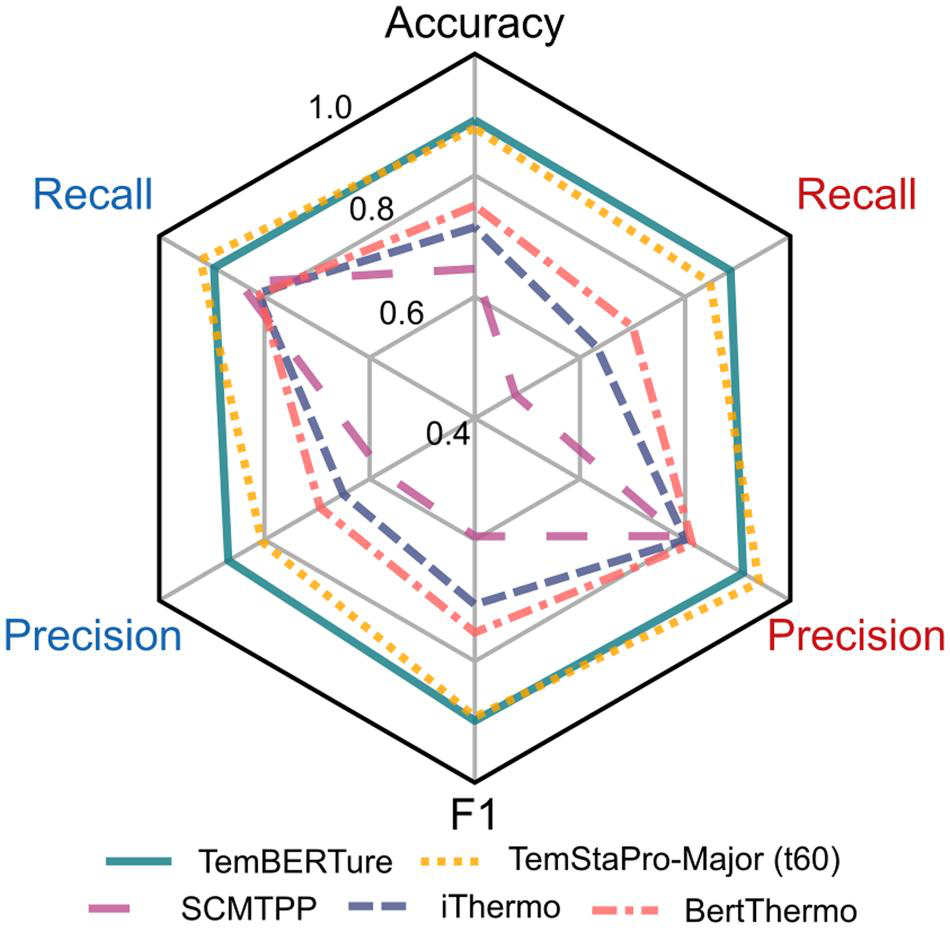
Comparison of TemBERTureTm with other common models’ prediction results
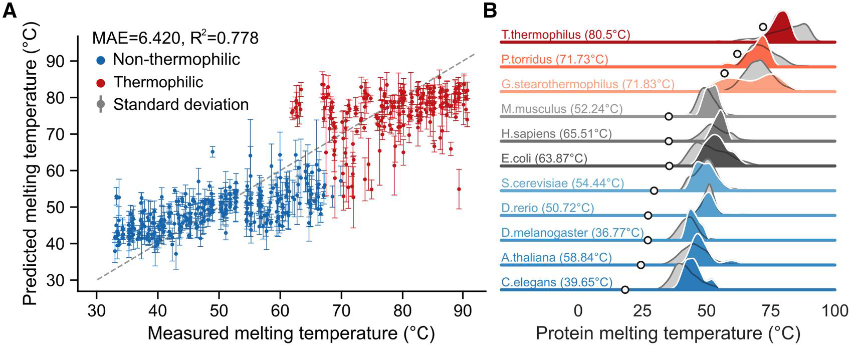
The protein sequence file in FASTA format.
The output result file is predicted_Tm.csv, containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Sequence ID |
| Tm | Predicted protein Melting Temperature ™ value |
| Thermostability Type | Predicted protein thermostability category: either Thermophilic or Non-thermophilic |
| Thermophilicity Prediction Score | Predicted probability score of protein thermophilicity, ranging from 0 to 1.0, where a higher score indicates a higher likelihood of the protein being thermophilic |
GMX Metadynamics Generation模块是生成可用于Metadynamics模拟的输入文件。
提交模拟体系的gro文件。该文件可以从MD Solvation模块获取。
Metadynamics模拟阶段是否考虑周期性边界条件,yes或者no。
组成集合变量CV的第一个组所包含的原子。
组成集合变量CV的第二个组所包含的原子。
组成集合变量CV的第三个组所包含的原子。
组成集合变量CV的第四个组所包含的原子。
备注:
集合变量DISTANCE对应的成分,其成分有x,y,z和xyz,分别表示计算DISTANCE仅考虑x,y,z维度以及xyz三个维度都考虑,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割。
施加的沉积高斯函数的高度,默认1.0
施加的沉积高斯函数的宽度或者标准差,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,默认0.05
施加的沉积高斯函数的频率,默认500,即每500个时间步长进行一次高斯函数沉积
集合变量的边界最小值,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割。无默认值时即不考虑边界,此时计算量会增加,强烈建议设置边界。
集合变量的边界最大值,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,无默认值时即不考虑边界,此时计算量会增加,强烈建议设置边界。
集合变量的窗口大小,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,默认等于metad_width的1/5
集合变量的窗口数量,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,默认等于150,CV Space和CV Bin的相乘等于CV Max和CV Min的差值,因此当CV Space和CV Bin同时设置时以对应窗口数最多的为准
是否考虑施加自适应沉积函数, geom或者diff,默认为不填,即不考虑自适应。
施加的自适应高斯函数的宽度或者标准差的最小值,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,默认等于0。
施加的自适应高斯函数的宽度或者标准差的最大值,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,默认等于0。
是否考虑重加权以获得重加权因子,对获得归一化偏势,yes或者no,默认no,即不考虑重加权,一般在体系收敛后才考虑重加权。
计算重加权因子时施加的高斯函数的个数,默认等于50。
计算重加权因子时集合变量的窗口数量,其值不能小于CV Bin的值,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,默认等于CV Bin。
是否考虑回火metadynamics模拟,yes或者no。
回火metadynamics模拟时对应的基础温度,默认等于300K
回火Metadynamics模拟时对应的偏置因子,其值等于(T+deltaT)/T,默认等于1,此时未进行偏置模拟,若进行偏置模拟,偏置因子应大于1
回火Metadynamics模拟时对应的施加的沉积高斯函数的高度,Height=kbDeltaTFrequency*TimeStep/TAU,默认等于0,即直接使用设置的沉积函数的高度代替。
Metadynamics模拟时指定的输出步长,默认100。
Metadynamics模拟时指定的沉积高斯函数的输出文件名。
Metadynamics模拟时指定的集合变量的输出文件名。
Metadynamics模拟时指定的CV Group的输出文件名,该文件中包含所有的CV Group的原子组,用于下一步Metadynamics的输入文件。
Metadynamics模拟时指定的参数的输出文件名,该文件中包含计算时所需的参数,用于下一步Metadynamics的输入文件。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| HILLS.dat | Metadynamics模拟时指定的沉积高斯函数输出 |
| COLVAR.dat | Metadynamics模拟时指定的集合变量的输出 |
| PLUMED.ndx | NDX文件指定的组成集合变量的原子组 |
| PLUMED.dat | 下一步Metadynamics计算所需的参数文件 |
上述两个生成的文件将作为下一步metadynamics模拟的输入文件。
The GMX Metadynamics Generation module is used to generate input files for Metadynamics simulations.
Submit the gro file of the simulation system. This file can be obtained from the MD Solvation module.
Whether to consider periodic boundary conditions during the Metadynamics simulation phase, yes or no.
Atoms included in the first group that makes up the collective variable (CV).
Atoms included in the second group that makes up the collective variable (CV).
Atoms included in the third group that makes up the collective variable (CV).
Atoms included in the fourth group that makes up the collective variable (CV).
Note:
The components corresponding to the DISTANCE collective variable, which can be x, y, z, and xyz, representing calculations of DISTANCE considering only the x, y, z dimensions or all three dimensions, respectively. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable components.
The height of the deposited Gaussian function, default is 1.0.
The width or standard deviation of the deposited Gaussian function. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable widths, default is 0.05.
The frequency of depositing the Gaussian function, default is 500, meaning a Gaussian function deposition occurs every 500 time steps.
The minimum boundary value of the collective variable. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable minimums. If there is no default value, the boundary will not be considered, which will increase the computational load. It is strongly recommended to set boundaries.
The maximum boundary value of the collective variable. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable maximums. If there is no default value, the boundary will not be considered, which will increase the computational load. It is strongly recommended to set boundaries.
The window size of the collective variable. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable window sizes, default is 1/5 of metad_width.
The number of windows for the collective variable. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable bin counts, default is 150. The product of CV Space and CV Bin equals the difference between CV Max and CV Min. Therefore, when both CV Space and CV Bin are set, the one with the highest corresponding window count will prevail.
Whether to consider applying an adaptive deposition function, geom or diff, default is not filled, which means adaptive deposition is not considered.
The minimum width or standard deviation of the applied adaptive Gaussian function. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable minimums, default is 0.
The maximum width or standard deviation of the applied adaptive Gaussian function. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable maximums, default is 0.
Whether to consider reweighting to obtain the reweighting factor for normalization of the bias potential, yes or no, default is no, which means reweighting is not considered. Reweighting is generally considered only after the system has converged.
The number of Gaussian functions applied when calculating the reweighting factor, default is 50.
The number of windows for the collective variable when calculating the reweighting factor, which cannot be less than the value of CV Bin. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable bin counts, default is equal to CV Bin.
Whether to consider simulated annealing in the Metadynamics simulation, yes or no.
The base temperature corresponding to the simulated annealing Metadynamics simulation, default is 300K.
The bias factor corresponding to the simulated annealing Metadynamics simulation, which equals (T + deltaT) / T, default is 1, meaning no bias simulation is performed. If a bias simulation is performed, the bias factor should be greater than 1.
The height of the deposited Gaussian function applied during the simulated annealing Metadynamics simulation, Height = kb * DeltaT * Frequency * TimeStep / TAU, default is 0, meaning the set deposition function height is used directly.
The specified output step length during the Metadynamics simulation, default is 100.
The output file name for the deposited Gaussian function during the Metadynamics simulation.
The output file name for the collective variable during the Metadynamics simulation.
The output file name for the CV Group during the Metadynamics simulation, which contains all the atom groups of the CV Group for the next step’s Metadynamics input file.
The output file name for the parameters during the Metadynamics simulation, which contains the parameters required for calculations for the next step’s Metadynamics input file.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| HILLS.dat | Output of the deposited Gaussian function specified during the Metadynamics simulation |
| COLVAR.dat | Output of the collective variable specified during the Metadynamics simulation |
| PLUMED.ndx | NDX file specifying the atom groups that make up the collective variable |
| PLUMED.dat | Parameter file required for the next step of Metadynamics calculation |
The two generated files above will serve as input files for the next step of the Metadynamics simulation.
Free Energy Surface Analysis模块是对基于PLUMED元动力学模拟后得到的模拟结果进行自由能计算。
基于PLUMED元动力学模拟后输出的沉积高斯函数文件,默认为HILLS.dat文件。
对沉积高斯函数文件进行自由能计算时是否考虑直方图分布方法,yes或者no,默认no。
当考虑直方图分布方法时高斯函数的宽度值,有多个集合变量(即CV)时用"//"进行分割,比如0.35//0.35。只有当Histogram值为no时Sigma参数才会生效,当有多个CV而只设置了一个宽度值时,则表示该宽度值适用于所有CV。默认0.05。
CV名称,对沉积高斯函数文件进行自由能计算时只考虑该指定的CV。当不指定CV时则考虑沉积高斯函数文件中包含的所有CV,当指定CV时则不能考虑直方图分布方法。
集合变量的边界最小值,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,比如0.1//0.3,强烈建议设置边界。当有多个CV而只设置了一个边界最小值时,则表示该最小值适用于所有CV。
集合变量的边界最大值,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,比如0.1//0.3,强烈建议设置边界。当有多个CV而只设置了一个边界最大值时,则表示该最大值适用于所有CV。
集合变量的窗口大小,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,比如0.1//0.3。仅当设置了CV Min和CV Max值时,Grid Size才会生效。当有多个CV而只设置了一个窗口大小值时,则表示该窗口大小值适用于所有CV。
集合变量的窗口数量,有多个集合变量时用"//"进行分割,比如150//300。仅当设置了CV Min和CV Max值时,Bin才会生效。当有多个CV而只设置了一个窗口数量值时,则表示该窗口数量值适用于所有CV。Grid Size和Bin相乘等于CV Max和CV Min的差值,因此当Grid Size和Bin同时设置时以对应窗口数最多的为准。
温度,对沉积高斯函数文件进行自由能计算时使用的温度值,默认300K
是否对输出的自由能数据进行归零处理,即将自由能数据进行相对移动以保证最小值移动到0的位置,yes或者no,默认no。
沉积高斯函数的数量,在对沉积高斯函数文件进行自由能计算时,每隔该指定的沉积高斯函数的数量进行一次自由能计算。当不设置该数量值时表示对所有的沉积高斯函数在整体上只进行一次自由能计算。
输出结果文件,文件中包含随CV变化的自由能数据,默认为FES.csv文件。当指定了Stride值时,默认文件为FES.dat.tar.gz。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| FES.csv | 随CV变化的自由能数据文件 |
| FES.dat.tar.gz | 随CV变化的自由能数据压缩文件 |
The Free Energy Surface Analysis module is used to to calculate the free energy based on the simulation results outputed from the metadynamics simulations.
The deposited Gaussian function file outputed from the metadymamics simulations. Default “HILLS.dat”.
Whether considers the Historgram method when calculates the free energy based on the deposited Gaussian function file. “yes” or “no”, default “no”.
Width of Gaussian Function used by the Historgram method, if there are multiple CVs, you can separated them by “//”, such as 0.35//0.35. Only effective when Historgram method is used. When there are multiple CVs and only one width value is set, it means that the width value will be applied to all CVs. Default 0.05.
The specified CV considered in the free energy calculation based on the deposited Gaussian function file. When CV is not specified, all CVs contained in the deposited Gaussian function file will be considered, and when CV is specified, histogram distribution methods cannot be considered.
The minimum boundary value of the collective variable. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable minimums, such as 0.1//0.3. It is strongly recommended to set boundaries. When there are multiple CVs and only one minimum value is set, it means that the minimum value will be applied to all CVs.
The maximum boundary value of the collective variable. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable maximums, such as 0.1//0.3. It is strongly recommended to set boundaries. When there are multiple CVs and only one maximum value is set, it means that the maximum value will be applied to all CVs.
The window size of the collective variable. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable window sizes, such as 0.1//0.3. Only effective when CV Min and CV Max values are set. When there are multiple CVs and only one window size value is set, it means that the window size value will be applied to all CVs.
The window number of the collective variable. Use “//” to separate multiple collective variable bin counts, such as 150//300. Only effective when CV Min and CV Max values are set. When there are multiple CVs and only one window number value is set, it means that the window number value will be applied to all CVs.The product of Grid Size and Bin equals the difference between CV Max and CV Min. Therefore, when both CV Space and CV Bin are set, the one with the highest corresponding window count will prevail.
The temperature value used in the free energy calculation based on the deposited Gaussian function file. Default 300K.
Whether mintozeros the obatined free energy data calculated based on the deposited Gaussian function file. “yes” or “no”, default “no”.
Specified number of the deposition Gauss function. When calculates the free energy based on the deposition Gauss function file, the free energy will be calculated every specified number of the deposition Gauss function. When this stride value is not set, it means that only one free energy calculation is performed for all deposition Gaussian functions as a whole.
The specified output file. The output file contains free energy data that varies with CV. Default FES.csv file. When the Stride value is specified, default FES.dat.tar.gz file.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| FES.csv | output file that contains free energy data that varies with CV |
| FES.dat.tar.gz | output tar.gz file that contains free energy data that varies with CV |
MD Clustering是对动力学轨迹进行归簇分析。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
聚类时结构的RMSD截断值(nm)
聚类算法:linkage, jarvis-patrick, monte-carlo, diagonalization, gromos, 默认使用gromos算法。
选择需要计算的结构组别:Backbone,Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| clusters.pdb | 差异较大的每个簇的代表性结构 |
| clust-size.xvg | 各个簇的帧数 |
| clust-size.xvg | 各个簇和轨迹帧号的对应关系 |
MD Clustering is a clustering analysis of molecular dynamics trajectories.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
RMSD cutoff value for clustering (in nm).
Clustering algorithm: linkage, jarvis-patrick, monte-carlo, diagonalization, gromos. The default method is gromos.
Select the structural group for calculation: Backbone, Protein, DNA, RNA. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| clusters.pdb | Representative structures of each cluster with significant differences |
| clust-size.xvg | Number of frames in each cluster |
| clust-size.xvg | Correspondence between clusters and trajectory frame numbers |
MD Hbond模板对于指定组别之间的氢键分析。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的氢键组别1:Protein,DNA,RNA。如果两个组相同则分析的是组内氢键。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
选择需要计算的氢键组别2:Protein,DNA,RNA。如果两个组相同则分析的是组内氢键。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的组1残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的组1原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的组2残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的组2原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hbnum.csv | 氢键分析CSV文件 |
| hbnum.xvg | 氢键分析XVG文件 |
| hbnum.png | 氢键分析PNG文件 |
其中hbnum.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | 时间 |
| Hydrogen bonds | 氢键数目 |
| Pairs within 0.35 nm | 两个组相距0.35nm内的接触的原子数目 |
MD Hbond template is used for analyzing hydrogen bonds between specified groups.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the hydrogen bond group 1 for calculation: Protein, DNA, RNA. If both groups are the same, it analyzes intra-group hydrogen bonds. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Select the hydrogen bond group 2 for calculation: Protein, DNA, RNA. If both groups are the same, it analyzes intra-group hydrogen bonds. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for group 1 calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for group 1 calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom residue numbers for group 2 calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for group 2 calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| hbnum.csv | Hydrogen bond analysis CSV file |
| hbnum.xvg | Hydrogen bond analysis XVG file |
| hbnum.png | Hydrogen bond analysis PNG file |
The hbnum.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | Time |
| Hydrogen bonds | Number of hydrogen bonds |
| Pairs within 0.35 nm | Number of atoms in contact within 0.35 nm between the two groups |

可根据起始帧数、结束帧数以及间隔帧数对平衡模拟进行轨迹提取,从而将其转换为GRO或者PDB轨迹文件。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run模块或者AlphaAutoMD模块中获取。
文件输出类型:GRO或者PDB。
输出文件是否保留水盒子。
起始位置(单位ps)。
结束位置(单位ps)。
间隔时间,单位ps。
索引文件,ndx格式。对于膜体系的轨迹提取是必填项。
是否保留体系中的溶剂(Water以及Ion):不保留(none),都保留(all),指定保留溶剂范围(specify)。
指定需要保留的特殊组别如:水(Water),离子(Ion);或者指定保留组别的范围,规定格式为:需要保留的溶剂组别(Water或者Ion):限定距离(单位Å):目标组别,中间使用冒号(:)进行分隔,例如Water:3:ligand。
注:组别名称可以通过MD Solvation模块的index文件查询;若目标组别是小分子,可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称,多个小分子可填写ligand表示。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| md_finally.pdb | 最后一帧结构文件 |
| md_center.pdb/.gro | PDB/GRO格式轨迹文件 |
The MD Trajectory module allows for the extraction of trajectories from equilibrium simulations based on the starting frame number, ending frame number, and frame interval, converting them into GRO or PDB trajectory files.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run module or the AlphaAutoMD module.
File output type: GRO or PDB.
Whether to retain the water box in the output files.
Starting time (in ps).
Ending time (in ps).
Time interval, in ps.
Index file in ndx format. This is a required parameter for extracting trajectories in membrane systems.
Whether to retain the solvents in the system (Water and Ion) : none (none), all (all), specify the solvent range (specify).
Specify special groups to be retained: Water, Ion; Or specify the range of reserved groups in the format: solvent group to be retained (Water or Ion) : limit distance (unit Å) : target group, separated by a colon (:), e.g., Water:3:ligand.
Note: The group name can be queried through the index file of the MD Solvation module. If the target group is a small molecule, the group name can be filled in according to the name of small molecule in PDB, and the ligand representation can be filled in for multiple small molecules.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| md_finally.pdb | Structure file of the final frame |
| md_center.pdb | PDB format trajectory file |
| md_center.gro | GRO format trajectory file |
MD Gyration回旋半径分析,可用来衡量体系模拟时的质权平均半径。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的结构组别:Backbone,Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
索引文件,格式为ndx
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| gyrate.csv | 回转半径CSV文件 |
| gyrate.xvg | 回转半径XVG文件 |
| gyrate.png | 回转半径PNG文件 |
其中gyrate.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Time (ps) | 时间 |
| Rg | 回旋半径 |
| Rg(X) | 绕着x轴的回旋半径 |
| Rg(Y) | 绕着y轴的回旋半径 |
| Rg(Z) | 绕着z轴的回旋半径 |
MD Gyration is a radius of gyration analysis used to measure the mass-weighted average radius of a system during simulation.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the structural group for calculation: Backbone, Protein, DNA, RNA. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
Index file in ndx format.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| gyrate.csv | Gyration radius CSV file |
| gyrate.xvg | Gyration radius XVG file |
| gyrate.png | Gyration radius PNG file |
The gyrate.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Time (ps) | Time |
| Rg | Radius of gyration |
| Rg(X) | Radius of gyration around the x-axis |
| Rg(Y) | Radius of gyration around the y-axis |
| Rg(Z) | Radius of gyration around the z-axis |
MD SASA模块是计算指定组别的溶剂可及表面积(solvent accessible surface area,SASA)。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的结构组别:Backbone,Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
索引文件,格式为ndx
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| area.csv | 溶剂可及表面积CSV文件 |
| area.xvg | 溶剂可及表面积XVG文件 |
| area.png | 溶剂可及表面积PNG文件 |
其中area.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | 时间 |
| Total Area (nm^2) | 溶剂可及表面积 |
| Hydrophobic (nm^2) | 疏水表面积 |
| Hydrophilic (nm^2) | 亲水表面积 |
The MD SASA module calculates the solvent accessible surface area (SASA) of specified groups.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the structural group for calculation: Backbone, Protein, DNA, RNA. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
Index file in ndx format.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| area.csv | Solvent accessible surface area CSV file |
| area.xvg | Solvent accessible surface area XVG file |
| area.png | Solvent accessible surface area PNG file |
The area.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | Time |
| Total Area (nm^2) | Total solvent accessible surface area |
| Hydrophobic (nm^2) | Hydrophobic surface area |
| Hydrophilic (nm^2) | Hydrophilic surface area |
MD Distance是针对分子动力学轨迹的距离分析模块,输出两个组之间距离 (质心距离或几何中心距离) 随时间的变化情况。自定义组别时需要注意,如果只需测量两个原子之间的距离则填写Custom Atom1和Custom Atom2即可;当同时填写Custom Resid1和Custom Atom1时,组别1的原子数是Custom Atom1与Custom Resid1交集的原子。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的组别1:Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
选择需要计算的组别1:Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的组1残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。自定义组别之间是并集。
自定义需要计算的组1原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续原子用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。自定义组别之间是并集。
自定义需要计算的组2残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。自定义组别之间是并集。
自定义需要计算的组2原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续原子用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。自定义组别之间是并集。
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| dist.csv | 距离分析CSV文件 |
| dist.xvg | 距离分析XVG文件 |
| dist.png | 距离分析PNG文件 |
其中dist.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | 时间 |
| Distance (nm) | 组别之间的距离 |
MD Distance is a distance analysis module for molecular dynamics trajectories, providing the variation of distance (center-of-mass distance or geometric center distance) between two groups over time. When defining custom groups, it is important to note that if you only need to measure the distance between two atoms, you can fill in Custom Atom1 and Custom Atom2. When both Custom Resid1 and Custom Atom1 are filled in, the number of atoms in group 1 is the intersection of Custom Atom1 and Custom Resid1.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, available in the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the group 1 for calculation: Protein, DNA, RNA.
You can enter the group name based on the name of the small molecule in the PDB.
Select the group 2 for calculation: Protein, DNA, RNA.
You can enter the group name based on the name of the small molecule in the PDB.
Custom residue numbers for group 1 that need to be calculated. Use “-” for continuous parameters and separate non-continuous residues with commas, for example: 1-10,15. Custom groups are unions of specified residues.
Custom atom numbers for group 1 that need to be calculated. Use “-” for continuous parameters and separate non-continuous atoms with commas, for example: 1-10,15. Custom groups are unions of specified atoms.
Custom residue numbers for group 2 that need to be calculated. Use “-” for continuous parameters and separate non-continuous residues with commas, for example: 1-10,15. Custom groups are unions of specified residues.
Custom atom numbers for group 2 that need to be calculated. Use “-” for continuous parameters and separate non-continuous atoms with commas, for example: 1-10,15. Custom groups are unions of specified atoms.
Time interval for each frame (in ns).
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| dist.csv | Distance analysis CSV file |
| dist.xvg | Distance analysis XVG file |
| dist.png | Distance analysis PNG file |
The dist.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | Time |
| Distance (nm) | Distance between the groups |

MMPBSA计算受体与配体之间的结合自由能,并且提供能量分解数据、结合常数(Ka)、抑制剂常数(Ki)。熵的计算采用的是张增辉教授的相互作用熵的方法,该方法直接从分子动力学模拟计算结合自由能的熵组分(相互作用熵或-TΔS),但是需要选取结构稳定部分进行计算。
本模块提供四种计算方法,其中 Trajectory 是针对进行分子动力学模拟轨迹后计算其受配体之间的结合自由能;One Structure 是针对一帧pdb结构或者对接得到的PDB结构计算受配体之间的结合自由能,MMPBSA of One Structure 计算流程中可以直接输入PDB进行计算。
Index Name 是输入受配体组别名称;Custom Name 则是输入受配体的在PDB中的残基编号。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD模块中获取。
受体名称,可以为Protein、DNA、RNA。
配体名称,可以为Protein、DNA、RNA。如果为小分子,填写其在PDB中的名称。如果体系中除了蛋白以外为配体(包括小分子)可用Other表示。
起始帧时间,单位ps。最好选取RMSD稳定时区进行计算,以消除结构不稳定时导致的整体熵偏大。
结束帧时间,单位ps。最好选取RMSD稳定时区进行计算,以消除结构不稳定时导致的整体熵偏大。
间隔时间,单位ps。
索引文件,ndx格式。当体系中存在膜结构的时候可以通过Membrane Solvation模块获取index.ndx文件。膜模拟中的受体为receptor,配体为ligand,膜为membrane。
定义受体组别进行结合能计算。组别中填写的为蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基的序号。例如1-213或者1-211,212-213。蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基序号从1开始重新编号,与初始pdb氨基酸编号无关。
定义配体组别进行结合能计算。组别中填写的为蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基的序号。例如1-213或者1-211,212-213。蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基序号从1开始重新编号,与初始pdb氨基酸编号无关。
拓扑文件,由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
结构文件,.gro格式,由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
体系参数压缩文件,tar.gz格式。由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA_result.txt | MMPBSA结果汇总文件。 |
| MMPBSA_Residue.csv | 能量分解数据CSV文件。 |
| MMPBSA.pdb | 原子对应的MMPBSA能量放到PDB文件。可以做对应能量类别的表面图,从图的颜色深浅可以看出哪些区域对结合能贡献值较大。 |
| MMPBSA.tar.gz | MMPBSA所有原始文件。包括_mmpbsa_residue_#.txt是每个残基对应的每个能量类别的数值,共包含7个能量类别:范德华能(VDW)、静电能(ELE)、溶剂化能极性部分(PB)、溶剂化能非极性部分(SA)、VDW+ELE=MM、PB+SA=PBSA、MM+PBSA=Binding/MMPBSA。_mmpbsa_residue.txt是对上述7个文件的总结,即为MMPBSA_Residue.csv对应的原始文件。_mmpbsa_atom#.pdb是将每个原子对应的能量类别放到pdb文件,与MMPBSA.pdb相似。 |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Duan L, Liu X, Zhang JZ. Interaction Entropy: A New Paradigm for Highly Efficient and Reliable Computation of Protein-Ligand Binding Free Energy. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 May 4;138(17):5722-8.
https://github.com/Electrostatics/apbs/blob/main/docs/index.rst
MMPBSA calculates the binding free energy between a receptor and a ligand, providing energy decomposition data, binding constants (Ka), and inhibitor constants (Ki). The entropy calculation uses the method of interaction entropy proposed by Professor Zhang Zenghui, which directly calculates the entropy component of the binding free energy (interaction entropy or -TΔS) from molecular dynamics simulations, but requires selecting stable structural regions for calculation. This module provides four calculation methods. Among them, Trajectory calculates the binding free energy between the receptor and ligand after molecular dynamics simulation trajectories; One Structure calculates the binding free energy between the receptor and ligand for a single frame PDB structure or a docked PDB structure; MMPBSA of One Structure allows direct input of a PDB for calculation. Index Name is the input receptor-ligand group name, while Custom Name is the input residue numbers of the receptor-ligand in the PDB.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, available in the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or AlphaAutoMD module.
Name of the receptor, can be Protein, DNA, or RNA.
Name of the ligand, can be Protein, DNA, or RNA. If it is a small molecule, enter its name in the PDB. Use ‘Other’ if the system contains a ligand (including small molecules) other than proteins.
Start frame time in ps. It is best to select a stable RMSD region for calculation to eliminate large overall entropy caused by structural instability.
End frame time in ps. It is best to select a stable RMSD region for calculation to eliminate large overall entropy caused by structural instability.
Time interval in ps.
Index file in ndx format. When there is a membrane structure in the system, you can obtain the index.ndx file through the Membrane Solvation module. In membrane simulations, the receptor is ‘receptor’, the ligand is ‘ligand’, and the membrane is ‘membrane’.
Define receptor groups for binding energy calculation. Enter the sequence numbers of protein amino acids or nucleic acid bases in the group. For example, 1-213 or 1-211,212-213. Protein amino acid or nucleic acid base numbers start from 1 and are independent of the initial pdb amino acid numbering.
Define ligand groups for binding energy calculation. Enter the sequence numbers of protein amino acids or nucleic acid bases in the group. For example, 1-213 or 1-211,212-213. Protein amino acid or nucleic acid base numbers start from 1 and are independent of the initial pdb amino acid numbering.
Topology file obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
Structure file in .gro format obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
System parameter compression file in tar.gz format. Obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA_result.txt | Summary file of MMPBSA results. |
| MMPBSA_Residue.csv | Energy decomposition data in CSV format. |
| MMPBSA.pdb | MMPBSA energy corresponding to atoms in a PDB file. This can be used to create a surface map of energy categories, where the color depth indicates the regions contributing significantly to the binding energy. |
| MMPBSA.tar.gz | All original MMPBSA files. Includes mmpbsa_residue#.txt which contains the values of each energy category for each residue, totaling 7 energy categories: van der Waals energy (VDW), electrostatic energy (ELE), polar part of solvation energy (PB), nonpolar part of solvation energy (SA), VDW+ELE=MM, PB+SA=PBSA, MM+PBSA=Binding/MMPBSA. _mmpbsa_residue.txt is a summary of the above 7 files, corresponding to the original file MMPBSA_Residue.csv. _mmpbsa_atom#.pdb assigns the energy categories to each atom in a pdb file, similar to MMPBSA.pdb. |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Duan L, Liu X, Zhang JZ. Interaction Entropy: A New Paradigm for Highly Efficient and Reliable Computation of Protein-Ligand Binding Free Energy. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 May 4;138(17):5722-8.
https://github.com/Electrostatics/apbs/blob/main/docs/index.rst
通过计算平衡模拟轨迹的均方根偏差(RMSD,Root Mean Square Deviation)和均方根波动(RMSF,Root Mean Square Fluctuation),从而分析结构的稳定性和结构变化情况。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在**GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)**模块中获取。
选择分析类型:RMSD或者RMSF(可多选)。
选择需要计算的组别。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。
自定义需要计算的原子编号,用逗号隔开,例如:CA,O,H。与Custom Resid是交集关系。
索引文件,可由Membrane Solvation模块得到。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| rmsd_result.csv | 所选组别的RMSD的CSV文件 |
| rmsd_result.png | 所选组别的RMSD的PNG文件 |
| rmsd_result.xvg | 所选组别的RMSD的XVG文件 |
| rmsf_*.csv | 所选组别的RMSF的CSV文件 |
| rmsf_*.png | 所选组别的RMSF的PNG文件 |
| rmsf_*xvg. | 所选组别的RMSF的XVG文件 |
| bfac.pdb | PDB中的B-Factor一列为原子RMSF值。RMSF值通过公式<Δr^2>=3B/(8π^2)转换为b-factor值。 |
By calculating the Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) and Root Mean Square Fluctuation (RMSF) of equilibrium simulation trajectories, the stability and structural changes of the system can be analyzed.
The path file obtained after MD simulation, which can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the type of analysis: RMSD or RMSF (multiple selections possible).
Select the group to be calculated.
Custom residue numbers to be calculated, continuous parameters can be represented by “-”, non-continuous residues are separated by commas, for example: 1-10,15.
Custom atom numbers to be calculated, separated by commas, for example: CA, O, H. This intersects with Custom Resid.
Index file obtained from the Membrane Solvation module.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| rmsd_result.csv | CSV file of RMSD for the selected group |
| rmsd_result.png | PNG file of RMSD for the selected group |
| rmsd_result.xvg | XVG file of RMSD for the selected group |
| rmsf_*.csv | CSV file of RMSF for the selected group |
| rmsf_*.png | PNG file of RMSF for the selected group |
| rmsf_*xvg. | XVG file of RMSF for the selected group |
| bfac.pdb | The B-Factor column in the PDB file represents the atomic RMSF value. The RMSF values are converted to B-factor values by the formula <Δr^2>=3B/(8π^2). |
N个原子的柔性大体系如蛋白,其运动轨迹需要3N维笛卡尔坐标来描述,这样高维的数据很难理解和直观分析。MD PCA(Principal component analysis,PCA)模块可以从高维数据中分析出主要的影响因素 (本征向量) 。前几个本征向量(主成分,如前两个主成份则为 PC1,PC2) 一般可以描述分子运动的大部分信息。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的结构组别:Backbone,Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
索引文件,格式为ndx
得到结果文件,每种类型的文件如果包含PNG、CSV以及XVG后缀,相同名称只是表现形式不同,数据一样
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Gibbs_2d.png/Gibbs_3d.png | 只计算两个主成分时的二维和三维自由能景观图 |
| average.pdb | 计算后的平均结构文件 |
| eigenvalues.xvg/.png/.csv | 本征值文件 |
| filtered.pdb | 计算的降维过滤后的轨迹文件 |
| proj1.xvg/.png/.csv | 对应的主成分PC1文件 |
| proj2.xvg/.png/.csv | 对应的主成分PC2文件 |
| proj_all.xvg | 计算的PC1到PC2的主成份合并文件 |
For a large flexible system with N atoms such as a protein, its motion trajectory requires 3N-dimensional Cartesian coordinates to describe, making it difficult to understand and analyze high-dimensional data. The MD PCA (Principal Component Analysis, PCA) module can analyze the main influencing factors (eigenvectors) from high-dimensional data. The first few eigenvectors (principal components, such as the first two principal components PC1, PC2) can generally describe most of the information about molecular motion.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the structural group for calculation: Backbone, Protein, DNA, RNA. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
Index file in ndx format.
Obtain the following result files. If the files have PNG, CSV, and XVG suffixes, they contain the same data but in different formats.
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Gibbs_2d.png/Gibbs_3d.png | 2D and 3D free energy landscape plots when only two principal components are considered |
| average.pdb | Computed average structure file |
| eigenvalues.xvg/.png/.csv | Eigenvalues file |
| filtered.pdb | Filtered trajectory file after dimensionality reduction |
| proj1.xvg/.png/.csv | Corresponding principal component PC1 file |
| proj2.xvg/.png/.csv | Corresponding principal component PC2 file |
| proj_all.xvg | Combined file of principal components PC1 to PC2 |
提交GROMACS对应文件,从而进行分子动力学模拟,得到平衡模拟后得到的轨迹文件。
提交模拟体系的gro文件。该文件可以从MD Solvation或者Membrane Solvation模块获取。
提交模拟体系的top文件。该文件可以从MD Solvation或者Membrane Solvation模块获取。
提交模拟体系的itp文件。该文件可以从MD Solvation或者Membrane Solvation模块获取。
提交进行最小化的参数化文件,文件格式为mdp。可以根据GMX MDP Generation模块的Minimization方法或者**GMX MDP Generation (Auto)**生成。
提交进行等压等温的参数化文件,文件格式为mdp。可以根据GMX MDP Generation模块的NPT方法或者**GMX MDP Generation (Auto)**生成。
提交进行平衡模拟的参数化文件,文件格式为mdp。可以根据GMX MDP Generation模块的MD方法或者**GMX MDP Generation (Auto)**生成。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| md.cpt | md模拟断点文件 |
| md.gro | md的分子坐标文件 |
| md.log | md记录文件 |
| md.tpr | md模拟所需的所有初始化数据(分子拓扑、初始结构等) |
| mini.gro | mini运行的分子坐标文件 |
| mini.log | mini运行记录文件 |
| mini.tpr | mini模拟运行所需的所有初始化数据(分子拓扑、初始结构等) |
| npt.gro | npt的分子坐标文件 |
| npt.log | npt记录文件 |
| npt.tpr | npt模拟所需的所有初始化数据(分子拓扑、初始结构等) |
| path.txt | 模拟轨迹文件存储路径,可用于后续分析模块的Path File输入。 |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Submit corresponding files to GROMACS to perform molecular dynamics simulations and obtain trajectory files after equilibrium simulations.
Submit the gro file of the simulated system. This file can be obtained from the MD Solvation or Membrane Solvation modules.
Submit the top file of the simulated system. This file can be obtained from the MD Solvation or Membrane Solvation modules.
Submit the itp file of the simulated system. This file can be obtained from the MD Solvation or Membrane Solvation modules.
Submit the script file for minimization, in mdp format. This file can be generated using the GMX MDP Generation module with the Minimization method or GMX MDP Generation (Auto).
Submit the script file for NPT (isothermal-isobaric) simulation, in mdp format. This file can be generated using the GMX MDP Generation module with the NPT method or GMX MDP Generation (Auto).
Submit the script file for equilibrium simulation, in mdp format. This file can be generated using the GMX MDP Generation module with the MD method or GMX MDP Generation (Auto).
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| md.cpt | Checkpoint file for the MD simulation |
| md.gro | Molecular coordinate file for the MD simulation |
| md.log | Log file for the MD simulation |
| md.tpr | All initial data required for the MD simulation (molecular topology, initial structure, etc.) |
| mini.gro | Molecular coordinate file for the minimization run |
| mini.log | Log file for the minimization run |
| mini.tpr | All initial data required for the minimization run (molecular topology, initial structure, etc.) |
| npt.gro | Molecular coordinate file for the NPT simulation |
| npt.log | Log file for the NPT simulation |
| npt.tpr | All initial data required for the NPT simulation (molecular topology, initial structure, etc.) |
| path.txt | Path to store the simulation trajectory files, which can be used as input for the Path File in subsequent analysis modules. |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.

Protenix (v0.5.0)是字节跳动公司AML AI4Science团队复现的pytorch版本的AlphaFold3模型。以下是ByteDance AML AI4Science团队的主要贡献概要:
- 模型性能:将Protenix与现有的模型进行了基准测试。Protenix在不同分子类型的结构预测中表现出强大的性能。作为一个完全开源的模型,它使研究人员能够生成新的预测并对模型进行微调,以满足特定的应用需求。
- 方法:在复现过程中,依据AF3的描述实现了Protenix,并优化了一些模糊步骤,纠正了排版错误,并根据模型行为进行了有针对性的调整。通过分享复现经验,希望支持社区在这些改进的基础上进一步推动该领域的发展。
- 可访问性:已将Protenix开源,提供了模型权重、推理代码和可训练代码供研究用途。
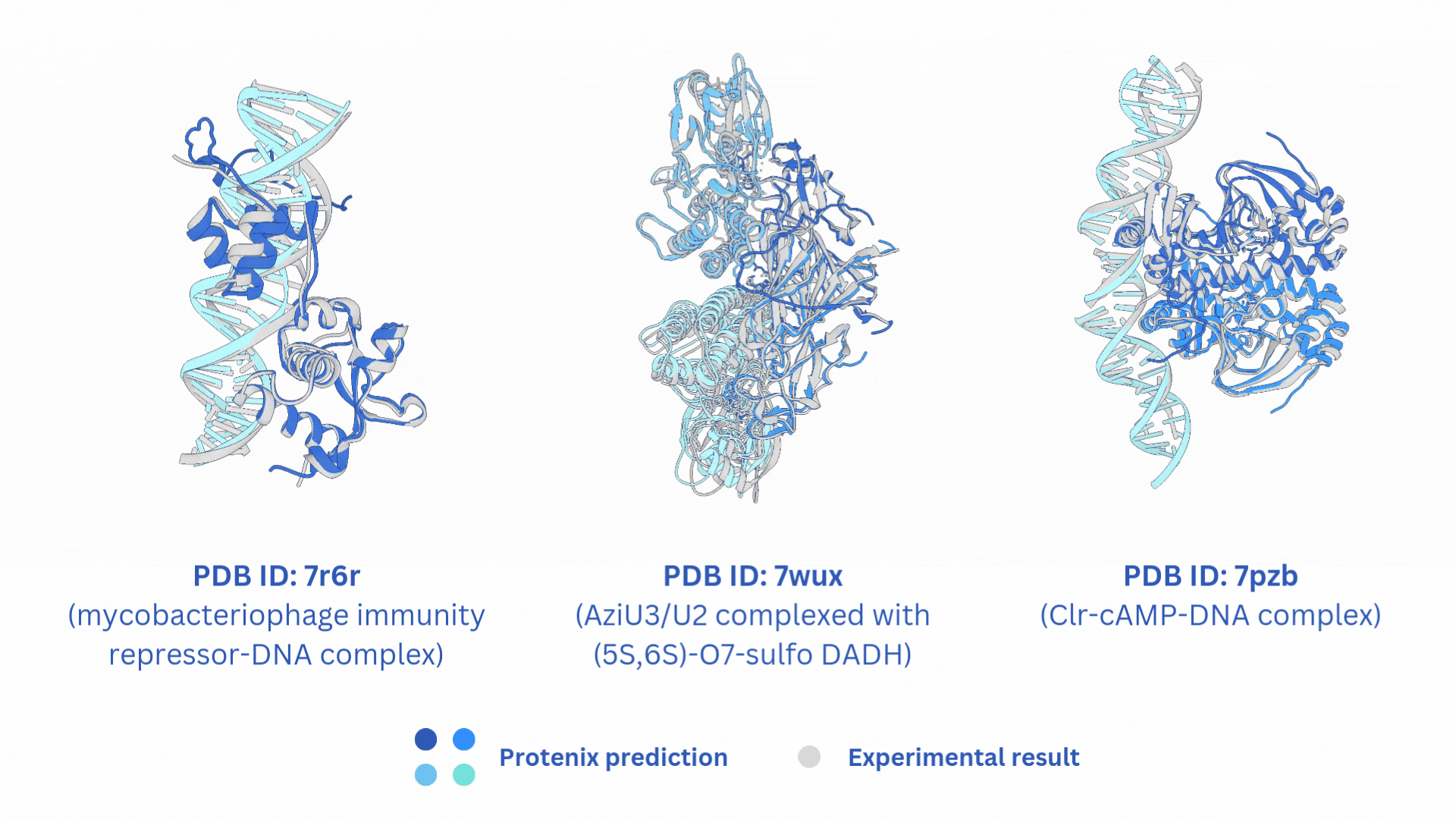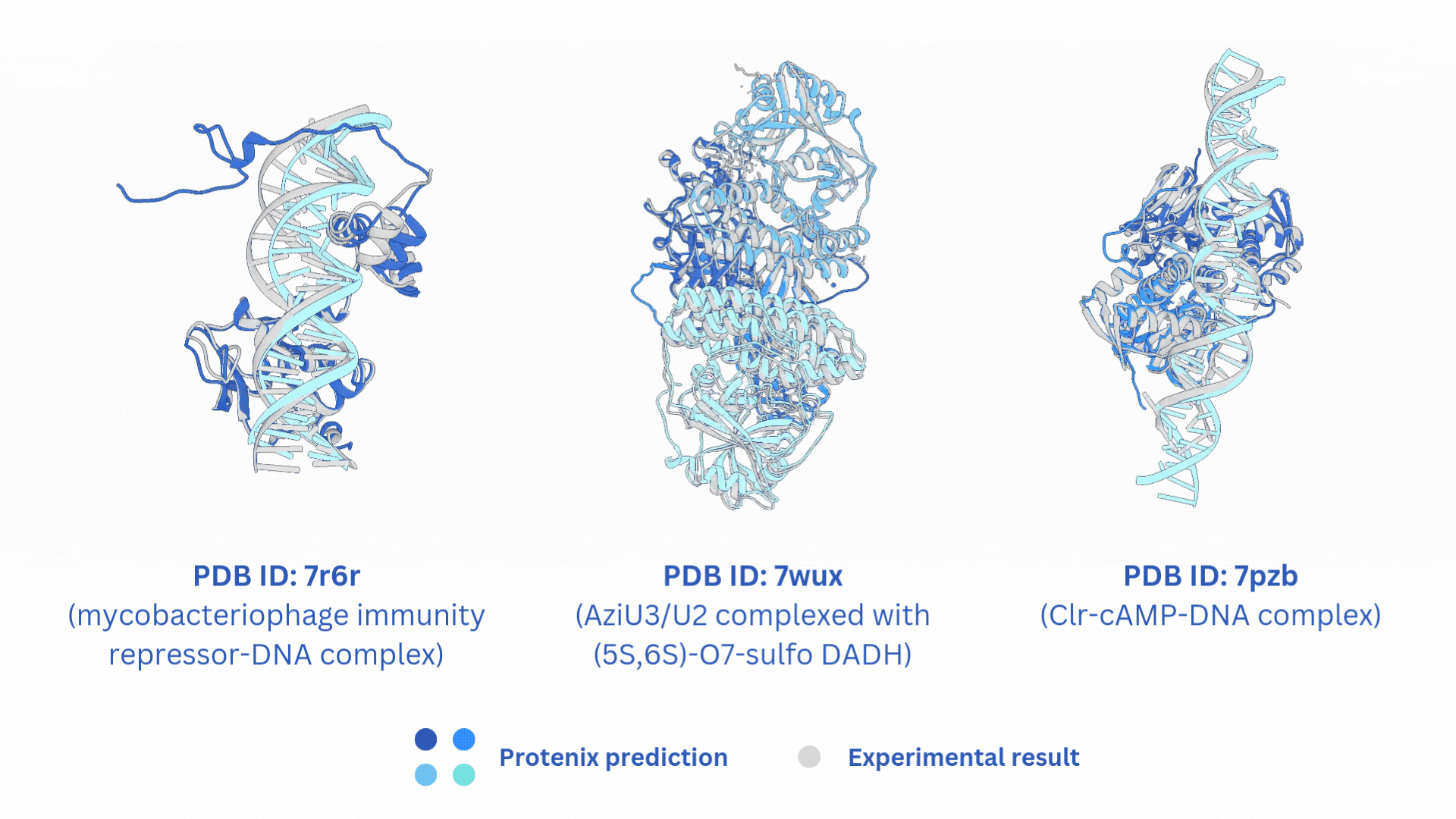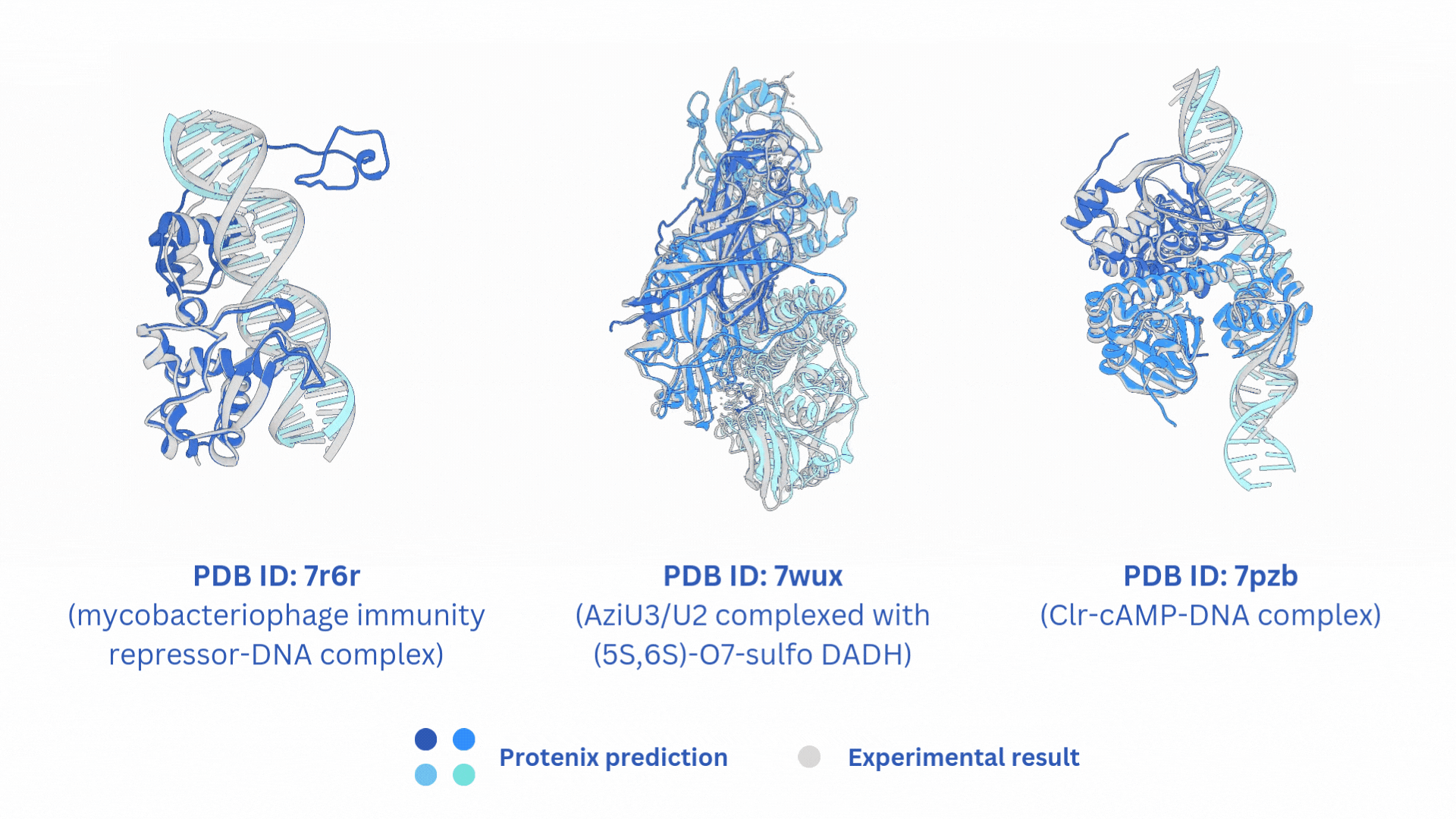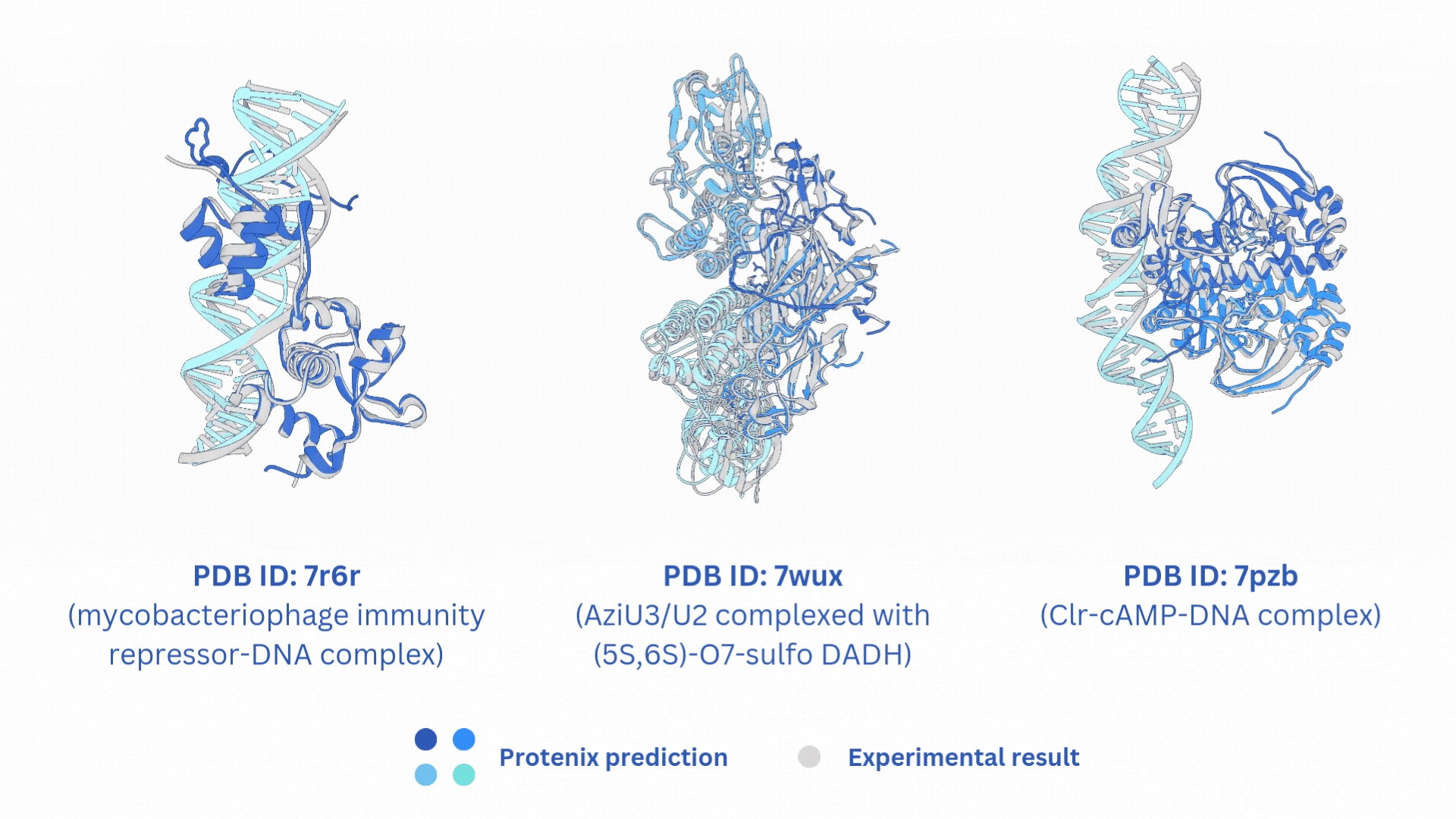
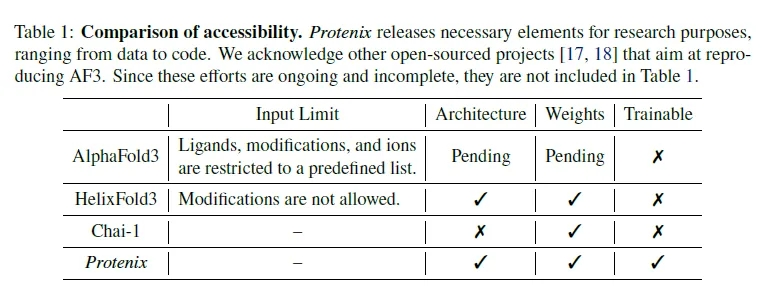

蛋白序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
注意:多蛋白复合物结构预测,其氨基酸序列输入格式如下:
>protein1
AASJ...
>protein2
AASJ...
>peptide
ASDF...
DNA序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
RNA序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
备注:当前支持计算的残基/碱基数量在1400个左右。
文本文件包含小分子信息,TXT格式。支持SMILES或 CCD Code(化学组分词典编号)。如果使用SMILES格式,每行应包含一个小分子;如果使用CCD Code,每行可以包含一个或多个小分子,使用逗号分隔,并加上CCD前缀。示例如下:
CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2
CCD,ATP,HY3,P1L
CCD,MG
注意:不适用于配体蛋白或多肽的氨基酸序列格式输入。
包含翻译后修饰(PTM)信息的文本文件,TXT格式。每行放置一个PTM信息,每个PTM信息由三部分组成:
1,HY3,1 表示第一条序列的第一个残基,发生了类型为HY3(CCD编号,为3-羟基脯氨酸,为脯氨酸的羟基化)的PTM1,HY3,1
1,P1L,5
2,HY3,3
共价键信息的文本文件,TXT格式。每行放置一个共价键信息,每个共价键信息包含两个原子信息,每个原子信息由三部分组成:
示例一:
当有2条蛋白序列,1条DNA序列,1条RNA序列,2个小分子时。对应的编号为:
第一条蛋白序列编号为1,第二条蛋白序列编号为2,DNA序列编号为3,RNA序列编号为4,第一个小分子对应的编号为5,第二个小分子对应的编号为6
示例二:
当有3条蛋白序列,2个小分子时。对应的编号为:
第一条蛋白序列编号为1,第二条蛋白序列编号为2,第二条蛋白序列编号为3,第一个小分子对应的编号为4,第二个小分子对应的编号为5
三部分由逗号分隔,例如:3,1,CA表示第三个实体(序列或小分子)中的第一个残基(或小分子)的CA原子
一个共价键是由两个原子信息组成,原子间用分号分隔,如:1,1,CA;2,1,CA
表示一个共价键,该共价键由两个原子组成,第一个原子为1,1,CA,第二个原子为2,1,CA
包含多个共价键信息的文件内容示例如下:
1,1,CA;2,1,CA
1,1,CA;3,1,CHA
离子名称,可以包含一个或多个离子,需写在一行文本中,不同的离子使用英文逗号分隔,支持输入离子数量,使用英文冒号分隔。示例如下:
MG:2,ZN,CU:3
表示2个MG离子,1个ZN离子,3个CU离子
输出结构的格式,支持PDB或CIF格式,默认为PDB格式。
该模式下,会默认使用1000个随机种子,每个随机种子进行5个结构采样,共进行5000个结构的大批量采样,并从中选择评分靠前的多个预测结构,最终获得更高精度的预测结构。该模式特别适用于抗原-抗体复合物结构的高精度预测,有研究表明该模式下抗体-抗原复合物结构预测准确性提升60%。该模式的输入参数与Single Mode一致,一次运行时间约10~20小时。
序列总长度不可超过1300。
输出结果文件为排名前5的复合物结构rank_1-5.cif和pred_scores_protenix.csv,csv中包含信息如下:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 复合物结构名称 |
| Ranking_Score | 对预测结构的质量排序的指标分数,值范围在-100至1.5之间,越大表示预测结构的质量越高。该分数综合考虑了四个指标:ptm, iptm, fraction_disordered,has_clash, 计算公式为: Ranking_Score = 0.8 × ipTM + 0.2 × pTM + 0.5 × disorder − 100 × has_clash 注意:结构为单体时,因为ipTM为0,整体的综合得分偏低,可参考pTM即可。 |
| pLDDT | 局部结构的可信度指标,值范围是0-100,该值越大说明预测的结构越可靠。低于70被认为可靠性较低,低于50基本认为是可信度非常低,为无序预测 |
| pTM | 预测的TM分数(the predicted template modeling score),衡量预测结构整体准确性,越大表示越准确,该分数大于0.5时,表示结构整体折叠可能与真实结构相似 |
| ipTM | 预测的亚基接触面的TM分数(the interface predicted template modeling score),当预测结构为复合物时才有该评价指标,衡量复合物中各个亚基之间相对位置的预测准确性,越大表示越准确,大于0.8表示高质量预测,小于0.6表示预测可能失败,0.6-0.8为灰色地带,预测正确与否不确定 |
https://github.com/bytedance/Protenix
Protenix (v0.5.0) is the PyTorch version of the AlphaFold3 model reproduced by the AML AI4Science team at ByteDance. Here is a summary of the main contributions from the ByteDance AML AI4Science team:
- Model Performance: Protenix has been benchmarked against existing models, demonstrating strong performance in structure prediction across different types of molecules. As a fully open-source model, it enables researchers to generate new predictions and fine-tune the model to meet specific application needs.
- Methodology: During the reproduction process, Protenix was implemented based on the description of AF3, optimizing some ambiguous steps, correcting typographical errors, and making targeted adjustments based on model behavior. By sharing our reproduction experience, we hope to support the community in further advancing the field based on these improvements.
- Accessibility: Protenix has been open-sourced, providing model weights, inference code, and training code for research purposes.
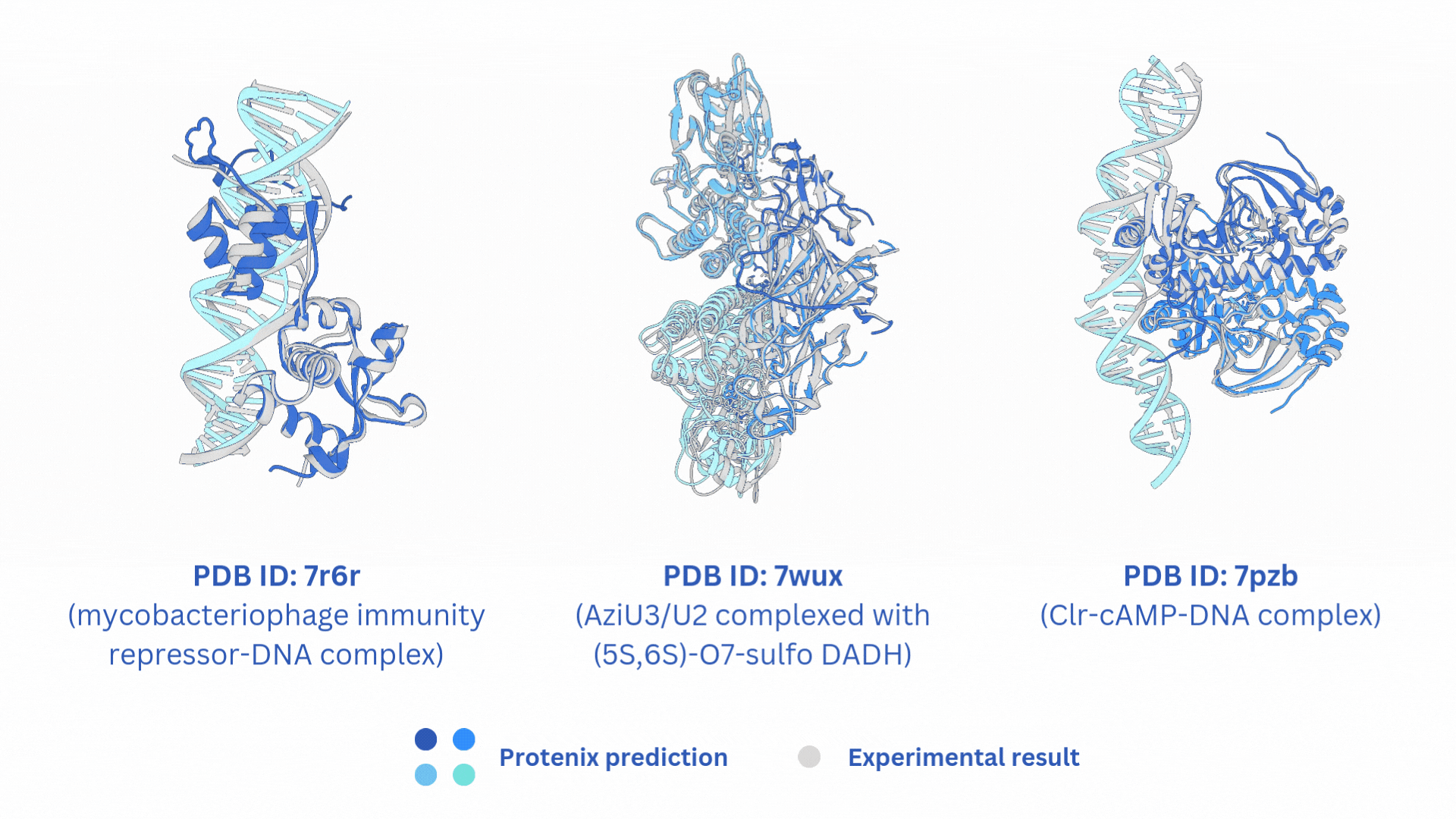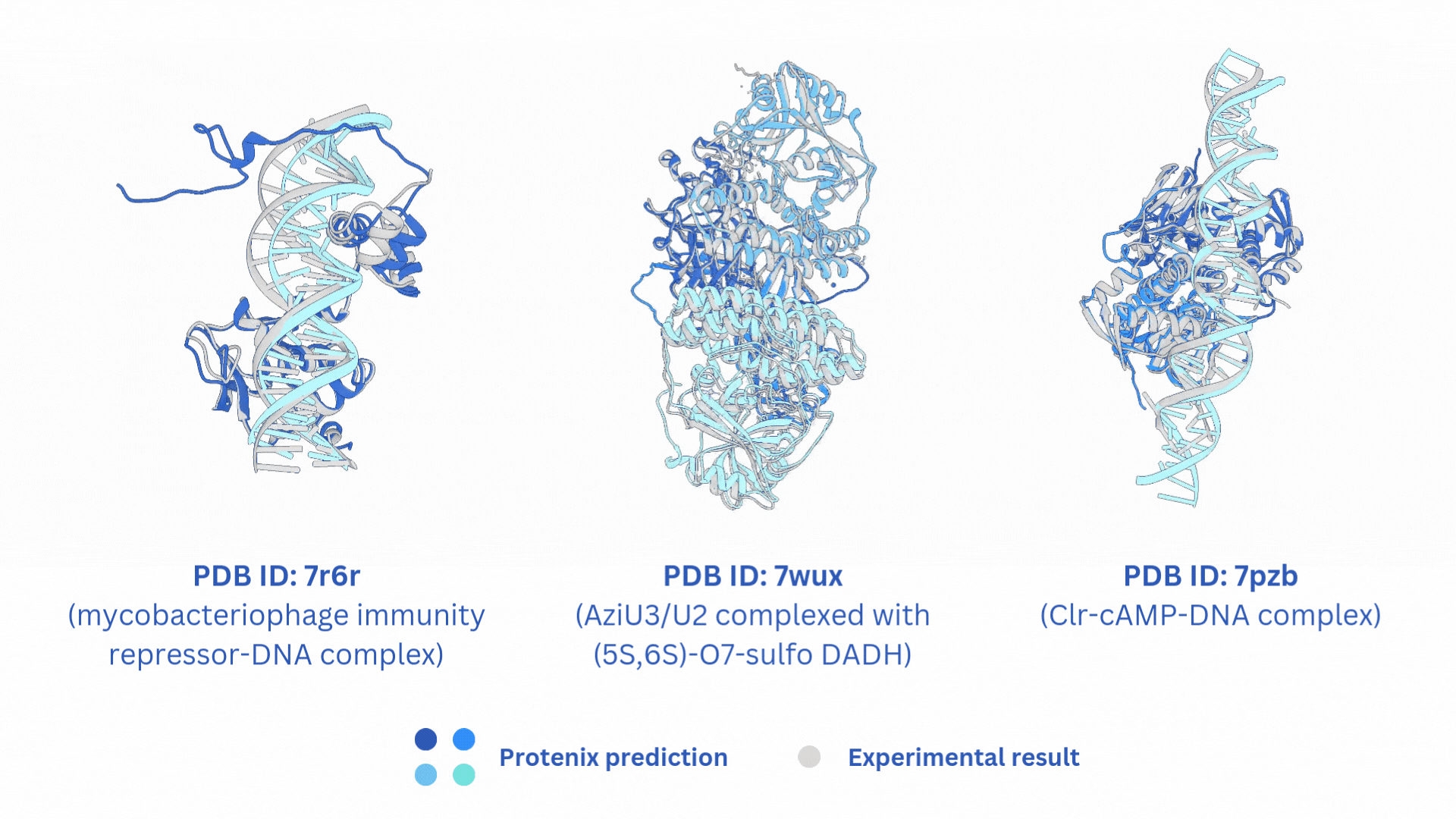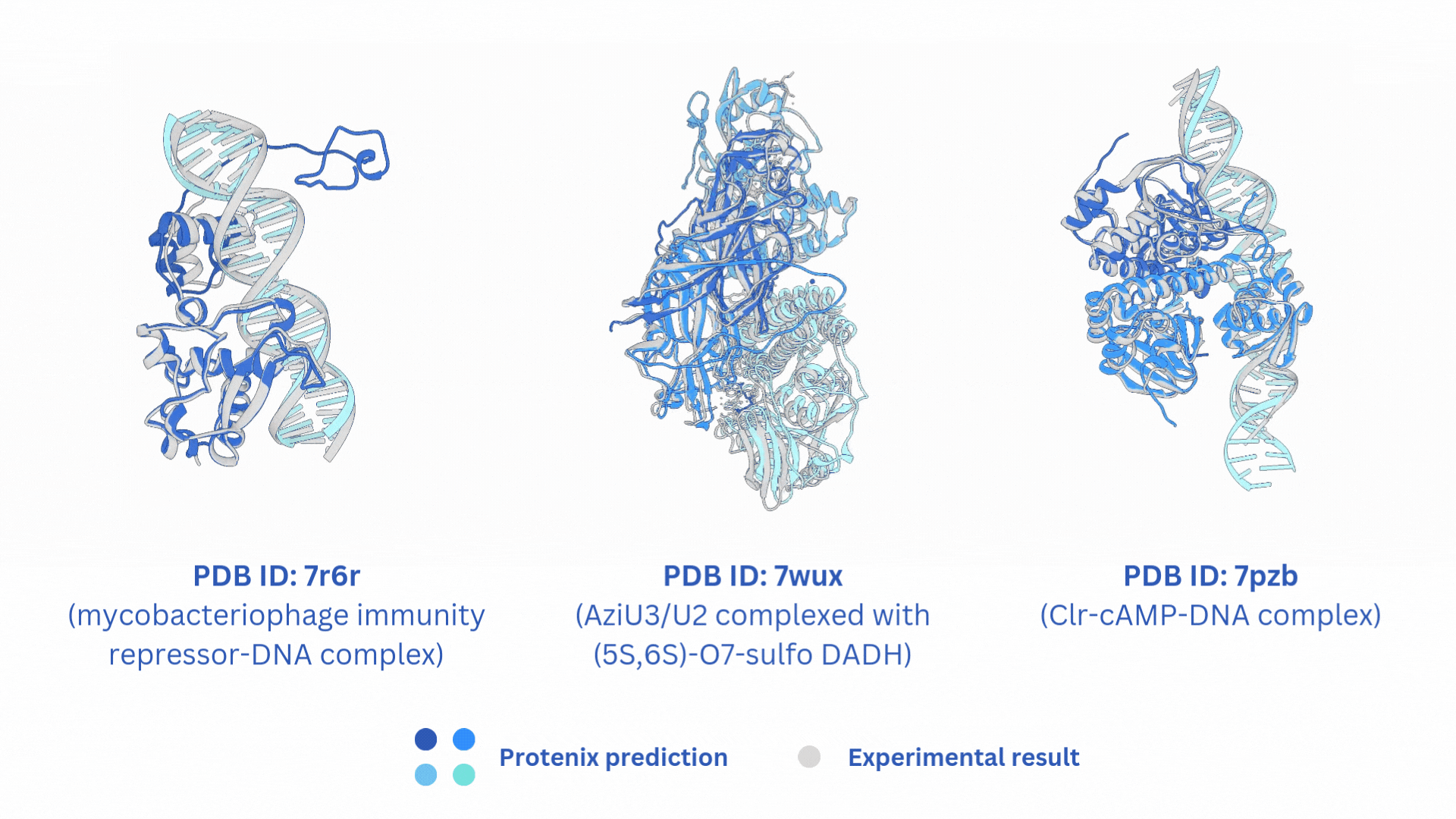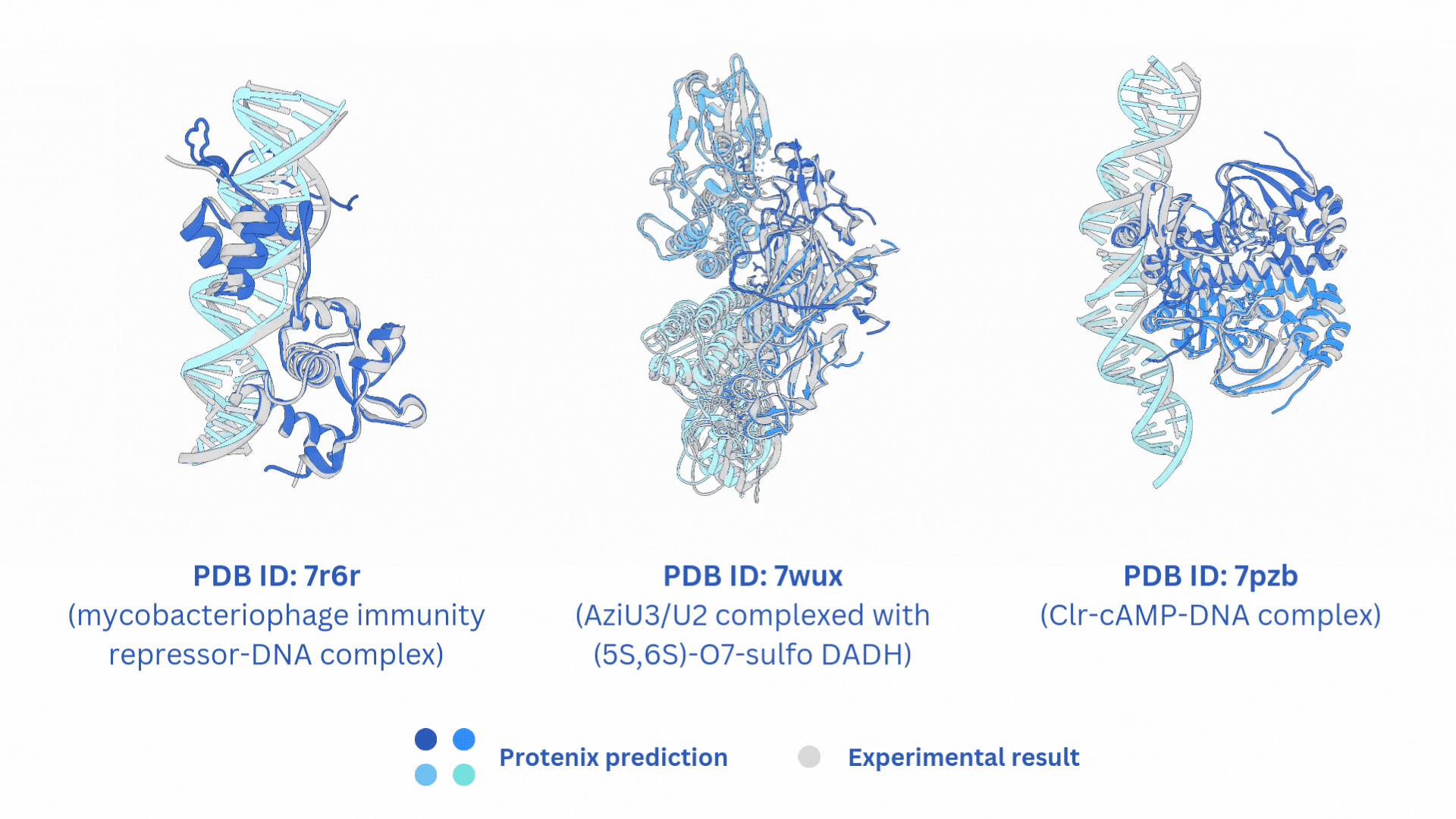


A sequence file for proteins in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
Note: For multi-protein complex structure prediction, the amino acid sequence input format is as follows:
>protein1
AASJ...
>protein2
AASJ...
>peptide
ASDF...
A sequence file for DNA nucleic acids in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
A sequence file for RNA nucleic acids in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
Note:The currently supported number of residues/bases for calculation is around 1,400.
A text file containing information about small molecules in TXT format. It supports SMILES or CCD Code (Chemical Component Dictionary number). If using the SMILES format, each line should contain one small molecule; if using CCD Code, each line can contain one or more small molecules, separated by commas, and prefixed with CCD. Examples are as follows:
CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2
CCD,ATP,HY3,P1L
CCD,MG
Note: Not applicable for amino acid sequence format input of ligand proteins or polypeptides.
An optional parameter that includes a text file with post-translational modification (PTM) information in TXT format. Each line contains one PTM entry, which consists of three parts:
1,HY3,1 indicates that a PTM of type HY3 (CCD number, which is 3-hydroxyproline, a hydroxylation of proline) occurs at the first residue of the first sequence.1,HY3,1
1,P1L,5
2,HY3,3
A text file containing covalent bond information in TXT format. Each line contains one covalent bond entry, which consists of two atom entries. Each atom entry consists of three parts:
Example 1:
When there are 2 protein sequences, 1 DNA sequence, 1 RNA sequence, and 2 small molecules, the corresponding numbers are as follows:
The first protein sequence is numbered 1, the second protein sequence is numbered 2, the DNA sequence is numbered 3, the RNA sequence is numbered 4, the first small molecule corresponds to the number 5, and the second small molecule corresponds to the number 6.
Example 2:
When there are 3 protein sequences and 2 small molecules, the corresponding numbers are as follows:
The first protein sequence is numbered 1, the second protein sequence is numbered 2, the third protein sequence is numbered 3, the first small molecule corresponds to the number 4, and the second small molecule corresponds to the number 5.
These three parts are separated by commas. For example, 3,1,CA indicates the CA atom of the first residue (or small molecule) in the third entity (sequence or small molecule).
A covalent bond is represented by two atom entries separated by a semicolon, such as: 1,1,CA;2,1,CA, indicating a covalent bond composed of two atoms, with the first atom being 1,1,CA and the second atom being 2,1,CA.
An example of a file containing multiple covalent bond entries is as follows:
1,1,CA;2,1,CA
1,1,CA;3,1,CHA
Ion names can include one or more ions, which should be written in a single line of text, with different ions separated by commas. It is also possible to specify the quantity of ions, using a colon to separate the ion name and its quantity. Examples are as follows:
MG:2,ZN,CU:3
The output structure format supports PDB or CIF, with PDB format as the default.
In this mode, a default of 1000 random seeds will be used, with each seed conducting 5 structural samplings, totaling 5000 structures for large-scale sampling. From these, multiple predicted structures with high scores will be selected to ultimately obtain a more accurate predicted structure. This mode is particularly suitable for high-precision prediction of antigen-antibody complex structures, and studies have shown that the accuracy of antibody-antigen complex structure prediction can be increased by 60% in this mode. The input parameters for this mode are consistent with those in Single Mode, and the runtime for one session is approximately 10 to 20 hours.
The total length of the sequence cannot exceed 1300.
The output result files are the structures of the top 5 complexes, rank_1-5.cif and pred_scores_protenix.csv. The CSV file contains the following information:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The name of the complex structure. |
| Ranking_Score | A score that ranks the quality of the predicted structure, with values ranging from -100 to 1.5, where a higher value indicates a better quality of the predicted structure. This score takes into account four indicators: ptm, iptm, fraction_disordered, and has_clash. The calculation formula is: Ranking_Score = 0.8 × ipTM + 0.2 × pTM + 0.5 × disorder − 100 × has_clash. Note: When the structure is monomeric, the Ranking_Score is relatively low because ipTM is 0. In such cases, you can refer to pTM alone. |
| pLDDT | The confidence score for local structure, with a range of 0-100. A higher value indicates a more reliable prediction. Values below 70 are considered low reliability, below 50 are generally regarded as very low confidence, indicating disordered predictions. |
| pTM | The predicted template modeling score, which measures the overall accuracy of the predicted structure. A higher score indicates greater accuracy. If the score is greater than 0.5, it suggests that the overall folding of the structure may be similar to the true structure. |
| ipTM | The interface predicted template modeling score, which measures the accuracy of the predicted relative positions of the subunits in the complex. A higher score indicates greater accuracy. Scores above 0.8 indicate high-quality predictions, while scores below 0.6 suggest potential failure of the prediction. Scores between 0.6 and 0.8 are in a gray area, where the accuracy of the prediction is uncertain. |

抗体人源化设计中基于Grafting以及Back Mutation Grouping的结果批量生成人源化后的序列。
Grafting模块生成的Graft Policy文件,JSON格式
Back Mutation Grouping模块生成的组合突变的Policy文件(combination_mutate_policy.json),JSON格式
输出人源化后的序列文件humanized_variants_esmfold.fasta,将轻重链的序列通过冒号:拼接成一条链,便于直接用于ESMFold模块进行批量结构预测。示例:
>L1H1
EIVLTQSPATLSLSPGERATLSCRASQFVGSSIHWYQQKPGQAPRLLIYYASESMSGIPARFSGSGSGTDFTLTISSLEPEDFAVYYCQQSHSWPFTFGQGTKLEIK:EVQLVESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFIFSNHYMSWVRQAPGKGLEWVSVIRSKSINSATYYADSVKGRFTISRDNSKNTLYLQMNSLRAEDTAVYYCARNYYGSTYDYWGQGTTVTVSS
>L1H2
EIVLTQSPATLSLSPGERATLSCRASQFVGSSIHWYQQKPGQAPRLLIYYASESMSGIPARFSGSGSGTDFTLTISSLEPEDFAVYYCQQSHSWPFTFGQGTKLEIK:EVQLVESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFIFSNHYMSWVRQAPGKGLEWVSEIRSKSINSATYYADSVKGRFTISRDNSKNTLYLQMNSLRAEDTAVYYCARNYYGSTYDYWGQGTTVTVSS
Generate humanized variant sequences based on the Grafting and Back Mutation Grouping results.
Graft policy file in JSON format generated by the Grafting module.
Combination mutate policy file generated by Back Mutation Grouping module in JSON format.
The output file humanized_variants_esmfold.fasta in which sequences of the light and heavy chains are concatenated into a single chain using a colon (:). This format facilitates direct use in the ESMFold module for batch structural prediction.
>L1H1
EIVLTQSPATLSLSPGERATLSCRASQFVGSSIHWYQQKPGQAPRLLIYYASESMSGIPARFSGSGSGTDFTLTISSLEPEDFAVYYCQQSHSWPFTFGQGTKLEIK:EVQLVESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFIFSNHYMSWVRQAPGKGLEWVSVIRSKSINSATYYADSVKGRFTISRDNSKNTLYLQMNSLRAEDTAVYYCARNYYGSTYDYWGQGTTVTVSS
>L1H2
EIVLTQSPATLSLSPGERATLSCRASQFVGSSIHWYQQKPGQAPRLLIYYASESMSGIPARFSGSGSGTDFTLTISSLEPEDFAVYYCQQSHSWPFTFGQGTKLEIK:EVQLVESGGGLVQPGGSLRLSCAASGFIFSNHYMSWVRQAPGKGLEWVSEIRSKSINSATYYADSVKGRFTISRDNSKNTLYLQMNSLRAEDTAVYYCARNYYGSTYDYWGQGTTVTVSS

Humanization Report v2.4是抗体人源化设计报告生成模块,用于生成最终的抗体人源化设计报告以及相应的专利实施例段落。相比v2.3,新增RMSD和能量信息。
Grafting模块生成的Graft Policy文件。
Back Mutation Grouping模块生成的Policy文件。
抗体类型,Antibody 标准双链抗体,Nanobody 纳米抗体。
Grafting模块生成的score文件,JSON格式
Mutation模块生成的score文件,CSV格式
抗体结构RMSD文件,由Antibody RMSD模块生成,CSV格式
从RMSD排序中取前N个RMSD值小的抗体
Absolute Folding Stability模块预测生成的蛋白稳定性文件,CSV格式
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BM.pptx | 回复突变位点汇总文件 |
| batch_registration_template.xlsx | 批量注册模板文件 |
| hotspot_summary.xlsx | 风险位点总结 |
| patent_example_template.docx | 人源化设计序列在相应的专利实施例段落 |
| patent_example_en_template.docx | 英文版人源化设计序列在相应的专利实施例段落 |
| back_mutation_grouping.md | 回复突变分组信息 |
| candidate_score.xlsx | 人源化抗体序列的结构和能量打分汇总 |
| humanized_variants.fasta | 抗体人源化设计序列文件,FASTA格式 |
| Report.docx | 抗体人源化设计报告,包括整个人源化设计过程涉及的序列、分组等信息 |
其中batch_registration_template.xlsx包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein Sequence | 蛋白序列 |
| Molecule Name | 分子名称 |
其中hotspot_summary.xlsx包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ID | 抗体序列名称 |
| Sequence-CDR | CDR序列区域 |
| Deamidation | 脱酰胺位点 |
| Isomerization | 异构化位点 |
| Cleavage | 酶切位点 |
| Hydrolysis | 水解位点 |
| Glycosylation | 糖基化位点 |
| Cys | 半胱氨酸数量 |
| Oxidation | 氧化位点 |
| High risk | 高风险率 |
| High risk sites | 高风险位点 |
The Humanization Report v2.4 is a module for generating reports on antibody humanization design, including the final antibody humanization design report and corresponding paragraphs for patent implementation examples. Compared with v2.3, RMSD and energy information are added.
The Graft Policy file generated by the Grafting module.
The Policy file generated by the Back Mutation Grouping module.
Antibody type, Antibody or Nanobody
Graft germline score file in JSON format generated by the Grafting module
Mutation score file in csv format generated by the Mutation module
Antibody structure RMSD file generated by Antibody RMSD module
Select the top N antibodies with the smallest RMSD values from the RMSD ranking
Protein folding stability file generated by Absolute Folding Stability module in CSV format
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BM.pptx | Summary file of back mutation sites |
| batch_registration_template.xlsx | Batch registration template file |
| hotspot_summary.xlsx | Summary of hotspot sites |
| patent_example_template.docx | Humanization design sequences in corresponding patent implementation example paragraphs (Chinese version) |
| patent_example_en_template.docx | Humanization design sequences in corresponding patent implementation example paragraphs (English version) |
| back_mutation_grouping.md | Grouping for back mutations |
| humanized_variants.fasta | Antibody humanization design sequence file in FASTA format |
| Report.docx | Antibody humanization design report, including information on sequences, grouping, etc., involved in the entire humanization design process |
| candidate_score.xlsx | Candidate sequences energy and structure scores |
The batch_registration_template.xlsx file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein Sequence | Protein sequence |
| Molecule Name | Molecule name |
The hotspot_summary.xlsx file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Antibody sequence name |
| Sequence-CDR | CDR sequence region |
| Deamidation | Deamidation site |
| Isomerization | Isomerization site |
| Cleavage | Cleavage site |
| Hydrolysis | Hydrolysis site |
| Glycosylation | Glycosylation site |
| Cys | Number of cysteines |
| Oxidation | Oxidation site |
| High risk | High-risk rate |
| High risk sites | High-risk sites |

百度螺旋桨PaddleHelix团队研发的HelixFold3,在常规的小分子配体、核酸分子(包括DNA和RNA)以及蛋白质的结构预测精度上已与AlphaFold3相媲美。为了评估其在蛋白质-配体结构预测中的效果,HelixFold3与其他主流方法在PoseBusters数据集上的表现进行了对比。HelixFold3即便在没有指定蛋白质结构的情况下,仍然展示出卓越的表现,成功率甚至超过了依赖已知蛋白质结构的方法,其预测精度与目前顶尖的AlphaFold3相当,这表明HelixFold3在蛋白质-配体相互作用预测领域的出色潜力。HelixFold3在蛋白质-蛋白质复合体结构预测方面已经略微超越了AlphaFold-Multimer的表现,展示出更强的预测能力。
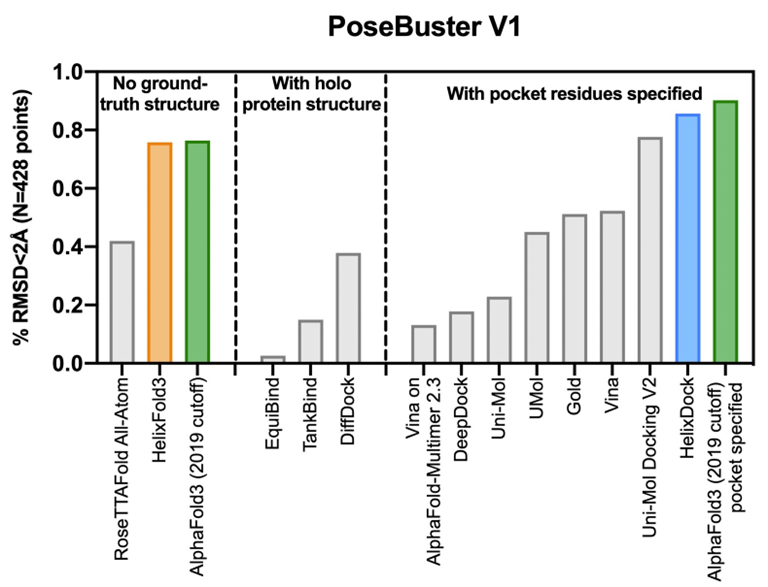
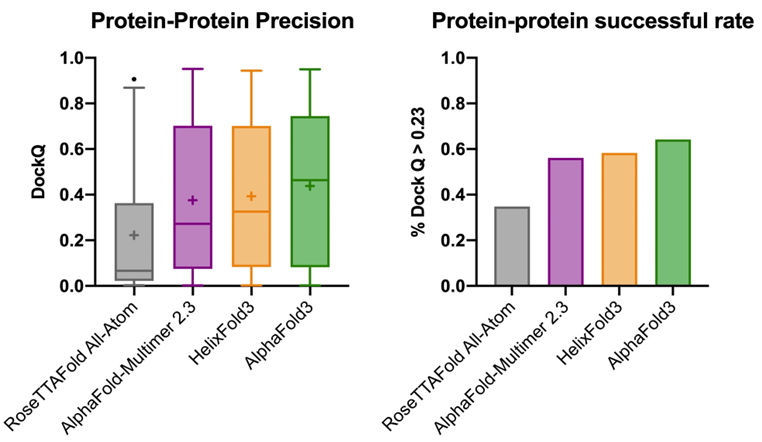
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
注意:多蛋白复合物结构预测,其氨基酸序列输入格式如下:
>protein1
AASJ...
>protein2
AASJ...
>peptide
ASDF...
DNA核酸的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
RNA核酸分子的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
序列总长度不可超过2000。
文本文件包含小分子信息,TXT格式。HF3支持绝大多数重核数量不超过50的配体,支持SMILES或 CCD Code(化学组分词典编号)。如果使用SMILES格式,每行应包含一个小分子;如果使用CCD Code,每行可以包含一个或多个小分子,使用逗号分隔,并加上CCD前缀,示例如下:
CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2
CCD,ATP,HY3,P1L
CCD,MG
注意:不适用于配体蛋白或多肽的氨基酸序列格式输入。
水、助剂和少量特殊的配体目前是模型所不支持的。模型会将这些配体从CCD列表中除去,如果您通过输入SMILES的方式进行了这些输入,可能会造成结果的表现下降。具体不支持的配体的CCD列表参见HF3 FAQ https://paddlehelix.baidu.com/app/tut/guide/all/helixfold3faq。每种配体数量不能超过50。
包含翻译后修饰(PTM)信息的文本文件,TXT格式。每行放置一个PTM信息,每个PTM信息由三部分组成:
1,HY3,1 表示第一条序列的第一个残基,发生了类型为HY3(CCD编号,为3-羟基脯氨酸,为脯氨酸的羟基化)的PTM。不同的氨基酸支持的CCD不同,具体参考https://paddlehelix.baidu.com/app/tut/guide/all/helixfold3json里的说明。备注:
1,HY3,1
1,P1L,5
2,HY3,3
目前支持的离子为:MG, ZN, CL, CA, NA, MN, MN3, K, FE, FE2, CU, CU1, CU3, CO
不支持分行书写,需要写在一行,可以包含一个或多个离子,不同的离子使用逗号分隔,冒号后对应的是离子的数量,每种离子数量不能超过50。示例如下:
MG:2,ZN,CU:3
输出结果文件为排名前5的复合物结构rank_1-5.cif和ranking_scores.csv,csv中包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 复合物结构名称 |
| Ranking_Score | 对预测结构的质量排序的指标分数,数值越大表示预测结构的质量越高。此分数综合了 ptm、iptm 和 has_clash,计算公式为: 0.8 × ipTM + 0.2 × pTM - 1 × has_clash。注意:结构为单体时,因为ipTM为0,整体的综合得分偏低,可参考pTM即可。 |
HelixFold3, developed by the Baidu PaddleHelix team, is comparable to AlphaFold3 in the accuracy of structure prediction of conventional small molecule ligands, nucleic acid molecules (including DNA and RNA), and proteins. To assess HelixFold3’s performance in protein-ligand structure prediction, we compared it against other leading methods using the PoseBusters dataset. HelixFold3 demonstrated exceptional performance even without specifying protein structures, surpassing methods that rely on known protein structures. Its prediction accuracy is comparable to the state-of-the-art AlphaFold3, indicating HelixFold3’s outstanding potential in protein-ligand interaction prediction. Currently, HelixFold3 has slightly surpassed AlphaFold-Multimer in protein-protein complex structure prediction, demonstrating stronger predictive power.


The sequence file of proteins in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
Note: For multi-protein complex structure prediction, the amino acid sequence input format is as follows:
>protein1
AASJ...
>protein2
AASJ...
>peptide
ASDF...
The sequence file of DNA nucleic acids in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
The sequence file of RNA nucleic acid molecules in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
The maximum length of this module is 2000.
A text file containing small molecule information in TXT format. HF3 supports most ligands with fewer than 50 heavy atoms. It supports SMILES or CCD Code (Chemical Component Dictionary number). If using the SMILES format, each line should contain one small molecule; if using the CCD Code, each line can contain one or more small molecules, separated by commas and prefixed with CCD. An example is as follows:
CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2
CCD,ATP,HY3,P1L
CCD,MG
Note: Not applicable for amino acid sequence format input of ligand proteins or polypeptides.
Water, adjuvants, and certain special ligands are not supported by the model. These ligands are excluded from the CCD list. If you input them using SMILES, it may result in degraded performance. For a list of unsupported ligands, refer to the HelixFold3 FAQ https://paddlehelix.baidu.com/app/tut/guide/all/helixfold3faq. The number of each ligand is not to exceed 50.
A text file containing post-translational modification (PTM) information in TXT format. Each line contains one PTM information entry, consisting of three parts:
1,HY3,1 indicates that the first residue of the first sequence undergoes a PTM of type HY3 (CCD number, which is 3-hydroxyproline, a hydroxylation of proline). Different amino acids support different CCDs, as shown in tutorial https://paddlehelix.baidu.com/app/tut/guide/all/helixfold3json.Note:
An example of a file containing multiple PTM information entries is as follows:
1,HY3,1
1,P1L,5
2,HY3,3
Currently supported ions include: MG, ZN, CL, CA, NA, MN, MN3, K, FE, FE2, CU, CU1, CU3, CO
It does not support multi-line writing; it must be written in a single line. It can contain one or multiple ions, with different ions separated by commas. The quantity of each ion is indicated after a colon, and the number of each ion cannot exceed 50. An example of a file containing different ion information is as follows:
MG:2,ZN,CU:3
The output result files are the top 5 ranked complex structures rank_1-5.cif and ranking_scores.csv, with the following information in the CSV:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the complex structure |
| Ranking_Score | A score indicating the quality ranking of the predicted structure, with higher values indicating better quality. This score considers three metrics: pTM, iptm and has_clash, calculated as: Ranking_Score = 0.8 × ipTM + 0.2 × pTM - 1 × has_clash. Note: When the structure is monomeric, the Ranking_Score is relatively low because ipTM is 0. In such cases, you can refer to pTM alone. |

针对抗体全长或者CDR区进行序列检索的模块。从专利中检索一条抗体可变区时,现有的BLAST程序(例如NCBI BLAST)通常是以全序列进行检索,但是对于抗体而言,功能主要取决于CDR,FR相对不重要,并且由于FR的通用性,许多不同抗体的FR是相同或高度同源的,而FR占序列的比重更高,就导致以抗体的可变区BLAST会得到很多FR相似但CDR不相似的序列。并且,专利申请时,除了保护可变区完整序列,很多情况也会对抗体CDR进行单独保护,以获得更大的保护范围,因此在抗体开发过程中,以CDR为目标进行同源序列检索就很有必要了。为此,唯信团队开发了该程序,可以从现有专利库中检索到与目标CDR最接近的序列。数据更新于:Dec 2024
例如,输入序列L的完整序列,进行检索后,返回检索到同源性较高的序列的CDR,如下图所示。

如果需要查看某个检索到的序列的出处,可以根据检索的CDR的序列编号,从任务输出的log文件中找到对应的专利名,
例如序列ATJ10081.1来自于US专利9493553(SEQ ID为39),并且US专利9670274、9890209等多个专利中也出现了该CDR片段,他们的比对情况包括同源性也展示在后面,如下图所示。
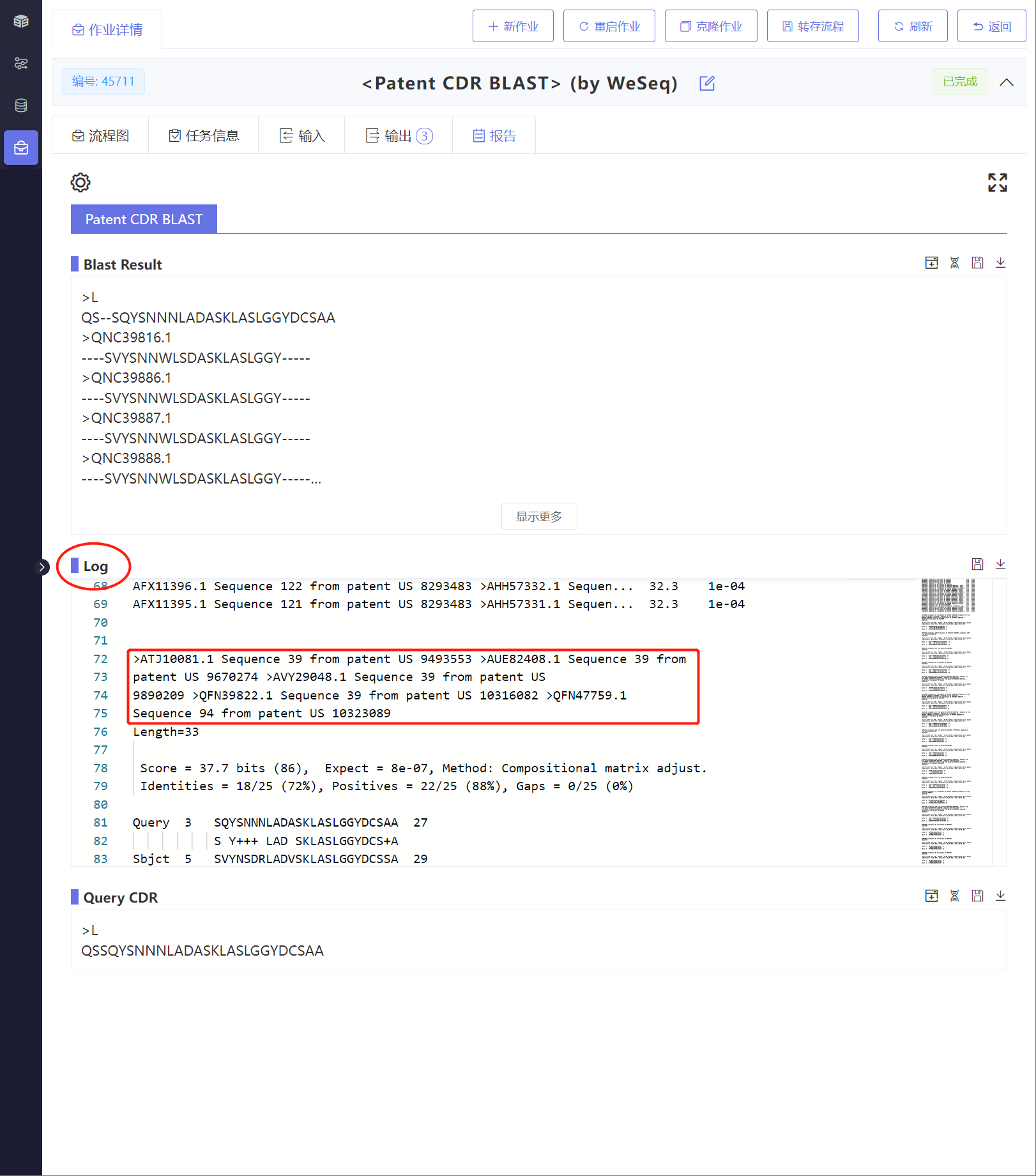
根据唯信团队经验,通常CDR的保护范围精确到具体序列,即差异一个以上氨基酸,即视为不在专利的保护范围之内,但不排除存在等同侵权的风险,仅供参考。
抗体序列文件, FASTA格式
指定序列比对数据库类型:抗体全长(full)或者抗体CDR区域 (cdr)。
CDR区域数据库为专利保护抗体数据库。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| align.fst | 序列比对结果文件 |
| blast.log | 序列比对日志文件 |
A module for sequence retrieval of antibody full-length or CDR region. When retrieving an antibody variable region from a patent, existing BLAST programs (such as NCBI BLAST) usually search the whole sequence, but for antibodies, the function mainly depends on the CDR, FR is relatively not important, and due to the generality of FR, FR of many different antibodies is the same or highly homologous. However, FR accounts for a higher proportion of sequences, resulting in a lot of sequences with similar FR but different CDR by BLAST in the variable region of antibodies. Moreover, in addition to protecting the complete sequence of the variable region during patent application, in many cases, the antibody CDR will also be protected separately to obtain a wider range of protection, so it is necessary to search for homologous sequences with CDR as the target in the process of antibody development. To this end, the Vixon team developed the program, which can retrieve the closest sequence to the target CDR from the existing patent library. Data updated: Dec 2024
For example, when inputting the complete sequence of antibody L for search, the returned CDR of the highly homologous sequences is shown in the image below.

If there is a need to check the source of a retrieved sequence, you can find the corresponding patent name based on the sequence number of the retrieved CDR from the log file output of the task. For example, sequence ATJ10081.1 is from US Patent 9493553 (SEQ ID 39), and the CDR fragment also appears in multiple patents such as US Patents 9670274, 9890209, etc., with their alignment details and homology shown as well, as depicted in the image below.

Based on the experience of the WeMol team, the protection range of CDRs is usually specified down to the specific sequence, meaning that a difference of one or more amino acids is considered outside the scope of patent protection. However, there may still be risks of equivalent infringement, so this information is for reference only.
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
Specifies the sequence alignment database type: antibody full-length (full) or antibody CDR region (cdr).
The CDR regional database is a patent protected antibody database.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| align.fst | Sequence alignment result file |
| blast.log | Sequence alignment log file |

CIF2PDB模块是基于BioPython将mmCIF文件转换成PDB文件。
单独化合物CIF转换部分存在问题。
mmCIF文件的结构。
输出PDB文件名称
输出PDB文件,默认为output.pdb。
The CIF2PDB module is based on BioPython to convert mmCIF files into PDB files.
mmCIF file of structure.
Output the PDB file name
Output pdb file; default is output.pdb.

基于MIT(麻省理工学院)的Boltz-2算法的AF3 like结构预测模型。Boltz-2是一种开源深度学习模型,融合了模型架构、速度优化和数据处理方面的创新,在预测生物分子复合物的 3D结构方面达到了 AlphaFold3 级的准确度。Boltz-2 在一系列不同的基准测试中表现出与最先进的商业模型相当的性能,为结构生物学中可商业化使用的工具树立了新的标杆。
更新
相比于Boltz-1x,Boltz-2新增亲和力预测。
Q1:Boltz‑2 为什么不默认开启 Steering(结构引导)?
A:Steering 会让推理变慢约 2 倍,而且当前参数是在不使用 Steering 的情况下优化的。未来可能默认开启,但需重新调参。
Q2:Steering Potential 会不会让结构偏离真实构象?
A:Steering 的目的是将采样引导回“真实分布流形”,不会盲目收缩采样空间,但需要在“有效性”与“物理合理性”之间找到平衡。
Q3:结构相似性是按口袋还是全结构算的?会不会数据泄漏?
A:使用的是全结构相似性,这确实存在争议,但现实中药物研发常常面对有序列信息的靶点。我们已尽力控制信息泄漏风险。
Q4:Boltz‑2 的亲和力预测是回归还是分类?
A:两者都有,输出包括:
Q5:亲和力数据怎么处理?不准确怎么办?
A:主要训练 ∆Ki(同一实验内的相对值),因为原始 Ki/IC50 数据误差大。用 Cheng–Prusoff 公式统一 Ki 与 IC50。训练集只保留剂量-反应测量,删除噪声高/不可重复实验。
Q6:Boltz‑2 对结构准确性要求高吗?
A:是的,只训练了 ipTM ≥ 0.75 的结构。结构质量是亲和力预测成功的前提。
Q7:Boltz‑2 是否支持金属离子相关配体?
A:不支持。带金属离子的复合物在数据准备阶段已被过滤掉。
Q8:适用于哪些分子体系?
A:蛋白、小分子、RNA、DNA 等多模态复合物。对于大构象变化或柔性蛋白,性能会下降。
Q9:Boltz‑2 和 OpenFE、FEP+ 比如何?
A:在公开 benchmark 上性能优于 OpenFE,略低于商业级 FEP+,但速度优势巨大(~1000× 快)。
Q10:在 Recursion 内部数据集上效果好吗?
A:效果一般,说明模型仍对真实分布存在泛化问题。
Q11:能用于蛋白–蛋白亲和力预测吗?
A:还不支持,但开发中,预计未来几个月会发布 PPI affinity 模块。
Q12:能预测 ADME 或毒性吗?
A:某些毒性通路是结合驱动的,可以利用结构模型辅助预测。参考 BioEmu(Frank Noé)相关研究。
Q13:能预测药物耐药性吗?
A:我们也想知道,希望后续能验证。
Q14:Boltz‑2 可以与 MD 数据结合使用吗?
A:有讨论过,但还没有标准策略,未来可能探索“Boltz + MD”混合建模框架。
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
注意:多蛋白复合物结构预测,其氨基酸序列输入格式如下:
>protein1
AASJ...
>protein2
AASJ...
>peptide
ASDF...
DNA核酸的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
RNA核酸分子的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
备注:当前22GB的GPU显存支持计算的残基/碱基数量在1100个左右。
文本文件包含小分子信息,TXT格式。支持SMILES或 CCD Code(化学组分词典编号)。如果使用SMILES格式,每行应包含一个小分子;如果使用CCD Code,每行可以包含一个或多个小分子,使用逗号分隔,并加上CCD前缀。示例如下:
CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2
CCD,ATP,HY3,P1L
CCD,MG
注意:不适用于配体蛋白或多肽的氨基酸序列格式输入。
包含翻译后修饰(PTM)信息的文本文件,TXT格式。每行放置一个PTM信息,每个PTM信息由三部分组成:
1,HY3,1 表示第一条序列的第一个残基,发生了类型为HY3(CCD编号,为3-羟基脯氨酸,为脯氨酸的羟基化)的PTM1,HY3,1
1,P1L,5
2,HY3,3
共价键信息的文本文件,TXT格式。每行放置一个共价键信息,每个共价键信息包含两个原子信息,每个原子信息由三部分组成:
示例一:
当有2条蛋白序列,1条DNA序列,1条RNA序列,2个小分子时。对应的编号为:
第一条蛋白序列编号为1,第二条蛋白序列编号为2,DNA序列编号为3,RNA序列编号为4,第一个小分子对应的编号为5,第二个小分子对应的编号为6
示例二:
当有3条蛋白序列,2个小分子时。对应的编号为:
第一条蛋白序列编号为1,第二条蛋白序列编号为2,第二条蛋白序列编号为3,第一个小分子对应的编号为4,第二个小分子对应的编号为5
3,1,CA表示第三个实体(序列或小分子)中的第一个残基(或小分子)的CA原子1,1,CA;2,1,CA1,1,CA,第二个原子为2,1,CA1,1,CA;2,1,CA
1,1,CA;3,1,CHA
结合位点类型限制信息的文本文件,TXT格式。每行放置一个结合位点信息,每个结合位点信息由两部分组成:
1,25 表示第一条序列中的第25个残基;可以定义多个残基信息,由英文分号“;”进行分隔,如1,25;1,27;1,32;1,38表示第一条序列中的第25/27/32/38号残基形成结合位点2;1,55;1,62;1,91;1,92;1,99;1,110表示第二个实体(序列或小分子)作为Binder,与第一条序列的第55/62/91/92/99/110号残基所形成的结合位点进行结合。2;1,55;1,62;1,91;1,92;1,99;1,110
3;1,25;1,27;1,32;1,38
指定要计算亲和力的小分子对应的顺序编号(顺序编号的定义请见Covalent Bond参数中原子所在序列或小分子的顺序编号的描述),进行亲和力评估,格式为正整数,且只能指定1个小分子,如:3表示要进行亲和力评估的是顺序编号为3的小分子。模型会评估复合物体系中该小分子与其他部分的结合亲和力。
定义的残基区域信息。模块将输出区域中所有残基平均的pLDDT数值。一个残基区域由序列顺序编号与残基组合编号组成:
1:24,28,32-40 表示第一条序列中的第24/28/32至40号残基所组成的区域,因为是第一条序列,数值1可以省略,等同于24,28,32-40 ,该区域的所有残基的平均pLDDT值将输出到结果文件中。残基区域支持定义多个,每个残基区域之间用英文“;”分隔,例如:
1:24,28,32-40;2:15,23,50-60表示定义了两个区域,区域一为第一条序列的第24/28/32至40号残基,区域二为第二条序列的第15/23/50至60号残基。两个区域各自的残基平均pLDDT值,将输出到结果文件中。
输出结构的格式,支持PDB或CIF格式,默认为PDB格式。
结构打分的结果文件名,默认为“pred_scores_boltz.csv”
亲和力打分的结果文件名,默认为“pred_affinity_boltz.csv”
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
每一条记录代表一个待预测的结构,每条记录的名称要唯一不能重复。一条记录中有多条链时,通过英文冒号(:)相连,文件内容示例如下:
>1
EVQLVESGGGVVQPGRSLRLS:NFMLTQPHSVSVL:ELFPQWHLPIKIAAIIAS
>2
YYCAKDRRDMGYFQHWGQGTLVTVSSQWYQQRPGSAPTTVIYEDNQRPSGTPPTFMIAVFLPIVVLIFKSILFL
表示有两个待预测的结构,第一条记录的名称为1,有三条蛋白链,用:进行分隔。第二条记录的名称为2,为单链。
DNA核酸的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
每一条序列记录代表一个待预测的结构,每条记录的名称要唯一不能重复(可与Protein参数中的记录名称一致,表示该记录的DNA序列与Protein序列归属于同一结构)。一条记录中有多条链时,通过英文冒号(:)相连,文件内容示例如下:
>dna
GACCTCT:CCTAGCT
>1
CCTAGCT
表示有两条记录,第一条的名称为dna,有两条DNA链,用:进行分隔,因为该名称不存在与Protein示例记录中,属于新结构。第二条的名称为1,有一条DNA链,因为该名称存在于Protein示例记录中,则表示同属一个结构(该结构同时包含Protein序列和该DNA序列)。
RNA核酸分子的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
每一条序列记录代表一个待预测的结构,每条记录的名称要唯一不能重复(可与DNA或Protein参数中的记录名称一致,表示该记录的RNA序列与上面的DNA序列或Protein序列归属于同一结构)。一条记录中有多条链时,通过英文冒号(:)相连,文件内容示例如下:
>1
AGCU
>rna
AGGCU:UGAUC
表示有两条记录,第一条的名称为1,为单链,因为该名称存在于DNA及Protein示例记录中,表示同属一个结构(该结构同时包含了Protein序列、DNA序列及该RNA序列)。第二条的名称为rna,有两条RNA链,用:进行分隔,因为该名称不存在于DNA或Protein示例记录中,属于新结构。
文本文件包含小分子信息,TXT格式。支持SMILES或 CCD Code(化学组分词典编号)。如果使用SMILES格式,每行应包含一个小分子;如果使用CCD Code,每行可以包含一个或多个小分子,使用逗号分隔。
每行代表一个待预测的结构,每行可放置多个ligand,且以唯一不重复的名称开头(该名称可与上述RNA,DNA或Protein参数中的记录名称一致,表示该行的所有ligands,与上述的RNA或DNA或Protein序列归属于同一结构),名称与所有ligands都以英文冒号(:)分隔。文件内容示例如下:
1:CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2:CCD,ATP,HY3
lig:CC1CC(CN2NC[N+](=C3CCC(OC(F)(F)F)CC3)C2=O)CC(C)C1OC(C)(C)C(=O)[O-]
表示有两条记录,第一条的名称为1,有三个ligand(一个SMILES,两个CCD codes),因为该名称存在于上述的RNA或DNA或Protein示例记录中,表示同属一个结构。第二条的名称为lig,有一个ligand(为SMILES),因为该名称不存在上述的RNA或DNA或Protein示例记录中,属于新结构。
包含翻译后修饰(PTM)信息的文本文件,TXT格式。每个PTM的信息与Single模式中一致(参考Single模式中的定义)。
每行定义一个结构的所有PTM信息,且以唯一名称开头(该名称必须存在于前述的Protein或DNA或RNA记录中),都以英文冒号(:)分隔。文件内容示例如下:
1:1,HY3,1:1,P1L,5:2,HY3,3
2:1,HY3,1:2,HY3,3
表示前述名称为1的结构中(Protein或DNA或RNA),有三个PTM。名称为2的结构中,有两个PTM。
共价键信息的文本文件,TXT格式。每个共价键的信息与Single模式中一致(参考Single模式中的定义)。
Batch模式下,每行定义一个结构的所有共价键,且以唯一名称开头(该名称必须存在于前述的Protein或DNA或RNA记录中),都以英文冒号(:)分隔。文件内容示例如下:
1:1,1,CA;2,1,CA:1,1,CA;3,1,CHA
2:1,1,CA;3,1,CHA
表示前述名称为1的结构中(Protein或DNA或RNA),有两个共价键。名称为2的结构中,有一个共价键。
结合位点类型限制信息的文本文件,TXT格式。每个结合位点信息的定义与Single模式中一致(参考Single模式中的定义)。
Batch模式下,每行定义一个结构的所有结合位点限制信息,且以唯一名称开头(该名称必须存在于前述的Protein或DNA或RNA记录中),都以英文冒号(:)分隔。文件内容示例如下:
1:2;1,55;1,62;1,91;1,92;1,99;1,110
2:1;2,15;2,17;2,18;2,56:1;3,76;3,78;3,96
表示前述名称为1的结构中(Protein或DNA或RNA),有一个结合位点限制。名称为2的结构中,有两个结合位点限制。
指定小分子顺序编号(定义见Bond参数),进行亲和力评估,每个亲和力信息的定义与Single模式一致。
Batch模式下,每行定义一个亲和力信息,且以唯一名称开头(该名称必须存在于前述的Protein或DNA或RNA记录中),都以英文冒号(:)分隔。文件内容示例如下:
1:4
2:5
表示前述名称为1的结构中(Protein或DNA或RNA),有亲和力计算,其小分子Binder的顺序编号为4。名称为2的结构中,有亲和力计算,其小分子Binder的顺序编号为5。
输出结构的格式,支持PDB或CIF格式,默认为PDB格式。
虚拟筛选模式中,每个小分子会单独与蛋白/核酸体系计算亲和力。当前一次运行支持最大100个小分子。
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。(同Single模式)
DNA核酸的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。(同Single模式)
RNA核酸分子的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。(同Single模式)
备注:当前24GB的GPU显存支持计算的残基/碱基数量在1000个左右。
文本文件包含小分子信息,TXT格式。支持SMILES或 CCD Code(化学组分词典编号)。如果使用SMILES格式,每行应包含一个小分子;如果使用CCD Code,每行可以包含一个或多个小分子,使用逗号分隔,并加上CCD前缀。示例如下:
CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2
CCD,ATP,HY3,P1L
CCD,MG
包含翻译后修饰(PTM)信息的文本文件,TXT格式。(同Single模式)
共价键信息的文本文件,TXT格式。(同Single模式,但共价键中小分子不能参与)
结合位点类型限制信息的文本文件,TXT格式。(同Single模式)
亲和力打分的结果文件名,默认为“pred_affinity_boltz.csv”
输出结果文件为排名前5的复合物结构rank_1-5.cif,pred_scores_boltz.csv以及pred_affinity_boltz.csv(如果指定了Affinity参数)。
pred_scores_boltz.csv中包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 复合物结构名称 |
| Confidence_Score | 对预测结构的质量排序的指标分数,数值在0~1.0之间,越大表示预测结构的质量越高。该分数综合考虑了两个指标:iptm(单体时为pTM), complex_plddt, 计算公式为: Confidence_Score = 0.8 × complex_plddt + 0.2 × ipTM |
| pTM | 对结构预测得到的TM score,衡量预测结构整体准确性,越大表示越准确,该分数大于0.5时,表示结构整体折叠可能与真实结构相似 |
| ipTM | 对结构中的相互作用界面预测得到的TM score,当预测结构为复合物时才有该评价指标,衡量复合物中各个亚基之间相对位置的预测准确性,越大表示越准确,大于0.8表示高质量预测,小于0.6表示预测可能失败,0.6-0.8为灰色地带,预测正确与否不确定 |
| Complex_pLDDT | 对复合物预测得到的平均pLDDT score,值范围是0-1.0,该值越大说明预测的结构越可靠。低于0.7被认为可靠性较低,低于0.5基本认为是可信度非常低,为无序预测 |
| Complex_ipLDDT | 将复合物中相互作用界面的权重提升后,预测得到的pLDDT score,值范围是0-1.0,该值越大说明预测的结构越可靠 |
| pLDDT_domain | 当设置Domain参数时,预测得到的区域残基的平均pLDDT数值,多个区域时,数值用英文分号";"分隔 |
pred_affinity_boltz.csv中包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Pred_Affinity(log(IC50)) | 预测的复合物中小分子与其他部分结合的亲和力数值,为IC50的对数值,即log(IC50),其中IC50的单位为μM,数值越低表示亲和力越强。 |
| Pred_Prob | 概率值,判断小分子是真正Binder的可能性,数值在0-1之间,越大表示小分子是Binder的可能性越大 |
final_results.tar.gz文件为Batch模式下额外生成一个所有预测结果的打包文件
虚拟筛选模式下输出:
pred_affinity_boltz.csv文件为亲和力预测结果,包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ID | 小分子顺序,从1开始 |
| Ligand | 小分子的SMILES或CCD代码 |
| Pred_Affinity(log(IC50)) | 预测的复合物中小分子与其他部分结合的亲和力数值,为IC50的对数值,即log(IC50),其中IC50的单位为μM,数值越低表示亲和力越强。 |
| Pred_Prob | 概率值,判断小分子是真正Binder的可能性,数值在0-1之间,越大表示小分子是Binder的可能性越大 |
final_results.tar.gz文件为所有预测结果的打包文件
Developed based on the Boltz-2 model, Boltz-2 is an open-source deep learning model that integrates innovations in model architecture, speed optimization, and data processing. It achieves AlphaFold3-level accuracy in predicting the 3D structures of biomolecular complexes. Boltz-2 demonstrates performance comparable to state-of-the-art commercial models across a range of benchmarks, setting a new standard for commercially usable tools in structural biology.
Q1: Why doesn’t Boltz-2 enable Steering (structural guidance) by default?
A: Steering slows inference by about 2x, and the current parameters are optimized without Steering. It may be enabled by default in the future, but parameter tuning will be required.
Q2: Does Steering Potential cause structures to deviate from their true conformations?
A: Steering aims to guide sampling back to the “manifold of true distributions” without blindly shrinking the sampling space. However, it requires a balance between “effectiveness” and “physical plausibility.”
Q3: Is structural similarity calculated based on the pocket or the entire structure? Could there be data leakage?
A: Structural similarity is calculated using the entire structure, which is indeed a controversial approach. However, in real-world drug discovery, target sequence information is often available. Efforts have been made to minimize the risk of information leakage.
Q4: Is Boltz-2’s affinity prediction regression-based or classification-based?
A: Both. The output includes:
Q5: How is affinity data processed? What happens if it’s inaccurate?
A: The model primarily trains on ∆Ki (relative values within the same experiment) due to large errors in raw Ki/IC50 data. Ki and IC50 values are unified using the Cheng–Prusoff equation. The training set excludes high-noise or non-reproducible experiments, focusing on dose-response measurements.
Q6: Does Boltz-2 require high structural accuracy?
A: Yes, it only trains on structures with ipTM ≥ 0.75. Structural quality is essential for successful affinity prediction.
Q7: Does Boltz-2 support ligands with metal ions?
A: No, complexes containing metal ions are filtered out during data preparation.
Q8: What molecular systems is Boltz-2 suitable for?
A: Protein, small molecules, RNA, DNA, and other multi-modal complexes. Performance decreases for systems with large conformational changes or flexible proteins.
Q9: How does Boltz-2 compare to OpenFE and FEP+?
A: It outperforms OpenFE on public benchmarks but slightly underperforms compared to the commercial-grade FEP+. However, Boltz-2 has a significant speed advantage (~1000× faster).
Q10: Does Boltz-2 perform well on Recursion’s internal datasets?
A: Performance is moderate, indicating the model still struggles with generalization to real-world distributions.
Q11: Can Boltz-2 predict protein–protein affinity?
A: Not yet, but development is underway. A PPI affinity module is expected in the coming months.
Q12: Can Boltz-2 predict ADME or toxicity?
A: Certain toxicity pathways are binding-driven, and structural models can assist in prediction. Related studies include BioEmu by Frank Noé.
Q13: Can Boltz-2 predict drug resistance?
A: We hope to explore this in future validations.
Q14: Can Boltz-2 be used with MD data?
A: There have been discussions, but no standard strategy exists yet. A future direction may involve exploring a “Boltz + MD” hybrid modeling framework.
The sequence file of proteins in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
Note: For multi-protein complex structure prediction, the amino acid sequence input format is as follows:
>protein1
AASJ...
>protein2
AASJ...
>peptide
ASDF...
The sequence file of DNA nucleic acids in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
The sequence file of RNA nucleic acid molecules in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
A text file containing small molecule information in TXT format. It supports SMILES or CCD Code (Chemical Component Dictionary number). If using the SMILES format, each line should contain one small molecule; if using the CCD Code, each line can contain one or more small molecules, separated by commas and prefixed with CCD. An example is as follows:
CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2
CCD,ATP,HY3,P1L
CCD,MG
Note: Not applicable for amino acid sequence format input of ligand proteins or polypeptides.
A text file containing post-translational modification (PTM) information in TXT format. Each line contains one PTM information entry, consisting of three parts:
1,HY3,1 indicates that the first residue of the first sequence undergoes a PTM of type HY3 (CCD number, which is 3-hydroxyproline, a hydroxylation of proline).Note:
An example of a file containing multiple PTM information entries is as follows:
1,HY3,1
1,P1L,5
2,HY3,3
A text file containing covalent bond information in TXT format. Each line contains one covalent bond information entry, and each entry includes two atom information entries, each consisting of three parts:
Example 1:
When there are 2 protein sequences, 1 DNA sequence, 1 RNA sequence, and 2 small molecules, the corresponding numbers are as follows:
The first protein sequence is numbered 1, the second protein sequence is numbered 2, the DNA sequence is numbered 3, the RNA sequence is numbered 4, the first small molecule corresponds to the number 5, and the second small molecule corresponds to the number 6.
Example 2:
When there are 3 protein sequences and 2 small molecules, the corresponding numbers are as follows:
The first protein sequence is numbered 1, the second protein sequence is numbered 2, the third protein sequence is numbered 3, the first small molecule corresponds to the number 4, and the second small molecule corresponds to the number 5.
The three parts are separated by commas. For example, 3,1,CA indicates the CA atom of the first residue (or small molecule) in the third entity (sequence or small molecule).
A covalent bond consists of two atom information entries, separated by a semicolon, such as 1,1,CA;2,1,CA, indicating a covalent bond composed of two atoms: the first atom is 1,1,CA, and the second atom is 2,1,CA.
An example of a file containing multiple covalent bond information entries is as follows:
1,1,CA;2,1,CA
1,1,CA;3,1,CHA
A text file with pocket type restriction information, in TXT format. Each line contains the information of one pocket, which is composed of two parts:
The sequential number of the Binder (consistent with the sequential number of the sequence or small molecule in the covalent bond definition), the Binder can be any one of small molecules, protein/nucleic acid sequences, and currently, only one Binder (i.e., one number) is supported for a pocket.
The residue information of the pocket, each residue information consists of the sequence number where it is located and the residue position number, separated by a comma, such as: 1,25 indicates the 25th residue in the first sequence; multiple residue information can be defined, separated by an English semicolon “;”, for example, 1,25;1,27;1,32;1,38 indicates that the 25th, 27th, 32nd, and 38th residues in the first sequence form the pocket.
The above two pieces of information are also separated by an English semicolon “;”. For example: 2;1,55;1,62;1,91;1,92;1,99;1,110 indicates that the second entity (sequence or small molecule) as a Binder, binds to the pocket formed by the 55th, 62nd, 91st, 92nd, 99th, and 110th residues in the first sequence.
An example of a file content containing multiple pockets information is as follows:
2;1,55;1,62;1,91;1,92;1,99;1,110
3;1,25;1,27;1,32;1,38
Please specify the sequential number of the small molecule for which the affinity is to be calculated (the definition of the sequential number can be found in the description of the sequential number of the atom’s sequence or small molecule under the Covalent Bond parameter). The format must be a positive integer, and only one small molecule can be specified. For example, 3 indicates that the small molecule with the serial number 3 is to be evaluated for affinity. The model will assess the binding affinity of this small molecule with other components in the complex system.
The defined residue region information. The module will output the average pLDDT value of all residues in the region. A residue region is composed of sequence order numbers and residue combination numbers:
Sequence order numbers (as defined in the Modification parameter), the value 1 can be omitted (i.e., defaulting to 1).
Residue combination numbers, using residue position numbers, with multiple residues separated by commas and specified residue ranges indicated by hyphen symbols. For example, “3,10,24-30” indicates the 3rd, 10th, and 24th to 30th residues on the target sequence.
For example: 1:24,28,32-40 indicates the region composed of the 24th, 28th, and 32nd to 40th residues in the first sequence. Since it is the first sequence, the number 1 can be omitted, equivalent to 24,28,32-40. The average pLDDT value of all residues in this region will be output to the result file.
Multiple residue regions are supported, with each residue region separated by an English semicolon “;”. For example: 1:24,28,32-40;2:15,23,50-60 defines two regions. Region one consists of the 24th, 28th, and 32nd to 40th residues in the first sequence, and region two consists of the 15th, 23rd, and 50th to 60th residues in the second sequence. The average pLDDT values of the residues in each of the two regions will be output to the result file.
The output structure format supports PDB or CIF, with PDB format as the default.
The filename for the structure scoring results, defaulting to “pred_scores_boltz.csv”.
The filename for the affinity scoring results, defaulting to “pred_affinity_boltz.csv”.
The protein sequence file in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences. Each record represents a structure to be predicted, and each record name must be unique. If a record contains multiple chains, they should be connected by a colon (:). Example content:
>1
EVQLVESGGGVVQPGRSLRLS:NFMLTQPHSVSVL:ELFPQWHLPIKIAAIIAS
>2
YYCAKDRRDMGYFQHWGQGTLVTVSSQWYQQRPGSAPTTVIYEDNQRPSGTPPTFMIAVFLPIVVLIFKSILFL
This indicates two structures to be predicted, with the first record named 1 containing three protein chains separated by colons. The second record is named 2 and contains a single chain.
The DNA sequence file in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences. Each sequence record represents a structure to be predicted, and each record name must be unique. (It can match the record names in the Protein parameter, indicating that the DNA sequence belongs to the same structure as the Protein sequence.) If a record contains multiple chains, they should be connected by a colon (:). Example content:
>dna
GACCTCT:CCTAGCT
>1
CCTAGCT
This indicates two records, with the first named dna containing two DNA chains separated by a colon. Since this name does not appear in the Protein example records, it represents a new structure. The second record is named 1, containing one DNA chain, and since this name exists in the Protein example records, it indicates that they belong to the same structure (which contains both Protein and DNA sequences).
The RNA sequence file in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences. Each sequence record represents a structure to be predicted, and each record name must be unique. (It can match the record names in the DNA or Protein parameters, indicating that the RNA sequence belongs to the same structure.) If a record contains multiple chains, they should be connected by a colon (:). Example content:
>1
AGCU
>rna
AGGCU:UGAUC
This indicates two records, with the first named 1, which is a single chain. Since this name exists in the DNA and Protein example records, it indicates that they belong to the same structure (which includes Protein, DNA, and this RNA sequence). The second record is named rna, containing two RNA chains separated by a colon. Since this name does not appear in the DNA or Protein example records, it represents a new structure.
A text file containing information on small molecules in TXT format. It supports either SMILES or CCD Code. If using SMILES format, each line should contain one small molecule; if using CCD Code, each line can contain one or more small molecules, separated by commas. Each line represents a structure to be predicted, and each line must start with a unique name (this name can match those in the RNA, DNA, or Protein parameters, indicating that all ligands in that line belong to the same structure). The name and all ligands are separated by a colon (:). Example content:
1:CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2:CCD,ATP,HY3
lig:CC1CC(CN2NC[N+](=C3CCC(OC(F)(F)F)CC3)C2=O)CC(C)C1OC(C)(C)C(=O)[O-]
This indicates two records, with the first named 1, containing three ligands (one SMILES and two CCD codes). Since this name exists in the RNA, DNA, or Protein example records, it indicates that they belong to the same structure. The second record is named lig, containing one ligand (in SMILES format). Since this name does not appear in the RNA, DNA, or Protein example records, it represents a new structure.
A text file containing post-translational modification (PTM) information in TXT format. Each PTM entry is consistent with that in Single mode (refer to the definitions in Single mode). Each line defines all PTM information for a structure, starting with a unique name (this name must exist in the previously defined Protein, DNA, or RNA records), separated by colons (:). Example content:
1:1,HY3,1:1,P1L,5:2,HY3,3
2:1,HY3,1:2,HY3,3
This indicates that the structure named 1 (Protein, DNA, or RNA) has three PTMs, while the structure named 2 has two PTMs.
A text file containing covalent bond information in TXT format. Each covalent bond entry is consistent with that in Single mode (refer to the definitions in Single mode). In Batch mode, each line defines all covalent bonds for a structure, starting with a unique name (this name must exist in the previously defined Protein, DNA, or RNA records), separated by colons (:). Example content:
1:1,1,CA;2,1,CA:1,1,CA;3,1,CHA
2:1,1,CA;3,1,CHA
This indicates that the structure named 1 (Protein, DNA, or RNA) has two covalent bonds, while the structure named 2 has one covalent bond.
A text file containing pockets information in TXT format. Each pocket is consistent with that in Single mode (refer to the definitions in Single mode). In Batch mode, each line defines all pockets for a structure, starting with a unique name (this name must exist in the previously defined Protein, DNA, or RNA records), separated by colons (:). Example content:
1:2;1,55;1,62;1,91;1,92;1,99;1,110
2:1;2,15;2,17;2,18;2,56:1;3,76;3,78;3,96
This indicates that the structure named 1 (Protein, DNA, or RNA) has one pocket, while the structure named 2 has two pockets.
The output structure format supports PDB or CIF, with PDB format as the default.
The output result files are the top 5 ranked complex structures rank_1-5.cif and pred_scores_boltz.csv, with the following information in the CSV:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the complex structure |
| Confidence_Score | A score indicating the quality ranking of the predicted structure, ranging from 0 to 1.0, with higher values indicating better quality. This score considers two metrics: iptm (pTM for monomers) and complex_plddt, calculated as: Confidence_Score = 0.8 × complex_plddt + 0.2 × ipTM |
| pTM | Predicted TM score for the complex |
| ipTM | Predicted TM score when aggregating at the interfaces |
| Complex_pLDDT | Average pLDDT score for the complex |
| Complex_ipLDDT | Average pLDDT score when upweighting interface tokens |
| pLDDT_domain | When setting the Domain parameter, the average pLDDT value of the domain residues. For multiple domains, the values are separated by semicolons “;”. |
final_results.tar.gz, An additional compressed file containing all predicted results generated in Batch mode.

基于Chai Discovery, Inc.(OpenAI投资)的Chai-1算法的AF3 like结构预测模型。Chai-1是一种用于分子结构预测的多模态基础模型,在各种基准测试中均表现出色,可以预测包括蛋白质、小分子、DNA、RNA、糖基化等。
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
注意:多蛋白复合物结构预测,其氨基酸序列输入格式如下:
>protein1
AASJ...
>protein2
AASJ...
>peptide
ASDF...
DNA核酸的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
RNA核酸分子的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
备注:当前24GB的GPU显存能计算的残基/碱基数量在1000个左右。
在Protein、DNA、RNA序列中,都支持残基或碱基的修饰,用CCD进行定义,CCD的介绍参考https://www.wwpdb.org/data/ccd 编号查询网址为https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe-srv/pdbechem/
定义残基或碱基修饰时,直接在序列中用英文括号‘()’包含CCD code即可,示例如下:
>seq
(ACE)GQLEEIAK
表示在序列的N端发生了乙酰化;
>seq
AGSHSMRYFSTSVSR(HY3)GRGEPRFIAVG
表示序列中的残基P发生了羟基化修饰,变成HY3(CCD code)
文本文件包含小分子的结构信息,用SMILES格式,支持多个小分子,每行放置一个,示例如下:
CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2
[Mg+2]
注意:不适用于配体蛋白或多肽的氨基酸序列格式输入。
包含残基间距离限制信息的文本文件。距离限制的类型有两种:两个残基间的距离限制,一个残基与一条链之间的距离限制。
两个残基间的距离限制的定义由五部分组成:
五部分由逗号分隔,例如:1,R84,3,G7,10.0
表示第1条序列中的84号残基R,与第3条序列中的7号残基G,之间的最大距离为10.0埃。
一个残基与一条链之间的距离限制表示该残基与链中任意一个残基的距离满足限制即可。其定义方式与上述类似,差异在于,残基1与残基2的符号及位置编号,其中一个需设置为0(不可同时为0),例如:1,R84,3,0,10.0
表示第1条序列中的84号残基R,与第3条链的任意一个残基/碱基的最大距离为10.0埃即可。
支持放置多个距离限制,每行放置一个即可,包含多个距离限制信息的文件内容示例如下:
1,H189,3,L4,8.0
1,R84,3,0,10.0
输出结果文件为排名前5的复合物结构rank_1-5.cif和pred_scores_chai1.csv,csv中包含信息如下:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 结构名称 |
| Aggregate_Score | 对预测结构的质量排序的指标分数,值范围在-100至1.0之间,越大表示预测结构的质量越高。该分数综合考虑了三个指标:ptm, iptm, has_clash, 计算公式为: Aggregate_Score = 0.8 × ipTM + 0.2 × pTM − 100 × has_clash。注意:结构为单体时,因为ipTM为0,整体的综合得分偏低,可参考pTM即可。 |
| pTM | 预测的TM分数(the predicted template modeling score),衡量预测结构整体准确性,越大表示越准确,该分数大于0.5时,表示结构整体折叠可能与真实结构相似 |
| ipTM | 预测的亚基接触面的TM分数(the interface predicted template modeling score),当预测结构为复合物时才有该评价指标,衡量复合物中各个亚基之间相对位置的预测准确性,越大表示越准确,大于0.8表示高质量预测,小于0.6表示预测可能失败,0.6-0.8为灰色地带,预测正确与否不确定 |
Based on Chai-1 structure prediction model implementation. Chai-1 is a multimodal basis model for molecular structure prediction that performs well on various benchmarks and can predict including proteins, small molecules, DNA, RNA, glycosylation, and more.

The sequence file of proteins in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
Note: For multi-protein complex structure prediction, the amino acid sequence input format is as follows:
>protein1
AASJ...
>protein2
AASJ...
>peptide
ASDF...
The sequence file of DNA nucleic acids in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
The sequence file of RNA nucleic acid molecules in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
** Note: Current 24GB GPU memory can calculate around 1000 residues/bases. **
In Protein, DNA, RNA sequences, all support the modification of residues or bases, which are defined by CCD, The introduction of the CCD reference https://www.wwpdb.org/data/ccd Number query url for https://www.ebi.ac.uk/pdbe-srv/pdbechem/
To define a residue or base modification, simply include the CCD code in parentheses’ () 'in the sequence, as shown in the following example:
>seq
(ACE)GQLEEIAK
Indicates acetylation at the N-terminus of the sequence;
>seq
AGSHSMRYFSTSVSR(HY3)GRGEPRFIAVG
Indicates that residue P in the sequence is hydroxylated and becomes HY3 (CCD code).
The text file contains structural information about small molecules, in SMILES format, supporting multiple small molecules, one per line, as shown in the following example:
CC(=O)OC1C[NH+]2CCC1CC2
[Mg+2]
Note: Not applicable for amino acid sequence format input of ligand proteins or polypeptides.
The five parts are separated by commas, for example: 1,R84,3,G7,10.0
Denote residue 84 R in the first sequence, and residue 7 G in the third sequence, with a maximum distance of 10.0 angstroms.
** The distance limit between a residue and a chain ** means that the distance between the residue and any residue in the chain satisfies the limit. It is defined in the same way as above, except that the symbol and position number of residue 1 and residue 2 need to be set to 0 (not both), e.g. 1,R84,3,0,10.0
Denotes residue 84 R in the first sequence, and a maximum distance of 10.0 angstroms from any residue/base of the third strand is sufficient.
Multiple distance limits are supported, one per line, and an example file containing multiple distance limits is as follows:
1,H189,3,L4,8.0
1,R84,3,0,10.0
The output files are the top 5 complex structures rank_1-5.cif and pred_scores_chai1.csv, which contain the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the complex structure |
| Aggregate_Score | Index scores that rank the quality of the predicted structure, with values ranging from -100 to 1.0, with larger values indicating higher quality of the predicted structure. The score takes into account three metrics: ptm, iptm, has_clash, and is calculated as follows: Aggregate_Score = 0.8 × ipTM + 0.2 × pTM − 100 × has_clash. Note: When the structure is monomeric, the Aggregate_Score is relatively low because ipTM is 0. In such cases, you can refer to pTM alone. |
| pTM | The predicted template modeling score, which measures the overall accuracy of the predicted structure. A higher score indicates greater accuracy. If the score is greater than 0.5, it suggests that the overall folding of the structure may be similar to the true structure. |
| ipTM | The interface predicted template modeling score, which measures the accuracy of the predicted relative positions of the subunits in the complex. A higher score indicates greater accuracy. Scores above 0.8 indicate high-quality predictions, while scores below 0.6 suggest potential failure of the prediction. Scores between 0.6 and 0.8 are in a gray area, where the accuracy of the prediction is uncertain. |

ADMET Prediction (v2)是一个基于机器学习的小分子ADMET性质预测模块。能快速批量预测小分子的ADMET性质,支持图注意力神经网络模型(GNN)、轻量梯度提升树模型(LGBM)、随机森林模型(RF)、梯度提升树模型(XGBT)4种常见高效的机器学习算法,分子特征支持分子指纹(Morgan FP)以及分子描述符(Descriptors)两种方法,能对小分子化合物库进行快速批量预测。模块支持27种ADMET性质,其中7种回归模型,20种分类模型。不同机器学习方法以及分子特征化方法预测性能如下:


模块自动选择最理想的机器学习算法和分子特征化方法的组合进行预测。
待预测的小分子文件,SDF格式。
ADMET预测列表,ADMET性质见结果说明部分。
输出的预测结果文件,默认为predicted_results.csv
输出结果中,如果是分类模型,输出0或1分类。如果是回归模型,预测出实际值。
ADMET性质信息如下:
| Dataset | Dataset Abbr. | ADMET Type | Dataset Type | Endpoints Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caco-2 (Cell Effective Permeability), Wang et al. | caco2 | Absorption | Regression | logPapp |
| PAMPA Permeability, NCATS | pampa | Absorption | Binary classification | high permeability (1) or low-to-moderate permeability (0) in PAMPA assay |
| HIA (Human Intestinal Absorption), Hou et al. | hia | Absorption | Binary classification | good permeability (1) or poor permeability (0) |
| Pgp (P-glycoprotein) Inhibition, Broccatelli et al. | pgp | Absorption | Binary classification | inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| Bioavailability, Ma et al. | bioavailability | Absorption | Binary classification | High (1) or low (0) bioavailability |
| Lipophilicity, AstraZeneca | lipophilicity | Absorption | Regression | octanol/water distribution coefficient (logD at pH 7.4) |
| Solubility, AqSolDB | solubility | Absorption | Regression | logS |
| Hydration Free Energy, FreeSolv | freesolv | Absorption | Regression | Hydration Free Energy (kcal/mol) |
| BBB (Blood-Brain Barrier), Martins et al. | bbbp | Distribution | Binary classification | High (1) or low (0) blood-brain barrier penetration |
| PPBR (Plasma Protein Binding Rate), AstraZeneca | ppbr | Distribution | Regression | Plasma Protein Binding Rate (0-100) |
| CYP P450 2C19 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp2c19_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 2C19 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP P450 2D6 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp2d6_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 2D6 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP P450 3A4 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp3a4_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 3A4 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP P450 1A2 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp1a2_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 1A2 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP P450 2C9 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp2c9_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 2C9 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP2C9 Substrate, Carbon-Mangels et al. | cyp2c9_substrate | Metabolism | Binary Classification | CYP2C9 substrate (1) or non-substrate (0) |
| CYP2D6 Substrate, Carbon-Mangels et al. | cyp2d6_substrate | Metabolism | Binary Classification | CYP2CD6 substrate (1) or non-substrate(0) |
| CYP3A4 Substrate, Carbon-Mangels et al. | cyp3a4_substrate | Metabolism | Binary Classification | CYP3A4 substrate (1) or non-substrate(0) |
| Microsome Clearance, AstraZeneca | clearance_microsome | Excretion | Regression | Microsome Clearance (CL) |
| Acute Toxicity LD50 | ld50 | Toxicity | Regression | Acute Toxicity LD50 |
| hERG blockers | herg_blockers | Toxicity | Binary classification | hERG blockers (1) or non-blockers (0) |
| hERG Karim et al. | herg_karim | Toxicity | Binary classification | hERG blockers (1) or non-blockers (0) |
| Ames Mutagenicity | ames | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) ames mutagenicity |
| DILI (Drug Induced Liver Injury) | dili | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) drug induced liver injury |
| Skin Reaction | skin | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) skin reaction |
| ClinTox | clintox | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) ClinTox |
| Carcinogens | carcinogens | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) Carcinogens |
ADMET Prediction (v2) is a machine learning-based module for predicting the ADMET properties of small molecules. It enables rapid batch predictions of ADMET properties and supports four common and efficient machine learning algorithms: Graph Attention Neural Network (GAT), Light Gradient Boosting Machine (LightGBM), Random Forest, and Gradient Boosting Machine (GBM). The module supports two methods for molecular feature representation: molecular fingerprints and molecular descriptors, allowing for quick batch predictions on libraries of small molecule compounds. It supports 27 ADMET properties, including 7 regression models and 20 classification models. Users can select the ideal machine learning algorithm and molecular characterization method based on the predictive performance data provided in the documentation. The predictive performance of different machine learning methods and molecular characterization methods is as follows:


The module selects the ideal machine learning algorithm and molecular characterization method automaticaly based on the predictive performance data provided in the documentation.
Small molecular structure file in SDF format
ADMET properties. Details can be seen in results.
Output prediction results file name with default predicted_results.csv
In the output results, if it is a classification model, the output will be a classification of 0 or 1. The predicted output will be the actual value if it is a regression model. The endpoint descriptions are as follows:
| Dataset | Dataset Abbr. | ADMET Type | Dataset Type | Endpoints Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Caco-2 (Cell Effective Permeability), Wang et al. | caco2 | Absorption | Regression | logPapp |
| PAMPA Permeability, NCATS | pampa | Absorption | Binary classification | high permeability (1) or low-to-moderate permeability (0) in PAMPA assay |
| HIA (Human Intestinal Absorption), Hou et al. | hia | Absorption | Binary classification | good permeability (1) or poor permeability (0) |
| Pgp (P-glycoprotein) Inhibition, Broccatelli et al. | pgp | Absorption | Binary classification | inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| Bioavailability, Ma et al. | bioavailability | Absorption | Binary classification | High (1) or low (0) bioavailability |
| Lipophilicity, AstraZeneca | lipophilicity | Absorption | Regression | octanol/water distribution coefficient (logD at pH 7.4) |
| Solubility, AqSolDB | solubility | Absorption | Regression | logS |
| Hydration Free Energy, FreeSolv | freesolv | Absorption | Regression | Hydration Free Energy (kcal/mol) |
| BBB (Blood-Brain Barrier), Martins et al. | bbbp | Distribution | Binary classification | High (1) or low (0) blood-brain barrier penetration |
| PPBR (Plasma Protein Binding Rate), AstraZeneca | ppbr | Distribution | Regression | Plasma Protein Binding Rate (0-100) |
| CYP P450 2C19 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp2c19_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 2C19 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP P450 2D6 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp2d6_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 2D6 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP P450 3A4 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp3a4_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 3A4 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP P450 1A2 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp1a2_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 1A2 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP P450 2C9 Inhibition, Veith et al. | cyp2c9_inhibition | Metabolism | Binary Classification | P450 2C9 inhibitor (1) or non-inhibitor (0) |
| CYP2C9 Substrate, Carbon-Mangels et al. | cyp2c9_substrate | Metabolism | Binary Classification | CYP2C9 substrate (1) or non-substrate (0) |
| CYP2D6 Substrate, Carbon-Mangels et al. | cyp2d6_substrate | Metabolism | Binary Classification | CYP2CD6 substrate (1) or non-substrate(0) |
| CYP3A4 Substrate, Carbon-Mangels et al. | cyp3a4_substrate | Metabolism | Binary Classification | CYP3A4 substrate (1) or non-substrate(0) |
| Microsome Clearance, AstraZeneca | clearance_microsome | Excretion | Regression | Microsome Clearance (CL) |
| Acute Toxicity LD50 | ld50 | Toxicity | Regression | Acute Toxicity LD50 |
| hERG blockers | herg_blockers | Toxicity | Binary classification | hERG blockers (1) or non-blockers (0) |
| hERG Karim et al. | herg_karim | Toxicity | Binary classification | hERG blockers (1) or non-blockers (0) |
| Ames Mutagenicity | ames | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) ames mutagenicity |
| DILI (Drug Induced Liver Injury) | dili | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) drug induced liver injury |
| Skin Reaction | skin | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) skin reaction |
| ClinTox | clintox | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) ClinTox |
| Carcinogens | carcinogens | Toxicity | Binary classification | high (1) or low (0) Carcinogens |

Evaluate Nucleic Acid (AlphaRNA)模块用于评估核酸序列的其表达量和半衰期、抗体滴度等。支持人、小鼠、大鼠、猪等种属。
核酸序列,必须为3的倍数,否则截断尾部序列以达到3的倍数序列,比如:GGAGCCGAGGCGGGCCGATTCACGATCGGTTCGCAAAAACTGTTTGGG
序列所属物种,Homo_Sapiens、Mamalian、Pig、Rat。
输出结果文件为result.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| AUP | AUP (Amino Acid Usage Pattern)指的是氨基酸使用模式的指标,通常用于评估特定氨基酸在序列中的使用频率。值越高,表示该氨基酸在序列中使用的频率越高。 |
| CAI | CAI (Codon Adaptation Index)是一个用于评估特定基因的密码子使用偏好度的指标,值范围从 0 到 1。接近 1 表示该基因的密码子使用模式与高表达基因的模式相似,通常与基因表达效率相关。 |
| GCR | GCR (Gene Codon Ratio)是基因密码子比率的指标,反映了基因中不同密码子的相对使用情况。值越高,表示基因中使用的密码子与参考密码子库的偏好越一致。 |
| MFE | MFE (Minimum Free Energy)是指核酸序列的最低自由能,通常用于评估 RNA 二级结构的稳定性。值越低表示结构越稳定。负值表示该序列在折叠时释放能量,形成稳定的构象。 |
| Aug Positions | Aug Positions表示在序列中发现的AUG(起始密码子)的位置。结果空时表示在序列中没有找到AUG密码子。 |
| Sequence | 根据输入的核酸序列翻译得到的氨基酸序列。 |
| Secondary Structure | RNA序列的预测二级结构。 |
The Evaluate Nucleic Acid (AlphaRNA) module is used to assess the expression levels, half-lives, antibody titers, and other characteristics of nucleic acid sequences.
The nucleic acid sequence must be a multiple of three; otherwise, the tail of the sequence will be truncated to achieve a length that is a multiple of three. For example: GGAGCCGAGGCGGGCCGATTCACGATCGGTTCGCAAAAACTGTTTGGG.
The species to which the sequence belongs, such as Homo_Sapiens, Mammalian, Pig, or Rat.
The output result file is result.csv, which contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| AUP | AUP (Amino Acid Usage Pattern) indicates the usage pattern of amino acids, typically used to assess the frequency of specific amino acids in the sequence. A higher value indicates a higher frequency of that amino acid in the sequence. |
| CAI | CAI (Codon Adaptation Index) is a metric used to evaluate the codon usage preference of a specific gene, with values ranging from 0 to 1. A value close to 1 indicates that the codon usage pattern of the gene is similar to that of highly expressed genes, which is often related to gene expression efficiency. |
| GCR | GCR (Gene Codon Ratio) is an indicator of the gene codon ratio, reflecting the relative usage of different codons within the gene. A higher value indicates that the codons used in the gene are more consistent with the preferences of the reference codon library. |
| MFE | MFE (Minimum Free Energy) refers to the minimum free energy of the nucleic acid sequence, typically used to assess the stability of RNA secondary structures. Lower values indicate more stable structures. Negative values indicate that the sequence releases energy when folded, forming a stable conformation. |
| Aug Positions | Aug Positions indicates the positions of AUG (start codon) found in the sequence. An empty result means that no AUG codons were found in the sequence. |
| Sequence | The amino acid sequence translated from the input nucleic acid sequence. |
| Secondary Structure | The predicted secondary structure of the RNA sequence. |

Back Mutation Grouping是抗体人源化设计流程中分组模块,根据Mutation Score模块输出的回复突变评分表对回复突变进行分组,并返回突变后的序列。
抗体CDR区嫁接后序列文件,FASTA格式,由Grafting模块生成
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式
人源化突变评分文件,CSV格式,由Mutation Score模块生成
指定输出的突变序列文件名称,FASTA格式
打分分组的截断值,逗号分割,例如:2,5,10表示将氨基酸突变评分大于10的为一组,5~10的氨基酸为一组,小于2的氨基酸分为一组。
指定输出的回复突变的文件
根据不同截断值得到突变分组结果文件mutate_policy.json。
Back Mutation Grouping is a grouping module in the humanization design process of antibodies, which groups back mutations based on the mutation score table output by the Mutation Score module and returns the mutated sequences.
Sequence file of the antibody CDR region after grafting, in FASTA format, generated by the Grafting module.
Sequence file of the antibody, in FASTA format.
Humanization mutation score file, in CSV format, generated by the Mutation Score module.
Specify the name of the output mutation sequence file, in FASTA format.
Cutoff values for scoring grouping, separated by commas. For example, 2,5,10 indicates grouping amino acid mutations with scores greater than 10 in one group, amino acids with scores between 5 and 10 in another group, and amino acids with scores less than 2 in a separate group.
Specify the file for the output of back mutations.
The mutation grouping results file, mutate_policy.json, is generated based on different cutoff values.

基于自定义的蛋白结构模板,采用colabfold进行蛋白结构预测。
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式
蛋白的模板结构,PDB格式
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| rank_001.pdb | 预测得到的最佳复合物结构。 |
| pdbs.tar.gz | 预测得到的前5个最佳复合物结构的压缩包文件。 |
| scores.csv | 预测结构的评分文件 |
其中scores.csv包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 预测结构的文件名 |
| pLDDT | 局部结构的可信度指标,值范围是0-100,该值越大说明预测的结构越可靠。低于70被认为可靠性较低,低于50基本认为是可信度非常低,为无序预测 |
| pTM | 预测的TM分数(the predicted template modeling score),衡量预测结构整体准确性,越大表示越准确,该分数大于0.5时,表示结构整体折叠可能与真实结构相似 |
| ipTM | 预测的亚基接触面的TM分数(the interface predicted template modeling score),当预测结构为复合物时才有该评价指标,衡量复合物中各个亚基之间相对位置的预测准确性,越大表示越准确,大于0.8表示高质量预测,小于0.6表示预测可能失败,0.6-0.8为灰色地带,预测正确与否不确定 |
Protein structure prediction is performed using ColabFold based on a custom protein structure template.
The sequence file of the protein in FASTA format.
The template structure of the protein in PDB format.
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| rank_001.pdb | The predicted best complex structure. |
| pdbs.tar.gz | A compressed file containing the top 5 best complex structures. |
| scores.csv | The scoring file for the predicted structures. |
The scores.csv file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The file name of the predicted structure. |
| pLDDT | The confidence score for local structure, with a range of 0-100. A higher value indicates a more reliable prediction. Values below 70 are considered low reliability, below 50 are generally regarded as very low confidence, indicating disordered predictions. |
| pTM | The predicted template modeling score, which measures the overall accuracy of the predicted structure. A higher score indicates greater accuracy. If the score is greater than 0.5, it suggests that the overall folding of the structure may be similar to the true structure. |
| ipTM | The interface predicted template modeling score, which measures the accuracy of the predicted relative positions of the subunits in the complex. A higher score indicates greater accuracy. Scores above 0.8 indicate high-quality predictions, while scores below 0.6 suggest potential failure of the prediction. Scores between 0.6 and 0.8 are in a gray area, where the accuracy of the prediction is uncertain. |

细胞免疫系统是人体免疫的重要组成部分,它使用 T 细胞受体 (TCR) 识别由主要组织相容性复合体 (MHC) 蛋白呈递的肽形式的抗原蛋白。准确定义TCR的结构基础及其与肽-MHC的结合可以为正常和异常免疫提供重要见解,并有助于指导疫苗和免疫疗法的设计。鉴于实验确定的TCR-肽-MHC结构数量有限,而每个个体内的TCR以及抗原靶标数量巨大,因此需要准确的建模方法。该模块基于TCRmodel2实现,TCRmodel2在AlphaFold基础上对TCR-肽-MHC复合物建模做了优化,与原生AlphaFold和其他基于基准测试的TCR-肽-MHC复合物建模方法相比,其准确度相似或更高,可在30分钟内完成复合物结构预测。
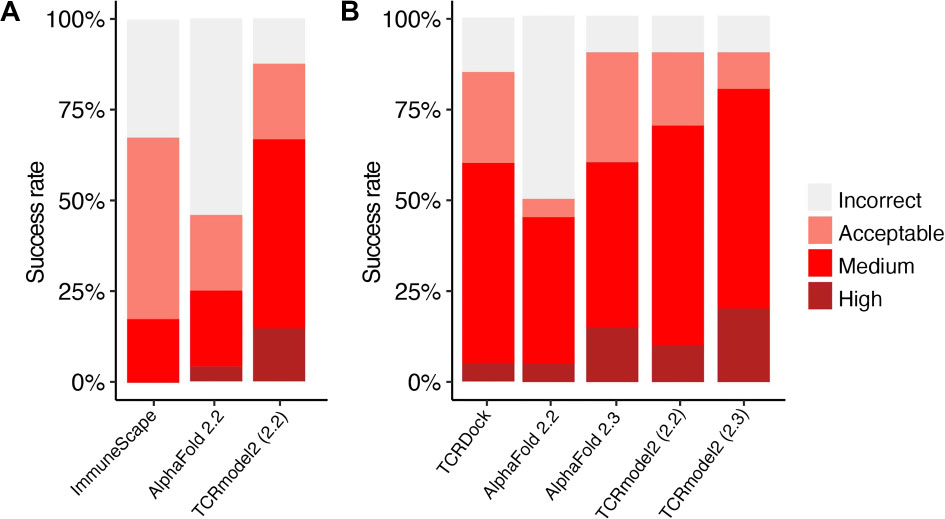
TCR α链的序列,如:AQEVTQIPAALSVPEGENLVLNCSFTDSAIYNLQWFRQDPGKGLTSLLLIQSSQREQTSGRLNASLDKSSGRSTLYIAASQPGDSATYLCAVTNQAGTALIFGKGTTLSVSS
TCR β链的序列,如:NAGVTQTPKFQVLKTGQSMTLQCSQDMNHEYMSWYRQDPGMGLRLIHYSVGAGITDQGEVPNGYNVSRSTTEDFPLRLLSAAPSQTSVYFCASSYSIRGSRGEQFFGPGTRLTVL
多肽序列,如:LAWEWWRTVAL
注:输入的多肽序列长度需要符合相应要求,如下:
I型TCR-pMHC复合物中,多肽的序列长度在8-15之间;
II型TCR-pMHC复合物中,多肽的长度为11。
MHC-I型序列或MHC-II α链序列。
当预测I型TCR-pMHC复合物时,输入MHC-I型序列,如:SHSLKYFHTSVSRPGRGEPRFISVGYVDDTQFVRFDNDAASPRMVPRAPWMEQEGSEYWDRETRSARDTAQIFRVNLRTLRGYYNQSEAGSHTLQWMHGCELGPDGRFLRGYEQFAYDGKDYLTLNEDLRSWTAVDTAAQISEQKSNDASEAEHQRAYLEDTCVEWLHKYLEKGKETLLH
当预测II型TCR-pMHC复合物时,输入MHC-II α链序列,如:IKADHVSTYAAFVQTHRPTGEFMFEFDEDEMFYVDLDKKETVWHLEEFGQAFSFEAQGGLANIAILNNNLNTLIQRSNHTQAT
MHC-II β链序列,当预测II型TCR-pMHC复合物时才需要输入,如:PENYLFQGRQECYAFNGTQRFLERYIYNREEFARFDSDVGEFRAVTELGRPAAEYWNSQKDILEEKRAVPDRMCRHNYELGGPMTLQR
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ranked_0.pdb | 预测得到的最佳复合物结构。 |
| pdbs.tar.gz | 预测得到的前5个最佳复合物结构的压缩包文件。 |
| scores.csv | 结构评分文件 |
其中scores.csv包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| PDB | 复合物PDB结构的文件名 |
| Model_Confidence | 结构的置信度评分,是pTM与ipTM评分的加权综合值,数值在0-1之间,越接近1表示结构模型质量越好 |
| pLDDT | 局部结构的可信度指标,值范围是0-100,该值越大说明预测的结构越可靠。低于70被认为可靠性较低,低于50基本认为是可信度非常低,为无序预测 |
| pTM | the predicted template modeling score预测的TM分数,衡量预测结构整体准确性,越大表示越准确,该分数大于0.5时,表示结构整体折叠可能与真实结构相似 |
| ipTM | the interface predicted template modeling score预测的亚基接触面的TM分数,衡量复合物中各个亚基之间相对位置的预测准确性,越大表示越准确,大于0.8表示高质量预测,小于0.6表示预测可能失败,0.6-0.8为灰色地带,预测正确与否不确定 |
| TCR-pMHC_ipTM | TCR与pMHC之间的ipTM值 |
The cellular immune system is a crucial component of the human immune response, utilizing T cell receptors (TCRs) to recognize peptide-form antigens presented by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins. Accurately defining the structural basis of TCRs and their binding to peptide-MHC complexes can provide important insights into both normal and abnormal immune responses and assist in guiding the design of vaccines and immunotherapies. Given the limited number of experimentally determined TCR-peptide-MHC structures and the vast number of TCRs and antigen targets within each individual, accurate modeling methods are needed. This module is based on TCRmodel2, which optimizes TCR-peptide-MHC complex modeling on the foundation of AlphaFold. It achieves comparable or higher accuracy than native AlphaFold and other benchmark-based TCR-peptide-MHC modeling methods, completing complex structure predictions within 30 minutes.


The sequence of the TCR α chain, for example: AQEVTQIPAALSVPEGENLVLNCSFTDSAIYNLQWFRQDPGKGLTSLLLIQSSQREQTSGRLNASLDKSSGRSTLYIAASQPGDSATYLCAVTNQAGTALIFGKGTTLSVSS
The sequence of the TCR β chain, for example: NAGVTQTPKFQVLKTGQSMTLQCSQDMNHEYMSWYRQDPGMGLRLIHYSVGAGITDQGEVPNGYNVSRSTTEDFPLRLLSAAPSQTSVYFCASSYSIRGSRGEQFFGPGTRLTVL
The peptide sequence, for example: LAWEWWRTVAL.
Note: The length of the input peptide sequence must meet the following requirements:
For Class I TCR-pMHC complexes, the peptide sequence length should be between 8-15;
For Class II TCR-pMHC complexes, the peptide length is 11.
The MHC-I sequence or MHC-II α chain sequence.
When predicting Class I TCR-pMHC complexes, input the MHC-I sequence, for example: SHSLKYFHTSVSRPGRGEPRFISVGYVDDTQFVRFDNDAASPRMVPRAPWMEQEGSEYWDRETRSARDTAQIFRVNLRTLRGYYNQSEAGSHTLQWMHGCELGPDGRFLRGYEQFAYDGKDYLTLNEDLRSWTAVDTAAQISEQKSNDASEAEHQRAYLEDTCVEWLHKYLEKGKETLLH.
When predicting Class II TCR-pMHC complexes, input the MHC-II α chain sequence, for example: IKADHVSTYAAFVQTHRPTGEFMFEFDEDEMFYVDLDKKETVWHLEEFGQAFSFEAQGGLANIAILNNNLNTLIQRSNHTQAT.
The MHC-II β chain sequence, which is required only when predicting Class II TCR-pMHC complexes, for example: PENYLFQGRQECYAFNGTQRFLERYIYNREEFARFDSDVGEFRAVTELGRPAAEYWNSQKDILEEKRAVPDRMCRHNYELGGPMTLQR.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ranked_0.pdb | The predicted best complex structure. |
| pdbs.tar.gz | A compressed file containing the top 5 predicted complex structures. |
| scores.csv | Structure scoring file. |
The scores.csv contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PDB | The filename of the complex PDB structure. |
| Model_Confidence | The confidence score of the structure, which is a weighted composite value of pTM and ipTM scores, ranging from 0 to 1, with values closer to 1 indicating better model quality. |
| pLDDT | A measure of the reliability of the local structure, ranging from 0 to 100; higher values indicate more reliable predictions. Values below 70 are considered low reliability, and below 50 are deemed very low reliability, indicating disordered predictions. |
| pTM | The predicted template modeling score, which measures the overall accuracy of the predicted structure; higher values indicate greater accuracy. A score greater than 0.5 suggests that the overall folding of the structure may resemble the true structure. |
| ipTM | The interface predicted template modeling score, which measures the accuracy of the predicted relative positions of subunits within the complex; higher values indicate greater accuracy. Scores above 0.8 indicate high-quality predictions, while scores below 0.6 suggest potential failure, and scores between 0.6 and 0.8 are in a gray area where correctness is uncertain. |
| TCR-pMHC_ipTM | The ipTM value between the TCR and pMHC. |

Alanine Scan (MMPBSA)是计算丙氨酸突变后的结合自由能,并且提供能量分解数据、结合常数(Ka)、抑制剂常数(Ki)。熵的计算采用的是张增辉教授的相互作用熵的方法,该方法直接从分子动力学模拟计算结合自由能的熵组分(相互作用熵或-TΔS),但是需要选取结构稳定部分进行计算。
本模块提供四种计算方法,其中 Trajectory 是针对进行分子动力学模拟轨迹后计算其受配体之间的结合自由能;One Structure 是针对一帧pdb结构或者对接得到的PDB结构计算受配体之间的结合自由能,MMPBSA of One Structure 计算流程中可以直接输入PDB进行计算。
Index Name 是输入受配体组别名称;Custom Name 则是输入受配体的在PDB中的残基编号。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD模块中获取。
受体名称,可以为Protein、DNA、RNA。
配体名称,可以为Protein、DNA、RNA。如果为小分子,填写其在PDB中的名称。如果体系中除了蛋白以外为配体(包括小分子)可用Other表示。
突变扫描为丙氨酸(ALA)的氨基酸位置。格式为res1:res2:res3:res4,其中“res1-res4”数字为残基编号。
丙氨酸扫描时使用的力场。
起始帧时间,单位ps。最好选取RMSD稳定时区进行计算,以消除结构不稳定时导致的整体熵偏大。
结束帧时间,单位ps。最好选取RMSD稳定时区进行计算,以消除结构不稳定时导致的整体熵偏大。
间隔时间,单位ps。
索引文件,ndx格式。当体系中存在膜结构的时候可以通过Membrane Solvation模块获取index.ndx文件。膜模拟中的受体为receptor,配体为ligand,膜为membrane。只能是AMBER力场下构建的膜体系才能进行计算。
定义受体组别进行结合能计算。组别中填写的为蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基的序号。例如1-213或者1-211,212-213。蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基序号从1开始重新编号,与初始pdb氨基酸编号无关。
定义配体组别进行结合能计算。组别中填写的为蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基的序号。例如1-213或者1-211,212-213。蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基序号从1开始重新编号,与初始pdb氨基酸编号无关。
拓扑文件,由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
结构文件,.gro格式,由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
体系参数压缩文件,tar.gz格式。由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA_result.txt | MMPBSA丙氨酸突变结果汇总文件。 |
| MMPBSA_Residue.csv | 丙氨酸突变能量分解数据CSV文件。 |
| MMPBSA.pdb | 丙氨酸突变后,原子对应的MMPBSA能量放到PDB文件。可以做对应能量类别的表面图,从图的颜色深浅可以看出哪些区域对结合能贡献值较大。 |
| MMPBSA.tar.gz | MMPBSA所有原始文件。包括_mmpbsa_residue_#.txt是每个残基对应的每个能量类别的数值,共包含7个能量类别:范德华能(VDW)、静电能(ELE)、溶剂化能极性部分(PB)、溶剂化能非极性部分(SA)、VDW+ELE=MM、PB+SA=PBSA、MM+PBSA=Binding/MMPBSA。_mmpbsa_residue.txt是对上述7个文件的总结,即为MMPBSA_Residue.csv对应的原始文件。_mmpbsa_atom#.pdb是将每个原子对应的能量类别放到pdb文件,与MMPBSA.pdb相似。 |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Duan L, Liu X, Zhang JZ. Interaction Entropy: A New Paradigm for Highly Efficient and Reliable Computation of Protein-Ligand Binding Free Energy. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 May 4;138(17):5722-8.
https://github.com/Electrostatics/apbs/blob/main/docs/index.rst
Alanine Scan (MMPBSA) calculates the binding free energy after alanine mutations and provides energy decomposition data, binding constants (Ka), and inhibitor constants (Ki). The entropy calculation uses the method of interaction entropy proposed by Professor Zhang Zenghui, which directly calculates the entropy component of the binding free energy (interaction entropy or -TΔS) from molecular dynamics simulations, but requires selecting stable structural regions for calculation. This module provides four calculation methods. Among them, Trajectory calculates the binding free energy between the receptor and ligand after molecular dynamics simulation trajectories; One Structure calculates the binding free energy between the receptor and ligand for a single frame PDB structure or a docked PDB structure; MMPBSA of One Structure allows direct input of a PDB for calculation. Index Name is the input receptor-ligand group name, while Custom Name is the input residue numbers of the receptor-ligand in the PDB.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, available in the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or AlphaAutoMD module.
Name of the receptor, can be Protein, DNA, or RNA.
Name of the ligand, can be Protein, DNA, or RNA. If it is a small molecule, enter its name in the PDB. Use ‘Other’ if the system contains a ligand (including small molecules) other than proteins.
Amino acid positions where mutations to alanine (ALA) are scanned. The format is res1:res2:res3:res4, where “res1-res4” are residue numbers.
Force field used for alanine scanning.
Start frame time in ps. It is best to select a stable RMSD region for calculation to eliminate large overall entropy caused by structural instability.
End frame time in ps. It is best to select a stable RMSD region for calculation to eliminate large overall entropy caused by structural instability.
Time interval in ps.
Index file in ndx format. When there is a membrane structure in the system, you can obtain the index.ndx file through the Membrane Solvation module. In membrane simulations, the receptor is ‘receptor’, the ligand is ‘ligand’, and the membrane is ‘membrane’. Only membrane systems built under the AMBER force field can be calculated.
Define receptor groups for binding energy calculation. Enter the sequence numbers of protein amino acids or nucleic acid bases in the group. For example, 1-213 or 1-211,212-213. Protein amino acid or nucleic acid base numbers start from 1 and are independent of the initial pdb amino acid numbering.
Define ligand groups for binding energy calculation. Enter the sequence numbers of protein amino acids or nucleic acid bases in the group. For example, 1-213 or 1-211,212-213. Protein amino acid or nucleic acid base numbers start from 1 and are independent of the initial pdb amino acid numbering.
Topology file obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
Structure file in .gro format obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
System parameter compression file in tar.gz format. Obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA_result.txt | Summary file of MMPBSA alanine mutation results. |
| MMPBSA_Residue.csv | Energy decomposition data for alanine mutations in CSV format. |
| MMPBSA.pdb | MMPBSA energy corresponding to atoms after alanine mutations in a PDB file. This can be used to create a surface map of energy categories, where the color depth indicates the regions contributing significantly to the binding energy. |
| MMPBSA.tar.gz | All original MMPBSA files. Includes mmpbsa_residue#.txt which contains the values of each energy category for each residue, totaling 7 energy categories: van der Waals energy (VDW), electrostatic energy (ELE), polar part of solvation energy (PB), nonpolar part of solvation energy (SA), VDW+ELE=MM, PB+SA=PBSA, MM+PBSA=Binding/MMPBSA. _mmpbsa_residue.txt is a summary of the above 7 files, corresponding to the original file MMPBSA_Residue.csv. _mmpbsa_atom#.pdb assigns the energy categories to each atom in a pdb file, similar to MMPBSA.pdb. |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Duan L, Liu X, Zhang JZ. Interaction Entropy: A New Paradigm for Highly Efficient and Reliable Computation of Protein-Ligand Binding Free Energy. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 May 4;138(17):5722-8.
https://github.com/Electrostatics/apbs/blob/main/docs/index.rst

通过序列比对在人类生殖系数据库中搜索与目标抗体序列最接近的同源模板,输出对应的模板序列以及序列一致性信息。
抗体的序列(纯序列信息,非FASTA格式文件)。
抗体编号类型:kabat、chothia、imgt。
输出同源性最高的n条序列。
抗体的序列文件,FASTA格式。
抗体编号类型:kabat、chothia、imgt。
输出同源性最高的n条序列。
| 输出参数 | 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Hits Sequence | hits.fasta | 包含同源性最高的n条序列的序列文件 |
| Result | result.json | 包含找到的Germline模板以及序列的一致性信息 |
抗体常用的germline模板:

临床后期及已上市抗体的germline配对分布情况(统计自Adimab数据集):



This module performs sequence alignment to search for the closest homologous template in the human germline database for a given target antibody sequence. It outputs the corresponding template sequence along with sequence similarity information.
The antibody sequence (pure sequence information, not in FASTA format).
Type of antibody numbering: kabat, chothia, imgt.
Number of top hits to output.
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
Type of antibody numbering: kabat, chothia, imgt.
Number of top hits to output.
| Output Parameter | Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hits Sequence | hits.fasta | File containing the top n sequences with the highest homology |
| Result | result.json | File containing the found Germline template and sequence similarity information |
Commonly used germline templates for antibodies:

Distribution of germline pairing for late-stage and marketed antibodies (statistics from the Adimab dataset):




Humanization Report是抗体人源化设计报告生成模块,用于生成最终的抗体人源化设计报告以及相应的专利实施例段落。
Grafting模块生成的Graft Policy文件。
Back Mutation Grouping模块生成的Policy文件。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BM.pptx | 回复突变位点汇总文件 |
| batch_registration_template.xlsx | 批量注册模板文件 |
| hotspot_summary.xlsx | 风险位点总结 |
| patent_example_template.docx | 人源化设计序列在相应的专利实施例段落 |
| humanized_variants.fasta | 抗体人源化设计序列文件,FASTA格式 |
| Report.docx | 抗体人源化设计报告,包括整个人源化设计过程涉及的序列、分组等信息 |
其中batch_registration_template.xlsx包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein Sequence | 蛋白序列 |
| Molecule Name | 分子名称 |
其中hotspot_summary.xlsx包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ID | 抗体序列名称 |
| Sequence-CDR | CDR序列区域 |
| Deamidation | 脱酰胺位点 |
| Isomerization | 异构化位点 |
| Cleavage | 酶切位点 |
| Hydrolysis | 水解位点 |
| Glycosylation | 糖基化位点 |
| Cys | 半胱氨酸数量 |
| Oxidation | 氧化位点 |
| High risk | 高风险率 |
| High risk sites | 高风险位点 |
The Humanization Report is a module for generating reports on antibody humanization design, including the final antibody humanization design report and corresponding paragraphs for patent implementation examples.
The Graft Policy file generated by the Grafting module.
The Policy file generated by the Back Mutation Grouping module.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BM.pptx | Summary file of back mutation sites |
| batch_registration_template.xlsx | Batch registration template file |
| hotspot_summary.xlsx | Summary of hotspot sites |
| patent_example_template.docx | Humanization design sequences in corresponding patent implementation example paragraphs |
| humanized_variants.fasta | Antibody humanization design sequence file in FASTA format |
| Report.docx | Antibody humanization design report, including information on sequences, grouping, etc., involved in the entire humanization design process |
The batch_registration_template.xlsx file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein Sequence | Protein sequence |
| Molecule Name | Molecule name |
The hotspot_summary.xlsx file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Antibody sequence name |
| Sequence-CDR | CDR sequence region |
| Deamidation | Deamidation site |
| Isomerization | Isomerization site |
| Cleavage | Cleavage site |
| Hydrolysis | Hydrolysis site |
| Glycosylation | Glycosylation site |
| Cys | Number of cysteines |
| Oxidation | Oxidation site |
| High risk | High-risk rate |
| High risk sites | High-risk sites |

Back Mutation Grouping是抗体人源化设计流程中分组模块,根据Mutation Score模块输出的回复突变评分表对回复突变进行分组,并返回突变后的序列。
抗体CDR区嫁接后序列文件,FASTA格式,由Grafting模块生成
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式
人源化突变评分文件,CSV格式,由Mutation Score模块生成
指定输出的突变序列文件名称,FASTA格式
打分分组的截断值,逗号分割,例如:2,5,10表示将氨基酸突变评分大于10的为一组,5~10的氨基酸为一组,小于2的氨基酸分为一组。
指定输出的回复突变的文件
根据不同截断值得到突变分组结果文件mutate_policy.json。
Back Mutation Grouping is a grouping module in the humanization design process of antibodies, which groups back mutations based on the mutation score table output by the Mutation Score module and returns the mutated sequences.
Sequence file of the antibody CDR region after grafting, in FASTA format, generated by the Grafting module.
Sequence file of the antibody, in FASTA format.
Humanization mutation score file, in CSV format, generated by the Mutation Score module.
Specify the name of the output mutation sequence file, in FASTA format.
Cutoff values for scoring grouping, separated by commas. For example, 2,5,10 indicates grouping amino acid mutations with scores greater than 10 in one group, amino acids with scores between 5 and 10 in another group, and amino acids with scores less than 2 in a separate group.
Specify the file for the output of back mutations.
The mutation grouping results file, mutate_policy.json, is generated based on different cutoff values.

Grafting模块是移植抗体的CDR到特定的框架区模板上,通常用于人源化设计。版本:v2.3
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式
抗体编号规则:kabat,imgt,chothia
指定输出抗体graft后的序列文件名称,FASTA格式
指定输出graft策略文件,JSON格式
指定输出抗体FR区序列比对同源性打分文件
指定轻链或重链使用特定germline模板,也可都指定,写法如下:
seq_name1:germline_name1,seq_name2:germline_name2
其中链名来自于流程第一步输入的fasta文件。
例1:以下语句为链"Infliximab.H"指定了模板"IGHV3-7*01":
Infliximab.H:IGHV3-7*01
例2:以下语句为两条链分别指定了模板:
Infliximab.H:IGHV3-7*01,Infliximab.L:IGKV1-39*01
指定参考模板序列,FASTA格式
指定输出FR区序列比对结果文件,FASTA格式
指定输出命中序列的数目
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| germline_hits.fasta | 输出FR区序列比对结果文件 |
| germline_score.json | 输出抗体FR区序列比对同源性打分文件 |
| grafted.fasta | 输出抗体graft后的序列文件名称 |
| graft_policy.json | 输出graft策略文件 |
The Grafting module is used to graft the CDRs of an antibody onto a specific framework region template, typically used for humanization design. Version: v2.3
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
Antibody numbering rule: kabat, imgt, chothia.
Specify the output file name for the grafted antibody sequence in FASTA format.
Specify the output grafting strategy file in JSON format.
Specify the output file for the homology scores of the antibody FR region sequences.
Specify the specific germline template to be used for the light chain or heavy chain, or both, in the format:
seq_name1:germline_name1,seq_name2:germline_name2
Where the chain names come from the FASTA file input in the first step of the process.
Example 1: The following statement specifies the template “IGHV3-7*01” for the chain “Infliximab.H”:
Infliximab.H:IGHV3-7*01
Example 2: The following statement specifies templates for two chains separately:
Infliximab.H:IGHV3-7*01,Infliximab.L:IGKV1-39*01
Specify the reference template sequence in FASTA format.
Specify the output file for the FR region sequence alignment results in FASTA format.
Specify the number of sequences to output.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| germline_hits.fasta | Output file for FR region sequence alignment results |
| germline_score.json | Output file for homology scores of the antibody FR region sequences |
| grafted.fasta | Output file name for the grafted antibody sequence |
| graft_policy.json | Output file for the grafting strategy |
.png)
Antibody Numbering v2是抗体编号模块,用于注释抗体可变区(Fv)或恒定区(包括 Fc), 支持几乎所有主流的抗体编号规则,如可变区广泛使用的Kabat、Chothia 和 IMGT,以及恒定区主要使用的EU规则。
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多序列模式。
编号规则,支持Kabat、Chothia、IMGT,可多选。
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多序列模式。
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| output_chothia(imgt\kabat).csv | 抗体可变区三种编号规则的csv文件 |
| output_chothia(imgt\kabat).json | 抗体可变区三种编号规则的json文件 |
三种不同编号规则的csv文件,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| molecule | 抗体序列名称 |
| chain_type | 抗体链类型:重链(VH)或者轻链(VL) |
| is_cdr | 判断是否为CDR区 |
| loc | 序列位置 |
| numbering | 序列编号 |
| insertion | 插入序列编号 |
| region | 抗体可变区类型:CDR1、CDR2或者CDR3 |
| domain | 区域 |
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| output_EU.csv | 抗体恒定区EU编号规则的csv文件 |
| output_EU.json | 抗体恒定区EU编号规则的json文件 |
其中output_EU.csv文件,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | 抗体序列链类型 |
| Position | 序列位置 |
| Eu numbering | 序列EU编号 |
| Residue | 抗体氨基酸缩写 |
| IgG1 Ref | IgG1氨基酸缩号 |
| Region | 抗体恒定类型:CH1、CH2、CH3、Hinge |
| Mutation(IgG1) | 原序列突变成IgG1的突变信息 |
Antibody Numbering v2 is the antibody numbering module for the annotations of antibody variable region (Fv) or constant region (including Fc). It supports almost all mainstream antibody numbering rules, such as Kabat, Chothia and IMGT, which are widely used in the variable region, and EU rules, which are mainly used in the constant region.
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
Numbering Scheme: Kabat, Chothia, and IMGT.
Visualize all three schemes of Fv numberings and CDR regions via a HTML page.
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| results.html | Visualize all three schemes of Fv numberings and CDR regions via a HTML page. |
| output_chothia(imgt\kabat).csv | Visualize all three schemes of Fv numberings and CDR regions via a csv file. |
| output_chothia(imgt\kabat).json | Visualize all three schemes of Fv numberings and CDR regions via a json file. |
Three csv files with different numbering rules contain the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| molecule | Antibody sequence name |
| chain_type | Antibody chain type: heavy chain (VH) or light chain (VL) |
| is_cdr | Check whether it is a CDR region |
| loc | Sequence position |
| numbering | Sequence numbering |
| insertion | Insertion sequence number |
| region | Antibody variable region type: CDR1, CDR2, or CDR3 |
| domain | Area |
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| output_EU.csv | EU numberings for constant region in csv file |
| output_EU.json | EU numberings for constant region in json file |
The output EU.csv file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain | Type of antibody sequence chain |
| Position | Sequence position |
| Eu numbering | Sequence EU numbering |
| Residue | Antibody amino acid abbreviation |
| IgG1 Ref | IgG1 amino acid abbreviation |
| Region | Constant Region type of antibody: CH1, CH2, CH3, Hinge |
| Mutation(IgG1) | Mutation information of the original sequence mutated into IgG1 |

WeADApt (Wecomput ADA prediction) 是一种基于多模融合架构的免疫原性预测系统。该方法有机地将多个与免疫原性相关的模型融合,构成一个高效的免疫反应模拟系统,可准确地模拟蛋白、抗体、多肽、疫苗等生物药的免疫原性,并能鉴别潜在的免疫原性的T细胞表位(引起临床人体免疫应答的肽段)。
该模块为备份版本,最新版本为:v4.2。
使用100多个临床及上市抗体的ADA数据的测试结果显示,预测的打分(MolScore)与ADA发生率的相关性达到R=0.68(下图)。
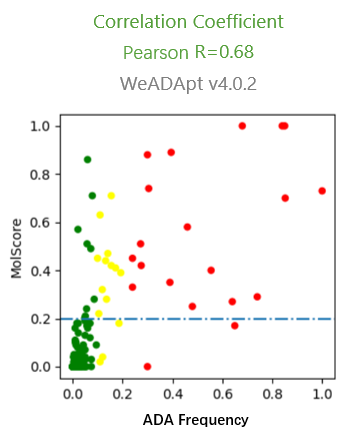
在同样的42个分子的数据集上,WeADApt预测的相关性超过了知名的商业软件EpiMatrix(R2=0.49 vs R2=0.42)。
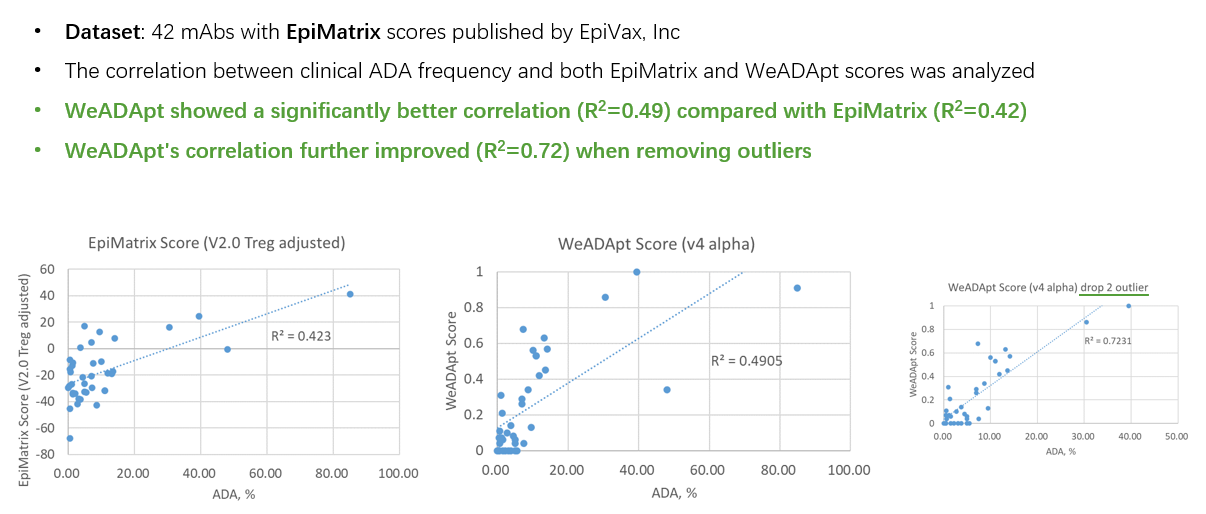
0.2分适合作为单抗的高/低风险的阈值(>20% ADA定义为高风险)。
这类分子仅需输入不重复的链即可
在唯信收集的双抗ADA数据集的测试表现如下图所示。以0.6的分数作为分界线,可以较好的区分高、低风险的双抗分子。双抗
注意,由于存在较多的B细胞清除双抗,其MOA会对ADA产生有较大的影响。
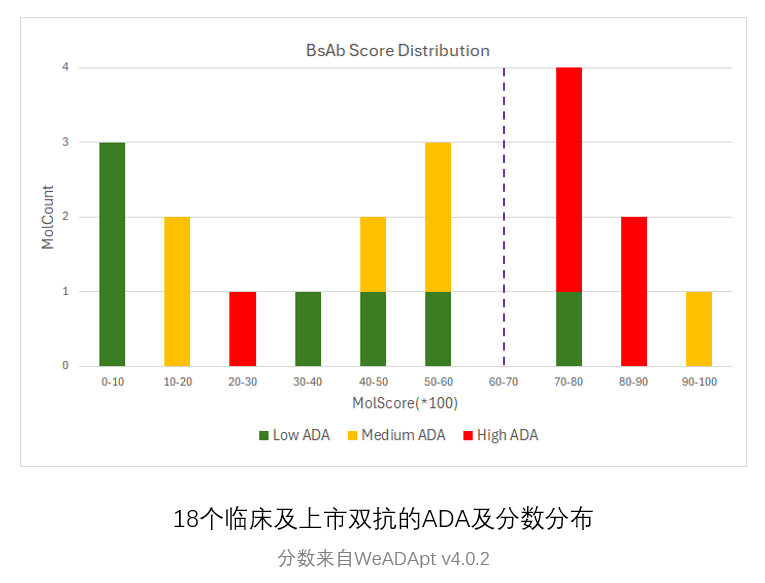
推荐从WeSeq中运行该功能,可以进行更多可视化交互

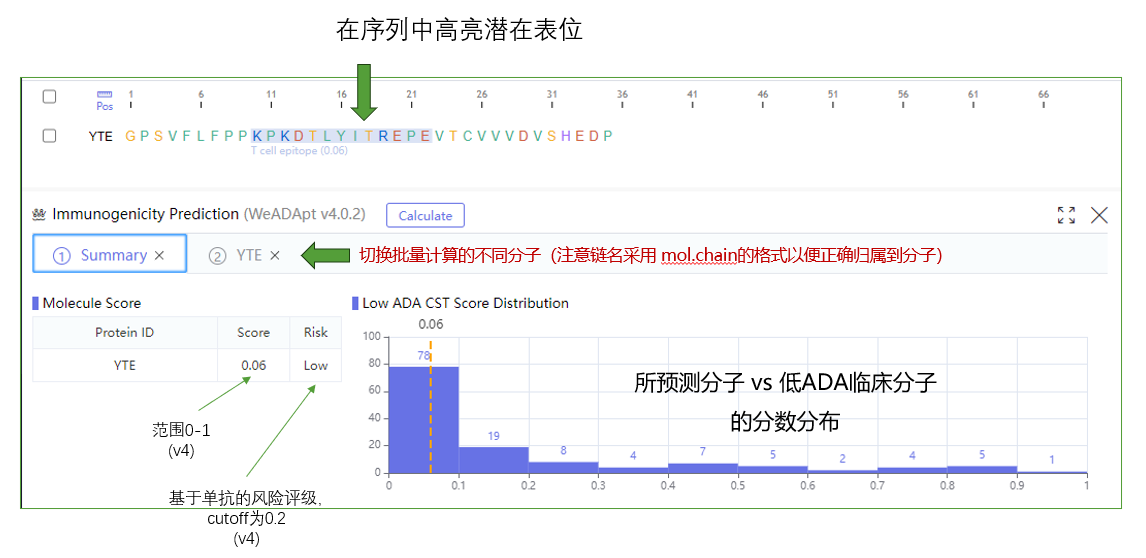
Score为预测的免疫原性风险评分(范围0-1),Risk为风险评级
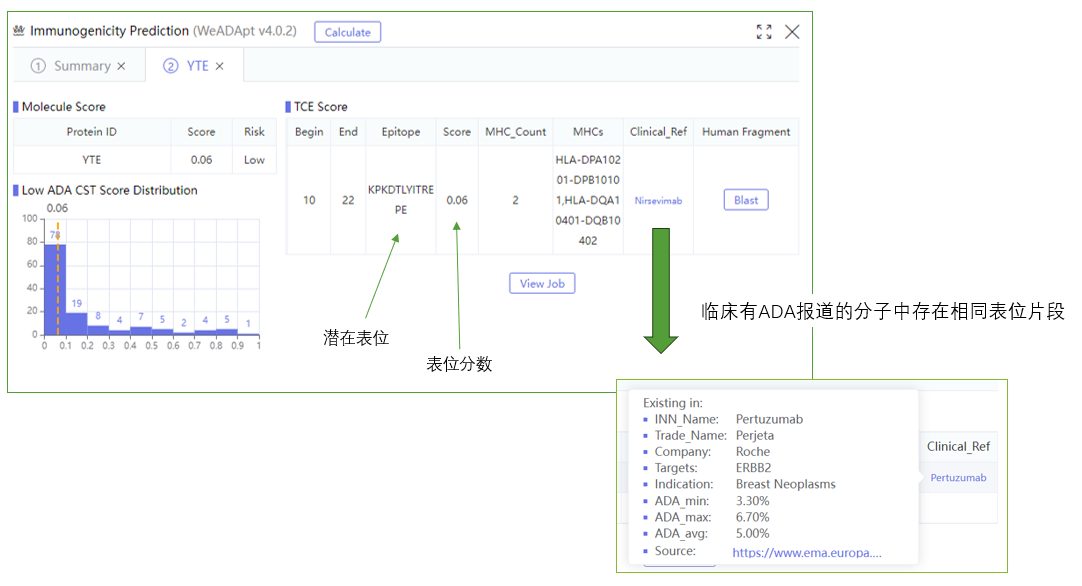
注意对照结构,排除不可及(包埋的)表位(下图)
最简单的方式是进行人源片段的替换,可以直接在WeSeq中进行(下图)。
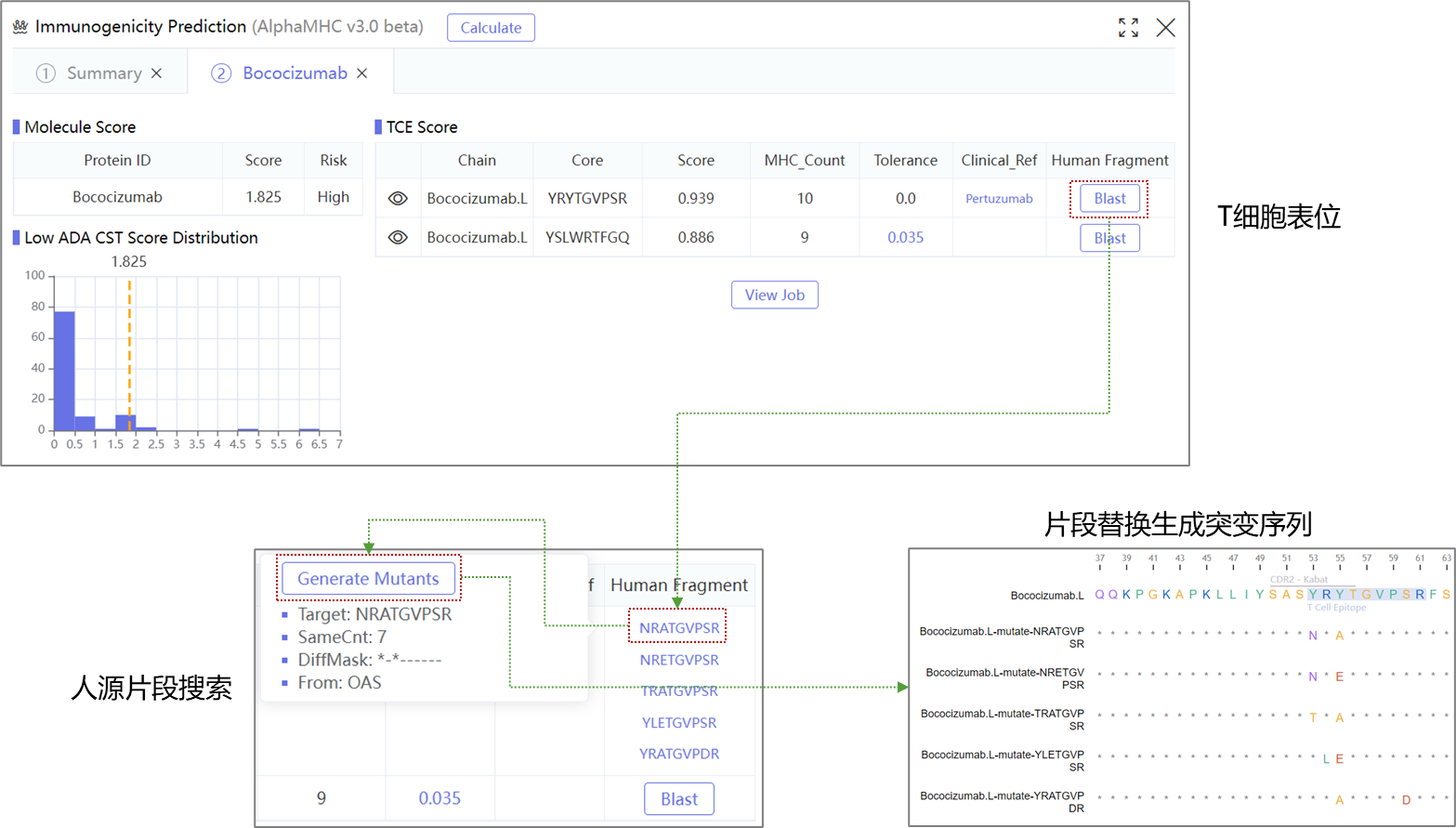
也可以通过频率分析功能引入人源突变。
突变完之后再对突变体预测一下免疫原性是否降低。
注意:从weseq中计算v4免疫原性的结果可以自动保存并且随时再打开的

WeADApt (Wecomput ADA prediction) is an immunogenicity prediction system based on a multi-modal fusion architecture. This method organically integrates multiple models related to immunogenicity to form an efficient immune response simulation system. It can accurately simulate the immunogenicity of biologics such as proteins, antibodies, peptides, and vaccines, and identify potential immunogenic T-cell epitopes (peptide segments that elicit clinical human immune responses). The module is the latest version: v4.1.0.
Testing results using ADA data from over 100 clinical and marketed antibodies show that the predicted scores (MolScore) correlate with ADA incidence at R=0.68 (see the figure below).

On the same dataset of 42 molecules, the correlation predicted by WeADApt exceeds that of the well-known commercial software EpiMatrix (R²=0.49 vs R²=0.42).

A score of 0.2 is suitable as a threshold for high/low risk in monoclonal antibodies (>20% ADA defined as high risk).
For these types of molecules, only non-redundant chains need to be input. The test performance on the bispecific ADA dataset collected by Weixin is shown in the figure below. With a score of 0.6 as the dividing line, high-risk and low-risk bispecific molecules can be better distinguished. Note that due to the presence of many B-cell depleting bispecifics, their MOA can significantly affect ADA.
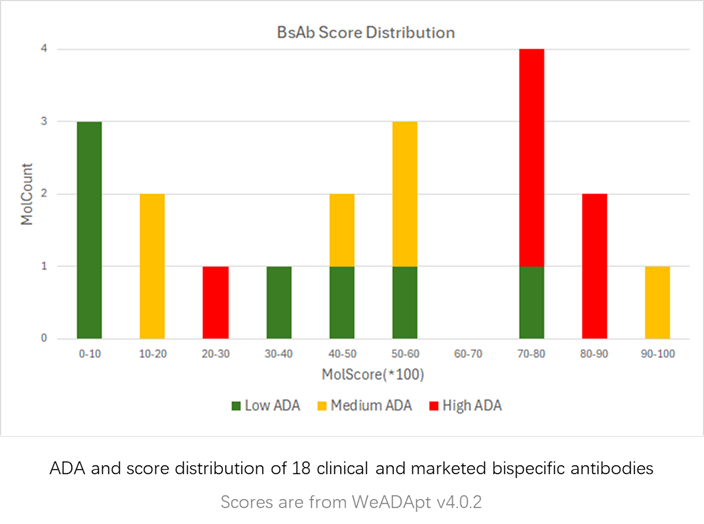
It is recommended to run this function from WeSeq for more visual interactions.
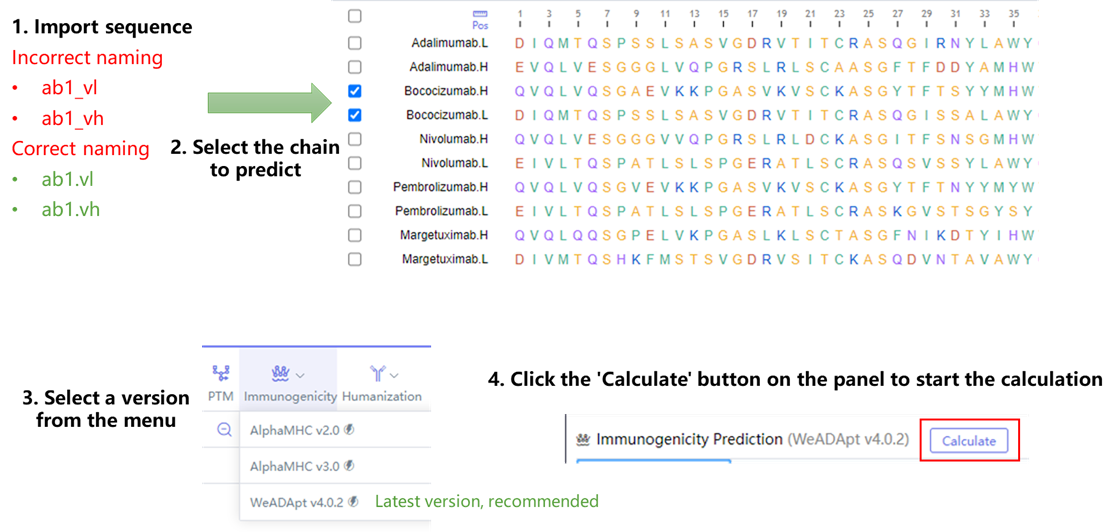

Score is the predicted immunogenicity risk score (range 0-1), and Risk is the risk rating.
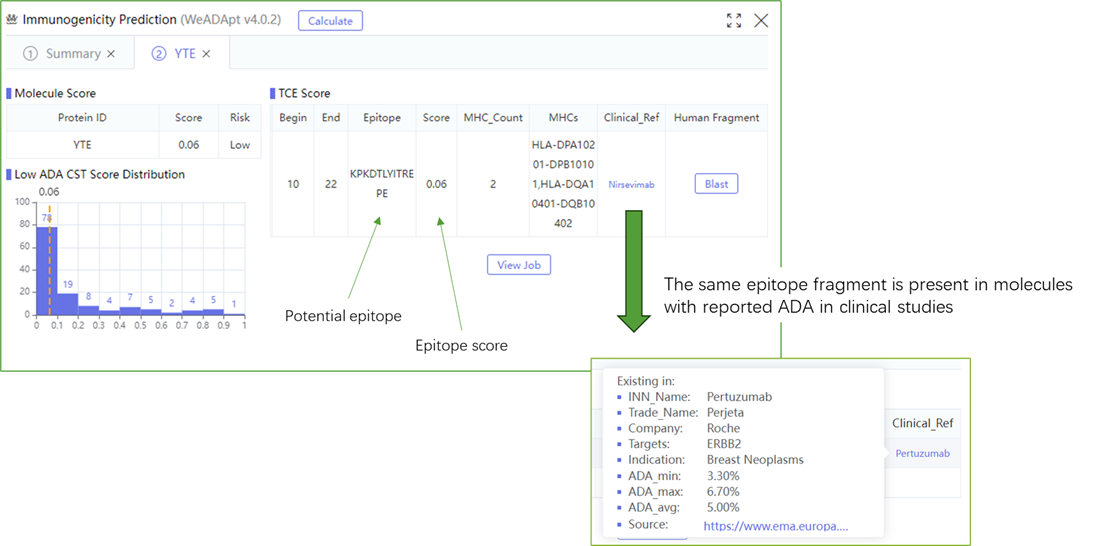
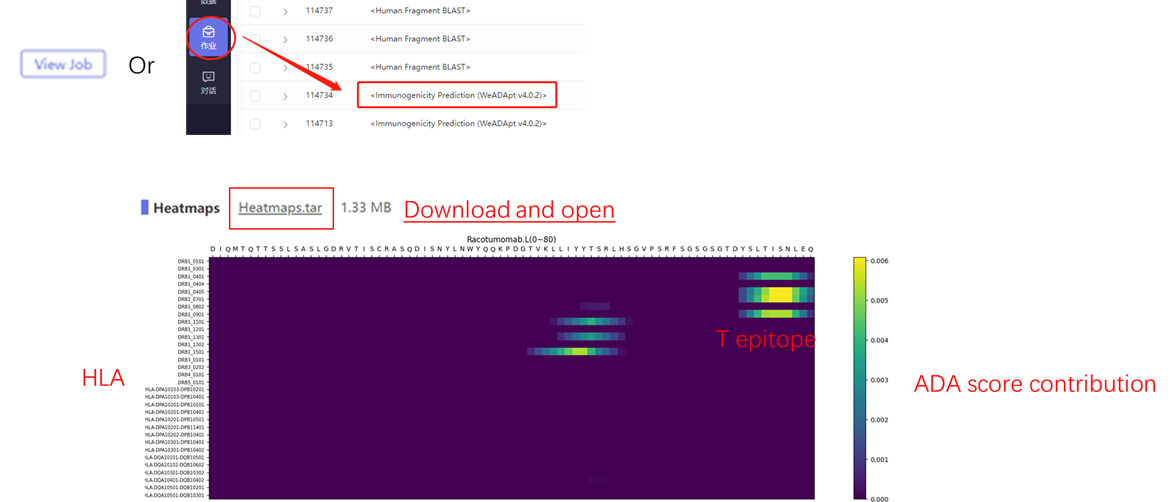
Note the reference structure and exclude inaccessible (embedded) epitopes (see the figure below).
The simplest way is to perform human fragment replacement, which can be done directly in WeSeq (see the figure below).
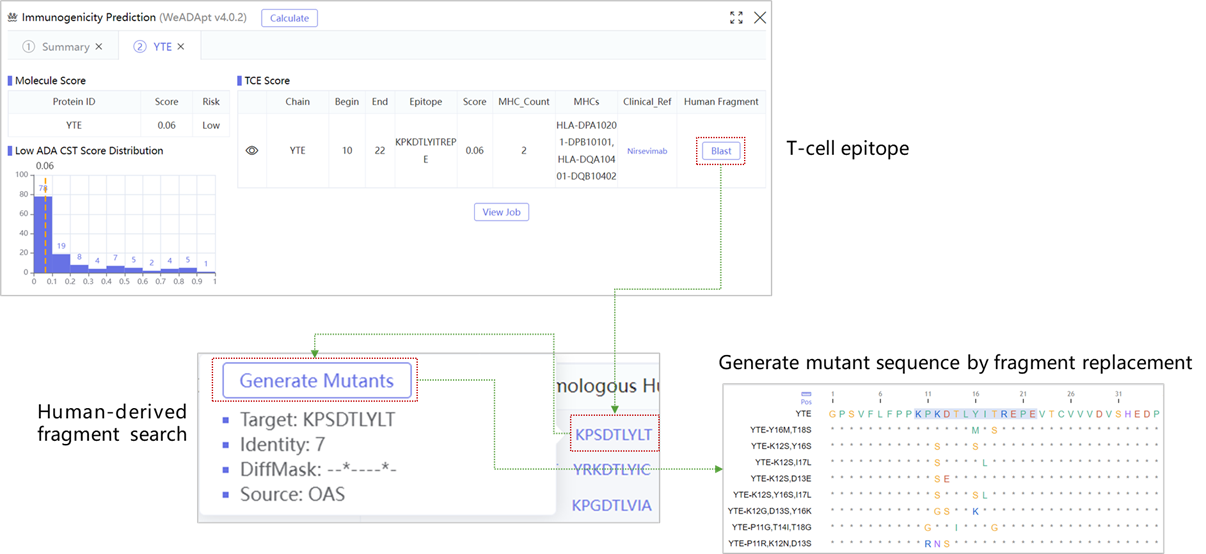
Human mutations can also be introduced through the frequency analysis feature. After mutation, predict the immunogenicity of the mutants to see if it has decreased.
Note: The results of calculating v4 immunogenicity in WeSeq can be automatically saved and reopened at any time.




Disulfide Bond Search模块计算蛋白质中潜在的二硫键位置,这对优化蛋白质的稳定性有所作用。二硫键作为对蛋白质的稳定性有极大的作用,但是加入不合理的二硫键也会容易引起聚集,表达量降低甚至错误折叠等不利影响。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式
指定需要设计的链,多条链用逗号分割,例如:A,B。
设置氨基酸序号,当参数Chain设置为A,C时,此参数如果设置为1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 23 25, 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 40意味着对A中的残基1 2 3…25和链C中的残基10 11 12…40进行设计。如果不填,则该链的所有残基都参与设计。
注意:这里的氨基酸序号是从1开始,而不是PDB文件中带有的氨基酸序号。同一条链的氨基酸序号用空格分隔,不同链的氨基酸用逗号分隔。
是否只选择链间的二硫键。
可设置Cβ之间的距离,默认5.0Å。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ss_bond.csv | 输出自然顺序编号、PDB文件中的残基编号以及Cβ之间的距离信息的CSV文件。 |
| ss_index.fasta | 序列名编号为自然顺序编号并将预测位点突变为CYS的FASTA文件。 |
| ss_uid.fasta | 序列名编号为PDB文件中的残基编号并将预测位点突变为CYS的的FASTA文件。 |
The Disulfide Bond Search module calculates potential disulfide bond positions in proteins, which can be useful for optimizing protein stability. Disulfide bonds play a significant role in stabilizing proteins, but improper addition of disulfide bonds can lead to aggregation, reduced expression levels, or even misfolding.
The structure file of the protein in PDB format.
Specify the chains to be designed. Multiple chains are separated by commas, e.g. A,B.
Set the amino acid sequence numbers. When the Chain parameter is set to A,C, setting this parameter to 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 23 25, 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 40 means designing residues 1 2 3...25 in chain A and residues 10 11 12...40 in chain C. If not specified, all residues in the chain will be included in the design.
Note: The amino acid sequence numbers here start from 1, not the residue numbers in the PDB file. Amino acid sequence numbers within the same chain are separated by spaces, and different chains are separated by commas.
Whether to select only interchain disulfide bonds.
The distance between Cβ atoms can be set, with a default of 5.0 Å.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ss_bond.csv | A CSV file containing information on the natural sequence number, residue number in the PDB file, and the distance between Cβ atoms. |
| ss_index.fasta | A FASTA file with sequence names numbered by natural sequence number, and predicted sites mutated to CYS. |
| ss_uid.fasta | A FASTA file with sequence names numbered by residue number in the PDB file, and predicted sites mutated to CYS. |

Pocket Finder模块基于几何特性和物理化学特性来识别这些口袋,其主要功能是快速、准确地识别蛋白质表面的潜在口袋。蛋白质口袋(或活性位点)是蛋白质表面的小区域,通常是药物分子或其他小分子结合的地方。识别这些口袋对于药物设计和蛋白质功能研究至关重要。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式。
最小alpha球的半径。
最大alpha球的半径。
距离阈值聚类算法
用于将Voronoi顶点分组的聚类方法:
s是单链接聚类(single linkage clustering)。m是完全链接聚类(complete linkage clustering)。a是平均链接聚类(average linkage clustering)。c是质心链接聚类(centroid linkage clustering)。聚类的距离度量方法:
e是欧几里得距离(euclidean distance)。b是曼哈顿距离(Manhattan distance)。每个口袋的最小alpha球数量。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| pocket_properties.csv | 口袋信息CSV文件 |
| pockets.tar.gz | 蛋白分析后得到的PDB文件压缩包 |
| pocket*_atm.pdb | 分别输出所有口袋的PDB(原子)文件格式 |
其中pocket_properties.csv包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 口袋顺序 | |
| Score | 口袋综合得分,考虑了口袋的大小、形状和疏水性等因素。打分越高说明口袋更好,更有可能在生物学上具有相关性或适合药物结合。 |
| Druggability Score | 评估口袋结合药物分子的潜力,打分越高说明口袋药物可及性越高。 |
| Total SASA | 口袋可被溶剂分子接触的总表面积,单位为平方埃Ų;SASA较大,可容纳配体结构越大。 |
| Polar SASA | 总SASA中的极性部分,表示可被水分子接触的表面积。反映了口袋的亲水性。 |
| Apolar SASA | 总SASA中的非极性部分,表示不可被水分子接触的表面积。反映了口袋的疏水性。 |
| Volume | 口袋的体积,单位为ų。较大的体积表示口袋较大,能够容纳更大的配体或多个结合位点。 |
The Pocket Finder module identifies pockets based on geometric and physicochemical properties. Its main function is to quickly and accurately identify potential pockets on the protein surface. Protein pockets (or active sites) are small regions on the protein surface where drug molecules or other small molecules typically bind. Identifying these pockets is crucial for drug design and protein function studies.
The structure file of the protein in PDB format.
The minimum radius of the alpha sphere.
The maximum radius of the alpha sphere.
The distance threshold for the clustering algorithm.
The clustering method used to group Voronoi vertices:
s for single linkage clustering.m for complete linkage clustering.a for average linkage clustering.c for centroid linkage clustering.The distance metric for clustering:
e for Euclidean distance.b for Manhattan distance.The minimum number of alpha spheres per pocket.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pocket_properties.csv | CSV file with pocket information |
| pockets.tar.gz | Compressed archive of PDB files obtained from the protein analysis |
| pocket*_atm.pdb | PDB (atom) file format for each pocket |
The pocket_properties.csv file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Pocket order | |
| Score | Comprehensive score of the pocket, considering factors such as size, shape, and hydrophobicity. A higher score indicates a better pocket, more likely to be biologically relevant or suitable for drug binding. |
| Druggability Score | Assesses the potential of the pocket to bind drug molecules. A higher score indicates higher druggability. |
| Total SASA | Total solvent-accessible surface area of the pocket, in square angstroms (Ų); larger SASA indicates the ability to accommodate larger ligand structures. |
| Polar SASA | The polar portion of the total SASA, indicating the surface area accessible to water molecules. Reflects the hydrophilicity of the pocket. |
| Apolar SASA | The apolar portion of the total SASA, indicating the surface area not accessible to water molecules. Reflects the hydrophobicity of the pocket. |
| Volume | The volume of the pocket, in cubic angstroms (ų). A larger volume indicates a larger pocket, capable of accommodating larger ligands or multiple binding sites. |

Restrained Complex Structure Prediction模块基于ColabDock框架实现,ColabDock框架通过整合多种实验限制条件,显著提升了蛋白-蛋白对接预测的准确性。其创新点包括:
ColabDock框架的工作流程分为两个主要阶段:
ColabDock主要关注两种类型的约束。第一种约束限制了残基对之间的距离低于某一阈值,属于残基-残基层面的约束(称为1v1约束)。这类约束包括源自交联质谱(XL-MS)的约束。第二种约束定义了在蛋白质表面上可能接触的两组残基之间的约束,但具体的接触信息未知。此类约束属于界面层面的约束(称为MvN约束),典型示例包括多种NMR实验和共价标记(CL)。
ColabDock在模拟约束条件下的性能验证情况如下图所示:
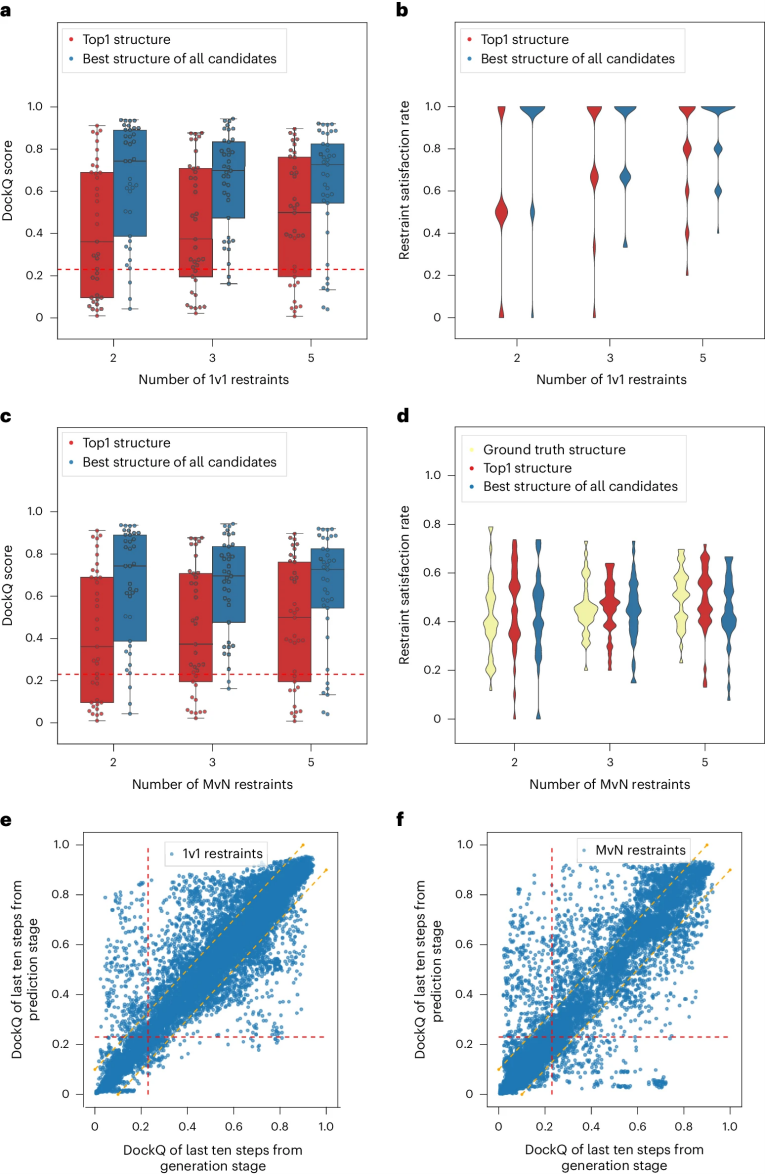
如图a所示,在仅提供两个1v1约束的情况下,81.08%的蛋白质复合物的最大DockQ值超过了0.23,尤其考虑到从这些约束中获取的结构信息相对有限。当提供三到五个约束时,成功率接近100%。如图b所示,对于含有两、三和五对约束的蛋白质复合物,其约束满足率分别为0.55、0.77和0.80。这些结果表明,ColabDock能够高效利用提供的约束来获得高质量的复合物结构。
评估ColabDock在MvN约束下的性能时,先基于上述1v1样本生成了MvN样本。这些样本的挑战性更大,因为MvN约束的模糊性使得多个1v1约束组合可能满足同一组MvN约束。如图c所示,111个样本中有100个预测结构的最大DockQ值超过了0.23。其中,75个样本的top1结构的DockQ值超过0.23。随着约束数量的增加,ColabDock的准确性也相应提高,top1结构的成功率从两个约束时的62.16%上升到三个和五个约束时的70.27%。在预测结构中,约束满足率与实验结构中的比例相似(图d)。这些结果表明,ColabDock同样能够高效利用模糊的约束条件来改善结构预测。
为了评估ColabDock中预测阶段的必要性,在上述1v1和MvN约束实验中,收集了最后十个优化步骤中的结构,大多数优化过程已经收敛。在生成阶段和预测阶段的DockQ值差异较大的情况下(这里定义为大于0.1),预测阶段在69.9%的1v1约束复合物中表现更好(图e),在MvN约束复合物中这一比例为68.8%(图f)。这些结果表明,AF2的能量景观可以帮助优化生成阶段的构象并提高预测的准确性。
ColabDock与传统限制性对接方法比较如下图所示:

基于37个蛋白质复合物的独立基准集。与HADDOCK和ClusPro进行了比较。对于基准集中的每个复合物,采样两、三和五个1v1约束来指导对接,最终生成了111个样本。ColabDock在大多数样本中优于HADDOCK和ClusPro(图a)。ColabDock的平均DockQ值为0.477,而HADDOCK和ClusPro的DockQ值分别为0.287和0.191。无论1v1约束的数量多少,ColabDock在三种方法中均表现最佳(图b)。这些结果表明,ColabDock在稀疏约束条件下有生成可靠结构的潜力,这与验证集的观察结果一致。
为了进一步评估ColabDock在界面级别约束下的表现,作为验证数据集,将上述描述的1v1约束转换为MvN约束。由于ClusPro在111个样本中有7个无法给出预测,将其排除,并对剩余的104个样本进行比较。与1v1约束下的表现相比,由于MvN约束的模糊性,ColabDock、HADDOCK和ClusPro在MvN约束下的表现有所下降,但ColabDock仍然优于其他两种方法(图c)。实验再次表明,无论MvN约束的数量多少,ColabDock在DockQ上均表现最佳(图d)。
实验衍生的约束中常常包含相距较远的残基,作者将其称为“松散约束”。为了测试模型在相关任务中的表现,有意在距离范围为8Å到20Å之间加入了松散约束。对于基准集中的每个复合物,松散约束的数量从1到5不等,而总约束数量固定为5个,共生成了185个样本。排除了9个ClusPro无法处理的样本,并对剩余的176个样本进行了三种方法的比较。结果显示,ColabDock表现最佳,平均DockQ值为0.344,平均α碳原子r.m.s.d.(Cα-r.m.s.d.)为6.55Å(图e)。这些结果表明,ColabDock对约束的质量依赖较低。当与高质量约束结合时,ColabDock能够预测出比其他两种方法更为精确的结构。
抗原抗体复合物预测
抗体-抗原复合物建模一直是一个长期存在的挑战,因为互补决定区(CDRs)的灵活性和缺乏共同进化信号。深度突变扫描(DMS)是一种常用技术,用于确定可能参与抗体-抗原结合的残基。基于一个包含45个复合物的抗体-抗原基准集,通过采样界面上的残基来模拟DMS衍生的约束。预测效果及与传统方法的比较情况如下图所示:
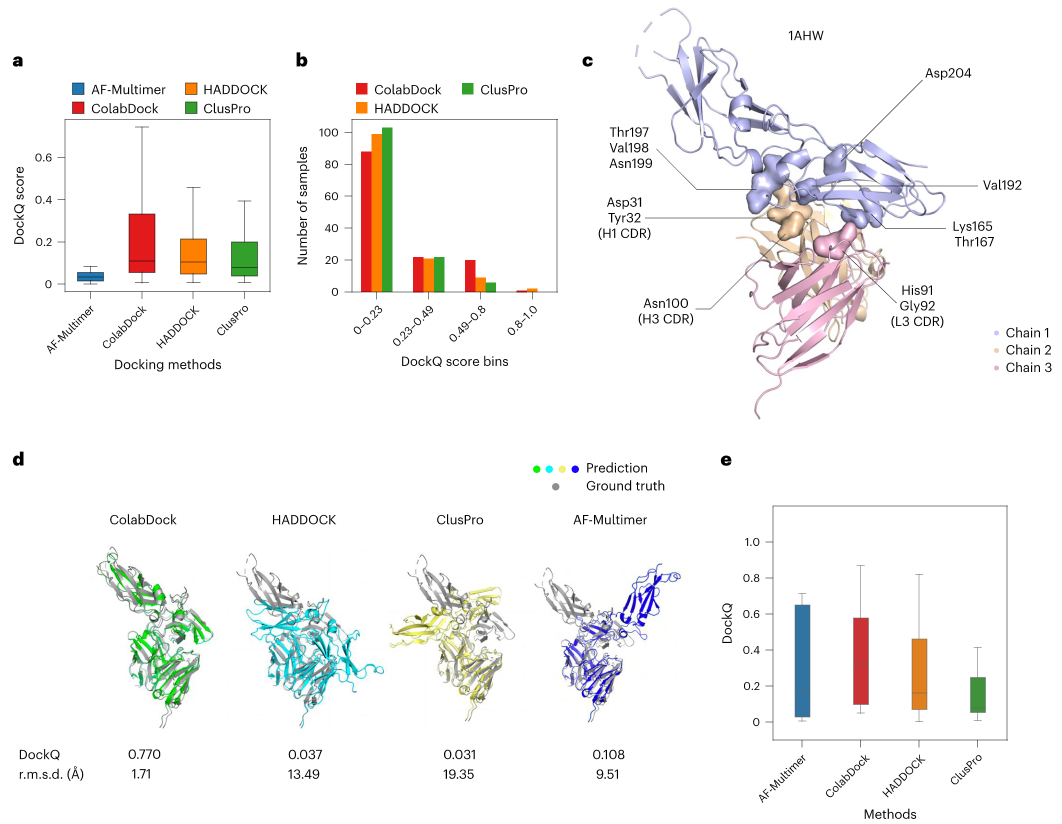
图a所示,ColabDock优于HADDOCK和ClusPro,其平均DockQ值为0.223,平均r.m.s.d.为9.57Å。对于DockQ值大于0.49的样本数量,ColabDock也超过了HADDOCK和ClusPro(图b)。
以1AHW为例:1AHW是一个人类组织因子-抗体(5G9)复合物,参与了血液凝固蛋白酶级联过程。如图c所示,随机从抗体中采样了五个界面残基(轻链的His91和Gly92,重链的Asp31、Tyr32和Asn100),以及从抗原中采样了七个界面残基(Lys165、Thr167、Val192、Thr197、Val198、Asn199和Asp204)。这些在抗体中采样的残基主要分布在L1 CDR、H1 CDR和H3 CDR区域。图d展示了AF-Multimer的预测结构以及三种对接方法的结构。如图e所示,ColabDock捕捉到了大多数界面上的天然接触,其DockQ值为0.770,r.m.s.d.为1.17Å,而其他方法的预测结构与天然构象有较大差异。这一案例研究表明,ColabDock在构象探索和构象排序方面都优于其他两种方法。
初始蛋白复合物结构文件,PDB格式
注:该结构由多条链组成,链与链之间的相对位置可任意放置,无要求。由于显存大小限制,当前最大支持的最终复合物尺寸大小不超过800个残基。
复合物中提取多条链,用于组成最终的复合物结构,链名之间用逗号分隔,如:A,H,L
提取的多条链中指定相对位置固定的每对链,支持定义多对,链名之间用逗号分隔,每行一对,示例如下:
H,L
A,H
表示链H与L之间的相对位置固定,链A与H之间的相对位置固定。
实验限制的距离阈值,表示设置限制的残基间的距离需小于该阈值。默认为8.0 Å,值范围为2.0 Å - 22.0 Å,建议采用默认值。
单个残基之间的限制条件,限制单个残基之间的距离在上述定义的阈值参数内,残基之间用逗号(,)分隔,支持定义多个条件(每行定义一个),示例如下:
A20,H50
A78,L98
该参数表示设置的限制条件有2个:
注意:残基编号为位置编号,即每条链按顺序从1开始进行编号,以下编号规则一致。
单个残基与残基组合之间的限制条件,限制单个残基与多个残基集合中至少一个残基之间的距离在上述定义的阈值参数内,单个残基与残基组合之间用逗号(,)分隔,残基组合内部用分号(;)分隔,可支持定义多个条件(每行定义一个),示例如下:
A10,H60-70;H78;L90
A78,H60-70;L56;L69
A120,L30-L36;H68;H72
2
该参数表示设置的限制条件有3个,分别是:
限制残基间排斥的距离阈值,表示设定的排斥残基间的距离需大于该阈值。默认为8.0 Å,值范围为2.0 Å - 22.0 Å,建议采用默认值。
单个残基间的排斥限制条件,限制单个残基之间的距离需大于上述定义的排斥阈值,残基之间用逗号(,)分隔,可支持定义多个条件(每行定义一个),示例如下:
15,98
60,205
该参数表示设置的排斥限制条件有2个:
输出1st_best.pdb结果文件,为预测得到的最优复合物结构文件。
输出pdbs.tar.gz文件,为预测得到的前5个最优复合物结构文件压缩包。
输出summary.txt文件,包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| pdb | 复合物结构文件名 |
| iptm | 复合物结构的质量好坏评价指标,0-1之间,越接近1表示预测结构的质量越好 |
| # of satisfied restraints | 限制条件的数量,以及预测的复合物结构能满足的条件数量,如:2/2表示有2个限制条件,预测得到的复合物结构都能满足;1/2表示有2个限制条件,但复合物结构只满足了其中1个 |
备注:
可能存在以下个别情况,属正常现象
The module is implemented based on the ColabDock framework, which significantly improves the accuracy of protein-protein docking predictions by integrating a variety of experimental constraints. Its innovations include:
The workflow of the ColabDock framework is divided into two main stages:
ColabDock focuses on two types of constraints. The first type of constraints restricts the distance between residue pairs to be below a certain threshold and are residue-residue level constraints (called 1v1 constraints). This type of constraints includes constraints derived from cross-linking mass spectrometry (XL-MS). The second type of constraints defines constraints between two groups of residues that may contact on the protein surface, but the specific contact information is unknown. This type of constraints belongs to the interface level constraints (called MvN constraints), and typical examples include various NMR experiments and covalent labeling (CL).
The performance verification of ColabDock under simulation constraints is shown in the following figure:
As shown in Figure a, with only two 1v1 constraints provided, 81.08% of the protein complexes had a maximum DockQ value of more than 0.23, especially considering the relatively limited structural information obtained from these constraints. When three to five constraints were provided, the success rate was close to 100%. As shown in Figure b, for protein complexes containing two, three, and five pairs of constraints, the constraint satisfaction rates were 0.55, 0.77, and 0.80, respectively. These results show that ColabDock can efficiently use the provided constraints to obtain high-quality complex structures.
When evaluating the performance of ColabDock under MvN constraints, MvN samples were first generated based on the above 1v1 samples. These samples are more challenging because the ambiguity of MvN constraints makes it possible for multiple 1v1 constraint combinations to satisfy the same set of MvN constraints. As shown in Figure c, 100 of the 111 samples have a maximum DockQ value of more than 0.23 for the predicted structures. Among them, 75 samples have a DockQ value of more than 0.23 for the top1 structure. As the number of constraints increases, the accuracy of ColabDock also increases accordingly, with the success rate of the top1 structure increasing from 62.16% with two constraints to 70.27% with three and five constraints. In the predicted structures, the constraint satisfaction rate is similar to that in the experimental structures (Figure d). These results show that ColabDock can also effectively use fuzzy constraints to improve structure prediction.
To evaluate the necessity of the prediction stage in ColabDock, structures from the last ten optimization steps were collected in the above 1v1 and MvN constrained experiments, and most of the optimization processes have converged. In cases where the difference in DockQ values between the generation stage and the prediction stage is large (here defined as greater than 0.1), the prediction stage performs better in 69.9% of the 1v1 constrained complexes (Figure e) and in 68.8% of the MvN constrained complexes (Figure f). These results suggest that the energy landscape of AF2 can help optimize conformations in the generation stage and improve the accuracy of predictions.
The comparison between ColabDock and traditional restrictive docking methods is shown in the figure below:
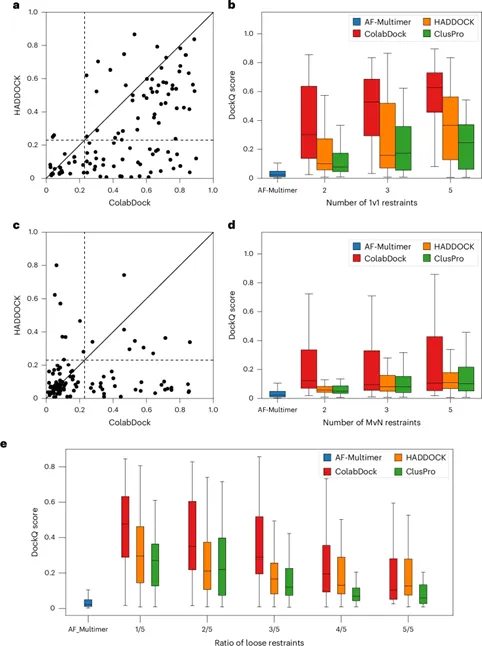
Based on an independent benchmark set of 37 protein complexes. Comparisons were made with HADDOCK and ClusPro. For each complex in the benchmark set, two, three, and five 1v1 constraints were sampled to guide docking, and 111 samples were finally generated. ColabDock outperformed HADDOCK and ClusPro in most samples (Figure a). The average DockQ value of ColabDock was 0.477, while the DockQ values of HADDOCK and ClusPro were 0.287 and 0.191, respectively. Regardless of the number of 1v1 constraints, ColabDock performed best among the three methods (Figure b). These results show that ColabDock has the potential to generate reliable structures under sparse constraints, which is consistent with the observations of the validation set.
To further evaluate the performance of ColabDock under interface-level constraints, the 1v1 constraints described above were converted to MvN constraints as a validation dataset. Since ClusPro could not give predictions for 7 out of 111 samples, it was excluded and the remaining 104 samples were compared. Compared with the performance under 1v1 constraints, the performance of ColabDock, HADDOCK, and ClusPro under MvN constraints declined due to the ambiguity of MvN constraints, but ColabDock still outperformed the other two methods (Figure c). The experiment again shows that ColabDock performs best on DockQ regardless of the number of MvN constraints (Figure d).
Experimentally derived constraints often contain residues that are far apart, which the authors call “loose constraints.” In order to test the performance of the model in related tasks, loose constraints were intentionally added with distances ranging from 8Å to 20Å. For each complex in the benchmark set, the number of loose constraints ranged from 1 to 5, while the total number of constraints was fixed at 5, generating a total of 185 samples. Nine samples that ClusPro could not handle were excluded, and the three methods were compared on the remaining 176 samples. The results showed that ColabDock performed best, with an average DockQ value of 0.344 and an average α-carbon atom r.m.s.d. (Cα-r.m.s.d.) of 6.55Å (Figure e). These results indicate that ColabDock has a low dependence on the quality of constraints. When combined with high-quality constraints, ColabDock is able to predict more accurate structures than the other two methods.
Antigen-antibody complex prediction
Modeling antibody-antigen complexes has been a long-standing challenge due to the flexibility of complementarity determining regions (CDRs) and the lack of co-evolutionary signals. Deep mutational scanning (DMS) is a commonly used technique to identify residues that may be involved in antibody-antigen binding. Based on an antibody-antigen benchmark set of 45 complexes, DMS-derived constraints were simulated by sampling residues on the interface. The prediction results and comparison with traditional methods are shown in the figure below:
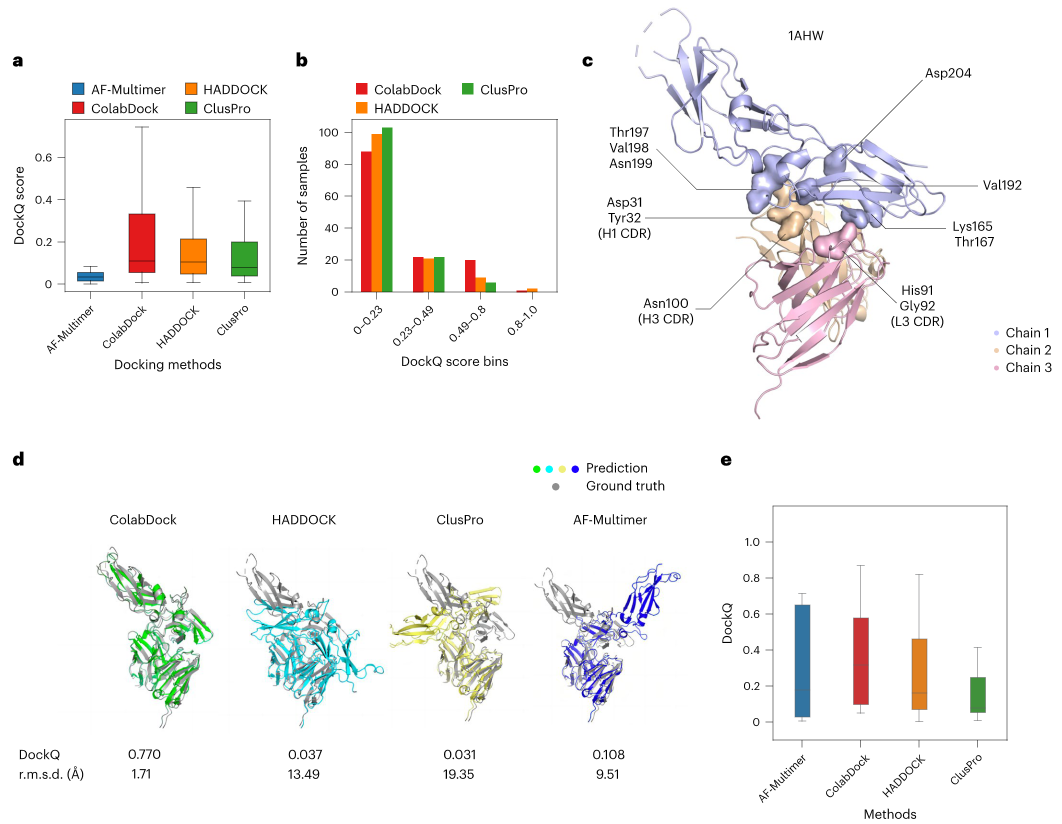
As shown in Figure a, ColabDock outperforms HADDOCK and ClusPro, with an average DockQ value of 0.223 and an average r.m.s.d. of 9.57 Å. For the number of samples with a DockQ value greater than 0.49, ColabDock also exceeds HADDOCK and ClusPro (Figure b).
Take 1AHW as an example: 1AHW is a human tissue factor-antibody (5G9) complex that participates in the blood coagulation protease cascade. As shown in Figure c, five interface residues were randomly sampled from the antibody (His91 and Gly92 of the light chain, Asp31, Tyr32 and Asn100 of the heavy chain), and seven interface residues were sampled from the antigen (Lys165, Thr167, Val192, Thr197, Val198, Asn199 and Asp204). These sampled residues in the antibody are mainly distributed in the L1 CDR, H1 CDR and H3 CDR regions. Figure d shows the predicted structure of AF-Multimer and the structures of the three docking methods. As shown in Figure e, ColabDock captures most of the natural contacts on the interface, with a DockQ value of 0.770 and an r.m.s.d. of 1.17Å, while the predicted structures of other methods are quite different from the natural conformation. This case study demonstrates that ColabDock outperforms the other two methods in both conformational exploration and conformational ranking.
Original protein complex structure file, PDB format
Note: This structure consists of multiple chains, and the relative positions between chains can be placed arbitrarily. Due to the limitation of GPU memory, the current maximum supported final complex size does not exceed 800 residues.
Multiple chains are extracted from the original complex to form the final complex structure. The chain names are separated by commas, such as: A,H,L
Specify each pair of chains with fixed relative positions among the extracted multiple chains. Multiple pairs can be defined. Chain names are separated by comma, with one pair per line. The example is as follows:
H,L
A,H
It means that the relative position between chains H and L is fixed, and the relative position between chains A and H is fixed.
The distance threshold of the experimental restraint, which means that the distance between the residues to set the restraint must be less than this threshold. The default value is 8.0 Å, and the value range is 2.0 Å - 22.0 Å. The default value is recommended.
Restrictions between single residues. Limit the distance between single residues to the threshold parameters defined above. Residues are separated by commas. Multiple conditions can be defined (one per line). The following is an example:
A20,H50
A78,L98
This parameter indicates that there are two restrictions set:
The restriction conditions between a single residue and a residue combination limit the distance between a single residue and at least one residue in a set of multiple residues to be within the threshold parameters defined above. Single residues and residue combinations are separated by commas, and residue combinations are separated by semicolons. Multiple conditions can be defined (one per line). The following is an example:
A10,H60-70;H78;L90
A78,H60-70;L56;L69
A120,L30-L36;H68;H72
2
This parameter indicates that there are three restrictions set, namely:
The distance threshold for limiting the repulsion between residues, indicating that the distance between the set repulsive residues must be greater than this threshold. The default value is 8.0 Å, and the value range is 2.0 Å - 22.0 Å. It is recommended to use the default value.
The exclusion constraint between single residues requires the distance between single residues to be greater than the exclusion threshold defined above. Residues are separated by comma. Multiple conditions can be defined (one per line). The following is an example:
15,98
60,205
This parameter indicates that there are two exclusion constraints set:
‘1st_best.pdb’ file, which is the predicted optimal complex structure file.
‘pdbs.tar.gz’ file, which is the compressed package of the top 5 predicted optimal complex structure files.
‘summary.txt’ file, which contains the following information:
| Fields | Introduction |
|---|---|
| pdb | File name of complex structure |
| iptm | An evaluation index of the quality of the complex structure, between 0 and 1, the closer to 1, the better the quality of the predicted structure |
| # of satisfied restraints | The total number of constraints and the number of constraints that the predicted complex structure can satisfy. For example, 2/2 means that there are 2 constraints and the predicted complex structure can satisfy them all; 1/2 means that there are 2 constraints, but the complex structure only satisfies one of them. |
Note:
The following individual cases may exist, which are normal:

Germline Blast模块基于IgBlastp实现,通过氨基酸序列比对从IMGT reference sequences数据库中搜索与目标抗体序列最接近的同源模板,输出对应的模板序列以及序列一致性等信息。数据库中默认检索的序列类型为:IMGT V genes(F+ORF+in-frame P)。
抗体的序列文件,FASTA格式,如包含多条序列,仅对第一条序列进行分析。
抗体编号类型:kabat和imgt
输出同源性最高的N条序列,默认值为10。
序列所属物种:Human,Mouse,Rat,Rabbit,Rhesus Monkey,默认值为Human。
| 输出参数 | 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Hits Sequence | hits.fasta | 包含同源性最高的n条序列的序列文件 |
| Result | result.csv | 包含找到的Germline序列以及序列的一致性信息 |
| Alignment Summary | align_info_top_germline.csv | 包含查询序列与同源性最高的Germline V基因序列的比对信息 |
The Germline Blast module is based on IgBlastp and searches for the most homologous templates to the target antibody sequence from the IMGT reference sequences database through sequence alignment. It outputs the corresponding template sequences and sequence identity information. The default sequence types searched in the database are: IMGT V genes (F+ORF+in-frame P).
The antibody sequence file in FASTA format. If multiple sequences are included, only the first sequence will be analyzed.
The antibody numbering scheme: kabat and imgt.
The number of top homologous sequences to output, with a default value of 10.
The species of the sequence: Human, Mouse, Rat, Rabbit, Rhesus Monkey, with the default value being Human.
| Output Parameter | Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Hits Sequence | hits.fasta | A sequence file containing the top N homologous sequences |
| Result | result.csv | Contains the identified germline sequences and sequence identity information |
| Alignment Summary | align_info_top_germline.csv | Contains alignment information between the query sequence and the top homologous germline V gene sequences |
Target-based Cyclic Peptide Design模块基于Evobind2模型实现,Evobind2模型是基于AF2实现的,旨在基于目标蛋白质序列设计新型首尾相接(Head-to-Tail)环肽。通过预测的置信度指标直接选择高亲和力结合环肽,支持指定结合位点。
EvoBind2设计环肽/多肽的流程如下:
环肽设计案例,展示了首尾相接酰胺键:

靶标蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式。
设计的环肽长度。长度的选择将直接影响设计的环肽大小和潜在结合能力,推荐长度范围为6-20。
肽的起始序列,如果提供了该参数,模块将以此序列为基础进行优化,如:ARDCPLVNPL。在已知的有效序列基础上进行优化,而不是从头开始,有助于加快设计过程和提高设计效率。
靶标序列上的环肽结合位点残基,编号从1开始。指定这些位点可以提高设计的准确性和成功率。多个位点通过逗号分隔,如:23,45,67。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| best.pdb | 最优设计的复合物结构文件 |
| design_pdbs.tar.gz | 评分前20的复合物结构压缩文件 |
| top20.csv | 评分前20的复合物结构名称及打分文件 |
其中top20.csv包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ID | 复合物结构ID |
| pLDDT | 预测得到的复合物LDDT评分,数值在0-100之间,越大表示结构质量越好 |
| Sequence | 环肽序列 |
The target-based Cyclic Peptide Design module is based on the Evobind2 model, which is based on AF2 and aims to design novel Head-to-Tail cyclic peptides based on Target protein sequences. The high affinity combination can be directly selected by the predicted confidence index, the binding site can be specified, and the adversarial design can be avoided by isomer evaluation, which greatly improves the success rate.
EvoBind2 design cyclic peptide/polypeptide process is as follows:
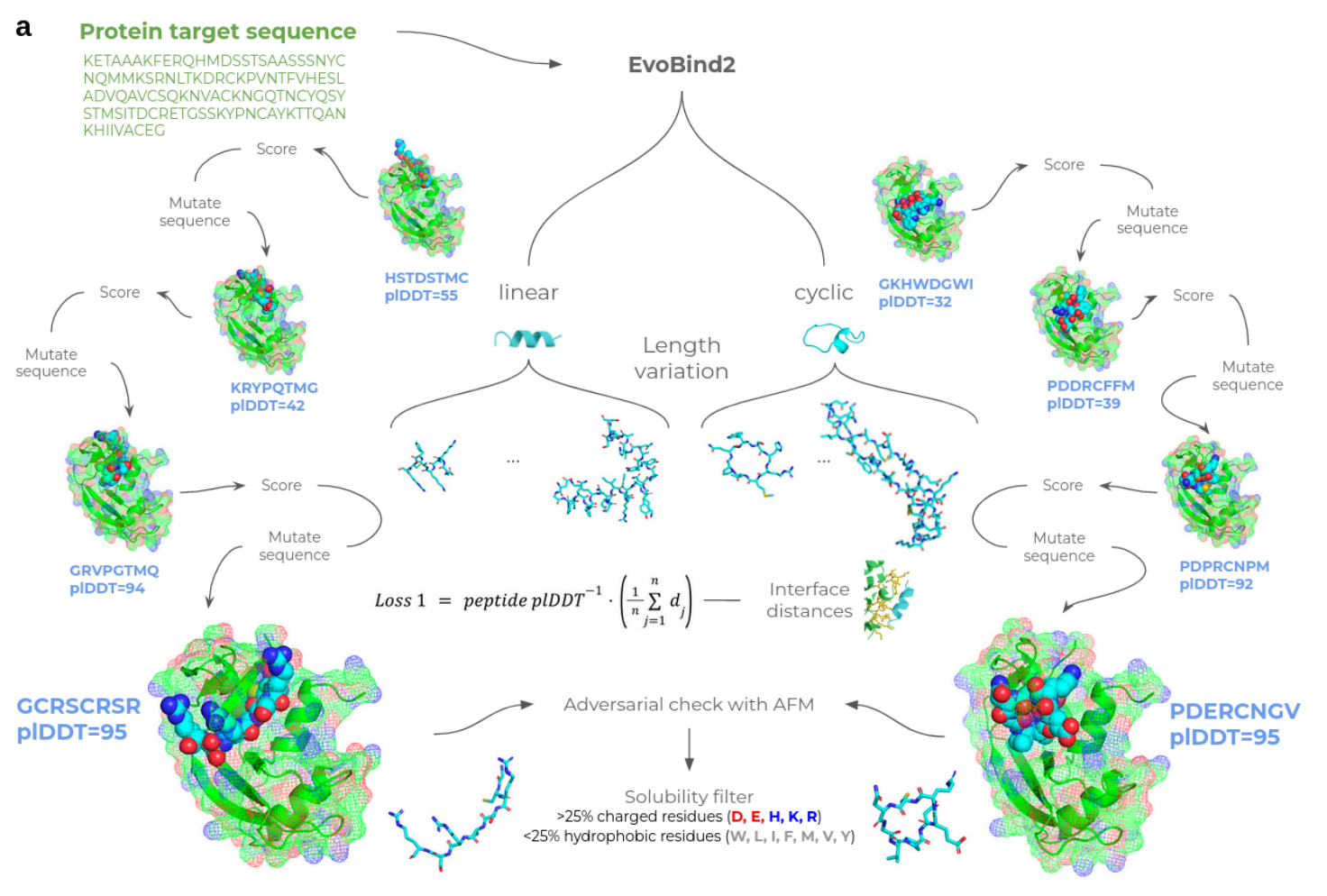
Cyclic peptide design case, demonstrating the end to end amide bond:
Target protein sequence file in FASTA format
Designed cyclic peptide length. The choice of length will directly affect the size and potential binding capacity of the designed cyclic peptide, and the recommended length range is 6-20.
The starting sequence of the peptide, on which the module will optimize if this parameter is provided, for example: ARDCPLVNPL. Optimizing on the basis of known effective sequences, rather than starting from scratch, helps speed up the design process and increase design efficiency.
Cyclic peptide binding site residues on the target sequence, numbered from 1. Specifying these sites can improve the accuracy and success of the design. Multiple sites are separated by commas, such as 23,45,67.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| best.pdb | Structure file of the best designed complex |
| design_pdbs.tar.gz | Compressed file containing the top 20 complex structures |
| top20.csv | File containing the names and scores of the top 20 complex structures |
The top20.csv file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Complex structure ID |
| pLDDT | Predicted LDDT score of the complex, ranging from 0 to 100, with higher values indicating better structure quality |
| Sequence | Cyclic peptide sequence |

Mutation Energy of Stability (ThermoMPNN)模块基于ThermoMPNN模型实现,此深度神经网络模型可根据蛋白初始结构,预测单点突变对应的稳定性变化。模型使用从ProteinMPNN(一种深度神经网络模型,可根据蛋白质的三维结构预测其氨基酸序列)中提取的结构特征,在已建立的基准数据集上实现了优秀的预测性能。通常认为,ddG < -0.5 kcal/mol 可能是一个有利于稳定性的突变。ThermoMPNN 在 Fireprot(HF)数据集上的正预测值为 56%(34/61 个预测为稳定的突变),在 Megascale 数据集上为 46%(1,312/2,852)。
模型架构与数据集分析如下图所示:

模型预测效果与其他方法效果比较见下图:
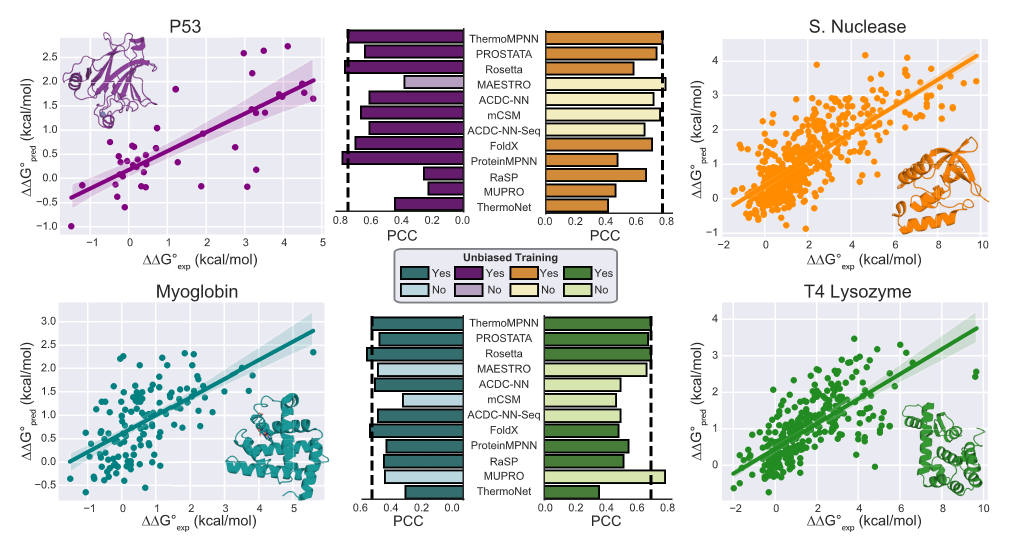
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式,支持单体或复合物结构
用于稳定性突变分析的链名称,仅支持单链,如:A
输出文件名称,默认pred_res.csv。
指定输出能量最优的前N个突变对应的序列,默认为100。
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列,默认为mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列,复合物中各链之间用分号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式),默认为mutant_seqs_complex.fasta。
输出result.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | 链名称,如:'A’表示A链 |
| Mutation | 单点突变信息,如:'G1A’表示序列编号为1的残基甘氨酸G,突变为丙氨酸A,序列编号从1开始按顺序编号(非PDB文件中的残基序号) |
| ddG_pred | 突变对应的能量变化,负值表示体系能量较低,体系变得更稳定。负得越多表示稳定性提升越多。ddG < -0.5 kcal/mol 可能是一个有利于稳定性的突变 |
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列,复合物中各链之间用冒号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式)mutant_seqs_complex.fasta。
The Mutation Energy of Stability (ThermoMPNN) module is based on the ThermoMPNN model. This deep neural network model predicts the stability changes corresponding to single-point mutations based on the initial structure of the protein. The model uses structural features extracted from ProteinMPNN (a deep neural network model that predicts amino acid sequences based on the three-dimensional structure of proteins) and has achieved excellent predictive performance on established benchmark datasets.If we consider a ΔΔG° < -0.5 kcal/mol to indicate a stabilizing mutation, ThermoMPNN achieves a PPV of 56% (34/61 predicted stabilizing mutations) on the Fireprot (HF) dataset and 46% (1,312/2,852) on the Megascale dataset.
The model architecture and dataset analysis are shown in the figure below:
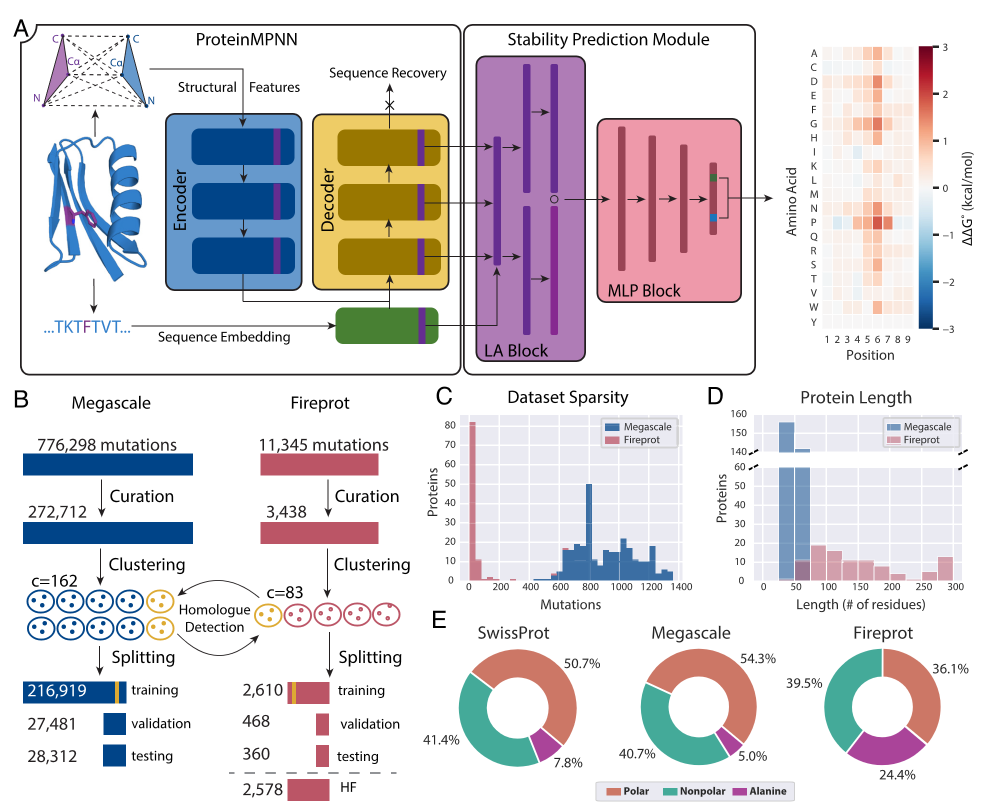
The comparison of the model’s predictive performance with other methods is shown in the figure below:
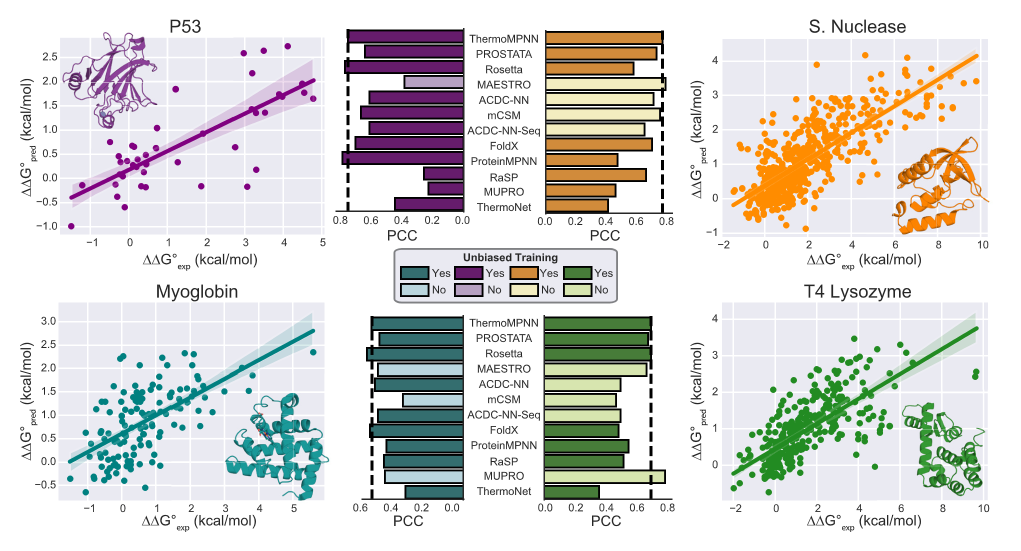
The structure file of the protein in PDB format, supporting monomer or complex structures.
The name of the chain for stability mutation analysis, supporting only single chains, e.g., A.
Output file name, pred_res.csv is the default.
Specify the sequences corresponding to the top N mutations with the optimal energy. The default value is 100.
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN.
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN. The chains within the complexes are separated by semicolons (;) (for batch mode structure prediction by Boltz2).
The output result.csv file contains the following information:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain | The name of the chain, e.g., ‘A’ for chain A |
| Mutation | Single-point mutation information, e.g., ‘G1A’ means the residue glycine G at sequence number 1 is mutated to alanine A. The sequence number starts from 1 in order (not the residue number in the PDB file) |
| ddG_pred | The energy change corresponding to the mutation. A negative value indicates lower system energy and increased stability. The more negative, the greater the stability improvement. ddG < -0.5 kcal/mol may indicate a stabilizing mutation |
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN. mutant_seqs.fasta
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN. The chains within the complexes are separated by : (for batch mode structure prediction by Boltz2). mutant_seqs_complex.fasta

Homology Tree模块用于生成同源性进化树。
蛋白序列文件,FASTA格式。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| alignment.fasta | 按树结构顺序输出的叠合后的序列文件的FASTA文件 |
| tree.png | 多重序列树结构图片 |
The Homology Tree module is used to generate homologous evolutionary trees.
Protein sequence file in FASTA format.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| alignment.fasta | FASTA file of the superimposed sequence of files output in order of tree structure. |
| tree.png | Tree structure picture of multiple sequence |

Structure Evolution模块基于ESMIF模型实现,ESMIF逆折叠模型旨在根据蛋白质主链原子坐标预测蛋白序列。该模型使用AlphaFold2预测的1200万个蛋白质结构进行训练,包含不变几何输入处理层,随后是一个序列到序列的Transformer,对于在结构上保持不变的主干序列实现51%的本地序列恢复率,对于埋藏残基实现72%的恢复率。该模型还经过跨度屏蔽训练,能够容忍缺失的主链坐标,因此可以预测部分被屏蔽结构的序列。该模块既可以用于亲和力成熟,也可以用于稳定性优化。
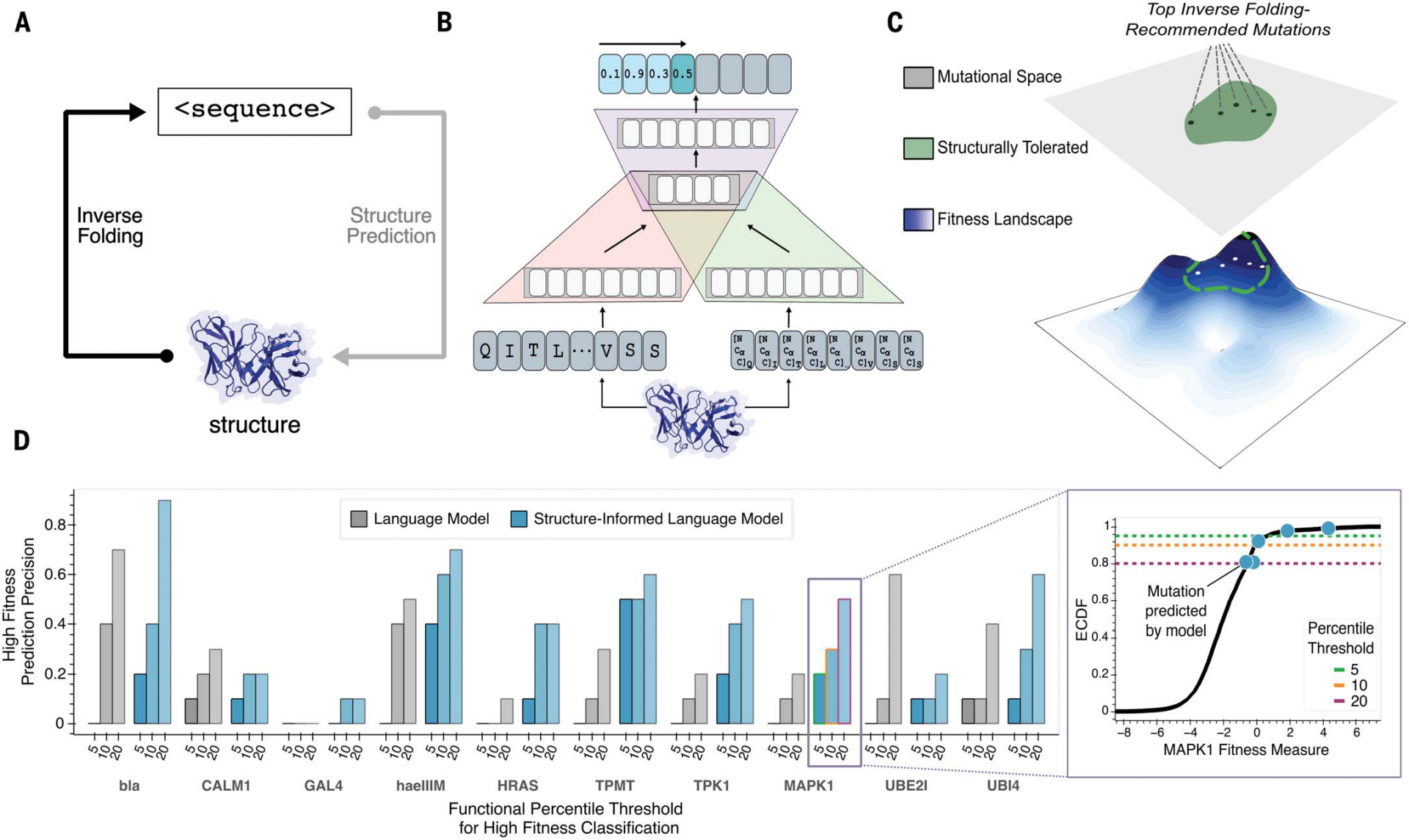
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式,支持单体或复合物结构
用于进化分析的链名称,默认为A链
指定目标链中的多个残基,进行多点突变分析。使用残基位置编号(从1开始),多个残基用逗号分隔,指定残基范围用横杠符号。如:“3,10,24-30”表示目标链上的第3、第10与第24至30号残基,参与多点突变分析。
备注:如不设置该参数,表示采用目标链的全长序列进行突变分析。
指定突变点最小数目,默认值为1,表示从单点突变开始进行突变分析。如设置为2,表示从两点组合突变开始进行突变分析。
指定突变点最大数目,默认值为3,表示至多进行三点组合突变。如设置为2时,表示最多进行两个点的多点组合突变。
指定参与多点突变分析的每个残基,其最大的替换数目,默认为5,表示每个残基最多突变为5种不同的其他残基。
备注:理论上,每种残基可以突变为其他19种天然残基,但因多点突变可能引起的组合爆炸,这里我们限制了最大替换数目。每个残基具体替换的其他残基类别,会根据ESMIF模型给出的该位置残基的概率分布,优先选择概率高的残基类别。
输出CSV文件名称,包含了突变以及对应的突变的可能性。
指定输出评分最优的前N个突变对应的序列,默认为100。
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列,默认为mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列,复合物中各链之间用冒号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式),默认为mutant_seqs_complex.fasta。
输出结果文件,包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Mutation | 单点突变信息,如:'WT’表示野生型原序列,'G1A’表示序列编号为1的残基甘氨酸G,突变为丙氨酸A,序列编号从1开始按顺序编号(非PDB文件中的残基序号) |
| Log_likelihood | 输入结构的全部序列对应的模型预测概率对数值,越大表示该突变序列越好 |
| Log_likelihood_target_chain | 输入结构的目标链序列(对应参数Target Chain)对应的模型预测概率对数值,越大表示该突变序列越好 |
注释:当输入结构为单链时,Log_likelihood与Log_likelihood_target_chain数值一致。当输入结构为复合物时,Log_likelihood对应的是复合物的全部序列的概率值,Log_likelihood_target_chain对应的是复合物中目标链序列(参数Target Chain)对应的概率值。
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列mutant_seqs_complex.fasta,复合物中各链之间用冒号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式)。
The Structure Evolution module is based on the ESMIF model and is used for structure-based single-point advantageous mutation analysis. The ESMIF inverse folding model aims to predict protein sequences from the coordinates of protein backbone atoms. This model is trained on 12 million protein structures predicted by AlphaFold2 and includes invariant geometric input processing layers followed by a sequence-to-sequence Transformer. It achieves a 51% local sequence recovery rate for backbone sequences that remain structurally invariant and a 72% recovery rate for buried residues. The model is also trained with span masking, allowing it to tolerate missing backbone coordinates and predict sequences for partially masked structures. This module can be used for both affinity maturation and stability optimization.
The structural file of the protein in PDB format, supporting both monomer and complex structures.
The name of the chain used for evolutionary analysis. Only single chains are supported. After uploading the structural file, you can select a chain name from the list of chains.
Multiple residues in the chain were labeled for multi-point mutation analysis. Use a residue location number (starting at 1), multiple residues are separated by commas, and a delimiter is used to specify the residue range. For example, “3,10,24-30” indicates residues 3,10, and 24 to 30 on the target chain, which participate in multipoint mutation analysis.
Specifies the minimum number of mutation points, the default is 1, indicating that mutation analysis starts with single mutation. If the value is set to 2, it indicates that the mutation analysis starts from the two-point mutation.
Specifies the maximum number of mutation points, the default is 3, indicating that at most three points of combination mutation can be made. If the value is set to 2, it indicates that a maximum of two points of combination mutation can be performed.
Specifies the maximum number of substitutions for each residue participating in multipoint mutation analysis, which defaults to 5, meaning that each residue mutates up to 5 different other residues.
Output CSV file containing the mutations and corresponding probabilities.
Designate the sequences corresponding to the top N mutations with the best scores, with a default value of 100.
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN, with a default file name of mutant_seqs.fasta.
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN. The chains within the complex are separated by colons(:) (for batch mode of Boltz2 structure prediction), with a default file name of mutant_seqs_complex.fasta.
The output file contains the following information:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Mutation | Single-point mutation information, e.g., ‘WT’ represents the wild-type original sequence, ‘G1A’ indicates that the residue glycine (G) at sequence position 1 is mutated to alanine (A). Sequence numbering starts from 1 in order (not the residue number in the PDB file). |
| Log_likelihood | The log value of the predicted probability of the sequences of input structure by the model. The higher the value, the better the mutated sequence. If this value is greater than the corresponding value of WT, it indicates that the mutation is advantageous. |
| Log_likelihood_target_chain | The log-likelihood value of the model’s predicted probability corresponding to the target chain sequence of the input structure (parameter Target Chain). The higher the value, the better the mutated sequence. If this value is greater than the corresponding value of WT, it indicates that the mutation is advantageous. |
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN mutant_seqs.fasta.
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN mutant_seqs_complex.fasta. The chains within the complex are separated by colons(:) (for batch mode of Boltz2 structure prediction) .
Note: When the input structure is a single chain, the value of Log_likelihood is consistent with that of Log_likelihood_target_chain. When the input structure is a complex, Log_likelihood corresponds to the probability value of the entire sequence of the complex, and Log_likelihood_target_chain corresponds to the probability value of the target chain sequence (parameter Target Chain) in the complex.

Structural Alignment (USalign)是基于USalign的结构叠合工具。
需要进行叠合的蛋白结构文件,PDB格式
叠合操作中位置保持不变的参考结构文件,PDB格式
输出的叠合后的结构文件名称
输出叠合后结构文件:aligned_structure.pdb,TM-Score值在stdout.txt文件中。
C Zhang, M Shine, AM Pyle, Y Zhang. US-align: Universal structure alignment of proteins, nucleic acids and macromolecular complexes. Nature Methods, 19: 1109-1115 (2022).
Structural Alignment (USalign) is a structural superposition tool based on USalign.
The protein structure file to be aligned, in PDB format.
The reference structure file that remains fixed during the alignment operation, in PDB format.
The name of the output file for the aligned structure.
The output includes the aligned structure file named aligned_structure.pdb and the TM-Score value in the stdout.txt file.
C Zhang, M Shine, AM Pyle, Y Zhang. US-align: Universal structure alignment of proteins, nucleic acids, and macromolecular complexes. Nature Methods, 19: 1109-1115 (2022).

Antibody Design (MEAN)模块基于MEAN模型实现,该模型采用多通道等变图注意力网络,可用于设计CDR的一维序列和三维结构。具体而言,MEAN 通过导入额外的结构信息(包括目标抗原和抗体的轻链)将抗体设计公式化为条件图翻译问题。然后,MEAN重新采用 E(3)-等变消息传递以及提出的注意机制来更好地捕捉不同结构信息之间的几何相关性。最后,它通过多轮渐进式全景模式输出一维序列和三维结构,与以前的自回归方法相比,它具有更高的效率和精度。MEAN在序列和结构建模、抗原结合CDR设计和结合亲和力优化方面明显超越了届时最优模型。具体而言,抗原结合CDR设计相对于基线模型改进约为23%,亲和力优化相对于基线模型改进约为34%。
MEAN模型架构如下图所示:

抗体-抗原复合物结构或抗体结构(建议采用复合物结构,设计效果更佳),PDB格式
指定结构中的抗体重链名称,默认值为H,注意如果上传的结构中抗体重链命名非H,请修改该参数为相应的链名
指定结构中的抗体轻链名称,默认值为L,注意如果上传的结构中抗体轻链命名非L,请修改该参数为相应的链名
设计模式,有两种设计模式:CDR-H3设计与亲和力优化(Optimized)
亲和力优化中,生成的结构数量,默认值为100
指定输出亲和力最优的前N个突变对应的序列,默认为100。
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列,默认为mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列,复合物中各链之间用冒号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式),默认为mutant_seqs_complex.fasta。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| cdrs.txt文件 | 包含设计的CDR-H3序列 |
| design.pdb文件 | 设计后的复合物结构文件,注意抗体结构只保留Fv区域 |
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ddg_scores.txt文件 | 优化后结构与原结构的亲和力差异评分 |
| opt_best.pdb文件 | 亲和力最优结构文件,注意抗体结构只保留Fv区域 |
| log.txt | 亲和力优化文件日志 |
| opt.zip | 优化后的多个结构的压缩文件 |
其中,ddg_scores.txt文件,包含信息如下:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 结构名称 |
| ddG | 与原结构的亲和力差异评分ddG,单位为kcal/mol,数值为负时表示亲和力有提升,负得越多表示亲和力提升越好 |
输出TopN对应的突变链的序列mutant_seqs.fasta。
输出TopN对应的复合物序列mutant_seqs_complex.fasta,复合物中各链之间用冒号:分隔(Boltz2结构预测的批量模式)。
The Antibody Design (MEAN) module is implemented based on the MEAN model, which employs a multi-channel equivariant graph attention network for designing the one-dimensional sequence and three-dimensional structure of the CDR (Complementarity-Determining Region). Specifically, MEAN formulates antibody design as a conditional graph translation problem by incorporating additional structural information, including the target antigen and the light chain of the antibody. MEAN then re-adopts E(3)-equivariant message passing and the proposed attention mechanism to better capture the geometric correlations between different structural information. Finally, it outputs the one-dimensional sequence and three-dimensional structure through multiple rounds of progressive panoramic mode. Compared to previous autoregressive methods, it has higher efficiency and accuracy. MEAN significantly outperforms the then state-of-the-art models in sequence and structure modeling, antigen-binding CDR design, and binding affinity optimization. Specifically, antigen-binding CDR design improves by approximately 23% over baseline models, and affinity optimization improves by approximately 34% over baseline models.
The MEAN model architecture is shown in the figure below:


The structure of the antibody-antigen complex or the antibody structure (the complex structure is recommended for better design results), in PDB format.
Specify the name of the antibody heavy chain in the structure, the default value is H. Note that if the antibody heavy chain in the uploaded structure is not named H, please modify this parameter to the corresponding chain name.
Specify the name of the antibody light chain in the structure, the default value is L. Note that if the antibody light chain in the uploaded structure is not named L, please modify this parameter to the corresponding chain name.
Design mode, there are two design modes: CDR-H3 design and affinity optimization (Optimized).
In affinity optimization, the number of generated structures, the default value is 100.
Specify the sequences corresponding to the top N mutations with the optimal energy. The default value is 100.
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN. Default is mutant_seqs.fasta.
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN. The chains within the complexes are separated by colon(:) (for batch mode structure prediction by Boltz2). Default is mutant_seqs_complex.fasta.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| cdrs.txt | Contains the designed CDR-H3 sequences |
| design.pdb | The designed complex structure file, note that only the Fv region of the antibody structure is retained |
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ddg_scores.txt | Affinity difference scores between the optimized structure and the original structure |
| opt_best.pdb | The structure file with the best affinity, note that only the Fv region of the antibody structure is retained |
| log.txt | Affinity optimization log file |
| opt.zip | Compressed file of multiple optimized structures |
The ddg_scores.txt file contains the following information:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Structure name |
| ddG | Affinity difference score ddG with the original structure, in kcal/mol. A negative value indicates an improvement in affinity, and the more negative, the better the improvement in affinity |
Output the sequences of the mutation chains corresponding to TopN mutant_seqs.fasta.
Output the sequences of the complexes corresponding to TopN mutant_seqs_complex.fasta. The chains within the complex are separated by colons(:) (for batch mode of Boltz2 structure prediction) .
Venn Diagram Plot是一个制作韦恩图(Venn diagram)模块,常用于比较两个集合的重叠区域以及提取公共部分内容。用于中药网络药理学分析中提取中药成分预测靶点与疾病相关靶点的交集。
集合A文件,TXT格式,每行一个元素。
集合B文件,TXT格式,每行一个元素。
作图时显示的图例,逗号分割,如:set A,set B
比较时是否大小写敏感:
Yes:区分大小写比较
No:不区分大小写比较
输出包含交集部分内容的文件名称,默认为intersection.txt
输出韦恩图文件venn_diagram.png以及交集部分内容的文本文件intersection.txt
The Venn Diagram Plot module is used to create Venn diagrams, which are commonly utilized to compare the overlapping regions of two sets and extract the common elements. This is particularly useful in traditional Chinese medicine network pharmacology analysis for identifying the intersection of predicted targets of herbal components and disease-related targets.
The file for set A, in TXT format, with one element per line.
The file for set B, in TXT format, with one element per line.
The labels to be displayed in the diagram, separated by commas, e.g., set A,set B.
Whether the comparison is case-sensitive:
The name of the output file containing the intersection elements, default is intersection.txt.
The output includes a Venn diagram file named venn_diagram.png and a text file containing the intersection elements named intersection.txt.

Protein-Protein Interaction (STRING)是基于STRING的提取蛋白相互作用模块。String是一个蛋白互作网络数据库,包含蛋白直接物理作用的互作关系以及间接作用的互作关系。
蛋白名称列表文件,TXT格式,一行一个蛋白名称
蛋白-蛋白关联性打分的截断值,0~1之间,只导出combined_score为截断值以上的蛋白-蛋白相互作用数据。
是否输出相关蛋白;
Yes:代表输出与输入蛋白相关的蛋白
No:代表只输出输入蛋白之间存在的相互作用
输出蛋白-蛋白相互作用文件string_interactions.tsv,每一列说明如下:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| node1 | 节点1的蛋白名称 |
| node2 | 节点2的蛋白名称 |
| node1_string_id | 节点1在STRING数据库中标准ID |
| node2_string_id | 节点1在STRING数据库中标准ID |
| neighborhood_on_chromosome | 基于基因组邻近性预测的相互作用得分。 |
| gene_fusion | 基于基因融合事件预测的相互作用得分。 |
| phylogenetic_cooccurrence | 基于共同出现(共现性)预测的相互作用得分。 |
| homology | 蛋白之间的同源性。 |
| coexpression | 基于共同表达(共表达)预测的相互作用得分。 |
| experimentally_determined_interaction | 基于实验数据(例如,酵母双杂交实验)预测的相互作用得分。 |
| database_annotated | 基于已知数据库信息预测的相互作用得分。 |
| automated_textmining | 基于文本挖掘预测的相互作用得分。 |
| combined_score | 综合所有上述信息计算得到的综合得分。 |
Protein-Protein Interaction (STRING) is a module based on the STRING database for extracting protein interaction data. STRING is a protein interaction network database that includes both direct physical interactions and indirect functional associations between proteins.
A file containing a list of protein names, in TXT format, with one protein name per line.
A cutoff value for the protein-protein association score, ranging from 0 to 1. Only protein-protein interactions with a combined score above this cutoff will be exported.
Whether to output related proteins:
The output is a protein-protein interaction file named string_interactions.tsv. Each column is described as follows:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| node1 | Protein name of node 1 |
| node2 | Protein name of node 2 |
| node1_string_id | Standard STRING ID for node 1 |
| node2_string_id | Standard STRING ID for node 2 |
| neighborhood_on_chromosome | Interaction score based on genomic neighborhood prediction |
| gene_fusion | Interaction score based on gene fusion events |
| phylogenetic_cooccurrence | Interaction score based on phylogenetic co-occurrence |
| homology | Homology between proteins |
| coexpression | Interaction score based on co-expression |
| experimentally_determined_interaction | Interaction score based on experimental data (e.g., yeast two-hybrid) |
| database_annotated | Interaction score based on known database information |
| automated_textmining | Interaction score based on text mining |
| combined_score | Combined score calculated from all the above information |
Gene Enrichment (DAVID)是基于DAVID的基因功能富集分析模块,DAVID是一个生物信息数据库,整合了生物学数据和分析工具,为大规模的基因或蛋白列表提供系统综合的生物功能注释信息。
基因列表文件,TXT格式,一行一个基因/蛋白。
基因名称类型,支持多种数据库基因名称。
P-value,基因富集中统计差异检验使用的p值的截断值,只保留低于该截断值的富集条目。
基因数目截断值,只保留大于该截断值的富集条目。
基因富集的类别,包括细胞组分(Cellular Component BP),分子功能(Molecular Function MF),生物学过程(Biological Proccess BP)。
输出基因富集的结果文件,TSV格式。
结果输出chartReport.tsv文件,文件中每一列代表说明如下:
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Category | 注释类别,例如GOTERM_BP_DIRECT(生物过程)、GOTERM_MF_DIRECT(分子功能)、GOTERM_CC_DIRECT(细胞组分)、KEGG_PATHWAY(KEGG通路)等。 |
| Term | 具体的注释术语或通路名称。 |
| Count | 输入基因集中注释到该术语的基因数目。 |
| % | 输入基因集中注释到该术语的基因占总输入基因的百分比。 |
| PValue | 富集分析的p值,表示注释到该术语的基因数目与随机情况下的期望数目之间的显著性差异。 |
| Benjamini | Benjamini-Hochberg校正后的p值,用于控制假发现率(FDR)。 |
| FDR | 假发现率,表示在所有显著结果中,预期的错误发现比例。 |
| Genes | 注释到该术语的输入基因的列表,通常以逗号分隔。 |
| List Total | 输入基因集中总的基因数目。 |
| Pop Hits | 背景基因集中注释到该术语的基因数目。 |
| Pop Total | 背景基因集的总基因数目。 |
| Fold Enrichment | 富集倍数,表示输入基因集中注释到该术语的基因数目相对于背景基因集中注释到该术语的基因数目的比例。 |
Gene Enrichment (DAVID) is a gene functional enrichment analysis module based on DAVID. DAVID is a bioinformatics database that integrates biological data and analytical tools to provide systematic and comprehensive biological functional annotation information for large-scale gene or protein lists.
A file containing the gene list in TXT format, with one gene/protein per line.
The type of gene name, supporting multiple database gene names.
P-value, the cutoff value of the p-value used in the statistical difference test of gene enrichment, retaining only enrichment entries below this cutoff value.
The cutoff value of the number of genes, retaining only enrichment entries with a gene count greater than this cutoff value.
The category of gene enrichment, including Cellular Component (CC), Molecular Function (MF), and Biological Process (BP).
The output file of gene enrichment results, in TSV format.
The results are output in the chartReport.tsv file, with each column representing the following descriptions:
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Category | Annotation category, such as GOTERM_BP_DIRECT (Biological Process), GOTERM_MF_DIRECT (Molecular Function), GOTERM_CC_DIRECT (Cellular Component), KEGG_PATHWAY (KEGG Pathway), etc. |
| Term | Specific annotation term or pathway name. |
| Count | The number of genes in the input gene set annotated to this term. |
| % | The percentage of genes in the input gene set annotated to this term. |
| PValue | The p-value of the enrichment analysis, indicating the significance of the difference between the number of genes annotated to this term and the expected number under random conditions. |
| Benjamini | The p-value after Benjamini-Hochberg correction, used to control the false discovery rate (FDR). |
| FDR | False discovery rate, indicating the expected proportion of false discoveries among all significant results. |
| Genes | The list of input genes annotated to this term, usually separated by commas. |
| List Total | The total number of genes in the input gene set. |
| Pop Hits | The number of genes in the background gene set annotated to this term. |
| Pop Total | The total number of genes in the background gene set. |
| Fold Enrichment | The fold enrichment, indicating the ratio of the number of genes annotated to this term in the input gene set to the number of genes annotated to this term in the background gene set. |

TCM Chemical Ingredients用于提取中药的化学成分的结构信息。
中药的名称,支持中文名、英文名、拼音名,支持多个名称,英文逗号分割。比如:人参,黄芪
是否对成分的结构进行去重处理
| 输出文件 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| ingredients.sdf | 化学成分的结构文件,SDF格式 |
| ingredients.csv | 化学成分的结构文件,CSV格式,里面包含SMILES等结构信息 |
Liu Z, Cai C, Du J. et al. TCMIO: a comprehensive database of traditional Chinese medicine on Immuno-oncology. Front Pharmacol 2020;11:439.
The TCM Chemical Ingredients module is used to extract structural information of chemical ingredients from traditional Chinese medicines (TCM).
The name(s) of the traditional Chinese medicine(s), supporting Chinese, English, or Pinyin names. Multiple names can be separated by commas. For example: 人参,黄芪.
Whether to remove duplicate structures of the ingredients:
The output includes the following files:
| Output File | Description |
|---|---|
| ingredients.sdf | Structural file of the chemical ingredients in SDF format |
| ingredients.csv | Structural file of the chemical ingredients in CSV format, containing SMILES and other structural information |
Liu Z, Cai C, Du J. et al. TCMIO: a comprehensive database of traditional Chinese medicine on Immuno-oncology. Front Pharmacol 2020;11:439.
Target Prioritization (OpenTargets) 是提取疾病相关靶点蛋白的模块,基于OpenTarget数据库及其疾病-靶点相关性打分方法。
疾病的英文名称,如rheumatoid arthritis
数据类型,包括直接关联和全部关联的数据。
direct:直接关联数据,指有直接证据表明该疾病和靶点存在关联。
all:全部关联数据,包括了间接关联数据,间接关联是基于本体论推断出来的疾病靶点关系。
详细可参考:https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/associations
疾病-靶点关系打分的截断值,只输出大于截断值的靶点信息。
靶点类型,默认为all 代表全部
输出疾病及靶点相关的文件,包括:
| 文件名称 | 文件说明 |
|---|---|
| disease_info.csv | 疾病信息表 |
| target_info.csv | 靶点信息表 |
| targets_by_data_source.csv | 基于数据来源的疾病-靶点关系打分表 |
| targets_by_data_type.csv | 基于数据类型的疾病-靶点关系打分表 |
| uniprot_ids.txt | 靶点的蛋白UniProt ID列表 |
| genes.txt | 靶点的基因名称列表 |
https://platform-docs.opentargets.org/
The Target Prioritization (OpenTargets) module is used to extract disease-related target proteins based on the OpenTargets database and its disease-target association scoring method.
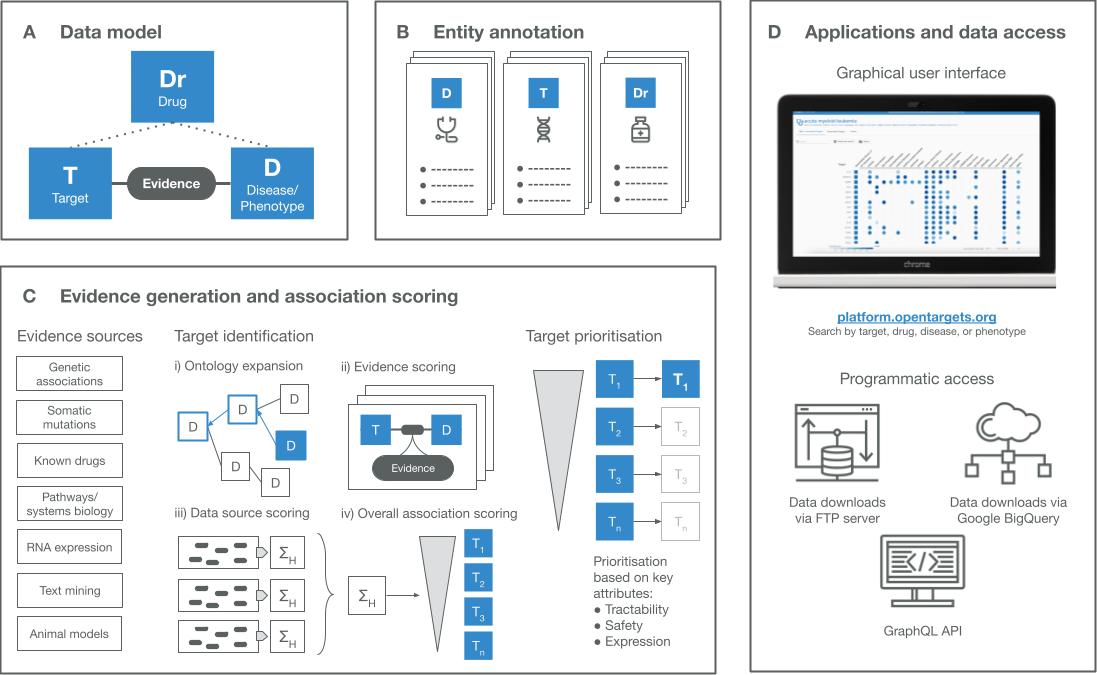
The English name of the disease, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
The type of data, including directly associated and all associated data.
The cutoff value for the disease-target association score. Only target information with a score greater than this cutoff will be output.
The type of target, default is all representing all target classes.
The output includes files related to the disease and its targets:
| File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| disease_info.csv | Disease information table |
| target_info.csv | Target information table |
| targets_by_data_source.csv | Disease-target association scores by data source |
| targets_by_data_type.csv | Disease-target association scores by data type |
| uniprot_ids.txt | List of target protein UniProt IDs |
| genes.txt | List of target gene names |

Structure Minimization是结构优化模块,支持氢原子优化、氨基酸侧链优化、整体优化三种方式。
结构文件,PDB格式。
优化类型,支持以下几种:
hydrogen:约束限制所有非氢原子,对结构上的氢原子进行优化。
sidechain:约束蛋白骨架,优化蛋白氨基酸侧脸,若存在小分子,整个小分子进行限制。
all:系统整体优化,不做任何限制约束。
可多选,进行多步优化。
能量优化的步数。
采用的分子力场,默认ff14SB。ff19SB, ff14SB适合蛋白和核酸的凝聚相模拟,也支持小分子。
约束力常数,单位为kcal/mol/Å^2,数值越大,约束能力越强。
输出文件名称,默认minimized_structure.pdb。
输出结果为优化后的结构文件minimized_structure.pdb,保留了输入文件中的链和氨基酸编号信息。
The Structure Minimization module is used for structural optimization, supporting three types of optimizations: hydrogen atom optimization, amino acid side chain optimization, and overall optimization.
The structure file in PDB format.
The type of optimization, supporting the following options:
The number of steps for energy optimization.
The molecular force field used, default is ff14SB. ff19SB and ff14SB are suitable for condensed phase simulations of proteins and nucleic acids, and also support small molecules.
The restrain force constant, in units of kcal/mol/Ų. The larger the value, the stronger the constraint.
The name of the output file, default is minimized_structure.pdb.
The output is the optimized structure file minimized_structure.pdb, retaining the chain and amino acid numbering information from the input file.


蛋白结构处理模块,用于补全缺失原子和残基,以及蛋白氨基酸残基的质子化判断以及加氢操作。采用pdbfixer补全缺失,采用propka3进行质子化判断。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式
提取指定链处理,默认all,代表选择全部链,输入链名,多条链用英文逗号隔开,如A,B表示从PDB文件中提取A,B链进行结构处理。注意链名之间不要用空格。
删除非标准蛋白或核酸残基,如水、离子、以及其他PDB中HETATM记录。
all:表示删除所有HETATM记录,包括水、离子、小分子等;
water:表示仅删除水;
ions:表示仅删除离子,默认为NA,CL;
custom:表示需要删除其他定制的残基名称,由Custom Heterogens参数指定。
Heterogens详细介绍可参考:https://www.wwpdb.org/documentation/file-format-content/format23/sect4.html
自定义Heterogens的残基名称,多个用英文逗号分隔,如ZN,MG
删除氢原子,Yes表示删除,No表示不删除。
添加缺失的重原子或者残基。
heavy:表示添加缺失重原子
residues:表示添加缺失残基,默认也会添加缺失的原子
是否进行质子化判断并添加氢原子,采用propka方法进行蛋白残基的质子化判断。
Yes:代表根据质子化判断结果进行加氢操作,
No:代表不加氢处理
用于蛋白质子化状态判断的pH值。
输出PDB文件中残基和原子的命名方式。
PDB:标准氨基酸格式,如组氨酸为HIS;
AMBER:AMBER格式,如组氨酸为HID/HIE/HIP;
CHARMM:CHARMM格式,如组氨酸为HSE/HSD/HSP。
输出的处理后的蛋白结构文件,PDB格式。默认文件名为:prepared_structure.pdb。
输出处理好的结构文件,PDB格式。文件中的原子和残基类型按照指定Naming Scheme方法。
The Structure Preparation module is used for completing missing atoms and residues in protein structures, as well as determining the protonation states of amino acid residues and adding hydrogen atoms. It uses pdbfixer for completing missing parts and propka3 for protonation state determination.
The protein structure file in PDB format.
Specify the chains to be processed. The default is all, which means all chains will be processed. To specify chains, input the chain names separated by commas without spaces, e.g., A,B to process chains A and B from the PDB file.
Remove non-standard protein or nucleic acid residues such as water, ions, and other HETATM records in the PDB.
NA,CL.Custom Heterogens parameter.For more details on Heterogens, refer to: Heterogen Information
Specify custom heterogens to be removed by their residue names, separated by commas, e.g., ZN,MG.
Remove hydrogen atoms.
Add missing heavy atoms or residues.
Determine protonation states and add hydrogen atoms using the propka method.
The pH value used for determining the protonation states of the protein residues.
The naming convention for residues and atoms in the output PDB file.
The name of the output processed protein structure file in PDB format. The default file name is prepared_structure.pdb.
The output is a processed structure file in PDB format. The atoms and residue types in the file follow the specified naming scheme.

Antibody RMSD模块对参考抗体结构及其他CDR相同的抗体结构,进行基于CDR区域的结构叠合,并计算CDR区域的RMSD值。支持普通抗体及纳米抗体。
应用场景:人源化后的抗体序列,预测抗体结构后,比较各结构CDR区域的RMSD差异。支持普通抗体及纳米抗体。
多个抗体结构PDB文件的压缩打包文件,TAR格式
进行RMSD计算的参考抗体结构,PDB格式
抗体叠合结构输出名称,TAR.GZ格式
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Reference Antibody | 参考抗体结构的名称 |
| The other Antibody | 用于计算RMSD的其他抗体结构名称 |
| RMSD_CDRs | CDR区域整体的RMSD值 |
| RMSD_CDR1 | CDR1的RMSD值 |
| RMSD_CDR2 | CDR2的RMSD值 |
| RMSD_CDR3 | CDR3的RMSD值 |
The Antibody RMSD module aligns the reference antibody structure with other antibodies having the same CDR regions, performs a structural overlay based on the CDR regions, and calculates the RMSD values of the CDR regions.
Application Scenario: After humanizing antibody sequences and predicting antibody structures, the module compares the RMSD differences in the CDR regions of various structures.
Compressed TAR file containing multiple antibody structure PDB files.
Reference antibody structure in PDB format for RMSD calculation.
Antibody composite structure output name, TAR.GZ format
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Reference Antibody | Name of the reference antibody structure |
| The other Antibody | Name of the other antibody structure used for RMSD calculation |
| RMSD_CDRs | RMSD value of the overall CDR regions |
| RMSD_CDR1 | RMSD value of CDR1 |
| RMSD_CDR2 | RMSD value of CDR2 |
| RMSD_CDR3 | RMSD value of CDR3 |

Target Prediction (FastTargetPred)是基于二维相似度的小分子靶点预测模块,活性分子及靶点数据来源于ChEMBL25数据库,相似度计算采用1024位ECFP4的分子指纹,特点是速度块,几小时完成数十万化合物的靶点预测。
小分子结构文件,SDF格式
相似度(Tanimoto)阈值。从ChEMBL中查找大于相似度阈值的化合物。
输出文件名称
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| result.csv | 靶点预测结果的csv文件 |
| result.html | 靶点预测结果的html文件 |
其中输出结果包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Query name | 查询分子名称 |
| Database molecule id | ChEMBL中相似找出的相似分子ID |
| Target id | 靶标分子ID |
| Score | 相似度数值 |
| Uniprot | 蛋白Uniprot ID |
| Uniprot name | Uniprot分子名称 |
| Status | 数据发表情况 |
| Protein names | 蛋白名称 |
| Gene names | 基因名称 |
| Organism | 物种名称 |
| CHEMBL | 靶点CHEMBL分子ID |
| Involvement in disease | 参与疾病类型 |
| Geneontology (biological process) | 谱系学(生物过程) |
| Cross-reference (Reactome) | 交叉引用(Reactome) |
Chaput L, Guillaume V, Singh N, Deprez B, Villoutreix BO. FastTargetPred: a program enabling the fast prediction of putative protein targets for input chemical databases. Bioinformatics. 2020 Aug 15;36(14):4225-4226.https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa494
Target Prediction (FastTargetPred) is a module for predicting small molecule targets based on 2D similarity. The active molecules and target data are sourced from the ChEMBL25 database. Similarity calculation uses 1024-bit ECFP4 molecular fingerprints. The main feature of this module is its speed, capable of predicting targets for hundreds of thousands of compounds within a few hours.
The structure file of small molecules in SDF format.
The similarity (Tanimoto) threshold. Compounds from ChEMBL with a similarity greater than this threshold will be considered.
The name of the output file.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result.csv | CSV file containing the target prediction results |
| result.html | HTML file containing the target prediction results |
The output results contain the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Query name | Name of the query molecule |
| Database molecule id | ID of the similar molecule found in ChEMBL |
| Target id | ID of the target molecule |
| Score | Similarity score |
| Uniprot | Uniprot ID of the protein |
| Uniprot name | Name of the Uniprot molecule |
| Status | Publication status of the data |
| Protein names | Names of the proteins |
| Gene names | Names of the genes |
| Organism | Name of the organism |
| CHEMBL | CHEMBL molecule ID of the target |
| Involvement in disease | Types of diseases involved |
| Geneontology (biological process) | Gene ontology (biological process) |
| Cross-reference (Reactome) | Cross-reference (Reactome) |

静电势(ESP,electrostatic potential)表面是指在分子周围某个曲面上静电势的分布,通过静电势对蛋白质表面着色有助于识别带电分子或极性分子的结合位点。正电位区域与负电荷互补,而负电位区域与正电荷互补。蛋白质静电势对于蛋白质的稳定性、折叠、酶催化、蛋白质间相互作用以及与其他分子的结合等方面起着关键作用。APBS(Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver )是业界著名的计算生物大分子结构静电势能的工具。
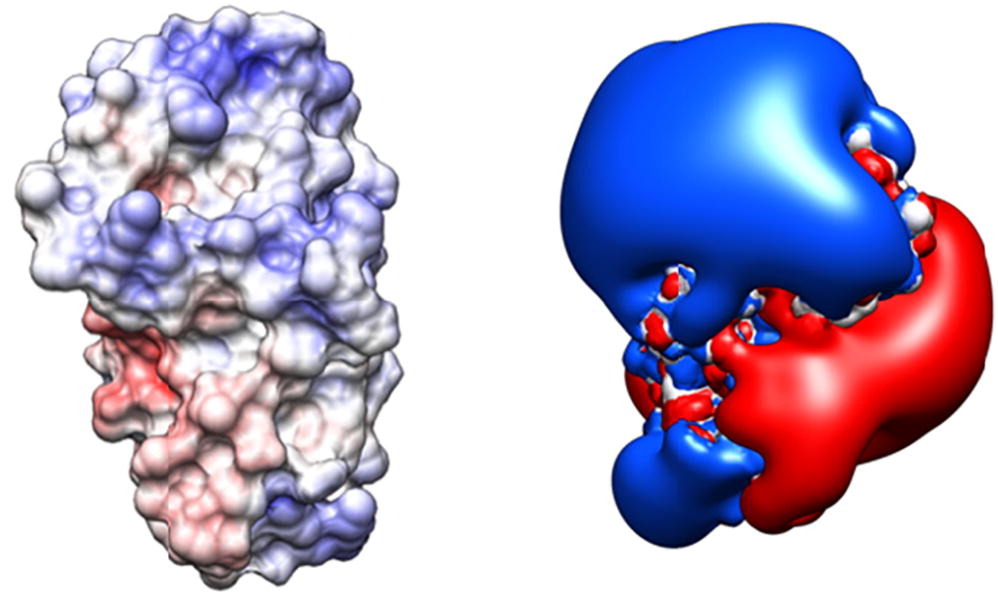
蛋白结构文件,PDB格式
输出文件格式,支持DX或者CUBE
输出静电势能结果文件potential.dx或者potential.cube,用于将静电势能渲染到蛋白表面上。
Electrostatic potential (ESP) surfaces represent the distribution of electrostatic potential around a molecule on a given surface. Coloring the protein surface based on electrostatic potential helps identify binding sites for charged or polar molecules. Regions with positive potential complement negatively charged molecules, while regions with negative potential complement positively charged molecules. Protein electrostatic potential plays a crucial role in protein stability, folding, enzymatic catalysis, protein-protein interactions, and binding with other molecules. APBS (Adaptive Poisson-Boltzmann Solver) is a renowned tool for calculating the electrostatic potential of biological macromolecules.

The protein structure file in PDB format.
The format of the output file, supporting DX or CUBE.
The output electrostatic potential result file, named potential.dx or potential.cube, can be used to render the electrostatic potential on the protein surface.

通过蛋白序列逆折叠模型ESM-IF,预测蛋白质的绝对稳定性ΔG。
传统的物理方法(如FoldX、Rosetta等)预测蛋白稳定性ΔG,依赖于高置信度结构pdb,如果突变太多,结构置信度降低,预测结果较差。在ProteinGym的benchmark结果表明,生成模型ESM-IF在zero-shot预测DMS数据的蛋白突变稳定性ΔΔG达到同类最佳水平。该方法是在突变预测基础上的延伸,利用ESM-IF模型直接预测完整蛋白折叠稳定性的绝对ΔG值。
经过测试,预测误差RMSE ≈ 1.5 kcal/mol,相关系数为0.7,是预测蛋白质的折叠稳定性ΔG的重大突破。
原理:
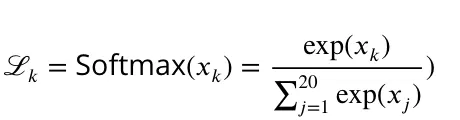
然后,将蛋白质所有氨基酸位点的Lk加和,得到蛋白整体的log-likelihood。
最后,通过线性整体log-likelihood与实验稳定性ΔG拟合得到拟合参数,根据a/b就可以将log-likelihood转换成蛋白稳定性ΔG了。
模型预测效果如下图所示:
在两个不同数据集的 265 种蛋白质的预测稳定性值和实验稳定性值进行了比较。Spearman相关系数 (ρs) 为0.69,误差RMSE约为1.36 kcal/mol,相关性较好。
与其他基线模型比较结果如下图所示:
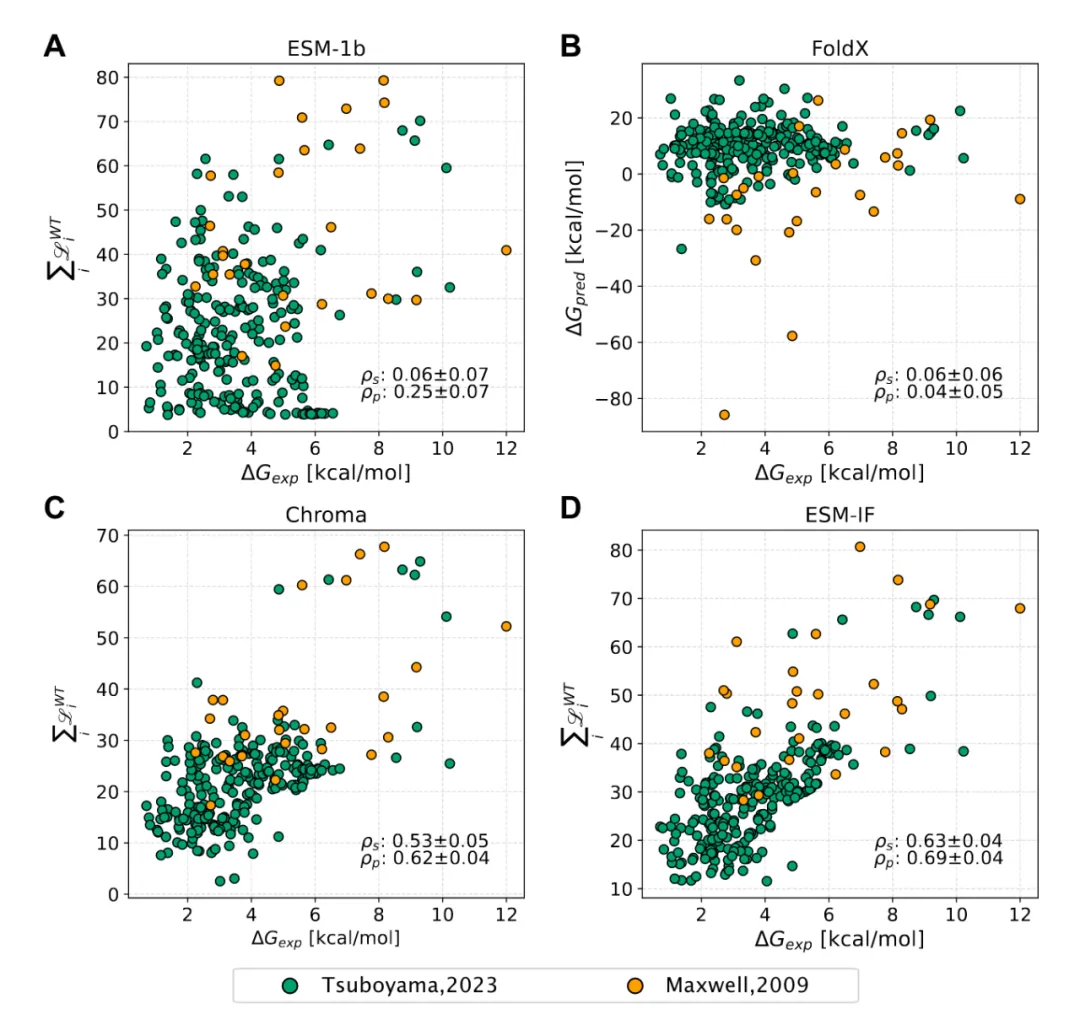
蛋白结构文件,PDB格式
多个蛋白结构PDB的压缩文件,TAR格式。
当同时上传蛋白结构PDB和压缩包时会合并计算。
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 结构名称 |
| Absolute_Folding_Stability (kcal/mol) | dG,越大越好,代表去折叠状态能量减去折叠状态能量,即去折叠需要的能量值,通常为正值,能量越大表示需要能量越多,折叠状态越稳定 |
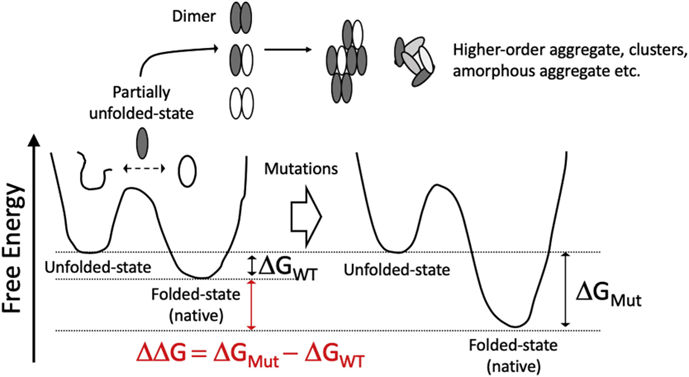
Predicting absolute protein folding stability using generative models Matteo Cagiada, Sergey Ovchinnikov, Kresten Lindorff-Larsen bioRxiv 2024.03.14.584940; https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.14.584940
The absolute folding stability ($\Delta G$) of a protein can be predicted using the inverse folding model ESM-IF. Traditional physical methods (such as FoldX, Rosetta, etc.) for predicting protein stability $\Delta G$ rely on high-confidence structure PDB files. If mutations are numerous, the structural confidence decreases, leading to poor prediction results. Benchmark results from ProteinGym show that the generative model ESM-IF achieves state-of-the-art performance in zero-shot prediction of protein mutation stability $\Delta \Delta G$ on DMS data. This method extends mutation prediction by using the ESM-IF model to directly predict the absolute $\Delta G$ value of the complete protein folding stability.
Testing shows a prediction error RMSE of approximately 1.5 kcal/mol and a correlation coefficient of 0.7, marking a significant breakthrough in predicting the folding stability $\Delta G$ of proteins.
Principle
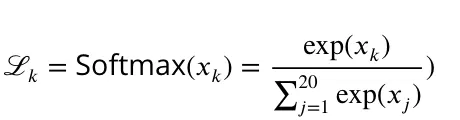
The log-likelihood of the entire protein is obtained by summing the $L_k$ values of all amino acid sites. Finally, the log-likelihood is linearly fitted to the experimental stability $\Delta G$ to obtain the fitting parameters. The log-likelihood can be converted into protein stability $\Delta G$ based on $a/b$.
Model Prediction Performance
The predicted stability values and experimental stability values for 265 proteins in two different datasets were compared. The Spearman correlation coefficient ($\rho_s$) is 0.69, and the error RMSE is about 1.36 kcal/mol, indicating good correlation.

Comparison with Other Baseline Models

The protein structure file in PDB format.
A compressed file containing multiple protein structure PDBs in TAR format. When both the protein structure PDB and the compressed file are uploaded, they will be calculated together.
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Structure name |
| Absolute_Folding_Stability (kcal/mol) | $\Delta G$, the higher the better, representing the energy difference between the unfolded and folded states. It is usually a positive value, with higher values indicating greater stability in the folded state. |


De novo Generation (REINVENT4)是基于阿斯利康开源的REINVENT4算法用于小分子全新生成的模块。支持多种分子生成方式:Reinvent - 从头开始创造新类药分子,Libinvent - 修饰一个骨架,Linkinvent - 设计两个片段之间的linker,Mol2Mol - 在用户定义的相似度范围内优化分子。
模型类型:Reinvent、LibInvent、LinkInvent、Mol2Mol
Reinvent是从头开始创造新分子,Libinvent修饰一个骨架,Linkinvent识别两个片段之间的连接器,而Mol2Mol 则在用户定义的相似度范围内优化分子。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。除了Reinvent外,其余模型为必填项。
输出唯一的标准化分子:true或者false
对原子进行随机“洗牌操作”:true或者false。“随机洗牌”是为了避免数据投入的顺序对网络训练造成影响。
生成的分子个数,注意:它乘以输入分子的个数为最终输出总分子数
仅在Mol2Mol使用:beamsearch或者multinomial
在 Mol2Mol 中,有5种不同的训练模型:
仅在Mol2Mol使用:多项抽样中的温度
使用GPU进行计算:true或者false
输出CSV文件名称
输出SDF文件名称
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| result.csv | 全新生成的化合物CSV文件,包含了SMILES信息 |
| denovo.sdf | 全新生成的化合物SDF文件 |
De novo Generation (REINVENT4) is a module based on AstraZeneca’s open-source REINVENT4 algorithm for generating new small molecules. It supports various molecule generation methods: Reinvent - creating new drug-like molecules from scratch, Libinvent - modifying a scaffold, Linkinvent - designing a linker between two fragments, and Mol2Mol - optimizing molecules within a user-defined similarity range.

Type of model to use: Reinvent, LibInvent, LinkInvent, Mol2Mol.
File containing small molecule structures in SDF or SMILES format. This is required for all models except Reinvent.
Whether to output unique standardized molecules: true or false.
Whether to perform random atom shuffling: true or false. “Random shuffling” helps to avoid the impact of input order on network training.
Number of molecules to generate. Note that this number multiplied by the number of input molecules gives the total number of output molecules.
Used only in Mol2Mol: beamsearch or multinomial.
In Mol2Mol, there are five different training models:
Used only in Mol2Mol: Temperature for multinomial sampling.
Whether to use GPU for computation: true or false.
Name of the output CSV file.
Name of the output SDF file.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result.csv | CSV file containing newly generated compounds, including SMILES information |
| denovo.sdf | SDF file containing newly generated compounds |

该模块基于物理模型(分子力学经验力场)计算多个蛋白结构的能量,并与参考蛋白结构的能量进行比较。
多个蛋白结构PDB文件的压缩打包文件,TAR格式
进行能量比对的参考蛋白结构,PDB格式
| 列名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 结构名称 |
| Score | 能量打分,数值负得越多表示能量越低 |
This module calculates the energy of multiple protein structures based on a physical model (empirical molecular force field) and compares these energies with the energy of a reference structure.
Compressed TAR file containing multiple protein structure PDB files.
Reference structure in PDB format for energy comparisons.
| Column Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Structure name |
| Score | Energy score, where a more negative value indicates lower energy |
该模块基于ESM大规模预训练蛋白语言模型实现。提取序列的向量化特征信息(embeddings),可用于下游序列性质(如:突变对应的亲和力变化、稳定性变化,抗体序列可开发性等)预测任务,为判别模型的训练提供序列特征。
ESM模型是通用蛋白质语言模型,采用UniRef50/90等序列数据库(数千万条序列)进行模型训练,提供了不同参数量(800万,3500万,1.5亿,6.5亿,30亿,150亿)的各类模型,可用于直接从蛋白序列预测结构、功能和其他蛋白质性质。如在结构预测中,ESM避免了对外部进化数据库、MSA和模板的需求,计算精度与AlphaFold2(存在MSA信息时)接近,无可用MSA信息时,计算精度ESM要显著优于AlphaFold2。计算速度比AlphaFold2快数十倍。
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式
注意:多条序列时,序列名称应避免重复,模块会对重复的序列名称进行重命名,格式为“原序列名_数字”
选择用于提取序列特征的模型,可用模型及特征维度说明如下:
| 模型名称 | 参数量 | 特征维度 | 模型层数 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESM1b_650M | 650M | 1280 | 33 |
| ESM1v_650M | 650M | 1280 | 33 |
| ESM2_8M | 8M | 320 | 6 |
| ESM2_35M | 35M | 480 | 12 |
| ESM2_150M | 150M | 640 | 30 |
| ESM2_650M | 650M | 1280 | 33 |
| ESM2_3B | 3B | 2560 | 36 |
| ESM2_15B | 15B | 5120 | 48 |
备注:“M”表示Million(百万),“B”表示Billion(十亿),ESM-2-15B模型需要的GPU卡显存大小约为32GB
每条序列会输出一个特征信息文件“序列名.pt”,包含了该序列的向量化特征信息,该特征信息由模型最后一层产生。多条序列会输出多个pt文件,并压缩为feats.tar压缩文件。
特征信息文件可通过torch加载,如下:
embs = torch.load(“序列名.pt”)
embs[‘mean_representations’][‘模型层数’]
This module is based on the ESM (Evolutionary Scale Modeling) large-scale pre-trained protein language model. It extracts vectorized feature information (embeddings) from sequences, which can be used for downstream sequence property prediction tasks such as changes in affinity and stability corresponding to mutations, developability of antibody sequences, etc., providing sequence features for discriminative model training.
The ESM model is a universal protein language model trained on sequence databases such as UniRef50/90 (tens of millions of sequences). It offers various models with different parameter sizes (8 million, 35 million, 150 million, 650 million, 3 billion, 15 billion) that can be used to predict protein structures, functions, and other protein properties directly from protein sequences. In structural prediction, ESM eliminates the need for external evolutionary databases, multiple sequence alignments (MSA), and templates. Its calculation accuracy is comparable to AlphaFold2 (when MSA information is available) and significantly superior to AlphaFold2 in accuracy when MSA information is not available. ESM is also several times faster than AlphaFold2.
The sequence file of the protein in FASTA format.
Note: When multiple sequences are provided, sequence names should be unique to avoid duplication. The module will rename duplicated sequence names in the format “original_sequence_name_number”.
Select the model used to extract sequence features. The available models and their feature dimensions are as follows:
| Model Name | Parameters | Feature Dimension | Number of Layers |
|---|---|---|---|
| ESM1b_650M | 650M | 1280 | 33 |
| ESM1v_650M | 650M | 1280 | 33 |
| ESM2_8M | 8M | 320 | 6 |
| ESM2_35M | 35M | 480 | 12 |
| ESM2_150M | 150M | 640 | 30 |
| ESM2_650M | 650M | 1280 | 33 |
| ESM2_3B | 3B | 2560 | 36 |
| ESM2_15B | 15B | 5120 | 48 |
Note: “M” stands for Million, “B” stands for Billion. The ESM-2-15B model requires approximately 32GB of GPU memory.
Each sequence will output a feature information file named “sequence_name.pt,” which contains the vectorized feature information of that sequence generated by the last layer of the model. For multiple sequences, multiple pt files will be output and compressed into a feats.tar file.
The feature information file can be loaded using torch as follows:
embs = torch.load(“sequence_name.pt”)
embs[‘mean_representations’][‘number_of_layers’]

该模块用于NGS测序后的DNA序列(抗体)分析,具体分析内容包括:
NGS测序后的DNA序列,FASTA/AB1格式
物种类型,支持2种:HUMAN, MOUSE。默认为HUMAN
编号规则,支持imgt, chothia, kabat
氨基酸序列聚类方案,支持2种:full, cdr。‘full’表示使用全长序列进行聚类,‘cdr’表示使用CDR序列进行聚类(具体CDR位置在参数‘CDRs’中设定),默认为‘cdr’
指定用于聚类的CDR区域,在‘Cluster’参数为cdr时生效。可选区域为(支持多选):CDR1,CDR2,CDR3。默认选择CDR3。
聚类中采用的序列一致性数值,范围在0-1之间,默认值为0.5
聚类前是否要求IGV基因名称一致的序列归为一组,默认为False
输出结果文件名,默认为NGS_res.csv
NGS测序后的蛋白序列,FASTA格式
物种类型,支持2种:HUMAN, MOUSE。默认为HUMAN
编号规则,支持imgt, chothia, kabat
氨基酸序列聚类方案,支持2种:full, cdr。‘full’表示使用全长序列进行聚类,‘cdr’表示使用CDR序列进行聚类(具体CDR位置在参数‘CDRs’中设定),默认为‘cdr’
指定用于聚类的CDR区域,在‘Cluster’参数为cdr时生效。可选区域为(支持多选):CDR1,CDR2,CDR3。默认选择CDR3。
聚类中采用的序列一致性数值,范围在0-1之间,默认值为0.5
聚类前是否要求IGV基因名称一致的序列归为一组,默认为False
输出结果文件名,默认为NGS_res.csv
输出result.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
| 列名 | 说明 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| ID | 序列名称 | |
| DNA_Seq | DNA序列 | |
| Protein_Seq | 翻译后的氨基酸序列 | |
| Chain | 链类型:IGH/IGK/IGL | |
| CDR1_AA | CDR1的氨基酸序列 | |
| CDR2_AA | CDR2的氨基酸序列 | |
| CDR3_AA | CDR3的氨基酸序列 | |
| CDR1_Length | CDR1的氨基酸序列长度 | |
| CDR2_Length | CDR2的氨基酸序列长度 | |
| CDR3_Length | CDR3的氨基酸序列长度 | |
| Unusual_Residue(ESM) | 基于ESM模型的不常见残基及优势突变 | 如:'V11L’表示序列中第11位的V是模型判定的该位置不常见残基,L为模型判定的该位置优势突变残基 |
| Unusual_Residue(IgLM) | 基于IgLM模型的不常见残基及优势突变 | 同上 |
| V_Gene_First | 匹配的首个IGV基因名称。 | IGV基因名称可能存在多个匹配,这里列出首个。注:输入为蛋白序列时,该字段忽略。 |
| V_Gene | IGV基因名称 | 如同时匹配多个基因名,用‘;’分隔 |
| D_Gene | IGD基因名称 | 同上,注:输入为蛋白序列时,该字段忽略。 |
| J_Gene | IGJ基因名称 | 同上,注:输入为蛋白序列时,该字段忽略。 |
| CDR1_Highrisk_Hotspots | CDR1中的PTM高风险位点 | 如:‘NG(1)’表示高风险位点‘NG’出现1次 |
| CDR2_Highrisk_Hotspots | CDR2中的PTM高风险位点 | 同上 |
| CDR3_Highrisk_Hotspots | CDR3中的PTM高风险位点 | 同上 |
| CDR1_Lowrisk_Hotspots | CDR1中的PTM低风险位点 | 同上 |
| CDR2_Lowrisk_Hotspots | CDR2中的PTM低风险位点 | 同上 |
| CDR3_Lowrisk_Hotspots | CDR3中的PTM低风险位点 | 同上 |
| Mutations(AA) | 与Germline序列比对所对应的突变,并标注了突变所在区域(FR或CDR),多个突变用分号分隔 | 如: 'V29I(CDR1)'表示编号29的残基存在突变,其中Germline序列中残基是V,当前抗体序列中残基为I,根据抗体编号规则所在的区域为CDR1 |
| SHM(AA) | 基于氨基酸序列计算得到的体系超突变率 | SHM: Somatic hypermutation,计算方式是将当前序列与Germline参考序列进行比对,序列突变总数量与序列长度的比值即为SHM |
| SHM(NA) | 基于DNA序列计算得到的体系超突变率 | 同上,注:输入为蛋白序列时,该字段忽略。 |
| pI | 等电点 | |
| kDa | 分子量(千道尔顿) | |
| Hydrophobicity | 疏水性指数 | 序列各氨基酸的Kyte-Doolittle疏水指数之和,主要用来快速粗略比较近似序列的相对疏水程度高低 |
| Pre_Cluster_Group | 聚类分析中的组别名称 | 序列聚类前先进行序列分组,各组内序列再进行聚类分析。当选择CDR聚类时,CDR序列长度一致的序列归为一组。组别名称由各聚类参数组合而成,如:组名为‘8_8_18’,表示该组由CDR1,2,3长度分别为8,8,18的多条序列组成。如果分组参数设定要求IGV基因名称一致,则IGV基因名称也会出现在组别名称中,如:‘8_8_18_IGKV1-12*01’ |
| Cluster_ID | 序列所属类别的名称 | 如:‘2_3’表示第2组第3个类别 |
| Cluster_Size | 序列所属类别包含的序列数目 | 如:‘5’表示该类别含有5条序列 |
| Cluster_Center | 序列是否为聚类中心 | '1’表示是,‘0’表示不是 |
| Cluster_Ident | 聚类后的类别中,成员序列与聚类中心序列的序列一致性 | 聚类时,如果选择全长序列聚类,这里即为全长序列的一致性;如选择CDR进行聚类,则为选中的CDR区域序列的整体一致性 |
| Cluster_CDR1_Ident | 聚类后的类别中,成员序列与聚类中心序列的CDR1序列的一致性 | |
| Cluster_CDR2_Ident | 聚类后的类别中,成员序列与聚类中心序列的CDR2序列的一致性 | |
| Cluster_CDR3_Ident | 聚类后的类别中,成员序列与聚类中心序列的CDR3序列的一致性 |
输出进化树信息,为打包文件tree.tar,包含多个进化树文件tree_clusterXXX.txt,每个进化树文件包含该聚类类别(cluster)中所有成员序列CDR区域的进化分析结果。
风险位点说明:
其中打勾标记的位点NXS, NXT, NG, DHK, DG, DD和Cys共7个位点为默认的潜在PTM高风险位点,通常需重点关注,其余为低风险位点。
The module is used for the analysis of the DNA sequence (antibody) after NGS sequencing. The analysis content includes:
-IGV, IGD, IGJ gene annotation(IGBLAST)
-DNA sequence is translated as amino acid sequence (antibody) and CDR recognition
-Based on protein (antibody) language model, analyze unusual residual and advantageous mutations (ESM, IgLM)
-PTM (post -translation modification) hotspot analysis, low and high risk hotspot
-Sequence property calculation (PI, molecular weight, hydrophobicity)
-Sequence clustering(MMSEQ2)
DNA sequence after NGS sequencing,FASTA/ab1 format
Type of Species,support two:HUMAN, MOUSE. The default is HUMAN
Numbering scheme: imgt, chothia and kabat
Scheme of sequence clustering,support two:full, cdr. ‘full’ means clustering by full length sequence,‘cdr’ means clustering by CDR. The default is ‘cdr’
Specify the CDRs for clustering,when the ‘Cluster’ is set to ‘cdr’. Mutiple choice are supported: CDR1, CDR2, CDR3
The sequence identity used for clustering,value range from 0 to 1, the default is 0.5
Whether the sequence of the IGV gene name is consistent for classification as a group before clustering. The default is False
Result file, default is NGS_res.csv
Protein sequence after NGS sequencing,FASTA format
Type of Species,support two:HUMAN, MOUSE. The default is HUMAN
Numbering scheme: imgt, chothia and kabat
Scheme of sequence clustering,support two:full, cdr. ‘full’ means clustering by full length sequence,‘cdr’ means clustering by CDR. The default is ‘cdr’
Specify the CDRs for clustering,when the ‘Cluster’ is set to ‘cdr’. Mutiple choice are supported: CDR1, CDR2, CDR3
The sequence identity used for clustering,value range from 0 to 1, the default is 0.5
Whether the sequence of the IGV gene name is consistent for classification as a group before clustering. The default is False
Result file, default is NGS_res.csv
Export the result file result.csv, which includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| ID | Sequence | name |
| DNA_Seq | DNA sequence | |
| Protein_Seq | Translated amino acid sequence | |
| Chain | Chain type: IGH/IGK/IGL | |
| CDR1_AA | Amino acid sequence of CDR1 | |
| CDR2_AA | Amino acid sequence of CDR2 | |
| CDR3_AA | Amino acid sequence of CDR3 | |
| CDR1_Length | Length of CDR1 amino acid sequence | |
| CDR2_Length | Length of CDR2 amino acid sequence | |
| CDR3_Length | Length of CDR3 amino acid sequence | |
| Unusual_Residue(ESM) | Uncommon residues and dominant mutations based on the ESM model | e.g., ‘V11L’ indicates that the V at position 11 in the sequence is determined by the model to be an uncommon residue, and L is determined by the model to be a dominant mutation residue at that position |
| Unusual_Residue(IgLM) | Uncommon residues and dominant mutations based on the IgLM model | Same as above |
| V_Gene_First | The name of the first IGV gene that matches. | There may be multiple matches for IGV gene names, the first of which is listed here |
| V_Gene | Name of the IGV gene | If multiple gene names match simultaneously, separate them with ‘;’ |
| D_Gene | Name of the IGD gene | Same as above |
| J_Gene | Name of the IGJ gene | Same as above |
| CDR1_highrisk_hotspots | PTM high-risk sites in CDR1 | e.g., ‘NG(1)’ indicates the high-risk site ‘NG’ appears 1 time |
| CDR2_Highrisk_hotspots | PTM high-risk sites in CDR2 | Same as above |
| CDR3_Highrisk_hotspots | PTM high-risk sites in CDR3 | Same as above |
| CDR1_Lowrisk_hotspots | PTM low-risk sites in CDR1 | Same as above |
| CDR2_Lowrisk_hotspots | PTM low-risk sites in CDR2 | Same as above |
| CDR3_Lowrisk_hotspots | PTM low-risk sites in CDR3 | Same as above |
| Mutations(AA) | corresponds to mutations compared to the Germline sequence and annotates the region where the mutation occurs (FR or CDR), with multiple mutations separated by semicolons. For example, ‘V29I(CDR1)’ indicates a mutation at residue 29, where the residue in the Germline sequence is V and the residue in the current antibody sequence is I, and based on the antibody numbering rules, the region is identified as CDR1. | |
| SHM(AA) | System hypermutation rate calculated based on amino acid sequence | SHM: Somatic hypermutation is calculated by aligning the current sequence with a Germline reference sequence. The ratio of the total number of sequence mutations to the sequence length is defined as SHM |
| SHM(NA) | System hypermutation rate calculated based on DNA sequence | Same as above |
| pI | Isoelectric point | |
| kDa | Molecular weight (kilodalton) | |
| Hydrophobicity | Hydrophobicity index | The sum of the Kyte-Doolittle hydrophobicity indices of each amino acid in the sequence, mainly used for a rough comparison of the relative hydrophobicity levels of approximate sequences |
| Pre_Cluster_Group | Group name in cluster analysis | Before sequence clustering, sequences are grouped, and sequences within each group are then analyzed for clustering. For example, when selecting CDR clustering, sequences with the same CDR length are grouped together. The group name is composed of various clustering parameters, e.g., ‘8_8_18’ indicates that the group consists of multiple sequences with CDR1, 2, 3 lengths of 8, 8, 18, respectively |
| Cluster_ID | Name of the category to which the sequence belongs | e.g., ‘2_3’ indicates the third category in the second group |
| Cluster_Size | Number of sequences contained in the category | e.g., ‘5’ indicates that this category contains 5 sequences |
| Cluster_Center | Whether the sequence is a cluster center | ‘1’ indicates yes, ‘0’ indicates no |
| Cluster_Ident | Consistency of member sequences with the cluster center sequence in the clustered category | During clustering, if full-length sequence clustering is selected, this represents the consistency of the full-length sequences; if CDR clustering is chosen, it represents the overall consistency of the selected CDR region sequences |
| Cluster_CDR1_Ident | Consistency of member sequences with the CDR1 sequence of the cluster center sequence in the clustered category | |
| Cluster_CDR2_Ident | Consistency of member sequences with the CDR2 sequence of the cluster center sequence in the clustered category | |
| Cluster_CDR3_Ident | Consistency of member sequences with the CDR3 sequence of the cluster center sequence in the clustered category |
Output evolutionary tree information into a packed file named tree.tar, which includes multiple evolutionary tree files named tree_clusterXXX.txt, with each evolutionary tree file containing the evolutionary analysis results of the CDR regions of all member sequences in that clustering category (cluster).
Risk Site Description:
The default potential PTM high-risk sites marked with check marks include NXS, NXT, NG, DHK, DG, DD, and Cys, totaling 7 sites. These sites typically require special attention, while the rest are considered low-risk sites.

基于输入的9肽, 在人源片段库中搜索最相似的9肽片段。
人源片段库来源:
九肽片段,多个肽段用逗号分隔,例如:
NFFWHLHFP,GKGITLSVR,TPEALFVMT,GGIPIINCA,CVAIAEDRK
相同氨基酸的最小数量(相同位置),默认为7。
输出文件名称
输出结果文件为result.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Query | 原始9肽 |
| SameCnt | 相同个数 |
| Target | 匹配到的9肽 |
| DiffMask | 以*号标记氨基酸不同的位置 |
| From | 生成片段的来源数据库 |
The Human Fragment BLAST is based on inputs of 9 peptides, searching the Germline, TCR, NextProt, OAS for the most similar 9 peptides.
The output file is result.csv and contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Query | original 9 peptide |
| SameCnt | Same number |
| Target | The resulting 9 peptides |
| DiffMask | The different positions of amino acids are marked with *. |
| From | The source database from which the fragment is generated. |

该模块基于RaptorX-Single算法实现,RaptorX-Single是一种基于单一序列的蛋白质结构预测方法,无需multiple sequence alignment(MSA)信息。它集成了多个蛋白质语言模型和一个结构生成模块,研究结果表明,RaptorX-Single除了比AlphaFold2等基于MSA的方法运行得更快之外,在预测抗体结构、极少同源序列的蛋白和单突变效应方面也优于AlphaFold2和其他无MSA的方法。当预测的蛋白序列有大量同源序列时,RaptorX-Single的预测结果也优于AlphaFold2。
RaptorX-Single的神经网络架构:
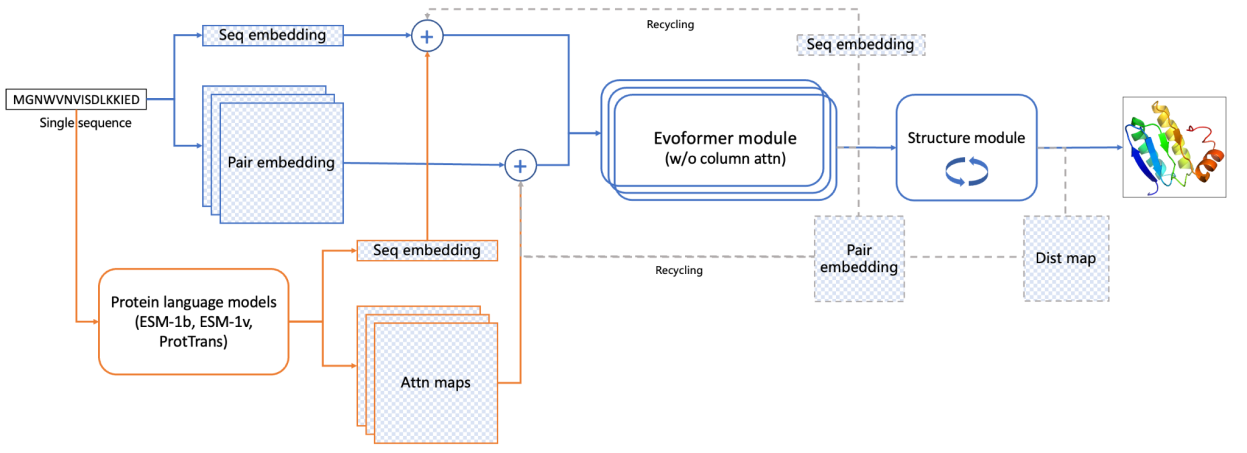
对抗体结构预测精度比较:
普通蛋白或抗体序列文件(不超过1000个氨基酸),FASTA格式,如:
>Nb21
MAQVQLVESGGGLVQAGGSLRLSCAVSGLGAHRVGWFRRAPGKEREFVAAIGANGGNTNYLDSVKGRFTISRDNAKNTIYLQMNSLKPQDTAVYYCAARDIETAEYTYWGQGTQVTVS
只支持预测单链蛋白或抗体,如果FASTA文件有多条链,每条链会单独预测为一个PDB结构。
选择预测结构时使用的模型,有两个模型可供选择:
protein表示蛋白模型,对应RaptorX-Single-ESM1b-ESM1v-ProtTrans.pt;
antibody表示抗体模型,对应RaptorX-Single-ESM1b-ESM1v-ProtTrans-Ab.pt。
如果预测蛋白,请选择前者,如果预测抗体,请选择后者
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| first.pdb | 默认输出第一条序列的预测结构。 |
| structs.tar | 针对含有多条序列的fasta文件,压缩包中含所有的序列的预测结构。 |
RaptorX-Single: exploring the advantage of single sequence based protein structure prediction. Xiaoyang Jing, Fandi Wu, Jinbo Xu. bioRxiv 2023.04.24.538081
https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.24.538081
The module is implemented based on the RaptorX-Single algorithm, which is a single sequence-based protein structure prediction method that does not require multiple sequence alignment (MSA) information. It integrates multiple protein language models and a structure generation module. The results show that RaptorX-Single, in addition to running faster than MSA-based methods such as AlphaFold2, also outperforms AlphaFold2 and other MSA-free methods in predicting antibody structures, proteins with very few homologous sequences, and single mutation effects. RaptorX-Single also outperforms AlphaFold2 when predicting protein sequences with a large number of homologous sequences.
Network Architecture for RaptorX-Single:

Comparison of the accuracy of antibody structure prediction:
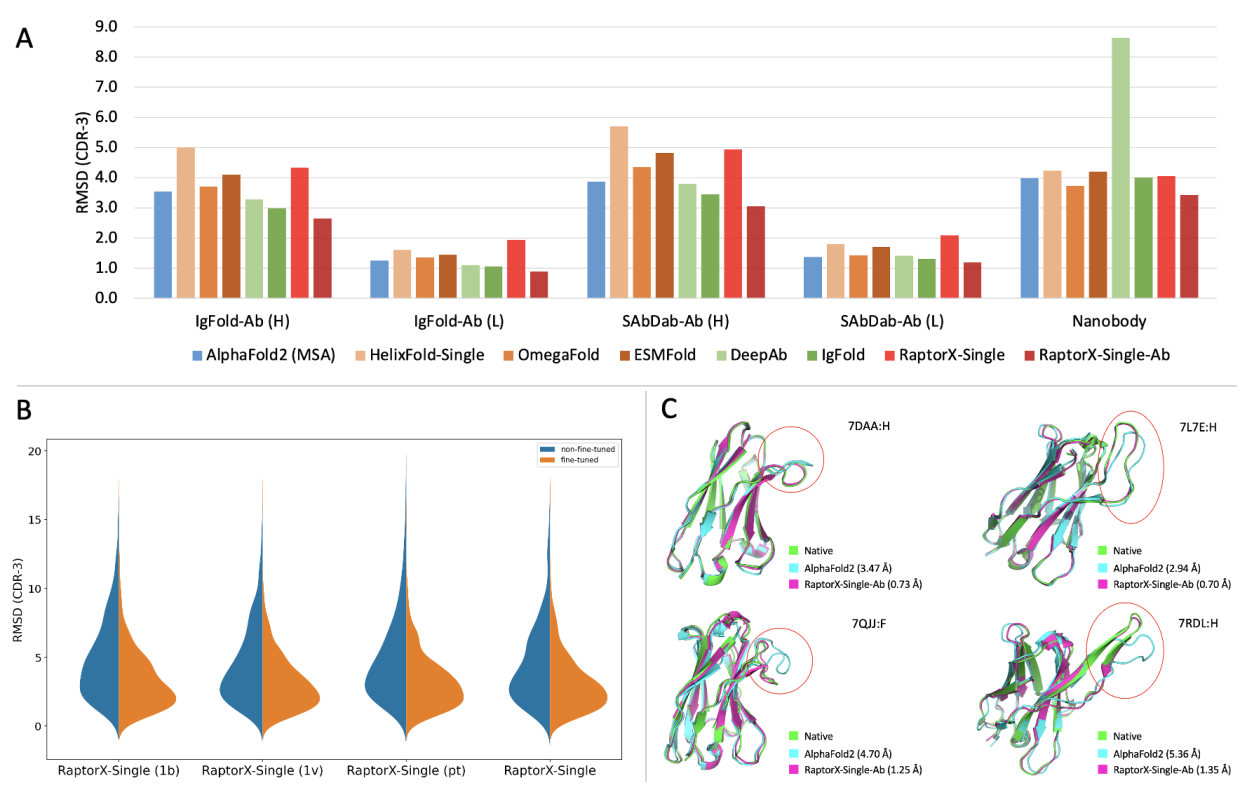
Protein or antibody sequence file (not more than 1000 amino acids) in FASTA format, example:
>Nb21
MAQVQLVESGGGLVQAGGSLRLSCAVSGLGAHRVGWFRRAPGKEREFVAAIGANGGNTNYLDSVKGRFTISRDNAKNTIYLQMNSLKPQDTAVYYCAARDIETAEYTYWGQGTQVTVS
This module only supports the prediction of single chain proteins or antibodies, if the fasta file has multiple chains, each chain will be predicted separately as a PDB structure.
There are two models to choose from when selecting the model to use in predicting the structure.
‘protein’ represents the protein model, corresponding to RaptorX-Single-ESM1b-ESM1v-ProtTrans.pt;
‘antibody’ indicates an antibody model, corresponding to RaptorX-Single-ESM1b-ESM1v-ProtTrans-Ab.pt.
Choose the former if predicting proteins and the latter if predicting antibodies.
The output includes:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| first.pdb | The default output is the prediction structure of the first sequence. |
| structs.tar | For fasta files with multiple sequences, the package contains the predictive structure for all sequences. |
RaptorX-Single: exploring the advantage of single sequence based protein structure prediction. Xiaoyang Jing, Fandi Wu, Jinbo Xu. bioRxiv 2023.04.24.538081
https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.24.538081

该模块输出指定的germline基因家族(部分或全部)的各位置的氨基酸频率分布,以供突变设计参考。
输入一条抗体序列(多条序列时只处理第一条序列)。
程序根据输入序列进行BLAST,判断其对应的基因家族,如IGHV1。
再输出对应家族的germline基因的AA频率分布。
不输入序列,则直接输出勾选的链类型(Group选项)或基因家族(Single选项)对应的germline的频率分布。
其中:
若勾选某Group,仅统计对应类型(kappa, lambda, heavy)的所有家族germline的频率分布。
若勾选Single中的某个family(如IGHV1),只输出指定的germline基因家族的AA频率分布(因为通常仅关注与目标序列同家族germline基因的频率分布情况,与我们序列不同家族的其他germline的频率分布的参考意义不大)。
抗体各位置的germline的氨基酸频率分布。
This module outputs the amino acid frequency distribution at each position of the specified germline gene family (partially or entirely) for reference in mutation design.
Input an antibody sequence (if multiple sequences are provided, only the first sequence is processed).
The program uses BLAST to determine the corresponding gene family of the input sequence, such as IGHV1.
Then it outputs the amino acid frequency distribution of the corresponding germline genes in that family.
If no sequence is provided, the module directly outputs the frequency distribution of the selected chain type (Group option) or gene family (Single option) of germline genes.
Specifically:
The amino acid frequency distribution of germline genes at each position in the antibody.

基于预训练的大规模蛋白质语言模型(也叫做PLM或pLLM),预测序列中每个氨基酸(AA)位置处20种AA出现的概率。与进化上更保守的AA类似,语言模型预测的高概率AA,有利于提升结构的稳定性、改善蛋白的折叠、提升蛋白质的表达能力等、甚至提升亲和力,比随机盲目突变具有潜在的优势。相比于基于MSA序列统计的PSSM,语言模型的预测速度更快,更多地考虑了序列内AA之间的相互作用,自身的变化也更敏感。
该模块基于ESM、IgLM等大规模预训练蛋白(抗体)语言模型实现。
目前WeMol中集成了多个PLM大模型,并基于PLM开发了多种应用,涉及的PLM模型如下:

ESM模型是一个通用蛋白质语言模型,主要采用UniRef序列数据库进行模型训练,提供了不同参数量(800万,3500万,1.5亿,6.5亿,30亿,150亿)的各类模型,可用于直接从蛋白序列预测结构、功能和其他蛋白质性质。ESM在预测蛋白结构时避免了对外部进化数据库、MSA和模板的需求,计算精度与AlphaFold2(存在MSA信息时)接近(无可用MSA信息时,计算精度ESM要显著优于AlphaFold2),计算速度比AlphaFold2快数十倍。模块中采用150亿参数的ESM2模型。
IgLM是一种用于构建合成抗体库的深度生成语言模型。与利用单向上下文生成序列的方法相比,IgLM 基于自然语言中的文本输入进行抗体设计。因此它能利用双向上下文重新设计抗体序列。IgLM基于5.58亿条抗体重链和轻链可变序列进行训练,并根据每个序列的链类型和来源物种进行了调整。
ESMIF逆折叠模型旨在根据蛋白质主链原子坐标预测蛋白序列。该模型使用AlphaFold2预测的1200万个蛋白质结构进行训练,包含不变几何输入处理层,随后是一个序列到序列的Transformer,对于在结构上保持不变的主干序列实现51%的本地序列恢复率,对于埋藏残基实现72%的恢复率。该模型还经过跨度屏蔽训练,能够容忍缺失的主链坐标,因此可以预测部分被屏蔽结构的序列。
AntiFold是使用抗体结构数据对ESMIF模型进行fine-tune微调得到,其在抗体CDR区序列恢复方面优于其他逆折叠工具,设计序列与已解析的序列具有高度结构相似性。此外,它在预测抗体-抗原结合亲和力时具有更强的相关性,同时在包括抗原信息的情况下性能会进一步增强。AntiFold为破坏与抗原结合的抗体残基突变给与低概率,并显示出在指导抗体优化的同时保留结构相关特性的前景
该模型用于预测纳米抗体序列中每个残基位置的20种残基出现的概率。模型采用类似AntiBerta(基于BERT的抗体语言模型)的网络架构,使用纳米抗体的序列数据集,进行模型训练得到。序列数据集包含开源序列与商业序列(未开源)两部分,其中开源序列整合了来自专利、NCBI GenBank、Protein Data Bank(PDB)以及科学出版物中的纳米抗体序列(约2.1万条),商业序列是基于新一代测序(NGS)技术,对多个商业研发项目进行测序得到的序列(约1100万条)。
蛋白序列,如:QVKLQESGAELARPGASVKLSCKASGYTFTNYWMQWVKQRPGQGLDWIGAIYPGDGNTRYTHKFKGKATLTADKSSSTAYMQLSSLASEDSGVYYCARGEGNYAWFAYWGQGTTVTVSS
如果是抗体,请将重链、轻链序列分开预测。
模型类型,可选esm2模型或者esm1b模型。
蛋白序列,如:QVKLQESGAELARPGASVKLSCKASGYTFTNYWMQWVKQRPGQGLDWIGAIYPGDGNTRYTHKFKGKATLTADKSSSTAYMQLSSLASEDSGVYYCARGEGNYAWFAYWGQGTTVTVSS
如果是抗体,请将重链、轻链序列分开预测。
抗体链类型,H表示重链,L表示轻链
物种类型,支持6种:HUMAN, CAMEL, MOUSE, RABBIT, RAT, RHESUS。
抗体序列,如:QVKLQESGAELARPGASVKLSCKASGYTFTNYWMQWVKQRPGQGLDWIGAIYPGDGNTRYTHKFKGKATLTADKSSSTAYMQLSSLASEDSGVYYCARGEGNYAWFAYWGQGTTVTVSS
抗体序列,需将重链、轻链序列分开预测。
物种类型,支持6种:HUMAN, CAMEL, MOUSE, RABBIT, RAT, RHESUS。
蛋白结构,pdb格式。
残基概率的阈值,概率大于该阈值的突变残基会输出到突变列表文件。
定义的残基区域,区域内突变概率大于阈值的残基,其突变信息会输出到突变列表文件,残基区域的格式为链名:残基区域,残基区域即指定PDB文件中的残基编号(注意是PDB文件中带有的残基索引编号,起始编号可能不为1),多个残基用逗号分隔,指定残基范围用横杠符号,如A:24,28,32-40 表示残基区域为蛋白A链的24/28/32至40号残基。
支持定义多个残基区域,每行定义一个,如:
A:24,28,32-40
B:12-24
抗体/纳米抗体,及与抗原的复合物结构文件,PDB格式。
填写输入pdb结构中的抗原链名。
注意:如果文件中有多个抗体/纳米抗体,识别按顺序排的最后一个。
纳米抗体序列(序列长度不超过198个残基,当序列长度超过198时,会自动识别抗体Fv区域并保留,序列其余部分去除),如:
seq
QLVSGPEVKKPGASVKVSCKASGYIFNNYGISWVRQAPGQGLEWMGWISTDNGNTNYAQKVQGRVTMTTDTSTSTAYMELRSLRYDDTAVYYCATNWGSYFEHWGQGTLVTVSS
输出result.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| WT | 序列中的初始AA |
| POS | AA的位置系引(从1开始) |
| Consensus | 该位置出现概率最大的AA |
| L,A,G,V… | 该位置每种AA出现的概率 |
输出chain_score.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 序列名称 |
| Chain_Score | 序列打分,是序列中每个位置残基的预测概率的算术平均值 |
All in One模式中,每一条序列都会输出5个文件,分别是:
1,ESM目录下的 '序列名.csv’文件,与上述result.csv格式一致
2,ESM目录下的’序列名_unusualAA.csv’文件,保存ESM模型预测得到的序列中不常见残基及其优势突变
3,IgLM目录下的 '序列名.csv’文件,与上述result.csv格式一致
4,IgLM目录下的’序列名_unusualAA.csv’文件,保存IgLM模型预测得到的序列中不常见残基及其优势突变
5,all目录下的 '序列名.csv’文件,保存序列每个位置由ESM与IgLM预测得到的可能优势突变及概率
输出result.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | PDB结构中的链名称 |
| WT | PDB结构中的初始AA |
| Pos | PDB文件中的AA编号 |
| Consensus | 该位置出现概率最大的AA |
| L,A,G,V… | 该位置每种AA出现的概率 |
1, Zeming Lin et al., Evolutionary-scale prediction of atomic-level protein structure with a language model.Science379,1123-1130(2023).DOI:10.1126/science.ade2574
https://www.science.org/doi/abs/10.1126/science.ade2574
2, Shuai et al., 2023, Cell Systems 14, 979–989.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cels.2023.10.001
Based on pre-trained large-scale protein language models (also known as PLMs or pLLMs), this module predicts the probability of each of the 20 amino acids (AA) appearing at each position in the sequence. Similar to evolutionarily more conservative AAs, high-probability AAs predicted by language models are beneficial for enhancing structural stability, improving protein folding, enhancing protein expression capabilities, and even increasing affinity, potentially offering advantages over random blind mutations. Compared to PSSMs based on MSA sequence statistics, language models provide faster predictions, consider more interactions between AAs within the sequence, and are more sensitive to their own changes.
This module is based on large-scale pre-trained protein (antibody) language models such as ESM and IgLM.
Several PLM large models are integrated into WeMol, and various applications have been developed based on PLMs, including the following PLM models:

The ESM model is a general protein language model that primarily uses the UniRef sequence database for model training. It offers various models with different parameter sizes (8 million, 35 million, 150 million, 650 million, 3 billion, 15 billion) that can be used to predict structure, function, and other protein properties directly from protein sequences. ESM avoids the need for external evolutionary databases, MSA, and templates when predicting protein structures. Its computational accuracy is close to AlphaFold2 (when MSA information is available) and significantly superior to AlphaFold2 in the absence of MSA information. ESM2 with 15 billion parameters is used in this module.

IgLM is a deep generative language model used to construct synthetic antibody libraries. Unlike methods that generate sequences based on unidirectional context, IgLM designs antibodies based on text inputs from natural language, allowing it to utilize bidirectional context for antibody sequence redesign. IgLM is trained on 558 million antibody heavy and light chain variable sequences and adjusted based on the chain type and source species of each sequence.

The ESMIF inverse folding model aims to predict protein sequences from their backbone atom coordinates. Trained on 12 million protein structures predicted by AlphaFold2, the ESMIF model consists of invariant geometric input processing layers followed by a sequence-to-sequence transformer. It achieves 51% native sequence recovery on structurally held-out backbones with 72% recovery for buried residues. The model is also trained with span masking to tolerate missing backbone coordinates and can predict sequences for partially masked structures.
AntiFold is fine-tuned using antibody structural data on the ESMIF model, outperforming other de novo folding tools in antibody CDR sequence recovery and exhibiting high structural similarity to the designed sequences and those resolved. Additionally, it shows stronger correlation in predicting antibody-antigen binding affinity, with performance further enhanced when antigen information is included. AntiFold predicts low probability mutations in antibody residues that disrupt antigen binding and demonstrates the prospect of retaining structural-relevant features while guiding antibody optimization.
This model predicts the probability of each of the 20 residues at every position in a nanobody sequence. It uses an AntiBerta - like (BERT based antibody language model) architecture and is trained on nanobody sequence datasets. These datasets have two parts: open-source sequences (around 21,000 from patents, NCBI GenBank, PDB, and publications) and commercial sequences (around 11 million from NGS of multiple R&D projects).
Protein sequence, e.g., QVKLQESGAELARPGASVKLSCKASGYTFTNYWMQWVKQRPGQGLDWIGAIYPGDGNTRYTHKFKGKATLTADKSSSTAYMQLSSLASEDSGVYYCARGEGNYAWFAYWGQGTTVTVSS
If it is an antibody, predict heavy and light chain sequences separately.
Model type, choose between esm2 model or esm1b model.
Protein sequence, e.g., QVKLQESGAELARPGASVKLSCKASGYTFTNYWMQWVKQRPGQGLDWIGAIYPGDGNTRYTHKFKGKATLTADKSSSTAYMQLSSLASEDSGVYYCARGEGNYAWFAYWGQGTTVTVSS
If it is an antibody, predict heavy and light chain sequences separately.
Antibody chain type, H for heavy chain, L for light chain.
Species type, supports 6 types: HUMAN, CAMEL, MOUSE, RABBIT, RAT, RHESUS.
Antibody sequence, e.g., QVKLQESGAELARPGASVKLSCKASGYTFTNYWMQWVKQRPGQGLDWIGAIYPGDGNTRYTHKFKGKATLTADKSSSTAYMQLSSLASEDSGVYYCARGEGNYAWFAYWGQGTTVTVSS
Antibody sequence, predict heavy and light chain sequences separately.
Species type, supports 6 types: HUMAN, CAMEL, MOUSE, RABBIT, RAT, RHESUS.
Protein structure, in pdb format.
The threshold for residue probability. Mutated residues with probabilities exceeding this threshold will be output to the mutation list file.
Defined residue regions. Mutation information for residues within these regions, whose mutation probability exceeds the threshold, will be output to the mutation list file. The format for residue regions is Chain:ResidueRegion, where ResidueRegion specifies the residue indices in the PDB file (note that the indices are the residue indices as they appear in the PDB file, which may not start from 1). Multiple residues can be separated by commas, and residue ranges can be specified using a hyphen, e.g., A:24,28,32-40 represents residues 24, 28, and 32 to 40 of chain A in the protein.
Multiple residue regions can be defined, with each region on a separate line, e.g.:
A:24,28,32-40
B:12-24
Structure files of antibodies/nanobodies and their complexes with antigens, in PDB format.
Enter the antigen chain name in the input PDB structure.
Note: If there are multiple antibodies/nanobodies in the file, identify the last one in sequential order.
Sequence of Nanobody, such as:
seq
QLVSGPEVKKPGASVKVSCKASGYIFNNYGISWVRQAPGQGLEWMGWISTDNGNTNYAQKVQGRVTMTTDTSTSTAYMELRSLRYDDTAVYYCATNWGSYFEHWGQGTLVTVSS
Only single-chain sequences can be submitted, and the sequence length must not exceed 198 residues.
Output result.csv file containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| WT | Initial AA in the sequence |
| POS | Position index of the AA (starting from 1) |
| Consensus | Most probable AA at that position |
| L, A, G, V… | Probability of each AA appearing at that position |
Output chain_score.csv file containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Sequence name |
| Chain_Score | Sequence score, the arithmetic mean of predicted probabilities of residues at each position in the sequence |
In the All in One mode, each sequence will output 5 files:
Output result.csv file containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain | Chain name in the PDB structure |
| WT | Initial AA in the PDB structure |
| Pos | Index of the AA in the PDB file |
| Consensus | Most probable AA at that position |
| L, A, G, V… | Probability of each AA appearing at that position |

Cyclic Peptide Structure Prediction模块利用线性肽的序列生成环肽的结构。
线性肽的氨基酸序列,示例:
GRCTQAWPPICFPD
只支持输入一条序列。
线性肽的结构文件,PDB格式
预测输出环肽的结构文件 pep_cyclic.pdb
Cyclic peptide structure prediction and design using AlphaFold. Stephen A. Rettie, Katelyn V. Campbell, Asim K. Bera, Alex Kang, Simon Kozlov, Joshmyn De La Cruz, Victor Adebomi, Guangfeng Zhou, Frank DiMaio, Sergey Ovchinnikov, Gaurav Bhardwaj; https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.25.529956
The Cyclic Peptide Structure Prediction module generates the structure of cyclic peptides based on the structures of linear peptides.
Amino acid sequence of the linear peptide, for example:
GRCTQAWPPICFPD
Only one sequence can be entered.
Structure file of the linear peptide in PDB format.
The predicted structure of the cyclic peptide is output as the structure file pep_cyclic.pdb.
Cyclic peptide structure prediction and design using AlphaFold. Stephen A. Rettie, Katelyn V. Campbell, Asim K. Bera, Alex Kang, Simon Kozlov, Joshmyn De La Cruz, Victor Adebomi, Guangfeng Zhou, Frank DiMaio, Sergey Ovchinnikov, Gaurav Bhardwaj; https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.25.529956

Immune Protein Structure Prediction模块是基于ImmuneBuilder的免疫蛋白结构预测模块。ImmuneBuilder是一组深度学习模型,可以准确预测抗体(ABodyBuilder2)、纳米抗体(NanoBodyBuilder2)和T细胞受体(TCRBuilder2)的结构;ImmuneBuilder生成的结构精度高,同时比AlphaFold2快得多。
抗体、纳米抗体或者TCER的序列文件,FASTA格式。
支持多条序列一次性计算,相应的序列顺序需满足以下要求:
对于抗体序列,每个抗体的重、轻链为一组,相邻放置即可(先后顺序没有要求),示例如下:
>seq1.H
xxxxxxxxxxxx
>seq1.L
xxxxxxxxx
>seq2.H
xxxxxxxxxxxx
>seq2.L
xxxxxxxxx
对于TCR序列,每个TCR的alpha、beta链为一组,相邻放置即可(先后顺序没有要求),示例如下
>seq1.A
xxxxxxx
>seq1.B
xxxxxxx
>seq2.A
xxxxxxx
>seq2.B
xxxxxxx
对于纳米抗体没有特殊要求。
预测蛋白结构类型:Antibody、Nanobody以及TCR。
抗体编号类型,支持kabat、chothia、imgt、raw。
输出文件名称,默认结构名称为model.pdb。
输出结果为预测的免疫蛋白pdb结构,默认名称为model.pdb。
可以进行批量生成结构文件,所有文件在model.tar压缩文件中。
https://github.com/oxpig/ImmuneBuilder
The Immune Protein Structure Prediction module is based on ImmuneBuilder and is used for predicting the structures of immune proteins. ImmuneBuilder is a set of deep learning models that accurately predict the structures of antibodies (ABodyBuilder2), nanobodies (NanoBodyBuilder2), and T cell receptors (TCRBuilder2). The structures generated by ImmuneBuilder are highly accurate and much faster than AlphaFold2.
Sequence file of the antibody, nanobody, or TCR in FASTA format.
Supports calculating multiple sequences at once, with the sequence order meeting the following requirements:
For antibody sequences, the heavy and light chain of an antibody constitute a pair, which should be placed adjacent to each other (the order does not matter), as shown below:
>seq1.H
xxxxxxxxxxxx
>seq1.L
xxxxxxxxx
>seq2.H
xxxxxxxxxxxx
>seq2.L
xxxxxxxxx
For TCR sequences, the alpha and beta chain of TCR constitute a pair, which can be placed adjacent to each other (the order does not matter), as shown below:
>seq1.A
xxxxxxx
>seq1.B
xxxxxxx
>seq2.A
xxxxxxx
>seq2.B
xxxxxxx
There are no specific naming requirements for nanobody sequences.
Type of protein structure to predict: Antibody, Nanobody, or TCR.
Antibody numbering scheme, supporting Kabat, Chothia, IMGT, and raw.
Name of the output file, with the default structure name as model.pdb.
The output result is the predicted immune protein PDB structure, with the default name as model.pdb.
Batch generation of structure files is supported, and all files are compressed in the model.tar file.

纳米抗体(Nanobody, Nbs)是最近出现的一类很有前景的生物医学和治疗应用抗体片段。尽管Nbs具有显著的理化特性,但它来自于驼科动物,可能需要 "人源化"才能提高临床试验的转化潜力。该模块基于Llamanade实现。Llamanade基于NGS(下一代测序)数据库和高分辨率结构,系统分析了Nbs的序列和结构特性。揭示了大量的框架多样性,并强调了Nbs与人类免疫球蛋白G(IgG)抗体之间的关键差异。确定了可能有助于提高溶解度、结构稳定性和抗原结合的保守残基,以促进Nbs的合理人源化。模块以Nbs序列为输入,提供序列特征、模型结构等信息,并优化Nbs人源化的解决方案。对给定的Nbs进行全面人源化分析只需不到一分钟时间。已成功应用于一批结构多样、强效的SARS-CoV-2中和Nbs人源化工作。
纳米抗体的序列,fasta格式,如:
Nb21
MAQVQLVESGGGLVQAGGSLRLSCAVSGLGAHRVGWFRRAPGKEREFVAAIGANGGNTNYLDSVKGRFTISRDNAKNTIYLQMNSLKPQDTAVYYCAARDIETAEYTYWGQGTQVTVS
输出humanized_data.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
Position:残基编号
Original AA:原来残基
Humanized?: 是否需要人源化,True表示需要,False表示不需要
Humanized AA: 人源化后的残基
备注:抗体编号方式采用Martin模式。
Llamanade: An open-source computational pipeline for robust nanobody humanization
Sang, Zhe et al. Structure, Volume 30, Issue 3, 418 - 429.e3
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2021.11.006
Nanobodies (Nanobody, Nbs) are a recently emerging class of promising antibody fragments for biomedical and therapeutic applications. Despite its remarkable physicochemical properties, Nbs are derived from camelids and may need to be “humanized” in order to improve translational potential in clinical trials. This module is implemented based on Llamanade, which systematically analyzes the sequence and structural properties of Nbs based on NGS (Next Generation Sequencing) databases and high-resolution structures. A large amount of framework diversity was revealed and key differences between Nbs and human immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies were highlighted. Conserved residues that may contribute to improved solubility, structural stability, and antigen binding were identified to facilitate the rational humanization of Nbs. This Module uses Nbs sequence as input to provide information on sequence characterization, model structure, and optimize solutions for Nbs humanization. It takes less than a minute to perform a comprehensive humanization analysis of a given Nbs. It has been successfully applied to humanize a group of structurally diverse and potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralized Nbs.

Nanobody sequence in FASTA format, such as:
Nb21
MAQVQLVESGGGLVQAGGSLRLSCAVSGLGAHRVGWFRRAPGKEREFVAAIGANGGNTNYLDSVKGRFTISRDNAKNTIYLQMNSLKPQDTAVYYCAARDIETAEYTYWGQGTQVTVS
The output csv file (humanized_data.csv) of humanization results includes:
Position: index of residue
Original AA: original residue
Humanized?: need to humanize,0 means no,1 means yes
Humanized AA: residue after humanization
Note: Antibodies are numbered in Martin mode.
Llamanade: An open-source computational pipeline for robust nanobody humanization
Sang, Zhe et al. Structure, Volume 30, Issue 3, 418 - 429.e3
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2021.11.006

该模块基于Smart5UTR模型实现,Smart5UTR 是一种新颖的深度生成模型,设计用于在 mRNA 序列中创建 N1-甲基假尿苷 (m1Ψ) 5’ UTR。Smart5UTR 利用多任务自动编码器框架,利用从大型数据集中学习到的潜在特征,有效地生成 5’ UTR 序列。Smart5UTR设计的mRNA的性能已通过体外和体内实验得到验证。这个强大的工具简化了m1Ψ-5’UTRs的设计,有助于开发更有效的mRNA疗法。
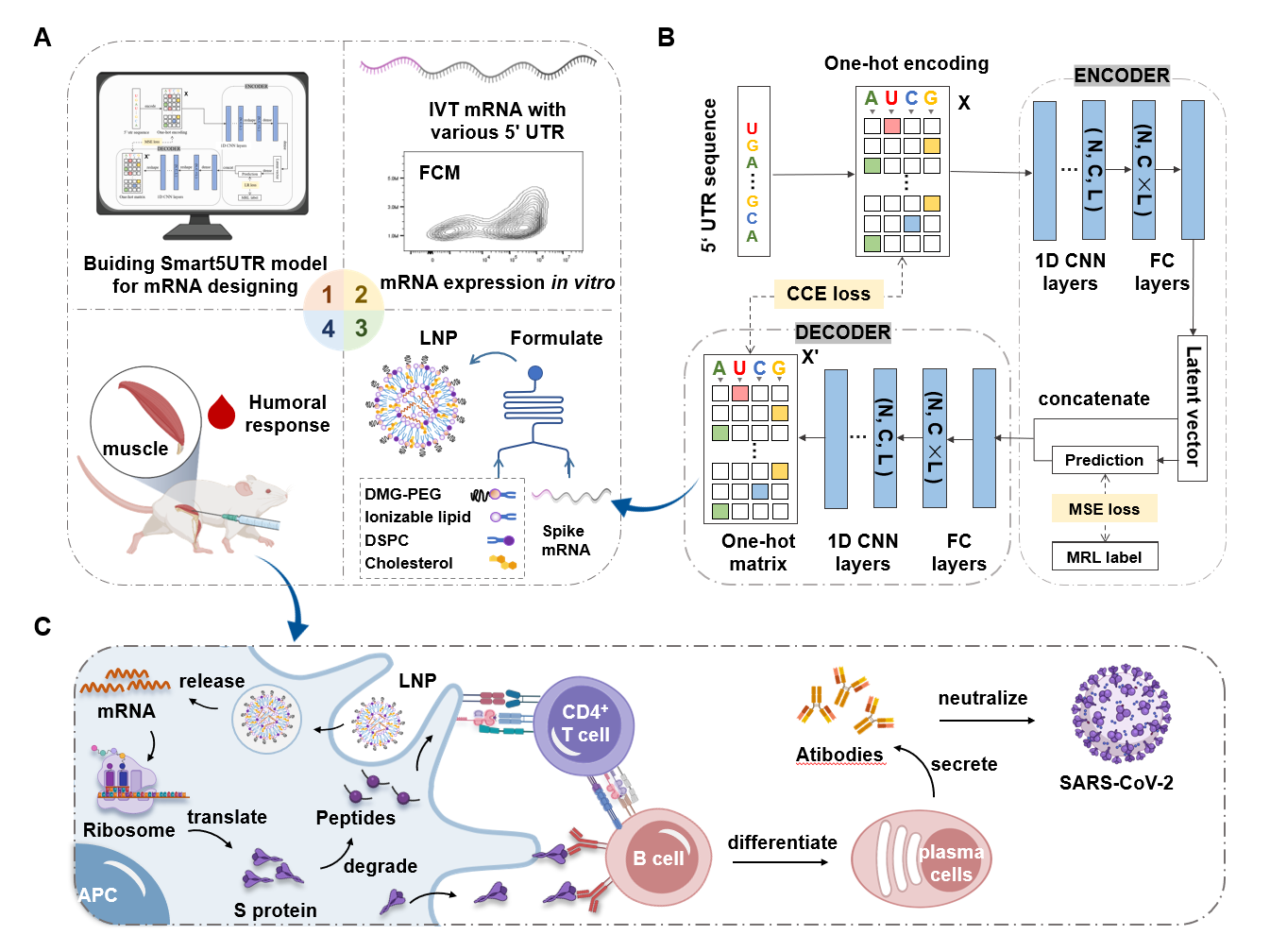
mRNA 5’UTR的序列,如:GGAGCCGAGGCGGGCCGATTCACGATCGGTTCGCAAAAACTGTTTGGGTT
备注:输入序列长度不超过50碱基。
输出result.csv结果文件,包含以下信息:
Original Sequence: 初始序列
Optimized Sequence: 优化后的序列
Optimized MRL: 优化序列预测的MRL值
MRL解释:
mean ribosome load (MRL) 平均核糖体加载值,是反映mRNA序列翻译效率的指标,值越大表示翻译效率越高,一般大于5.0
Xiaoshan Tang, et al., A novel deep generative model for mRNA vaccine development: Designing 5ʹ UTRs with N1-methyl-pseudouridine modification, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2023
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2023.11.003
Smart5UTR is a novel deep generative model designed for creating N1-methyl-pseudouridine (m1Ψ) 5’ UTRs in mRNA sequences. Utilizing a multi-task autoencoder framework, Smart5UTR efficiently generates 5’ UTR sequences by leveraging the latent features learned from a large dataset. The performance of Smart5UTR-designed mRNA has been validated through in vitro and in vivo experiments. This powerful tool streamlines the design of m1Ψ-5’ UTRs, contributing to the development of more effective mRNA therapeutics.
Sequence of mRNA 5’UTR, such as: GGAGCCGAGGCGGGCCGATTCACGATCGGTTCGCAAAAACTGTTTGGGTT
Note: The input sequence length should not exceed 50bp.
The output csv file of optimized sequence includes Original Sequence, Optimized Sequence and Optimized MRL.
MRL is a metric of the average number of ribosomes associated to a given RNA and a proxy for translation efficiency. Higher values indicate higher translation efficiency, generally greater than 5.0
Xiaoshan Tang, et al., A novel deep generative model for mRNA vaccine development: Designing 5ʹ UTRs with N1-methyl-pseudouridine modification, Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2023
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2023.11.003

AlphaMHC v3.0在多个方面相比v2.0进行了大幅优化,
主要包括:
1、风险评分优化,能更好的反映多重HLA激活的风险贡献;
2、引入新的EL和TCR等更多来源的数据,提升了对可递呈表位的预测能力,对TCR分子的支持更好;
3、全新的结果可视化面板(通过WeSeq运行);
为了更好的交互体验和对结果进行可视化,推荐从WeSeq中使用本功能。
测试数据:
从FDA和EMA的临床试验中收集了已知免疫原性的分子及其ADA的分布,使用模型对ADA明显较高(ADA>20%)及较低(ADA<5%)的分子进行分类以测试其预测性能。
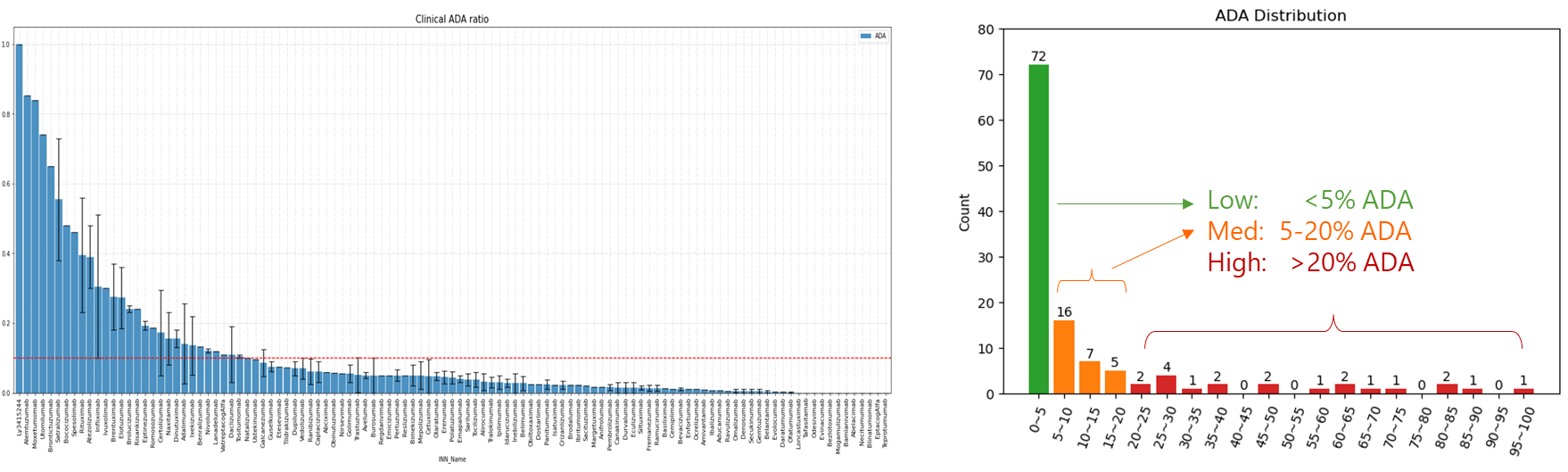
测试结果:
AlphaMHC v3.0全面超越常见算法及v2.0,性能同类最佳(SOTA)
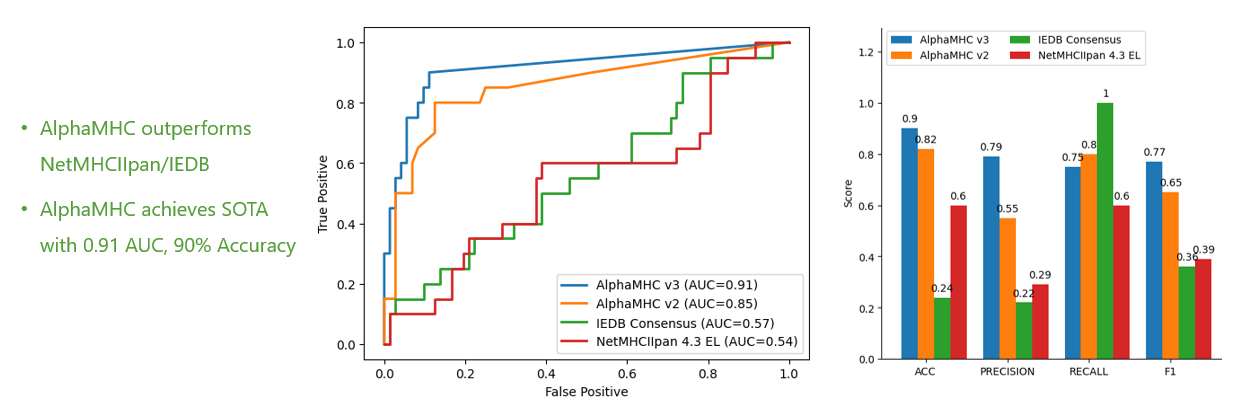
右图中:
蛋白序列文件,FASTA格式。支持多条链以及多分子模式。
对于多分子模式,序列名称规则为:分子名.链名,例如:
>mol1.A
XXXXXXX
>mol1.B
XXXXXXX
>mol2.A
XXXXXXX
>mol2.B
XXXXXXX
Molecule Score 包含以下信息:
| 指标 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein ID | 输入蛋白的名称,如果是多条序列组成的蛋白,会自动合并 |
| Score | 预测的免疫原性风险评分,值越大,风险越高。为所预测短肽的TCE score的求和 |
| Risk | 对应的免疫原性风险等级 |
TCE Score 包含以下信息:
| 指标 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein ID | 所在分子的名称,同个分子的多条序列组成的蛋白会自动合并 |
| Sequence ID | 所在序列的名称 |
| Core_Pos | 表位序列的起始位置 |
| Core | 表位序列(TCE) |
| Score | 表位序列的风险评分,分数越高越可能引起免疫原性。其范围是0-不限 |
| MHC_Count | 可激活的MHC亚型数,考虑了MHC-II的递呈 |
| Tolerance | 免疫耐受的可能性 |
| Germline | 是否存在于人胚系基因中 |
| NextProt | 是否存在于人蛋白组中 |
| OAS | 在NGS人源抗体中出现的频率 |
| TCR | 是否存在于人TCR基因中 |
| LAC | 是否存在于低ADA临床药物(Low ADA CST)中 |
AlphaMHC v3.0 has undergone significant optimizations compared to v2.0 in several aspects, including:
For a better interactive experience and visualization of results, it is recommended to use this feature through WeSeq.
Test Data:
Molecules with known immunogenicity and their ADA distributions collected from clinical trials by the FDA and EMA were used to test the predictive performance of the model on molecules with significantly high ADA (>20%) and low ADA (<5%).

Test Results:
AlphaMHC v3.0 surpasses common algorithms and v2.0 comprehensively, achieving state-of-the-art performance (SOTA).

In the image on the right:
Protein sequence file in FASTA format. Supports multiple chains and multiple molecule modes.
For multiple molecule mode, the sequence naming convention is: molecule name.chain name, for example:
>mol1.A
XXXXXXX
>mol1.B
XXXXXXX
>mol2.A
XXXXXXX
>mol2.B
XXXXXXX
Translation into English:
Molecule Score contains the following information:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein ID | Name of the input protein; if the protein is composed of multiple sequences, they will be automatically merged |
| Score | Predicted immunogenicity risk score; higher values indicate higher risk. It is the sum of the TCE scores predicted for the peptide |
| Risk | Corresponding immunogenicity risk level |
TCE Score contains the following information:
| Indicator | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein ID | Name of the molecule it belongs to; proteins composed of multiple sequences within the same molecule will be automatically merged |
| Sequence ID | Name of the sequence it belongs to |
| Core_Pos | Starting position of the epitope sequence |
| Core | Epitope sequence (TCE) |
| Score | Risk score of the epitope sequence; higher scores are more likely to cause immunogenicity. The range is from 0 to unlimited |
| MHC_Count | Number of activatable MHC subtypes, considering MHC-II presentation |
| Tolerance | Possibility of immunological tolerance |
| Germline | Whether it exists in human germline genes |
| NextProt | Whether it exists in the human proteome |
| OAS | Frequency of occurrence in NGS-derived human antibodies |
| TCR | Whether it exists in human TCR genes |
| LAC | Whether it exists in Low ADA CST (Low ADA Clinical Study Treatment) medications |

Mutation Score是抗体人源化设计中核心模块,是一个基于结构的自动化评分模块。该模块基于抗体的结构信息以及CDR嫁接后的序列信息,对移植抗体(graft)后的FR区的每个氨基酸在替换前后的变化程度进行量化评分。评分越高,说明CDR嫁接过程中氨基酸的替换对CDR区的构象可能影响较大,需要进行回复突变。模块输出每个氨基酸的打分值,用于抗体人源化设计流程中后续的分组和人源化抗体序列的生成。
抗体Fv区序列文件,FASTA格式。
抗体结构文件,PDB格式。
抗体CDR区Graft后的序列文件,FASTA格式。
指定输出打分文件的名称,CSV格式。
抗体类型:
输出结果文件为score.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | 轻链或重链 |
| UID | 为残基的标准编号(默认为 Kabat) |
| Position | 残基在序列中的位置 |
| Donor Residue | 原始氨基酸 |
| Template Residue | 人源模板的目标氨基酸 |
| score | 回复突变智能评分,Score 越高,认为其回复突变的必要性越高。通常Score>10为高优先级,5-10为中优先级,其他为低优先级 |
Mutation Score is a core module in antibody humanization design, serving as a structure-based automated scoring module. This module quantitatively scores the degree of change for each amino acid in the FR region after grafting CDRs based on the antibody’s structure and the sequence information post-CDR grafting. A higher score indicates that the replacement of amino acids during CDR grafting may have a significant impact on the CDR region’s conformation, suggesting the need for revertant mutations. The module outputs a score for each amino acid, which is used in subsequent grouping and generation of humanized antibody sequences in the antibody humanization design process.
Sequence file of the antibody Fv region in FASTA format.
Antibody structure file in PDB format.
Sequence file of the antibody CDR region after grafting in FASTA format.
Specify the name of the output scoring file in CSV format.
Type of antibody:
The output result file is named score.csv and includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain | Light chain or heavy chain |
| UID | Standard numbering for residues (default is Kabat) |
| Position | Position of the residue in the sequence |
| Donor Residue | Original amino acid |
| Template Residue | Target amino acid from the human template |
| Score | Revertant mutation intelligence score, where a higher score suggests a higher necessity for a revertant mutation. Typically, a Score > 10 is high priority, 5-10 is medium priority, and others are low priority. |
Ramachandran Plots模块是对同源建模后模型质量的评估,仅仅考虑蛋白的构象是否合理,并不涉及能量问题。Ramachandran Plot中φ(phi)表示一个肽单位中α碳左边C-N键的旋转角度, ψ(psi)表示α碳右边C-C键的旋转角度。一般来说落在允许区和最大允许区的氨基酸残基占整个蛋白质的比例高于90%的,可以认为该模型的构象符合立体化学的规则。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式。
选择作图链名称,不填默认为all。
图片分辨率(以每英寸点为单位)。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| result_General.png | 通常情况下的拉氏图 |
| result_Glycine.png | 甘氨酸的拉氏图 |
| result_PreProline.png | 脯氨酸前一个残基的拉氏图 |
| result_Proline.png | 脯氨酸的拉氏图 |
图中绿色为最大允许区,浅绿色为允许区,白色为不允许区,青色圆点代表在允许区域的氨基酸,红色圆点代表在不允许区域的氨基酸。在白色区域的氨基酸小于5%时,蛋白结构较为合理。
Sud M. MayaChemTools: An Open Source Package for Computational Drug Discovery. J Chem Inf Model. 2016 Dec 27;56(12):2292-2297.
Lovell SC, Davis IW, Arendall WB 3rd, de Bakker PI, Word JM, Prisant MG, Richardson JS, Richardson DC. Structure validation by Calpha geometry: phi,psi and Cbeta deviation. Proteins. 2003 Feb 15;50(3):437-50.
The Ramachandran Plots module is used to evaluate the quality of models after homology modeling, focusing on the reasonableness of the protein’s conformation without considering energy issues. In a Ramachandran Plot, φ (phi) represents the rotation angle of the C-N bond to the left of the alpha carbon in a peptide unit, and ψ (psi) represents the rotation angle of the C-C bond to the right of the alpha carbon. Generally, if the proportion of amino acid residues falling within the allowed regions and the most favored regions in the Ramachandran Plot is over 90%, the conformation of the model is considered to comply with the rules of stereochemistry.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result_General.png | Ramachandran plot for general residues |
| result_Glycine.png | Ramachandran plot for glycine residues |
| result_PreProline.png | Ramachandran plot for residues before proline |
| result_Proline.png | Ramachandran plot for proline residues |
In the plots, green represents the most favored regions, light green represents allowed regions, white represents disallowed regions, cyan dots represent amino acids in allowed regions, and red dots represent amino acids in disallowed regions. When the percentage of amino acids in the white region is less than 5%, the protein structure is considered reasonable.

Therapeutic Antibody Profiler (TAP) 基于抗体可变区的结构计算抗体的可开发性性质。TAP 计算以下5个性质,以确定输入抗体的可开发性指标是否与临床阶段抗体的属性相匹配:
针对851的治疗性抗体(临床I期及之后)的Fv区计算的可开发性指标范围如下(最新更新日期为2025年2月24日):
| Property | Amber Region | Red Region |
|---|---|---|
| Total CDR Length (L) | 37 ≤ L ≤ 42 | L < 37 |
| 55 ≤ L ≤ 65 | L > 65 | |
| Patches of Surface Hydrophobicity (PSH) | 95.77 ≤ PSH ≤ 111.40 | PSH < 95.77 |
| 167.64 ≤ PSH ≤ 211.65 | PSH > 211.65 | |
| Patches of Positive Charge (PPC) | 1.34 ≤ PPC ≤ 4.20 | PPC > 4.24 |
| Patches of Negative Charge (PNC) | 1.99 ≤ PNC ≤ 4.43 | PNC > 5.67 |
| Structural Fv Charge Symmetry Parameter (SFvCSP) | -30.60 ≤ SFvCSP ≤ -6.00 | SFvCSP < -30.60 |
Amber Region: 指标在851个治疗性抗体(临床I期及之后)的Fv区计算的指标范围内,属于合理区域
Red Region:指标不合理区域,需要调整
Amber Region和Red Region的区域范围定义如下表所示。
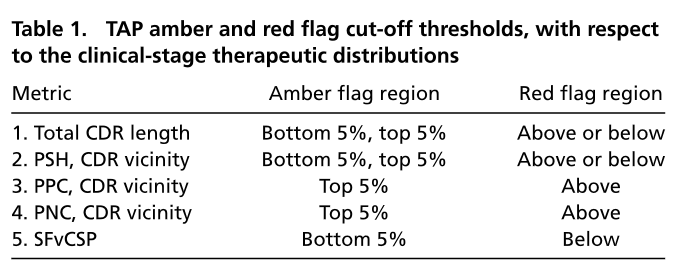
抗体结构文件,PDB格式
多个抗体Fv结构的压缩文件,TAR格式
当同时上传抗体结构PDB和压缩包时会合并计算。
输出打分文件,CSV格式
输出TAP打分文件,CSV格式,输出以下信息:
Total CDR Length:CDR区域氨基酸长度
CDR Vicinity PSH Score (Kyte & Doolittle):CDR区域及其周围的表面疏水性程度
CDR Vicinity PPC Score:CDR区域及其周围的表面正电荷程度
CDR Vicinity PNC Score:CDR区域及其周围的表面负电荷程度
SFvCSP Score:Fv区的重、轻链之间的净电荷失衡程度
Five computational developability guidelines for therapeutic antibody profiling. Matthew I. J. Raybould, Claire Marks, Konrad Krawczyk, Bruck Taddese, Jaroslaw Nowak, Alan P. Lewis, Alexander Bujotzek, Jiye Shi, and Charlotte M. Deane, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2019, 116 (10) 4025-4030
https://opig.stats.ox.ac.uk/webapps/sabdab-sabpred/sabpred/tap
The Therapeutic Antibody Profiler (TAP) compares your antibody variable domain sequence against multiple developability guidelines derived from clinical-stage therapeutic values.
TAP calculates the following properties to see if your antibody design is commenserate with those of clinical-stage therapeutics:
The TAP Guidelines were last updated on 24th February 2025:
| Property | Amber Region | Red Region |
|---|---|---|
| Total CDR Length (L) | 37 ≤ L ≤ 42 | L < 37 |
| 55 ≤ L ≤ 65 | L > 65 | |
| Patches of Surface Hydrophobicity (PSH) | 95.77 ≤ PSH ≤ 111.40 | PSH < 95.77 |
| 167.64 ≤ PSH ≤ 211.65 | PSH > 211.65 | |
| Patches of Positive Charge (PPC) | 1.34 ≤ PPC ≤ 4.20 | PPC > 4.24 |
| Patches of Negative Charge (PNC) | 1.99 ≤ PNC ≤ 4.43 | PNC > 5.67 |
| Structural Fv Charge Symmetry Parameter (SFvCSP) | -30.60 ≤ SFvCSP ≤ -6.00 | SFvCSP < -30.60 |
Amber Region: Within the reasonable region of 851 post Phase-I therapeutic Fvs
Red Region: Unreasonable region, the developability needs to be optimized
The following table defines the scope of Amber Region and Red Region.
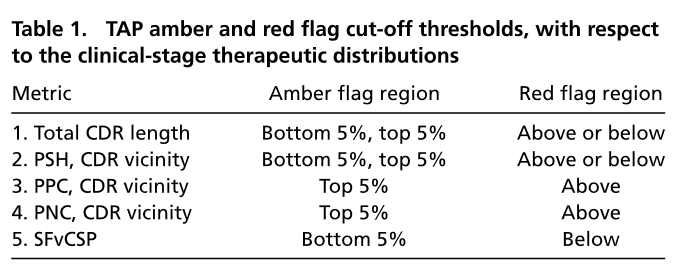
Antibody Structure file in PDB format
Multiple antibody Fv structure compressed file, TAR format
Output score file in CSV format
The output csv file of TAP properties includes Total CDR Length, CDR Vicinity PSH Score (Kyte & Doolittle), CDR Vicinity PPC Score, CDR Vicinity PNC Score, SFvCSP Score.
Five computational developability guidelines for therapeutic antibody profiling. Matthew I. J. Raybould, Claire Marks, Konrad Krawczyk, Bruck Taddese, Jaroslaw Nowak, Alan P. Lewis, Alexander Bujotzek, Jiye Shi, and Charlotte M. Deane, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2019, 116 (10) 4025-4030
https://opig.stats.ox.ac.uk/webapps/sabdab-sabpred/sabpred/tap

IgG Modeling对抗体全长序列进行建模,用于构建抗体IgG完整的三维结构,支持单特异性和双特异性抗体。
自动识别全长序列中的可变区(Fv)序列并通过SOTA的方法(目前为ESMFold)进行建模,IgG的其余部分包括Fc和linker以已知全长抗体的晶体结构为模板通过空间约束条件进行同源模建,效果比直接用AF2等方法预测完整IgG结构更优。
抗体的第一条重链的序列。
抗体的第一条轻链的序列。
抗体的第二条重链的序列,非必填,仅在双抗建模时输入。
抗体的第二条轻链的序列,非必填,仅在双抗建模时输入。
IgG亚型,目前支持IgG1和IgG4两种类型。
注意:
1)当待建模序列为单抗时,只需要写入H1与L1即可,H1与H2相同,L1与L2相同,最终模型包含2条相同的重链和2条相同的轻链。
2)当待建模序列为双抗时,需要输入四条链的序列,最终模型包含2条不同重链和2条不同轻链。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| antibody_001.pdb-antibody_003.pdb | 输出三个抗体全长的结构 |
| scores.csv | 抗体全长结构打分,其中MolPDF是Modeller的评估打分,此分数越小越推荐使用。 |
IgG Modeling is used to model the full-length sequence of antibodies to construct the complete three-dimensional structure of antibody IgG, supporting both monospecific and bispecific antibodies. It automatically identifies the variable region (Fv) sequence in the full-length sequence and models it using state-of-the-art methods (currently ESMFold). The remaining parts of IgG, including Fc and linker, are modeled homologously based on the crystal structure of known full-length antibodies as templates, using spatial constraints, which yields better results compared to directly predicting the complete IgG structure using methods like AF2.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| antibody_001.pdb-antibody_003.pdb | Structures of three full-length antibodies |
| scores.csv | Scoring of the full-length antibody structures, where MolPDF is the evaluation score from Modeller; a smaller score is more favorable. |

Substructure Search模块是小分子子结构搜索模块,实现在化合物库中查询出含有特定子结构的分子并输出到SDF文件中。子结构搜索是化学信息学研究中的常用操作,也可以用于虚拟筛选,从小分子商业库中搜索出含有特定功能片段的分子用于后续实验验证。
搜索子结构文件,SDF或者SMI格式
通过WeDraw界面画模板小分子,只允许单个小分子。
搜索子结构SMILES字符,例如
c1ccccc1
CC(N)=O
选择用于相似性搜索的分子库,该模块提供17个公共分子数据库用于进行相似性搜索:
提示说明:Public Library与Private Library选填其中一个。
用于搜索的个人分子库,仅支持SDF格式。
提示说明:Public Library与Private Library选填其中一个。
输出文件名称,默认matched_molecules.sdf。
结果文件为分子库中含有子结构的化合物matched_molecules.sdf。
Public Library与Private Library选填其中一个。
用于搜索的个人分子库,仅支持SDF格式。
Public Library与Private Library选填其中一个。
输出文件名称,默认matched_molecules.sdf。
结果文件为分子库中含有子结构的化合物matched_molecules.sdf。
The Substructure Search module is a tool for searching for specific substructures within a compound library and outputting them to an SDF file. Substructure searching is a common operation in cheminformatics research and can be used for virtual screening to identify molecules in commercial small molecule libraries containing specific functional fragments for subsequent experimental validation.
File containing the substructure to search for, in SDF or SMI format.
Draw a template small molecule using the WeDraw interface, allowing only a single small molecule.
SMILES string of the substructure to search for, for example:
c1ccccc1
CC(N)=O
Select the public molecular library for the substructure search module, which provides 16 public molecular databases for substructure searching.
Personal molecular library for searching, supporting SDF format.
Note: Choose either Public Library or Private Library.
Name of the output file, default is matched_molecules.sdf.
The result file contains compounds from the compound library that contain the specified substructure, saved as matched_molecules.sdf.

Small Molecule Minimization是针对小分子结构进行能量最小化优化并得到优化后的3D结构。支持UFF和MMFF两种分子力场,支持SDG, ETDG, KDG, ETKDG四种构象采样方法,用于生成初始3D构象。注意,每个分子只输出一个能量最低构象,构象搜索推荐使用 3D Conf (AlphaConf)模块。
小分子文件,支持Mol (.mol), SD (.sdf, .sd), SMILES (.smi .csv, .tsv, .txt)。
输出文件名称,仅支持SDF格式,默认为minimized_struture.sdf。
3D构象方法:SDG, ETDG, KDG, ETKDG, None.
用于能量最小化的力场方法,包括UFF(Universal Force Field)和MMFF(Merck Molecular Mechanics Force Field)。
使用并行计算。
在基于力场优化期间针对每个分子执行的最大迭代次数,默认500。
随机数,用于重现优化后的结构。
得到能量最小化后的小分子3D结构文件minimized_struture.sdf。
Sud M. MayaChemTools: An Open Source Package for Computational Drug Discovery. J Chem Inf Model. 2016 Dec 27;56(12):2292-2297.
Riniker, S.; Landrum, G. A. Better informed distance geometry: Using what we know to improve conformation generation. JCIM. 2015, 55, 2562-2574.
Rappe, A.K.; Casewit, C.J.; Colwell, K.S.; Goddard III, W.A.; Skiff, W.M. UFF, a full periodic table force field for molecular mechanics and molecular dynamics simulations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10024-10035.
Halgren, T.A.; Merck Molecular Force Field. I. Basis, Form, Scope, Parameterization, and Performance of MMFF94. 1996, J. Comput. Chem., 17, 490-519.
Halgren, T.A.; Merck molecular force field. V. Extension of MMFF94 using experimental data, additional computational data, and empirical rules. J. Compt. Chem. 1996, 17, 616-641.
Small Molecule Minimization is a tool module designed to perform energy minimization optimization on small molecule structures and obtain the optimized 3D structure. It supports two molecular force fields, UFF and MMFF, as well as four conformation sampling methods: SDG, ETDG, KDG, and ETKDG, used to generate initial 3D conformations. Note that only one energy-minimized conformation is output for each molecule, and for conformational search, it is recommended to use the 3D Conf (AlphaConf) module.
Input file for the small molecule, supporting Mol (.mol), SD (.sdf, .sd), SMILES (.smi .csv, .tsv, .txt) formats.
Name of the output file, only supports SDF format, default is minimized_structure.sdf.
3D conformation method: SDG, ETDG, KDG, ETKDG, None.
Force field method for energy minimization, including UFF (Universal Force Field) and MMFF (Merck Molecular Mechanics Force Field).
Utilize parallel computing.
Maximum number of iterations performed for each molecule during force field optimization, default is 500.
Random number used to reproduce the optimized structure.
Obtain the energy-minimized 3D structure file for the small molecule as minimized_structure.sdf.

PDB ReNumbering是针对蛋白残基重新编号的工具模块,同时支持抗体kabat,imgt以及chothia的重编号。输入蛋白结构PDB文件,输出重新编号后的PDB文件。
输入蛋白结构文件,PDB格式。
重编号类型,支持指定链从指定数字开始编号,同时支持抗体结构重新编号。
numeric:氨基酸序号重编号
kabat:抗体kabat编号规则重编号
imgt:抗体imgt编号规则重编号
chothia:抗体chothia编号规则重编号
链名,指定具体的链名进行重编号操作。
针对氨基酸序号重编号,指定起始编号数字。
重编号后的文件名称。
重编号后的结构文件名称,默认输出renumbering.pdb。
注意:如果输入是抗体结构,输出结构中重链的链名会自动改为H,轻链链名会改为L。
PDB ReNumbering is a tool module for renumbering protein residues, supporting renumbering according to the kabat, imgt, and chothia numbering schemes for antibodies. Input a protein structure PDB file and get the renumbered PDB file as output.
Input protein structure file in PDB format.
Renumbering type, supports starting numbering from a specified number for a specific chain, and also supports renumbering for antibody structures.
Chain name, specifies the chain to perform renumbering.
For renumbering amino acid residues numerically, specifies the starting number.
Name of the renumbered file.
The renumbered structure file is named by default as renumbering.pdb.
Note: If the input is an antibody structure, the chain names in the output structure will be automatically changed to H for the heavy chain and L for the light chain.

AC2SDF模块是一个格式转换工具,用于将AlphaConf模块生成的构象压缩二进制文件AC.GZ转为便于查看结构的SDF文件。
输入构象文件,AC.GZ格式,由AlphaConf模块生成
片段库文件,AUX.GZ格式,由AlphaConf模块生成
转换生成的SDF文件名称
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ligands_confs.sd | 转换生成的SDF文件,可通过WeView直接查看构象 |
The AC2SDF module is a format conversion tool used to convert the compressed binary conformation file AC.GZ generated by the AlphaConf module into an SDF file for easier visualization of the structure.
Input conformation file in AC.GZ format generated by the AlphaConf module.
Fragment library file in AUX.GZ format generated by the AlphaConf module.
Name of the converted SDF file.
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ligands_confs.sd | Converted SDF file that can be viewed directly using WeView for conformation visualization. |

Sequence Mutation是蛋白序列突变模块,用于针对特定位点批量生成突变序列,支持多样的突变策略,包括设定不同的突变位置及突变类型。
突变策略包括:
突变类型支持:
蛋白原始序列或者fasta格式的序列
突变位点,支持多个位点,英文逗号分割,例如:2,3
突变类型,支持三种类型:Ala 丙氨酸突变,His 组氨酸突变,Sat 饱和突变
链名,输出突变信息时加上指定链名
生成突变序列的文件名称,FASTA格式
蛋白突变信息文件,TXT格式
蛋白原始序列或者fasta格式的序列
同源序列,一般由序列比对产生的结果文件,FASTA 格式
序列比对的方法,mafft或者muscle
频数截断值,大于截断值的氨基酸才会选择作为突变目标
链名,输出突变信息时加上指定链名
生成突变序列的文件名称,FASTA格式
蛋白突变信息文件,TXT格式
蛋白原始序列或者fasta格式的序列
抗体CDR编号规则:kabat, imgt, chothia
突变类型,支持三种类型:Ala 丙氨酸突变,His 组氨酸突变,Sat 饱和突变
链名,输出突变信息时加上指定链名
生成的包含蛋白突变序列的文件名称,FASTA格式
生成的包含蛋白突变信息的文件名称,TXT格式
蛋白原始序列或者fasta格式的序列
抗体CDR编号规则:kabat, imgt, chothia
同源序列,一般由序列比对产生的结果文件,FASTA 格式
序列比对的方法,mafft或者muscle
频数截断值,大于截断值的氨基酸才会选择作为突变目标
链名,输出突变信息时加上指定链名
生成的包含蛋白突变序列的文件名称,FASTA格式
生成的包含蛋白突变信息的文件名称,TXT格式
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| mutants.fasta | 生成突变序列的文件名称,FASTA格式 |
| mutations.txt | 蛋白突变信息文件,TXT格式,每行一个突变记录,例如:Q2A 代表第2位氨基酸Q突变为氨基酸A |
Sequence Mutation is a protein sequence mutation module that allows for batch generation of mutated sequences at specific positions, supporting various mutation strategies including setting different mutation positions and types.
Mutation strategies include:
Supported mutation types include:
Original protein sequence or sequence in FASTA format.
Mutation positions, support for multiple positions separated by commas, e.g., 2,3.
Mutation types, supporting three types: Ala (Alanine mutation), His (Histidine mutation), Sat (Saturation mutation).
Chain name to be included in the mutation information output.
File name for generated mutated sequences in FASTA format.
Protein mutation information file in TXT format.
Original protein sequence or sequence in FASTA format.
Homologous sequences, typically generated from sequence alignment results in FASTA format.
Alignment methods for sequence alignment: mafft or muscle.
Frequency cutoff value, only amino acids with frequencies greater than the cutoff value will be selected as mutation targets.
Chain name to be included in the mutation information output.
File name for generated mutated sequences in FASTA format.
Protein mutation information file in TXT format.
Original protein sequence or sequence in FASTA format.
Antibody CDR numbering rule: kabat, imgt, chothia.
Mutation types, supporting three types: Ala (Alanine mutation), His (Histidine mutation), Sat (Saturation mutation).
Chain name to be included in the mutation information output.
File name for generated mutated protein sequences in FASTA format.
File name for generated protein mutation information in TXT format.
Original protein sequence or sequence in FASTA format.
Antibody CDR numbering rule: kabat, imgt, chothia.
Homologous sequences, typically generated from sequence alignment results in FASTA format.
Alignment methods for sequence alignment: mafft or muscle.
Frequency cutoff value, only amino acids with frequencies greater than the cutoff value will be selected as mutation targets.
Chain name to be included in the mutation information output.
File name for generated mutated protein sequences in FASTA format.
File name for generated protein mutation information in TXT format.
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| mutants.fasta | File name for generated mutated sequences in FASTA format. |
| mutations.txt | Protein mutation information file in TXT format, with each line representing a mutation record, e.g., Q2A represents the mutation of amino acid Q at position 2 to amino acid A. |
MD Distance是针对分子动力学轨迹的距离分析模块,输出两个组之间距离 (质心距离或几何中心距离) 随时间的变化情况。自定义组别时需要注意,如果只需测量两个原子之间的距离则填写Custom Atom1和Custom Atom2即可;当同时填写Custom Resid1和Custom Atom1时,组别1的原子数是Custom Atom1与Custom Resid1交集的原子。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的组别1:Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
选择需要计算的组别1:Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的组1残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。自定义组别之间是并集。
自定义需要计算的组1原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续原子用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。自定义组别之间是并集。
自定义需要计算的组2残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。自定义组别之间是并集。
自定义需要计算的组2原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续原子用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。自定义组别之间是并集。
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| dist.csv | 距离分析CSV文件 |
| dist.xvg | 距离分析XVG文件 |
| dist.png | 距离分析PNG文件 |
其中dist.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | 时间 |
| Distance (nm) | 组别之间的距离 |
MD Distance is a distance analysis module for molecular dynamics trajectories, providing the variation of distance (center-of-mass distance or geometric center distance) between two groups over time. When defining custom groups, it is important to note that if you only need to measure the distance between two atoms, you can fill in Custom Atom1 and Custom Atom2. When both Custom Resid1 and Custom Atom1 are filled in, the number of atoms in group 1 is the intersection of Custom Atom1 and Custom Resid1.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, available in the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the group 1 for calculation: Protein, DNA, RNA.
You can enter the group name based on the name of the small molecule in the PDB.
Select the group 2 for calculation: Protein, DNA, RNA.
You can enter the group name based on the name of the small molecule in the PDB.
Custom residue numbers for group 1 that need to be calculated. Use “-” for continuous parameters and separate non-continuous residues with commas, for example: 1-10,15. Custom groups are unions of specified residues.
Custom atom numbers for group 1 that need to be calculated. Use “-” for continuous parameters and separate non-continuous atoms with commas, for example: 1-10,15. Custom groups are unions of specified atoms.
Custom residue numbers for group 2 that need to be calculated. Use “-” for continuous parameters and separate non-continuous residues with commas, for example: 1-10,15. Custom groups are unions of specified residues.
Custom atom numbers for group 2 that need to be calculated. Use “-” for continuous parameters and separate non-continuous atoms with commas, for example: 1-10,15. Custom groups are unions of specified atoms.
Time interval for each frame (in ns).
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| dist.csv | Distance analysis CSV file |
| dist.xvg | Distance analysis XVG file |
| dist.png | Distance analysis PNG file |
The dist.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | Time |
| Distance (nm) | Distance between the groups |
Peptide VS模块集成了AutoDock Vina与AutoDock CrankPep进行蛋白-多肽的分子对接,从而预测蛋白-多肽的构象、得到分子对接的能量以及结合亲和力。AutoDock CrankPep则是一个专门用于多肽对接工具,其基于蛋白折叠和刚性受体网格能量背景下,采用蒙特卡罗方法对多肽的折叠进行计算,产生多肽的对接构象。
受体结构文件,PDB格式。
多肽的氨基酸序列,多肽的氨基酸序列,可以成功对接长度达20个氨基酸的肽。一行一条序列,例如:
AINMDSFHTWKVLECGRPQY
HRIAQCSDKW
IYSADCLPKG
AAAAIS
对接口袋中心的三维坐标(XYZ),空格分割。例如:10 2 -11。
对接口袋长方体盒子的大小,必须是整数,空格分割,例如 30 30 30。
每个多肽与蛋白对接后输出的构象数目,默认为10。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Scores.csv | 提交多肽与受体的打分文件。 |
| output_complex_top1.pdb | 展示打分第一的多肽与受体的复合物构象。 |
| output_complex_topn.tar.gz | TopN多肽“Out Pose”构象数与受体形成的复合物结构PDB文件压缩包。 |
其中Scores.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 对接多肽名称 |
| Score(kcal/mol) | 对接打分,该值越低说明结合亲和力越高。 |
| Cluster RMSD | 聚类后,构象之间的RMSD |
| Average RMSD | 平均RMSD |
| Complex File Name | 复合物文件名称 |
J. Eberhardt, D. Santos-Martins, A. F. Tillack, and S. Forli. (2021). AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling.
O. Trott, A. J. Olson, AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading, Journal of Computational Chemistry 31 (2010) 455-461.
Podtelezhnikov, A.A., Wild, D.L. CRANKITE: A fast polypeptide backbone conformation sampler. Source Code Biol Med 3, 12 (2008).
The Peptide VS module integrates AutoDock Vina and AutoDock CrankPep for protein-polypeptide molecular docking, predicting the conformation of protein-polypeptide complexes, docking energy, and binding affinity. AutoDock Vina is a molecular docking tool that compares the binding affinities between multiple molecules, used for screening, designing, and optimizing drug molecules. AutoDock CrankPep is a specialized tool for peptide docking that uses a Monte Carlo method to calculate peptide folding based on protein folding and rigid receptor grid energy background, generating docking conformations for peptides. This module has been successfully demonstrated to redock peptides of up to 20 amino acids in length.
Structure file of the receptor in PDB format.
Structure file of the peptide ligand in SDF format. Obtained from the Peptide Structure Generation module.
Three-dimensional coordinates (XYZ) of the docking pocket center, separated by spaces. For example: -44.497 -22 -5.
Size of the docking pocket rectangular box, must be integers, separated by spaces, for example 30 30 30.
Specify the top N small molecules for scoring as output files, default is 100.
Number of conformations output for each peptide-protein docking, default is 10.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Scores.csv | Scoring file for the docking of peptides with the receptor. |
| output_complex_top1.pdb | Conformation of the top scoring peptide-receptor complex. |
| output_complex_topn.tar.gz | Compressed PDB files of the top N peptide “Out Pose” conformations forming complexes with the receptor. |
The Scores.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Name of the docked peptide |
| Score(kcal/mol) | Docking score, lower values indicate higher binding affinity. |
| Complex File Name | Name of the complex file |
J. Eberhardt, D. Santos-Martins, A. F. Tillack, and S. Forli. (2021). AutoDock Vina 1.2.0: New Docking Methods, Expanded Force Field, and Python Bindings. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling.
O. Trott, A. J. Olson, AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization and multithreading, Journal of Computational Chemistry 31 (2010) 455-461.
Podtelezhnikov, A.A., Wild, D.L. CRANKITE: A fast polypeptide backbone conformation sampler. Source Code Biol Med 3, 12 (2008).

Alanine Scan (MMPBSA)是计算丙氨酸突变后的结合自由能,并且提供能量分解数据、结合常数(Ka)、抑制剂常数(Ki)。熵的计算采用的是张增辉教授的相互作用熵的方法,该方法直接从分子动力学模拟计算结合自由能的熵组分(相互作用熵或-TΔS),但是需要选取结构稳定部分进行计算。
本模块提供四种计算方法,其中 Trajectory 是针对进行分子动力学模拟轨迹后计算其受配体之间的结合自由能;One Structure 是针对一帧pdb结构或者对接得到的PDB结构计算受配体之间的结合自由能,MMPBSA of One Structure 计算流程中可以直接输入PDB进行计算。
Index Name 是输入受配体组别名称;Custom Name 则是输入受配体的在PDB中的残基编号。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD模块中获取。
受体名称,可以为Protein、DNA、RNA。
配体名称,可以为Protein、DNA、RNA。如果为小分子,填写其在PDB中的名称。如果体系中除了蛋白以外为配体(包括小分子)可用Other表示。
突变扫描为丙氨酸(ALA)的氨基酸位置。格式为res1:res2:res3:res4,其中“res1-res4”数字为残基编号。
丙氨酸扫描时使用的力场。
起始帧时间,单位ps。最好选取RMSD稳定时区进行计算,以消除结构不稳定时导致的整体熵偏大。
结束帧时间,单位ps。最好选取RMSD稳定时区进行计算,以消除结构不稳定时导致的整体熵偏大。
间隔时间,单位ps。
索引文件,ndx格式。当体系中存在膜结构的时候可以通过Membrane Solvation模块获取index.ndx文件。膜模拟中的受体为receptor,配体为ligand,膜为membrane。只能是AMBER力场下构建的膜体系才能进行计算。
定义受体组别进行结合能计算。组别中填写的为蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基的序号。例如1-213或者1-211,212-213。蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基序号从1开始重新编号,与初始pdb氨基酸编号无关。
定义配体组别进行结合能计算。组别中填写的为蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基的序号。例如1-213或者1-211,212-213。蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基序号从1开始重新编号,与初始pdb氨基酸编号无关。
拓扑文件,由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
结构文件,.gro格式,由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
体系参数压缩文件,tar.gz格式。由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA_result.txt | MMPBSA丙氨酸突变结果汇总文件。 |
| MMPBSA_Residue.csv | 丙氨酸突变能量分解数据CSV文件。 |
| MMPBSA.pdb | 丙氨酸突变后,原子对应的MMPBSA能量放到PDB文件。可以做对应能量类别的表面图,从图的颜色深浅可以看出哪些区域对结合能贡献值较大。 |
| MMPBSA.tar.gz | MMPBSA所有原始文件。包括_mmpbsa_residue_#.txt是每个残基对应的每个能量类别的数值,共包含7个能量类别:范德华能(VDW)、静电能(ELE)、溶剂化能极性部分(PB)、溶剂化能非极性部分(SA)、VDW+ELE=MM、PB+SA=PBSA、MM+PBSA=Binding/MMPBSA。_mmpbsa_residue.txt是对上述7个文件的总结,即为MMPBSA_Residue.csv对应的原始文件。_mmpbsa_atom#.pdb是将每个原子对应的能量类别放到pdb文件,与MMPBSA.pdb相似。 |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Duan L, Liu X, Zhang JZ. Interaction Entropy: A New Paradigm for Highly Efficient and Reliable Computation of Protein-Ligand Binding Free Energy. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 May 4;138(17):5722-8.
https://github.com/Electrostatics/apbs/blob/main/docs/index.rst
Alanine Scan (MMPBSA) calculates the binding free energy after alanine mutations and provides energy decomposition data, binding constants (Ka), and inhibitor constants (Ki). The entropy calculation uses the method of interaction entropy proposed by Professor Zhang Zenghui, which directly calculates the entropy component of the binding free energy (interaction entropy or -TΔS) from molecular dynamics simulations, but requires selecting stable structural regions for calculation. This module provides four calculation methods. Among them, Trajectory calculates the binding free energy between the receptor and ligand after molecular dynamics simulation trajectories; One Structure calculates the binding free energy between the receptor and ligand for a single frame PDB structure or a docked PDB structure; MMPBSA of One Structure allows direct input of a PDB for calculation. Index Name is the input receptor-ligand group name, while Custom Name is the input residue numbers of the receptor-ligand in the PDB.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, available in the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or AlphaAutoMD module.
Name of the receptor, can be Protein, DNA, or RNA.
Name of the ligand, can be Protein, DNA, or RNA. If it is a small molecule, enter its name in the PDB. Use ‘Other’ if the system contains a ligand (including small molecules) other than proteins.
Amino acid positions where mutations to alanine (ALA) are scanned. The format is res1:res2:res3:res4, where “res1-res4” are residue numbers.
Force field used for alanine scanning.
Start frame time in ps. It is best to select a stable RMSD region for calculation to eliminate large overall entropy caused by structural instability.
End frame time in ps. It is best to select a stable RMSD region for calculation to eliminate large overall entropy caused by structural instability.
Time interval in ps.
Index file in ndx format. When there is a membrane structure in the system, you can obtain the index.ndx file through the Membrane Solvation module. In membrane simulations, the receptor is ‘receptor’, the ligand is ‘ligand’, and the membrane is ‘membrane’. Only membrane systems built under the AMBER force field can be calculated.
Define receptor groups for binding energy calculation. Enter the sequence numbers of protein amino acids or nucleic acid bases in the group. For example, 1-213 or 1-211,212-213. Protein amino acid or nucleic acid base numbers start from 1 and are independent of the initial pdb amino acid numbering.
Define ligand groups for binding energy calculation. Enter the sequence numbers of protein amino acids or nucleic acid bases in the group. For example, 1-213 or 1-211,212-213. Protein amino acid or nucleic acid base numbers start from 1 and are independent of the initial pdb amino acid numbering.
Topology file obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
Structure file in .gro format obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
System parameter compression file in tar.gz format. Obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA_result.txt | Summary file of MMPBSA alanine mutation results. |
| MMPBSA_Residue.csv | Energy decomposition data for alanine mutations in CSV format. |
| MMPBSA.pdb | MMPBSA energy corresponding to atoms after alanine mutations in a PDB file. This can be used to create a surface map of energy categories, where the color depth indicates the regions contributing significantly to the binding energy. |
| MMPBSA.tar.gz | All original MMPBSA files. Includes mmpbsa_residue#.txt which contains the values of each energy category for each residue, totaling 7 energy categories: van der Waals energy (VDW), electrostatic energy (ELE), polar part of solvation energy (PB), nonpolar part of solvation energy (SA), VDW+ELE=MM, PB+SA=PBSA, MM+PBSA=Binding/MMPBSA. _mmpbsa_residue.txt is a summary of the above 7 files, corresponding to the original file MMPBSA_Residue.csv. _mmpbsa_atom#.pdb assigns the energy categories to each atom in a pdb file, similar to MMPBSA.pdb. |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Duan L, Liu X, Zhang JZ. Interaction Entropy: A New Paradigm for Highly Efficient and Reliable Computation of Protein-Ligand Binding Free Energy. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 May 4;138(17):5722-8.
https://github.com/Electrostatics/apbs/blob/main/docs/index.rst

MMPBSA计算受体与配体之间的结合自由能,并且提供能量分解数据、结合常数(Ka)、抑制剂常数(Ki)。熵的计算采用的是张增辉教授的相互作用熵的方法,该方法直接从分子动力学模拟计算结合自由能的熵组分(相互作用熵或-TΔS),但是需要选取结构稳定部分进行计算。
本模块提供四种计算方法,其中 Trajectory 是针对进行分子动力学模拟轨迹后计算其受配体之间的结合自由能;One Structure 是针对一帧pdb结构或者对接得到的PDB结构计算受配体之间的结合自由能,MMPBSA of One Structure 计算流程中可以直接输入PDB进行计算。
Index Name 是输入受配体组别名称;Custom Name 则是输入受配体的在PDB中的残基编号。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD模块中获取。
受体名称,可以为Protein、DNA、RNA。
配体名称,可以为Protein、DNA、RNA。如果为小分子,填写其在PDB中的名称。如果体系中除了蛋白以外为配体(包括小分子)可用Other表示。
起始帧时间,单位ps。最好选取RMSD稳定时区进行计算,以消除结构不稳定时导致的整体熵偏大。
结束帧时间,单位ps。最好选取RMSD稳定时区进行计算,以消除结构不稳定时导致的整体熵偏大。
间隔时间,单位ps。
索引文件,ndx格式。当体系中存在膜结构的时候可以通过Membrane Solvation模块获取index.ndx文件。膜模拟中的受体为receptor,配体为ligand,膜为membrane。
定义受体组别进行结合能计算。组别中填写的为蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基的序号。例如1-213或者1-211,212-213。蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基序号从1开始重新编号,与初始pdb氨基酸编号无关。
定义配体组别进行结合能计算。组别中填写的为蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基的序号。例如1-213或者1-211,212-213。蛋白氨基酸或者核酸碱基序号从1开始重新编号,与初始pdb氨基酸编号无关。
拓扑文件,由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
结构文件,.gro格式,由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
体系参数压缩文件,tar.gz格式。由MD Solvation模块或者Membrane Solvation模块得到。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA_result.txt | MMPBSA结果汇总文件。 |
| MMPBSA_Residue.csv | 能量分解数据CSV文件。 |
| MMPBSA.pdb | 原子对应的MMPBSA能量放到PDB文件。可以做对应能量类别的表面图,从图的颜色深浅可以看出哪些区域对结合能贡献值较大。 |
| MMPBSA.tar.gz | MMPBSA所有原始文件。包括_mmpbsa_residue_#.txt是每个残基对应的每个能量类别的数值,共包含7个能量类别:范德华能(VDW)、静电能(ELE)、溶剂化能极性部分(PB)、溶剂化能非极性部分(SA)、VDW+ELE=MM、PB+SA=PBSA、MM+PBSA=Binding/MMPBSA。_mmpbsa_residue.txt是对上述7个文件的总结,即为MMPBSA_Residue.csv对应的原始文件。_mmpbsa_atom#.pdb是将每个原子对应的能量类别放到pdb文件,与MMPBSA.pdb相似。 |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Duan L, Liu X, Zhang JZ. Interaction Entropy: A New Paradigm for Highly Efficient and Reliable Computation of Protein-Ligand Binding Free Energy. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 May 4;138(17):5722-8.
https://github.com/Electrostatics/apbs/blob/main/docs/index.rst
MMPBSA calculates the binding free energy between a receptor and a ligand, providing energy decomposition data, binding constants (Ka), and inhibitor constants (Ki). The entropy calculation uses the method of interaction entropy proposed by Professor Zhang Zenghui, which directly calculates the entropy component of the binding free energy (interaction entropy or -TΔS) from molecular dynamics simulations, but requires selecting stable structural regions for calculation. This module provides four calculation methods. Among them, Trajectory calculates the binding free energy between the receptor and ligand after molecular dynamics simulation trajectories; One Structure calculates the binding free energy between the receptor and ligand for a single frame PDB structure or a docked PDB structure; MMPBSA of One Structure allows direct input of a PDB for calculation. Index Name is the input receptor-ligand group name, while Custom Name is the input residue numbers of the receptor-ligand in the PDB.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, available in the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or AlphaAutoMD module.
Name of the receptor, can be Protein, DNA, or RNA.
Name of the ligand, can be Protein, DNA, or RNA. If it is a small molecule, enter its name in the PDB. Use ‘Other’ if the system contains a ligand (including small molecules) other than proteins.
Start frame time in ps. It is best to select a stable RMSD region for calculation to eliminate large overall entropy caused by structural instability.
End frame time in ps. It is best to select a stable RMSD region for calculation to eliminate large overall entropy caused by structural instability.
Time interval in ps.
Index file in ndx format. When there is a membrane structure in the system, you can obtain the index.ndx file through the Membrane Solvation module. In membrane simulations, the receptor is ‘receptor’, the ligand is ‘ligand’, and the membrane is ‘membrane’.
Define receptor groups for binding energy calculation. Enter the sequence numbers of protein amino acids or nucleic acid bases in the group. For example, 1-213 or 1-211,212-213. Protein amino acid or nucleic acid base numbers start from 1 and are independent of the initial pdb amino acid numbering.
Define ligand groups for binding energy calculation. Enter the sequence numbers of protein amino acids or nucleic acid bases in the group. For example, 1-213 or 1-211,212-213. Protein amino acid or nucleic acid base numbers start from 1 and are independent of the initial pdb amino acid numbering.
Topology file obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
Structure file in .gro format obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
System parameter compression file in tar.gz format. Obtained from the MD Solvation module or Membrane Solvation module.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| MMPBSA_result.txt | Summary file of MMPBSA results. |
| MMPBSA_Residue.csv | Energy decomposition data in CSV format. |
| MMPBSA.pdb | MMPBSA energy corresponding to atoms in a PDB file. This can be used to create a surface map of energy categories, where the color depth indicates the regions contributing significantly to the binding energy. |
| MMPBSA.tar.gz | All original MMPBSA files. Includes mmpbsa_residue#.txt which contains the values of each energy category for each residue, totaling 7 energy categories: van der Waals energy (VDW), electrostatic energy (ELE), polar part of solvation energy (PB), nonpolar part of solvation energy (SA), VDW+ELE=MM, PB+SA=PBSA, MM+PBSA=Binding/MMPBSA. _mmpbsa_residue.txt is a summary of the above 7 files, corresponding to the original file MMPBSA_Residue.csv. _mmpbsa_atom#.pdb assigns the energy categories to each atom in a pdb file, similar to MMPBSA.pdb. |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Duan L, Liu X, Zhang JZ. Interaction Entropy: A New Paradigm for Highly Efficient and Reliable Computation of Protein-Ligand Binding Free Energy. J Am Chem Soc. 2016 May 4;138(17):5722-8.
https://github.com/Electrostatics/apbs/blob/main/docs/index.rst
N个原子的柔性大体系如蛋白,其运动轨迹需要3N维笛卡尔坐标来描述,这样高维的数据很难理解和直观分析。MD PCA(Principal component analysis,PCA)模块可以从高维数据中分析出主要的影响因素 (本征向量) 。前几个本征向量(主成分,如前两个主成份则为 PC1,PC2) 一般可以描述分子运动的大部分信息。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的结构组别:Backbone,Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
索引文件,格式为ndx
得到结果文件,每种类型的文件如果包含PNG、CSV以及XVG后缀,相同名称只是表现形式不同,数据一样
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| average.pdb | 计算后的平均结构文件 |
| filtered.xtc | 计算的降维过滤后的轨迹文件 |
| eigenvalues.xvg | 本征值文件 |
| proj1.xvg | 对应的主成分PC1文件 |
| proj2.xvg | 对应的主成分PC2文件 |
| proj_all.xvg | 计算的PC1到PC2的主成份合并文件 |
| Gibbs_2d.png/Gibbs_3d.png | 只计算两个主成分时的二维和三维自由能景观图 |
For a large flexible system with N atoms such as a protein, its motion trajectory requires 3N-dimensional Cartesian coordinates to describe, making it difficult to understand and analyze high-dimensional data. The MD PCA (Principal Component Analysis, PCA) module can analyze the main influencing factors (eigenvectors) from high-dimensional data. The first few eigenvectors (principal components, such as the first two principal components PC1, PC2) can generally describe most of the information about molecular motion.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the structural group for calculation: Backbone, Protein, DNA, RNA. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
Index file in ndx format.
Obtain the following result files. If the files have PNG, CSV, and XVG suffixes, they contain the same data but in different formats.
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| average.pdb | Computed average structure file |
| filtered.xtc | Filtered trajectory file after dimensionality reduction |
| eigenvalues.xvg | Eigenvalues file |
| proj1.xvg | Corresponding principal component PC1 file |
| proj2.xvg | Corresponding principal component PC2 file |
| proj_all.xvg | Combined file of principal components PC1 to PC2 |
| Gibbs_2d.png/Gibbs_3d.png | 2D and 3D free energy landscape plots when only two principal components are considered |
MD SASA模块是计算指定组别的溶剂可及表面积(solvent accessible surface area,SASA)。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的结构组别:Backbone,Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
索引文件,格式为ndx
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| area.csv | 溶剂可及表面积CSV文件 |
| area.xvg | 溶剂可及表面积XVG文件 |
| area.png | 溶剂可及表面积PNG文件 |
其中area.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | 时间 |
| Total Area (nm^2) | 溶剂可及表面积 |
| Hydrophobic (nm^2) | 疏水表面积 |
| Hydrophilic (nm^2) | 亲水表面积 |
The MD SASA module calculates the solvent accessible surface area (SASA) of specified groups.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the structural group for calculation: Backbone, Protein, DNA, RNA. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
Index file in ndx format.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| area.csv | Solvent accessible surface area CSV file |
| area.xvg | Solvent accessible surface area XVG file |
| area.png | Solvent accessible surface area PNG file |
The area.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | Time |
| Total Area (nm^2) | Total solvent accessible surface area |
| Hydrophobic (nm^2) | Hydrophobic surface area |
| Hydrophilic (nm^2) | Hydrophilic surface area |
MD Hbond模板对于指定组别之间的氢键分析。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的氢键组别1:Protein,DNA,RNA。如果两个组相同则分析的是组内氢键。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
选择需要计算的氢键组别2:Protein,DNA,RNA。如果两个组相同则分析的是组内氢键。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的组1残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的组1原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的组2残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的组2原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hbnum.csv | 氢键分析CSV文件 |
| hbnum.xvg | 氢键分析XVG文件 |
| hbnum.png | 氢键分析PNG文件 |
其中hbnum.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | 时间 |
| Hydrogen bonds | 氢键数目 |
| Pairs within 0.35 nm | 两个组相距0.35nm内的接触的原子数目 |
MD Hbond template is used for analyzing hydrogen bonds between specified groups.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the hydrogen bond group 1 for calculation: Protein, DNA, RNA. If both groups are the same, it analyzes intra-group hydrogen bonds. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Select the hydrogen bond group 2 for calculation: Protein, DNA, RNA. If both groups are the same, it analyzes intra-group hydrogen bonds. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for group 1 calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for group 1 calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom residue numbers for group 2 calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for group 2 calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| hbnum.csv | Hydrogen bond analysis CSV file |
| hbnum.xvg | Hydrogen bond analysis XVG file |
| hbnum.png | Hydrogen bond analysis PNG file |
The hbnum.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Time (ns) | Time |
| Hydrogen bonds | Number of hydrogen bonds |
| Pairs within 0.35 nm | Number of atoms in contact within 0.35 nm between the two groups |
MD Gyration回旋半径分析,可用来衡量体系模拟时的质权平均半径。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
选择需要计算的结构组别:Backbone,Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
索引文件,格式为ndx
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| gyrate.csv | 回转半径CSV文件 |
| gyrate.xvg | 回转半径XVG文件 |
| gyrate.png | 回转半径PNG文件 |
其中gyrate.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Time (ps) | 时间 |
| Rg | 回旋半径 |
| Rg(X) | 绕着x轴的回旋半径 |
| Rg(Y) | 绕着y轴的回旋半径 |
| Rg(Z) | 绕着z轴的回旋半径 |
MD Gyration is a radius of gyration analysis used to measure the mass-weighted average radius of a system during simulation.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the structural group for calculation: Backbone, Protein, DNA, RNA. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10, 15.
Custom atom numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10, 15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
Index file in ndx format.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| gyrate.csv | Gyration radius CSV file |
| gyrate.xvg | Gyration radius XVG file |
| gyrate.png | Gyration radius PNG file |
The gyrate.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Time (ps) | Time |
| Rg | Radius of gyration |
| Rg(X) | Radius of gyration around the x-axis |
| Rg(Y) | Radius of gyration around the y-axis |
| Rg(Z) | Radius of gyration around the z-axis |
MD Clustering是对动力学轨迹进行归簇分析。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)模块中获取。
聚类时结构的RMSD截断值(nm)
聚类算法:linkage, jarvis-patrick, monte-carlo, diagonalization, gromos, 默认使用gromos算法。
选择需要计算的结构组别:Backbone,Protein,DNA,RNA。
可以根据PDB中小分子的名称填写组别名称。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
自定义需要计算的原子编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15
每一帧的间隔时间(单位ns)
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| clusters.pdb | 差异较大的每个簇的代表性结构 |
| clust-size.xvg | 各个簇的帧数 |
| cluster.xvg | 各个簇和轨迹帧号的对应关系 |
MD Clustering is a clustering analysis of molecular dynamics trajectories.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
RMSD cutoff value for clustering (in nm).
Clustering algorithm: linkage, jarvis-patrick, monte-carlo, diagonalization, gromos. The default method is gromos.
Select the structural group for calculation: Backbone, Protein, DNA, RNA. You can specify group names based on the names of small molecules in the PDB file.
Custom residue numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous residues and commas to separate non-continuous residues. For example: 1-10,15.
Custom atom numbers for calculation. Use “-” for continuous atoms and commas to separate non-continuous atoms. For example: 1-10,15.
Time interval between frames (in ns).
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| clusters.pdb | Representative structures of each cluster with significant differences |
| clust-size.xvg | Number of frames in each cluster |
| cluster.xvg | Correspondence between clusters and trajectory frame numbers |

GMX MDP Generation (Auto)模块主要是根据所选体系(膜,受体,配体)自动生成分子动力学模拟过程中所需的MDP文件,此文件是Gromacs分子动力学模拟需要用到输入文件,里面包含各种参数。
选择体系中存在的结构类型:membrane代表膜结构,receptor代表大分子结构(蛋白或者核酸),ligand代表小分子结构。
模拟时长,单位为ns
时间步长,单位ps
参考温度,单位为K
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| mini.mdp | 最小化MDP文件 |
| npt.mdp/npt.tar.gz | NPT MDP文件 |
| md.mdp/md.tar.gz | MD MDP文件 |
The GMX MDP Generation (Auto) module is designed to automatically generate the MDP files required for molecular dynamics simulations based on the selected system (membrane, receptor, ligand). The MDP file is an input file required for Gromacs molecular dynamics simulations, containing various parameters.
Select the type of structure present in the system: membrane for membrane structure, receptor for macromolecular structure (protein or nucleic acid), ligand for small molecule structure.
Duration of the simulation, in units of ns.
Time step for the simulation, in units of ps.
Reference temperature for the temperature coupling, in units of K.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| mini.mdp | MDP file for minimization |
| npt.mdp/npt.tar.gz | MDP file for NPT ensemble simulation |
| md.mdp/md.tar.gz | MDP file for MD simulation |

siRNA Designer基于靶点基因序列,设计siRNA分子序列。该方法考虑了多条siRNA设计规则,如下:
靶点基因序列,支持多条,FASTA格式。
输出结果文件为siRNAcandidates_序列名称.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Target starting position | 靶点基因序列的起始位置 |
| Target ending position | 靶点基因序列的终止位置 |
| Target sequence(21nt target + 2nt overhang) | 靶点序列 |
| Target score | 靶点打分,越高越好 |
| Guide sequence(5’->3’) | 结合靶点基因的序列,也称为antisense sequence |
| Passenger sequence(5’->3’) | 与Guide sequence配对的序列 |
| Guide Tm | Guide sequence计算的Melting Temperature值,一般情况下Tm值越低,发生副作用的可能性越小 |
| Passenger Tm | Passenger sequence计算的Melting Temperature值 |
siRNA Designer designs siRNA molecule sequences based on target gene sequences. This method considers multiple siRNA design rules as follows:
Target gene sequences, supports multiple sequences in FASTA format.
The output result file is named siRNAcandidates_sequence_name.csv, and it includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Target starting position | Starting position of the target gene sequence |
| Target ending position | Ending position of the target gene sequence |
| Target sequence (21nt target + 2nt overhang) | Target sequence |
| Target score | Score assigned to the target, higher scores are better |
| Guide sequence (5’->3’) | Sequence that binds to the target gene, also known as the antisense sequence |
| Passenger sequence (5’->3’) | Sequence that pairs with the Guide sequence |
| Guide Tm | Melting Temperature value calculated for the Guide sequence. In general, lower Tm values indicate a lower likelihood of side effects |
| Passenger Tm | Melting Temperature value calculated for the Passenger sequence |

Membrane Solvation对输入的膜,受体,配体文件加入水盒子和离子。
膜拓扑文件,top格式,可由GMX Membrane Parameterization模块生成。
膜结构文件,gro格式,可由GMX Membrane Parameterization模块生成。
膜参数压缩文件,tar.gz格式,可由GMX Membrane Parameterization模块生成。
受体拓扑文件,top格式,可由GMX Receptor Parameterization模块生成。
受体结构文件,gro格式,可由GMX Receptor Parameterization模块生成。
受体参数压缩文件,tar.gz格式,可由GMX Receptor Parameterization模块生成。
配体结构文件,多配体输入压缩文件,gro格式,可由GMX Ligand Parameterization模块生成。
配体参数压缩文件,tar.gz格式,可由GMX Ligand Parameterization模块生成。
体系拓扑文件的输出名称
体系结构文件的输出名称
体系参数压缩文件的输出名称
体系索引文件的输出名称
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| system.gro | 体系的分子坐标文件 |
| system_itp.tar.gz | 体系平衡模拟时固定原子位置所施加的力 |
| system.top | 体系的拓扑文件 |
| index.ndx | 体系的索引文件 |
Membrane Solvation adds water boxes and ions to the input membrane, receptor, and ligand files.
Topology file of the membrane in .top format, can be generated by the GMX Membrane Parameterization module.
Structure file of the membrane in .gro format, can be generated by the GMX Membrane Parameterization module.
Compressed parameter file of the membrane in .tar.gz format, can be generated by the GMX Membrane Parameterization module.
Topology file of the receptor in .top format, can be generated by the GMX Receptor Parameterization module.
Structure file of the receptor in .gro format, can be generated by the GMX Receptor Parameterization module.
Compressed parameter file of the receptor in .tar.gz format, can be generated by the GMX Receptor Parameterization module.
Structure file of the ligand, multiple ligands input as a compressed file in .gro format, can be generated by the GMX Ligand Parameterization module.
Compressed parameter file of the ligand in .tar.gz format, can be generated by the GMX Ligand Parameterization module.
Output name of the system topology file.
Output name of the system structure file.
Output name of the compressed system parameter file.
Output name of the system index file.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| system.gro | Molecular coordinate file of the system |
| system_itp.tar.gz | Force applied to fix atom positions during equilibrium simulations of the system |
| system.top | Topology file of the system |
| index.ndx | Index file of the system |
GMX Membrane Parameterization模块是根据Amber或者Charmm生成膜结构的GRO,ITP以及TOP文件。
膜结构文件,PDB格式,必须是纯膜结构,并允许水和离子存在
只支持“amber”力场和“charmm”力场。默认的“amber”力场。
需要特别注意的是:
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| membrane.top | 膜的拓扑文件 |
| membrane.gro | 膜的结构文件 |
| membrane_itp.tar.gz | 膜的参数压缩文件 |
The GMX Membrane Parameterization module is used to generate GRO, ITP, and TOP files for membrane structures based on Amber or Charmm force fields.
The membrane structure file in PDB format. It must be a pure membrane structure and can contain water and ions.
Supports only the “amber” force field and the “charmm” force field. The default is the “amber” force field. It is important to note:
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| membrane.top | Topology file for the membrane |
| membrane.gro | Structure file for the membrane |
| membrane_itp.tar.gz | Compressed parameter file for the membrane |
Membrane System Construction构建膜结构的PDB文件。
需要注意的是:Amber参数涉及有大分子的AMBER力场、小分子的GAFF力场、糖的GLYCAM以及磷脂的LIPID力场,这四个力场是可以兼容的。Charmm也有自己一套力场,涉及有CHARMM力场(适用于大分子、糖、磷脂)和CGenFF力场(适用于小分子),这两个力场是相互兼容的。
目前WEMOL上只支持GAFF力场的小分子计算,所以当存在小分子时,膜的成分必须为AMBER力场下的。
必须遵循格式:lipid1:lipid2//lipid3,“//”用于区分上膜和下膜,没有“//”表示上膜和下膜中相同的脂质成分!
注:在charmm力场作用下,支持以下38种脂质构建膜:
CHL1 SITO ERG1 DLPA DLPC DLPE DLPG DLPS DMPA DMPC DMPE DMPG DMPS DOPA DOPC DOPE DOPG DOPS DPPA DPPC DPPE DPPG DPPS DSPA DSPC DSPE DSPG DSPS POPA POPC POPE POPG POPS SOPA SOPC SOPE SOPG SOPS
注:在charmm力场作用下,还支持以下26种心磷脂膜:
LACH LACL LBCH LBCL LCCH LCCL LDCH LDCL OACH OACL OCCH OCCL PACL PMCH PMCL POCH POCL PVCL TLCH TLCL TMCH TMCL TOCH TOCL TYCH TYCL
注:在amber力场作用下,支持以下253种脂质构建膜:
CHL1 AHPA AHPC AHPE AHPG AHPS ALPA ALPC ALPE ALPG ALPS AMPA AMPC AMPE AMPG AMPS AOPA AOPC AOPE AOPG AOPS APPA APPC APPE APPG APPS ASPA ASPC ASPE ASPG ASPS DAPA DAPC DAPE DAPG DAPS DHPA DHPC DHPE DHPG DHPS DLPA DLPC DLPE DLPG DLPS DMPA DMPC DMPE DMPG DMPS DOPA DOPC DOPE DOPG DOPS DPPA DPPC DPPE DPPG DPPS DSPA DSPC DSPE DSPG DSPS HAPA HAPC HAPE HAPG HAPS HLPA HLPC HLPE HLPG HLPS HMPA HMPC HMPE HMPG HMPS HOPA HOPC HOPE HOPG HOPS HPPA HPPC HPPE HPPG HPPS HSPA HSPC HSPE HSPG HSPS LAPA LAPC LAPE LAPG LAPS LHPA LHPC LHPE LHPG LHPS LMPA LMPC LMPE LMPG LMPS LOPA LOPC LOPE LOPG LOPS LPPA LPPC LPPE LPPG LPPS LSPA LSPC LSPE LSPG LSPS MAPA MAPC MAPE MAPG MAPS MHPA MHPC MHPE MHPG MHPS MLPA MLPC MLPE MLPG MLPS MOPA MOPC MOPE MOPG MOPS MPPA MPPC MPPE MPPG MPPS MSPA MSPC MSPE MSPG MSPS OAPA OAPC OAPE OAPG OAPS OHPA OHPC OHPE OHPG OHPS OLPA OLPC OLPE OLPG OLPS OMPA OMPC OMPE OMPG OMPS OPPA OPPC OPPE OPPG OPPS OSPA OSPC OSPE OSPG OSPS PAPA PAPC PAPE PAPG PAPS PHPA PHPC PHPE PHPG PHPS PLPA PLPC PLPE PLPG PLPS PMPA PMPC PMPE PMPG PMPS POPA POPC POPE POPG POPS PSPA PSPC PSPE PSPG PSPS SAPA SAPC SAPE SAPG SAPS SHPA SDPA SHPC SDPC SHPE SDPE SHPG SDPG SHPS SDPS SLPA SLPC SLPE SLPG SLPS SMPA SMPC SMPE SMPG SMPS SOPA SOPC SOPE SOPG SOPS SPPA SPPC SPPE SPPG SPPS PSM SSM
膜成分比例,格式为ratio1:ratio2//ratio3
膜成分数量比例,格式为number1:number2//number3
定向结构文件,pdb格式
添加离子类型,格式为ion1:ion2//ion3,“//”用于区分上下膜,没有“//”表示上下膜中离子成分相同!支持以下5种离子:NA、K、CL、CA、MG。
离子成分比例,格式为conc1:conc2//conc3,与Ion参数顺序相同
离子成分数量比例,格式为number1:number2//number3,与Ion参数顺序相同
只支持“amber”力场和“charmm”力场。默认的“amber”力场
膜的X轴和Y轴长度,默认为50 Å
膜的Z轴长度,默认为100 Å
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| membrane_lipid.pdb | 纯膜体系下生成的结构文件,当存在配体或者受体时不会生成该文件。 |
| membrane_orientation.pdb | 膜与受体/配体/复合物的结构文件,纯膜时不生成该文件。 |
| orientation.pdb | 受体/配体/复合物的取向结构,纯膜时不生成该文件。 |
Membrane System Construction is used to build PDB files for membrane structures. It is important to note that the Amber parameters involve the AMBER force field for macromolecules, the GAFF force field for small molecules, the GLYCAM force field for sugars, and the LIPID force field for phospholipids. These four force fields are compatible. Charmm also has its own set of force fields, including the CHARMM force field (for macromolecules, sugars, and phospholipids) and the CGenFF force field (for small molecules), which are mutually compatible. Currently, WEMOL only supports calculations for small molecules using the GAFF force field, so when small molecules are present, the membrane components must be under the AMBER force field.
Must follow the format: lipid1:lipid2//lipid3. “//” is used to differentiate between the upper and lower membrane components. If there is no “//”, it indicates the same lipid component in the upper and lower membranes.
Note: Under the Charmm force field, the membrane construction supports the following 38 lipid types:
CHL1 SITO ERG1 DLPA DLPC DLPE DLPG DLPS DMPA DMPC DMPE DMPG DMPS DOPA DOPC DOPE DOPG DOPS DPPA DPPC DPPE DPPG DPPS DSPA DSPC DSPE DSPG DSPS POPA POPC POPE POPG POPS SOPA SOPC SOPE SOPG SOPS
Under the Charmm force field, it also supports the following 26 sphingomyelin membranes:
LACH LACL LBCH LBCL LCCH LCCL LDCH LDCL OACH OACL OCCH OCCL PACL PMCH PMCL POCH POCL PVCL TLCH TLCL TMCH TMCL TOCH TOCL TYCH TYCL
Under the Amber force field, the membrane construction supports 253 lipid types:
CHL1 AHPA AHPC AHPE AHPG AHPS ALPA ALPC ALPE ALPG ALPS AMPA AMPC AMPE AMPG AMPS AOPA AOPC AOPE AOPG AOPS APPA APPC APPE APPG APPS ASPA ASPC ASPE ASPG ASPS DAPA DAPC DAPE DAPG DAPS DHPA DHPC DHPE DHPG DHPS DLPA DLPC DLPE DLPG DLPS DMPA DMPC DMPE DMPG DMPS DOPA DOPC DOPE DOPG DOPS DPPA DPPC DPPE DPPG DPPS DSPA DSPC DSPE DSPG DSPS HAPA HAPC HAPE HAPG HAPS HLPA HLPC HLPE HLPG HLPS HMPA HMPC HMPE HMPG HMPS HOPA HOPC HOPE HOPG HOPS HPPA HPPC HPPE HPPG HPPS HSPA HSPC HSPE HSPG HSPS LAPA LAPC LAPE LAPG LAPS LHPA LHPC LHPE LHPG LHPS LMPA LMPC LMPE LMPG LMPS LOPA LOPC LOPE LOPG LOPS LPPA LPPC LPPE LPPG LPPS LSPA LSPC LSPE LSPG LSPS MAPA MAPC MAPE MAPG MAPS MHPA MHPC MHPE MHPG MHPS MLPA MLPC MLPE MLPG MLPS MOPA MOPC MOPE MOPG MOPS MPPA MPPC MPPE MPPG MPPS MSPA MSPC MSPE MSPG MSPS OAPA OAPC OAPE OAPG OAPS OHPA OHPC OHPE OHPG OHPS OLPA OLPC OLPE OLPG OLPS OMPA OMPC OMPE OMPG OMPS OPPA OPPC OPPE OPPG OPPS OSPA OSPC OSPE OSPG OSPS PAPA PAPC PAPE PAPG PAPS PHPA PHPC PHPE PHPG PHPS PLPA PLPC PLPE PLPG PLPS PMPA PMPC PMPE PMPG PMPS POPA POPC POPE POPG POPS PSPA PSPC PSPE PSPG PSPS SAPA SAPC SAPE SAPG SAPS SHPA SDPA SHPC SDPC SHPE SDPE SHPG SDPG SHPS SDPS SLPA SLPC SLPE SLPG SLPS SMPA SMPC SMPE SMPG SMPS SOPA SOPC SOPE SOPG SOPS SPPA SPPC SPPE SPPG SPPS PSM SSM
The ratio of membrane components, format is ratio1:ratio2//ratio3.
The number ratio of membrane components, format is number1:number2//number3.
The oriented structure file in PDB format.
Types of ions to add, format is ion1:ion2//ion3. “//” is used to differentiate between the upper and lower membranes. If there is no “//”, it indicates the same ion component in the upper and lower membranes. It supports the following 5 types of ions: NA, K, CL, CA, MG.
The concentration ratio of ions, format is conc1:conc2//conc3, in the same order as the Ion parameter.
The number ratio of ion components, format is number1:number2//number3, in the same order as the Ion parameter.
Supports only the “amber” force field and the “charmm” force field. Default is the “amber” force field.
The length of the membrane along the X and Y axes, default is 50 Å.
The length of the membrane along the Z axis, default is 100 Å.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| membrane_lipid.pdb | Generated structure file for the pure membrane system. This file is not generated when ligands or receptors are present. |
| membrane_orientation.pdb | Structure file of the membrane with the receptor/ligand/complex. This file is not generated for a pure membrane system. |
| orientation.pdb | Orientation structure of the receptor/ligand/complex. This file is not generated for a pure membrane system. |
Molecule In Membrane模块是生成受体/配体/复合物取向位置与膜的结构文件。
受体结构,PDB格式。如果一个受体含有配体,可以把它们组合成一个受体结构。
“center”,“upper”或“upper”,默认“upper”,即受体相对于膜的位置
“inside”或“outside”,默认为“outside”,即n端相对于膜的取向,只有受体在“center”时才有效。
“yes”或“no”,默认“no”,即当受体定向时是否考虑受体结构中的非受体分子,仅当受体位于“center”时有效。
受体结构的向Z轴位移距离,仅当受体处于“center”时有效。
配体结构,PDB格式。通常是指相对于受体的独立配体分子
“center”、“upper”或“lower”,当受体不在“center”时默认为“center”,当受体在“center”时默认为“upper”,即配体相对于膜的位置
“inside”或“outside”,默认为“outside”,即n端相对于膜的取向,只有配体在“center”时才有效。
配体结构的向Z轴位移距离,仅当配体处于“center”时有效。
配体分子数,默认为1。只有配体在“upper”或“lower”时才有效
膜的X轴和Y轴长度,默认为50 Å
膜的Z轴长度,默认为100 Å
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| orientation.pdb | 受体/配体/复合物的结构文件 |
| orientation_dum.pdb | 显示受体/配体/复合物与膜的相对位置的结构文件 |
The Molecule In Membrane module is used to generate structural files of the orientation of receptors/ligands/complexes relative to a membrane.
The structure of the receptor in PDB format. If a receptor contains a ligand, they can be combined into a single receptor structure.
“center”, “upper”, or “lower”, default is “upper”, indicating the position of the receptor relative to the membrane.
“inside” or “outside”, default is “outside”, indicating the orientation of the N-terminus of the receptor relative to the membrane. This parameter is only effective when the receptor is in the “center” position.
“yes” or “no”, default is “no”, indicating whether non-receptor molecules in the receptor structure should be considered when orienting the receptor. This parameter is only effective when the receptor is in the “center” position.
The distance the receptor structure is shifted along the Z-axis. This parameter is only effective when the receptor is in the “center” position.
The structure of the ligand in PDB format. Typically, this refers to an independent ligand molecule relative to the receptor.
“center”, “upper”, or “lower”, default is “center” when the receptor is not in the “center” position, and default is “upper” when the receptor is in the “center” position, indicating the position of the ligand relative to the membrane.
“inside” or “outside”, default is “outside”, indicating the orientation of the N-terminus of the ligand relative to the membrane. This parameter is only effective when the ligand is in the “center” position.
The distance the ligand structure is shifted along the Z-axis. This parameter is only effective when the ligand is in the “center” position.
The number of ligand molecules, default is 1. This parameter is only effective when the ligand is in the “upper” or “lower” position.
The length of the membrane along the X and Y axes, default is 50 Å.
The length of the membrane along the Z axis, default is 100 Å.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| orientation.pdb | Structural file of the receptor/ligand/complex |
| orientation_dum.pdb | Structural file showing the relative position of the receptor/ligand/complex with respect to the membrane |

基于蛋白质结构(PDB文件),计算各个残基的溶剂暴露程度(溶液可及化表面积,solvent accessible surface area, SASA)。
蛋白氨基酸残基的相对溶剂可及表面积(Relative SASA,RSASA)可以衡量残基在溶剂中的暴露程度,其计算公式如下:
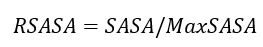
其中,SASA是溶剂可及表面积,MaxSASA是氨基酸最大溶剂可及表面积,单位均为Å。
为了测量氨基酸侧链的相对溶剂可及表面积,通常采用从Gly-X-Gly三肽中获得的MaxSASA值,其中X为需要计算的氨基酸残基。几种MaxSASA量表如下所示。
| Residue | Tien et al. 2013 (theor.)[1] | Tien et al. 2013 (emp.)[1] | Miller et al. 1987[2] | Rose et al. 1985[3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine | 129.0 | 121.0 | 113.0 | 118.1 |
| Arginine | 274.0 | 265.0 | 241.0 | 256.0 |
| Asparagine | 195.0 | 187.0 | 158.0 | 165.5 |
| Aspartate | 193.0 | 187.0 | 151.0 | 158.7 |
| Cysteine | 167.0 | 148.0 | 140.0 | 146.1 |
| Glutamate | 223.0 | 214.0 | 183.0 | 186.2 |
| Glutamine | 225.0 | 214.0 | 189.0 | 193.2 |
| Glycine | 104.0 | 97.0 | 85.0 | 88.1 |
| Histidine | 224.0 | 216.0 | 194.0 | 202.5 |
| Isoleucine | 197.0 | 195.0 | 182.0 | 181.0 |
| Leucine | 201.0 | 191.0 | 180.0 | 193.1 |
| Lysine | 236.0 | 230.0 | 211.0 | 225.8 |
| Methionine | 224.0 | 203.0 | 204.0 | 203.4 |
| Phenylalanine | 240.0 | 228.0 | 218.0 | 222.8 |
| Proline | 159.0 | 154.0 | 143.0 | 146.8 |
| Serine | 155.0 | 143.0 | 122.0 | 129.8 |
| Threonine | 172.0 | 163.0 | 146.0 | 152.5 |
| Tryptophan | 285.0 | 264.0 | 259.0 | 266.3 |
| Tyrosine | 263.0 | 255.0 | 229.0 | 236.8 |
| Valine | 174.0 | 165.0 | 160.0 | 164.5 |
通常有以下标准:
rASA >0.5(50%):残基被认为是暴露于溶液的(solvent-exposed)
rASA < 0.2(20%):残基被认为是埋藏在蛋白质内部的(buried)
0.2 ≤ rASA ≤ 0.5:残基处于部分暴露状态。
具体阈值的选择可能取决于研究的目的。例如,某些分析可能使用更严格或宽松的标准来划分。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式。
计算出来的各种溶剂可及表面积值,可根据需求选择需要的类型:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ResidueType | 残基类型 |
| Chain ID | 链名称 |
| Residue Number | 残基编号 |
| total | Total SASA of residue |
| polar | Polar SASA(极性) |
| apolar | Apolar SASA(非极性) |
| mainChain | Main chain SASA |
| sideChain | Side chain SASA |
| relativeTotal* | Relative total SASA |
| relativePolar | Relative polar SASA |
| relativeApolar | Relative Apolar SASA |
| relativeMainChain | Relative main chain SASA |
| relativeSideChain* | Relative side chain SASA |
*常用的比如:
通常有以下标准:
rASA >0.5(50%):残基被认为是暴露于溶液的(solvent-exposed)
rASA < 0.2(20%):残基被认为是埋藏在蛋白质内部的(buried)
0.2 ≤ rASA ≤ 0.5:残基处于部分暴露状态。
具体阈值的选择可能取决于研究的目的。例如,某些分析可能使用更严格或宽松的标准来划分。
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Relative_accessible_surface_area
Tien MZ, Meyer AG, Sydykova DK, Spielman SJ, Wilke CO. Maximum allowed solvent accessibilites of residues in proteins. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 21;8(11):e80635.
Miller S, Lesk AM, Janin J, Chothia C. The accessible surface area and stability of oligomeric proteins. Nature. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2;328(6133):834-6.
Rose GD, Geselowitz AR, Lesser GJ, Lee RH, Zehfus MH. Hydrophobicity of amino acid residues in globular proteins. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):834-8.
https://freesasa.github.io/doxygen/Geometry.html
Based on protein structure (PDB file), calculates the solvent exposure of each residue (solvent accessible surface area, SASA). The relative solvent accessible surface area (RSASA) of protein amino acid residues measures the exposure of residues in the solvent. The calculation formula is as follows:
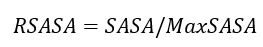
Here, SASA is the solvent accessible surface area, and MaxSASA is the maximum solvent accessible surface area of the amino acid, both in Å units. To measure the relative solvent accessible surface area of amino acid side chains, the MaxSASA value obtained from the Gly-X-Gly tripeptide is typically used, where X represents the amino acid residue being calculated. Several MaxSASA scales are shown below.
| Residue | Tien et al. 2013 (theor.)[1] | Tien et al. 2013 (emp.)[1] | Miller et al. 1987[2] | Rose et al. 1985[3] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alanine | 129.0 | 121.0 | 113.0 | 118.1 |
| Arginine | 274.0 | 265.0 | 241.0 | 256.0 |
| Asparagine | 195.0 | 187.0 | 158.0 | 165.5 |
| Aspartate | 193.0 | 187.0 | 151.0 | 158.7 |
| Cysteine | 167.0 | 148.0 | 140.0 | 146.1 |
| Glutamate | 223.0 | 214.0 | 183.0 | 186.2 |
| Glutamine | 225.0 | 214.0 | 189.0 | 193.2 |
| Glycine | 104.0 | 97.0 | 85.0 | 88.1 |
| Histidine | 224.0 | 216.0 | 194.0 | 202.5 |
| Isoleucine | 197.0 | 195.0 | 182.0 | 181.0 |
| Leucine | 201.0 | 191.0 | 180.0 | 193.1 |
| Lysine | 236.0 | 230.0 | 211.0 | 225.8 |
| Methionine | 224.0 | 203.0 | 204.0 | 203.4 |
| Phenylalanine | 240.0 | 228.0 | 218.0 | 222.8 |
| Proline | 159.0 | 154.0 | 143.0 | 146.8 |
| Serine | 155.0 | 143.0 | 122.0 | 129.8 |
| Threonine | 172.0 | 163.0 | 146.0 | 152.5 |
| Tryptophan | 285.0 | 264.0 | 259.0 | 266.3 |
| Tyrosine | 263.0 | 255.0 | 229.0 | 236.8 |
| Valine | 174.0 | 165.0 | 160.0 | 164.5 |
Protein structure file in PDB format.
Calculated solvent accessible surface area values for various residue types can be selected as needed:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ResidueType | Residue type |
| Chain ID | Chain name |
| Residue Number | Residue number |
| total | Total SASA of residue |
| polar | Polar SASA |
| apolar | Apolar SASA |
| mainChain | Main chain SASA |
| sideChain | Side chain SASA |
| relativeTotal* | Relative total SASA |
| relativePolar | Relative polar SASA |
| relativeApolar | Relative Apolar SASA |
| relativeMainChain | Relative main chain SASA |
| relativeSideChain* | Relative side chain SASA |
*Commonly used include:
Typically, the following criteria are used:
rASA > 0.5 (50%): Residues are considered solvent-exposed.
rASA < 0.2 (20%): Residues are considered buried within the protein.
0.2 ≤ rASA ≤ 0.5: Residues are in a partially exposed state.
The choice of specific thresholds may depend on the purpose of the study. For example, some analyses may use stricter or more lenient criteria for classification.
Relative accessible surface area - Wikipedia
Tien MZ, Meyer AG, Sydykova DK, Spielman SJ, Wilke CO. Maximum allowed solvent accessibilities of residues in proteins. PLoS One. 2013 Nov 21;8(11):e80635.
Miller S, Lesk AM, Janin J, Chothia C. The accessible surface area and stability of oligomeric proteins. Nature. 1987 Aug 27-Sep 2;328(6133):834-6.
Rose GD, Geselowitz AR, Lesser GJ, Lee RH, Zehfus MH. Hydrophobicity of amino acid residues in globular proteins. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):834-8.
Geometry - FreeSASA Documentation

基于MAFFT的多序列比对工具,支持蛋白和核酸序列的比对。
蛋白或者核酸的序列文件,FASTA格式
输出结果为多序列比对后的结果文件:alignment.fasta
Katoh K, Kuma K, Toh H, Miyata T. MAFFT version 5: improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 20;33(2):511-8.
https://mafft.cbrc.jp/alignment/software/manual/manual.html
MAFFT-based tool for multiple sequence alignment, supports alignment of both protein and nucleic acid sequences.
Sequence file containing protein or nucleic acid sequences in FASTA format.
The output result is the aligned sequences saved in the file: alignment.fasta.
Katoh K, Kuma K, Toh H, Miyata T. MAFFT version 5: improvement in accuracy of multiple sequence alignment. Nucleic Acids Res. 2005 Jan 20;33(2):511-8.
MAFFT Manual

Antibody Sequence Prediction(IgLM)模块是抗体序列生成与优化,该方法从Observed Antibody Space (OAS) 收集抗体序列。OAS数据库包含六个物种的天然抗体序列:人类、小鼠、大鼠、兔子、恒河猴和骆驼。为了研究模型能力的影响,训练了两个版本的模型: IgLM和IgLM-S,分别有13M和1.4M的训练参数。两个IgLM模型都在558万非冗余序列上训练,这些序列基于95%相似性聚类。在训练过程中,随机屏蔽了抗体序列中10到20个残基,以便在推理过程中实现任意跨度的多样化。此外,还对序列中的链型(重链或轻链)和原产物种进行了限定,提供这样的背景能够控制物种特异性抗体序列的产生。该方法被证明可以从各种物种中产生全长的重链和轻链序列,以及具有改进可开发性的填充CDR环库。该方法是一个强大的抗体设计工具,可应用于各种抗体序列设计场景。
抗体序列,仅支持1条序列,FASTA格式。
设定为抗体重链或轻链,值为"H" 或 “L”。
指定序列中进行改造优化的氨基酸起始值,整数值,从1开始。需要说明的是,并不是说从优化起始值-终止值的氨基酸就会完全一对一的进行修改,模型里是指定开始到结束的残基作为1个MASK TOKEN提供给模型进行生成,具体生成多少个残基,是看模型学习的情况。
指定序列中进行改造优化的氨基酸终止值,整数值。需要说明的是,并不是说从优化起始值-终止值的氨基酸就会完全一对一的进行修改,模型里是指定开始到结束的残基作为1个MASK TOKEN提供给模型进行生成,具体生成多少个残基,是看模型学习的情况。
设定物种信息,默认是人源。
设定设计的序列数量,默认100。
输出结果文件为generated_seqs.fasta,包含生产的序列信息,fasta格式。
The Antibody Sequence Prediction (IgLM) module is designed for antibody sequence generation and optimization. This method collects antibody sequences from the Observed Antibody Space (OAS) database, which includes natural antibody sequences from six species: human, mouse, rat, rabbit, cynomolgus monkey, and camel. To study the impact of model capacity, two versions of the model were trained: IgLM and IgLM-S, with 13M and 1.4M training parameters, respectively. Both IgLM models were trained on 5.58 million non-redundant sequences clustered at 95% similarity. During training, 10 to 20 residues in the antibody sequences were randomly masked to achieve diversity across arbitrary spans during inference. Additionally, constraints were placed on the chain type (heavy or light chain) and original species in the sequences to control the generation of species-specific antibody sequences. This method has been shown to generate full-length heavy and light chain sequences from various species, along with a diversified CDR loop library for improved developability. It serves as a powerful antibody design tool applicable to various antibody design scenarios.
Antibody sequence in FASTA format, supporting only one sequence.
Specify the antibody chain type as heavy (“H”) or light (“L”).
Specify the starting amino acid index for optimization in the sequence, an integer value starting from 1. Note that the optimization does not necessarily modify each amino acid from the start to end index one-to-one. The model treats the specified residues from the start to end as one MASK TOKEN for generating sequences, and the actual number of residues generated depends on the model’s learning.
Specify the ending amino acid index for optimization in the sequence, an integer value. Similarly, the optimization does not necessarily modify each amino acid from the start to end index one-to-one.
Set the species information, default is human.
Set the number of sequences to be designed, default is 100.
The output result file is named generated_seqs.fasta, containing the information of the generated sequences in FASTA format.

PTM Hotspot by Structure模块通过快速的蒙特卡罗模拟采样,获得蛋白的多样性构象,通过分析多构象的溶剂暴露情况和结构波动情况来预测天冬氨酸(ASP)的异构化的概率。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式。
输出结果文件为result.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain | 蛋白链名称 |
| Residue Index | 氨基酸索引(PDB文件中) |
| Pred_Score | 预测得到的ASP残基异构化评分,分数值在0-1之间,越大表示异构化的可能性越高 |
| Labile | 最终判别异构化的值,1表示预测发生异构化,0表示预测无异构化 |
The PTM Hotspot by Structure module uses rapid Monte Carlo simulation sampling to obtain diverse protein conformations. By analyzing the solvent exposure and structural fluctuations of multiple conformations, it predicts the probability of aspartic acid (ASP) isomerization.
Protein structure file in PDB format.
The output result file is named result.csv, containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain | Name of the protein chain |
| Residue Index | Amino acid index (in the PDB file) |
| Pred_Score | Predicted score for ASP residue isomerization, with values ranging from 0 to 1; higher values indicate a higher likelihood of isomerization |
| Labile | Final determination of isomerization; 1 indicates predicted isomerization, 0 indicates predicted non-isomerization |

Protein Isoelectric Point(pI),即分子不带净电荷的pH值,是影响分子理化性质甚至功能的关键参数。该模块使用多种不同的算法,基于序列计算分子的pI数值,并可以对多条链的结果进行合并计算。
基于唯信团队使用部分内部抗体实测pI数据的对比,Sillero算法的精度相对更高,推荐采用。
唯信测试用的抗体分子和对应的实测pI数值区间和均值如下图所示。
用不同算法计算的pI数值与实测均值的差值及相关性如下图所示。
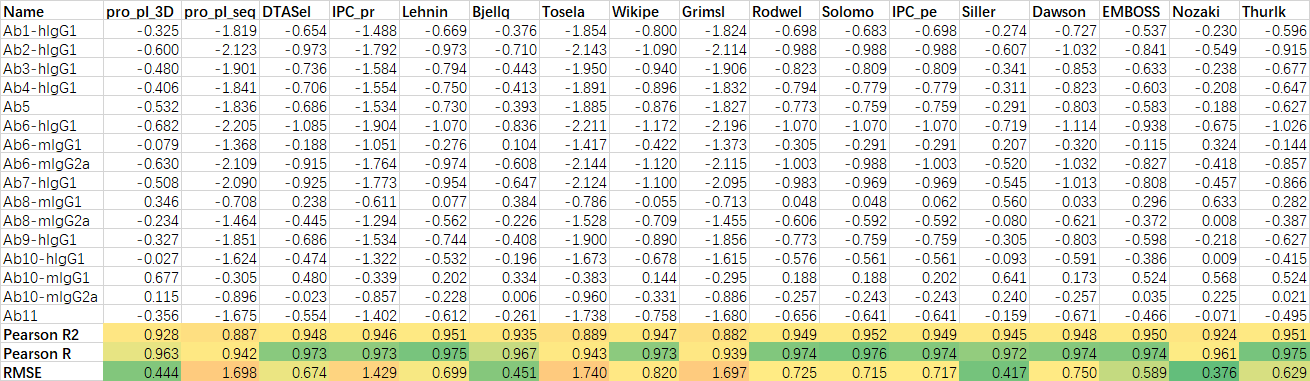
基于R和RMSE等指标,Sillero的相关性略优于其他算法。
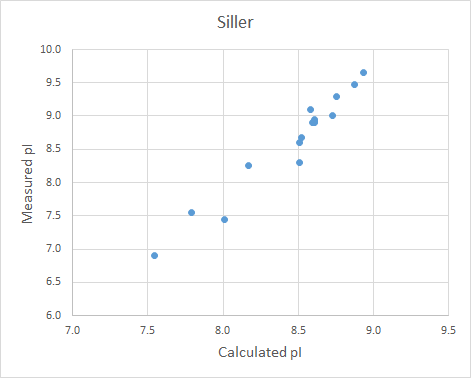
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式。
使用所选模型预测pI的输出文件,默认名称result.csv。
绘制二维散点图,默认False。
二维散点图(分子量与等电点)表示为热图,默认名称result.png。
根据链名,将来自同一序列的多条链的pI值进行合并计算。
例如:mol1.chain1与mol1.chain2将被合并为mol1分子的结果。同名的链也会被视为同一个分子。
仅当merge_chain=True时可用。默认值:merged.csv。
并行任务数,默认为1。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| result.png | 当Plot=True时输出二维散点图(分子量与等电点),热图形式 |
| result.csv | 使用所选模型预测pI的输出文件 |
| merged.csv | 多条链的pI合并输出文件 |
其中result.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein ID | 蛋白序列名称 |
| Molecular weight (Da) | 蛋白分子量 |
| pI | 蛋白等电点 |
Kozlowski LP. IPC - Isoelectric Point Calculator. Biol Direct. 2016 Oct 21;11(1):55.
Protein Isoelectric Point (pI), the pH at which a molecule carries no net charge, is a key parameter that influences the physical and functional properties of a molecule. This module uses various algorithms to calculate the pI value of a molecule based on its sequence and can merge results for multiple chains.
Based on a comparison of experimentally measured pI data from a subset of internal antibodies by the WeiXin team, the Sillero algorithm demonstrates relatively higher accuracy and is recommended for use.
The figure below shows the antibody molecules used in the WeiXin tests along with the corresponding ranges and averages of experimentally measured pI values.
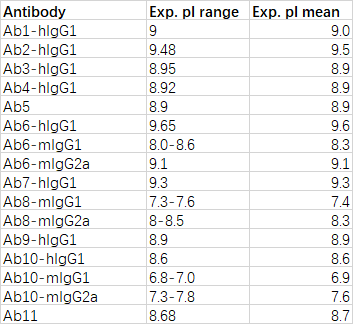
The figure below illustrates the differences and correlations between the pI values calculated using different algorithms and the experimentally measured averages.

Based on metrics such as R and RMSE, the Sillero algorithm shows slightly better correlation compared to other algorithms.

File containing the protein sequence in FASTA format.
Output file for predicted pI values using the selected model, default name is result.csv.
Whether to plot a two-dimensional scatter plot, default is False.
Graphical representation of the two-dimensional scatter plot (molecular weight vs. isoelectric point), default name is result.png.
Merge pI values of multiple chains from the same sequence based on chain names.
For example: mol1.chain1 and mol1.chain2 will be merged into the result for the molecule mol1. Chains with the same name are considered as part of the same molecule.
Available only when merge_chain=True, default value is merged.csv.
Number of parallel tasks, default is 1.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result.png | Output of the two-dimensional scatter plot (molecular weight vs. isoelectric point) if Plot=True, in heatmap format |
| result.csv | Output file for predicted pI values using the selected model |
| merged.csv | Merged output file for pI values of multiple chains |
The result.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein ID | Protein sequence name |
| Molecular weight (Da) | Protein molecular weight |
| pI | Protein isoelectric point |
Kozlowski LP. IPC - Isoelectric Point Calculator. Biol Direct. 2016 Oct 21;11(1):55.

AlphaFold2是目前业界优秀的蛋白质结构预测方法。由Deepmind 团队开发,在2020年的蛋白质结构预测大赛CASP14中, AlphaFold 2 得到了接近90分的成绩,排名第一,大幅度领先第二名,对大部分蛋白质结构的预测与真实结构只差一个原子的宽度,达到了人类利用冷冻电镜等复杂仪器观察预测的水平,这是蛋白质结构预测史无前例的巨大进步。后续更新版本支持复合物结构预测,包括蛋白-多肽复合物的预测。
当前版本:v2.3.2, 是截止于2023年10月的最新版本。
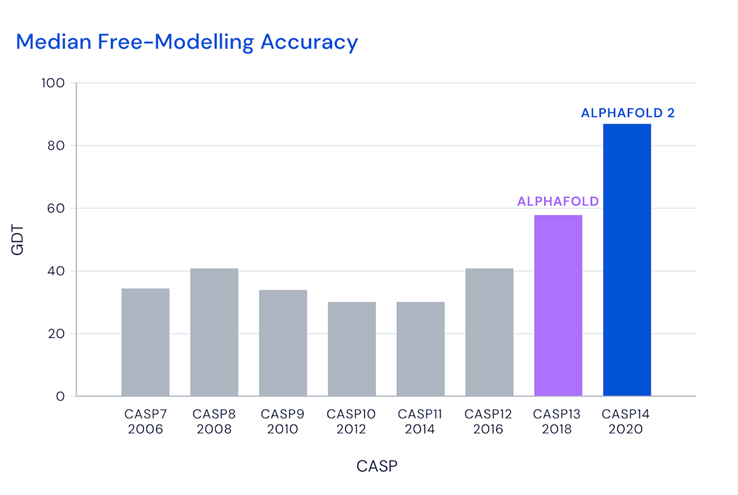
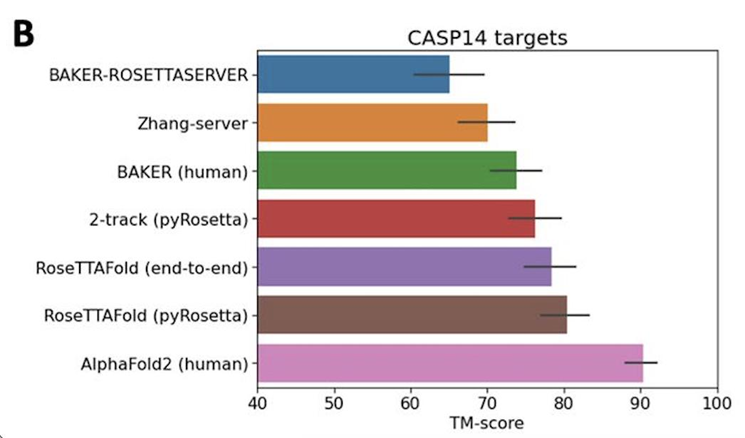
上图:蛋白单体预测精度
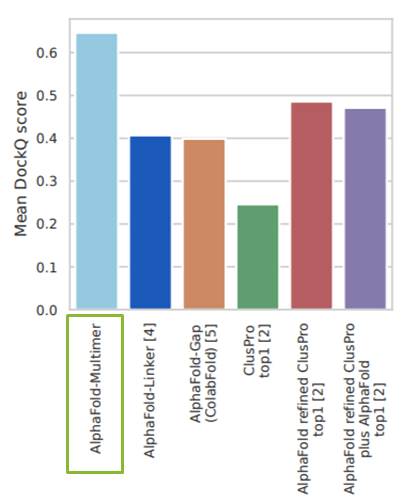
上图:蛋白复合物预测精度
输入序列文件,fasta格式
预测任务类型,monomer 或者 multimer
monomer:单体蛋白,单条链
multimer:复合物,多条链,最大可以6条链,超过6条系统不处理
优化结构模式
all:优化所有的结构
best:只优化打分最高的结构,这个模式只输出一个结构
none:不做优化
多序列比对使用的数据库
full_dbs:全库,更耗时,但相比reduced_db更精确
reduced_dbs:精简库,速度更快,但是牺牲准确性
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ranking_debug.csv | 预测模型可信度评估文件,其中包含用于执行模型排名的pLDDT, ipTM, pTM值,以及到原始模型名称的映射。 |
| ranked_*.pdb | 预测最终蛋白结构文件。默认提供1个打分最高的优化后的结构 |
| PAE_0.csv | 当预测为复合物结构时,生成最优模型的Predicted aligned error(PAE)热图CSV数据。 |
| PAE_Heatmap_0.png | 当预测为复合物结构时,生成最优模型的Predicted aligned error(PAE)热图。 |
| PAE.tar.gz | 当预测为复合物结构时,生成所有模型的Predicted aligned error(PAE)热图。 |
其中评估结构预测可信度指标分为pLDDT和ipTM:
pLDDT > 90:Very high
90 > pLDDT > 70:Confident
70 > pLDDT > 50:Low
pLDDT < 50:Very low
model confidence = 0.8 · ipTM + 0.2 · pTM,值范围是0-1,该值越大说明预测的复合物结构越可靠。
ipTM >= 0.80:High quality
0.6 <= ipTM < 0.80:Acceptable quality
0.00 <= ipTM < 0.6:Incorrect
对结构准确性分析应该综合考虑所有指标,包括pTM、ipTM、pLDDT 和 PAE。
AlphaFold2 is currently the best protein structure prediction method in the industry. Developed by the DeepMind team, in the 2020 CASP14 protein structure prediction competition, AlphaFold 2 achieved a score close to 90, ranking first and significantly outperforming the second-place competitor. It predicted the structures of most proteins within the width of a single atom from the ground truth, reaching a level comparable to human observation using complex instruments like cryo-electron microscopy. This represents an unprecedented advancement in protein structure prediction. Subsequent updates support the prediction of complex structures, including protein-peptide complexes.
Current Version: v2.3.2, the latest version as of October 2023.



Above: Protein monomer prediction accuracy

Above: Protein complex prediction accuracy
Input sequence file in FASTA format.
Prediction task type, either monomer or multimer.
monomer: Single protein, single chain.
multimer: Complex, multiple chains, with a maximum of 6 chains. Systems with more than 6 chains are not processed.
Structure optimization mode.
all: Optimize all structures.
best: Optimize only the highest-scoring structure; this mode outputs only one structure.
none: No optimization.
Database used for multiple sequence alignment.
full_dbs: Full database, more time-consuming but more accurate compared to reduced_db.
reduced_dbs: Reduced database, faster but sacrifices accuracy.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ranking_debug.csv | Confidence evaluation file of the prediction model, containing pLDDT, ipTM, pTM values used for model ranking and mapping to the original model names. |
| ranked_*.pdb | Final predicted protein structure files. By default, the optimized highest-scoring structure is provided. |
| PAE_0.csv | For complex structure predictions, generates a Predicted Aligned Error (PAE) heatmap CSV data for the best model. |
| PAE_Heatmap_0.png | For complex structure predictions, generates a Predicted Aligned Error (PAE) heatmap for the best model. |
| PAE.tar.gz | For complex structure predictions, generates PAE heatmaps for all models. |
The confidence metrics for structure prediction include pLDDT and DockQ:
pLDDT > 90: Very high
90 > pLDDT > 70: Confident
70 > pLDDT > 50: Low
pLDDT < 50: Very low
model confidence = 0.8 · ipTM + 0.2 · pTM. The value ranges from 0 to 1, with higher values indicating a more reliable predicted complex structure.
ipTM >= 0.80: High quality
0.6 <= ipTM < 0.80: Acceptable quality
0.00 <= ipTM < 0.6: Incorrect

粘度是影响抗体药物开发的重要因素,临床上抗体往往需要静脉内或皮下给药,需要高浓度的抗体溶液(>100mg/mL)才能以小剂量注射获得与治疗相关的剂量,但是高浓度的抗体往往表现出高粘度,这对抗体药物的开发,制造和给药提出了挑战。研究发现,抗体序列是决定抗体粘度的关键因素,文献报道抗体粘度与Fv区域的电荷、VH和VL区域电荷的不对称性FvCSP和Fv区域的疏水指数HI存在相关性,基于抗体序列预测抗体粘度是一个有效方法。
本模块集成了两种粘度预测方法:Sharma 与 DeepViscosity
Sharma 粘度计算方法如下所示:
η,cP(180 mg/mL,25°C)=10^[0.15+1.26(0.60)∗ϕ−0.043(0.047)∗q−0.020(0.015)∗qsym
其中,ϕ代表Fv区域的疏水指数HI,q代表Fv电荷,qsym代表VH和VL区域电荷的不对称性FvCSP。
DeepViscosity模型是一个集成了102个人工神经网络模型的集成学习系统。该模型利用从抗体序列(特别是Fv区)提取的30种特征,对单抗进行粘度分类。分类标准基于150mg/mL浓度下的粘度值,区分低粘度(≤20 cP)和高粘度(>20 cP)的抗体。使用了包含 229 种不同单抗及其在150mg/mL浓度下实验测定粘度值的大型数据集来训练 DeepViscosity。该数据集是目前该领域公开报道的最大的同类数据集,为模型的稳健性提供了坚实基础。 在两个独立的测试集上进行的评估结果显示,DeepViscosity 表现出色。该模型在这两个测试集上分别达到了 87.5% 和 89.5% 的粘度分类准确率,其性能显著超越了以往依赖实验数据或复杂计算模拟的预测模型。
抗体的序列文件,FASTA格式,支持批量抗体,不支持纳米抗体序列。按顺序放置每个抗体的序列(重、轻链先后顺序没有要求,序列名称都使用抗体名称,如不一致,会采用重链序列名称作为抗体名称),示例如下:
> 抗体A
重链序列XXXXXX
> 抗体A
轻链序列XXXXXX
> 抗体B
轻链序列XXXXXX
> 抗体B
轻链序列XXXXXX
输出结果文件,默认为vis_pred_res_SM.csv
抗体的序列文件,FASTA格式(格式要求同Sharma模式)
输出结果文件,默认为vis_pred_res_DV.csv
Sharma算法输出vis_pred_res_SM.csv文件,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Sequence ID | 抗体序列名称 |
| Fv Heavy Chain Charge | 重链电荷 |
| Fv Light Chain Charge | 轻链电荷 |
| Fv Charge Symmetry Parameter | 电荷对称性指标 |
| Fv Hydrophobicity Index | 疏水性指数 |
| Viscosity | 抗体粘度 |
DeepViscosity算法输出vis_pred_res_DV.csv文件,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Sequence ID | 抗体序列名称 |
| Viscosity Type | 预测的抗体粘度类别,0表示低粘度(≤20 cP),1表示高粘度(>20 cP) |
| Probability | 预测的概率值,数值在0-1之间,大于0.5时Viscosity Type为1,反之为0 |
Viscosity is an important factor affecting the development of antibody drugs. Clinically, antibodies often need to be administered intravenously or subcutaneously, requiring a high concentration of antibody solution (>100mg/mL) to obtain a therapeutic dose at a small dose. However, high concentrations of antibodies often exhibit high viscosity, which poses a challenge to the development, manufacture and administration of antibody drugs. It has been found that antibody sequence is the key factor to determine antibody viscosity. It has been reported that antibody viscosity is correlated with charge in Fv region, charge asymmetry in VH and VL region, FvCSP, and hydrophobic index HI in Fv region. It is an effective method to predict antibody viscosity based on antibody sequence.
This module integrates two viscosity prediction methods: Sharma and DeepViscosity.
Sharma method:
η,cP(180 mg/mL,25°C)=10^[0.15+1.26(0.60)∗ϕ−0.043(0.047)∗q−0.020(0.015)∗qsym
Among them, ϕ represents the hydrophobic index (HI) of the Fv region, q represents the charge of the Fv region, and qsym represents the asymmetry of the charge in the VH and VL regions (FvCSP).
The DeepViscosity model is an ensemble learning system that incorporates 102 artificial neural network models. It uses 30 features extracted from antibody sequences (especially the Fv region) to classify monoclonal antibodies based on their viscosity. The classification criterion is based on the viscosity value at a concentration of 150 mg/mL, distinguishing between low viscosity (≤20 cP) and high viscosity (>20 cP) antibodies. The model was trained using a large dataset containing 229 different monoclonal antibodies and their experimentally measured viscosity values at a concentration of 150 mg/mL. This dataset is the largest of its kind reported in the field to date, providing a solid foundation for the robustness of the model. Evaluation results on two independent test sets show that DeepViscosity performs remarkably well. The model achieved viscosity classification accuracies of 87.5% and 89.5% on the two test sets, respectively, significantly outperforming previous prediction models that relied on experimental data or complex computational simulations.
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format. Supports multiple antibodies, but does not support nanobody sequences. Place the sequences of each antibody in order (The order of the heavy and light chains is not required. The sequence names should all use the antibody name. If there is inconsistency, the name of the heavy chain sequence will be used as the antibody name.), as shown in the example below.:
> Antibody A
XXXXXX(Heavy chain)
> Antibody A
XXXXXX(Light chain)
> Antibody B
XXXXXX(Light chain)
> Antibody B
XXXXXX(Heavy chain)
The output result file, default name is vis_pred_res_SM.csv
The sequence file of the antibody, in FASTA format (the format requirements are the same as those in Sharma mode)
The output result file, default name is vis_pred_res_DV.csv
A result.csv file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Sequence ID | Antibody sequence name |
| Fv Heavy Chain Charge | Fv heavy chain charge |
| Fv Light Chain Charge | Fv light chain charge |
| Fv Charge Symmetry Parameter | Fv charge symmetry index |
| Fv Hydrophobicity Index | Fv hydrophobicity index |
| Viscosity | Antibody viscosity |
The output file of the DeepViscosity algorithm is named vis_pred_res_DV.csv, which contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Sequence ID | Name of the antibody sequence |
| Viscosity Type | Predicted viscosity category of the antibody. 0 indicates low viscosity (≤20 cP), and 1 indicates high viscosity (>20 cP) |
| Probability | The predicted probability value ranges between 0 and 1. When it is greater than 0.5, the Viscosity Type is 1; otherwise, it is 0. |

Molecular Docking (DiffDock)是一种扩散生成模型,主要用于小分子和蛋白对接。DiffDock在PDBBind上获得了38%的top-1成功率(RMSD<2A),大大超过了以前传统对接(23%)和深度学习(20%)方法的最先进水平。此外,以前的方法无法对接计算上的折叠结构(最大精度为10.4%),而DiffDock保持了明显更高的精度(21.7%)。最后,DiffDock具有快速的推理时间,并提供具有高选择性精度的置信度估计值。
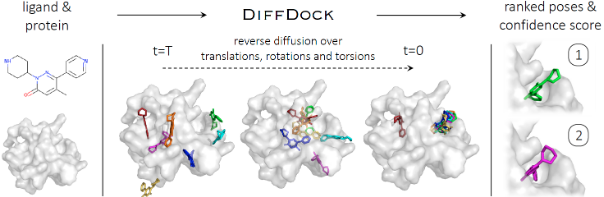
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式。最多支持1022个氨基酸。
小分子结构文件,SDF格式
每个配体与受体对接时得到的构象数,默认为10。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Scores.csv | 所有配体(≤2000)与受体的打分文件。 |
| output_ligand.sdf | 对接后所有配体SDF文件。 |
| output_complex_topn.tar.gz | TopN小分子中每个配体与受体打分最高的复合物构象PDB文件压缩包。 |
| display_complex.pdb | 展示配体与受体的复合物构象文件。 |
其中Scores.csv包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Ligand ID | 配体编号ID |
| Confidence | 对接置信度打分,虽然解读和比较不同复合物或不同蛋白质构象的置信度分数可能会很困难,可以通过以下标准粗略比较(c是最佳构象的置信度分数):c > 0高置信度;-1.5 < c < 0中等置信度;c < -1.5低置信度 |
| Complex File Name | 复合物名称 |
Molecular Docking (DiffDock) is a diffusion-based model primarily used for the docking of small molecules with proteins. DiffDock has achieved a top-1 success rate of 38% (RMSD < 2A) on PDBBind, significantly surpassing the state-of-the-art levels of previous traditional docking methods (23%) and deep learning methods (20%). Furthermore, previous methods were unable to dock computationally folded structures (maximum accuracy of 10.4%), while DiffDock maintains significantly higher accuracy (21.7%). Finally, DiffDock features fast inference times and provides confidence estimates with high selectivity accuracy.

Structure file of the protein in PDB format. Supports up to 1022 amino acids.
Structure file of the small molecule in SDF format.
The number of conformations obtained for each ligand docked with the receptor, default is 10.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Scores.csv | Scoring file for all ligands (≤2000) with the receptor. |
| output_ligand.sdf | SDF file containing all ligands after docking. |
| output_complex_topn.tar.gz | Compressed file containing the PDB files of the top scoring complex conformations for each ligand among the TopN small molecules. |
| display_complex.pdb | File displaying the complex conformation of the ligand and receptor. |
The Scores.csv contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Ligand ID | Ligand identification ID. |
| Confidence | Docking confidence score. Although interpreting and comparing confidence scores of different complexes or different protein conformations can be challenging, a rough comparison can be made using the following criteria (c is the confidence score of the top pose): c > 0 indicates high confidence; -1.5 < c < 0 indicates moderate confidence; c < -1.5 indicates low confidence. |
| Complex File Name | Name of the complex. |
Synthetic Accessibility Score是一个化合物合成可行性评估指标,反映了化合物是否容易合成。其将小分子合成难易程度用1到10区间数值进行评价,越靠近1表明越容易合成,越靠近10表明合成越困难。SA Score基于片段贡献和复杂度惩罚从而评估化合物合成的难易程度,其中片段贡献值根据PubChem数据库中上百万分子计算共性进行计算,复杂度则考虑分子中非标准结构特征的占比,例如大环、非标准环的合并、立体异构和分子量大小等方面。SA Score方法已被验证,通过将40个化合物分别采用SA Score和经验丰富的药物化学家评估其合成难易程度,并且比较得到二者评分的相关性R2高达0.89,表明其在识别可合成难易程度上的可靠性较高。SA Score已成为一种普遍使用的指标,可用于预测新化合物的合成可行性,加速化合物筛选和药物发现过程。

小分子结构文件,支持SDF和SMILES格式。
小分子结构,SMILES格式,支持多个小分子,一行一个SMILES,例如:
CSC1=C(c2ccc©s2)/C(=N/C©©C)C1
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CN3CCN(CC3)C)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CC=C5
输出结果文件为sa_score.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| smiles | 小分子smiles结构 |
| Name | 小分子名称 |
| sa_score | 化合物合成可行性评估指标数值 |
The Synthetic Accessibility Score is an indicator of the feasibility of synthesizing a compound, reflecting how easily a compound can be synthesized. It evaluates the difficulty of synthesizing small molecules on a scale of 1 to 10, with values closer to 1 indicating easier synthesis and values closer to 10 indicating more challenging synthesis. The SA Score assesses the ease of compound synthesis based on fragment contributions and complexity penalties. The fragment contribution values are calculated based on the commonality of millions of molecules in the PubChem database, while complexity considers the proportion of non-standard structural features in the molecule, such as macrocycles, fused non-standard rings, stereoisomers, molecular weight, and other aspects. The SA Score method has been validated by comparing the SA Scores with evaluations of synthesis difficulty by experienced medicinal chemists for 40 compounds. The high correlation coefficient (R2 = 0.89) between the two sets of scores demonstrates the reliability of the SA Score in identifying the feasibility of synthesis. The SA Score has become a widely used metric for predicting the synthetic feasibility of new compounds, accelerating compound screening and drug discovery processes.

Small molecule structure file in SDF or SMILES format.
SMILES format of small molecule structures, supports multiple small molecules with one SMILES string per line, for example:
CSC1=C(c2ccc©s2)/C(=N/C©©C)C1
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CN3CCN(CC3)C)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CC=C5
The output file is sa_score.csv, containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| smiles | SMILES structure of the small molecule |
| Name | Name of the small molecule |
| sa_score | Synthetic Accessibility Score value for the compound |
Proteotypic Cleavage Site Predictor模块基于深度学习,用于预测8种常用蛋白酶(trypsin, ArgC, chymotrypsin, GluC, LysC, AspN, LysN, and LysargiNase)的蛋白型裂解位点。它整合了卷积神经网络和长短时记忆网络,以实现高准确性和稳健性。与传统的机器学习算法(逻辑回归、随机森林和支持向量机)相比,对所有8种蛋白酶都有更准确的预测精度。
以下是八种常用蛋白酶的蛋白型裂解位点预测:
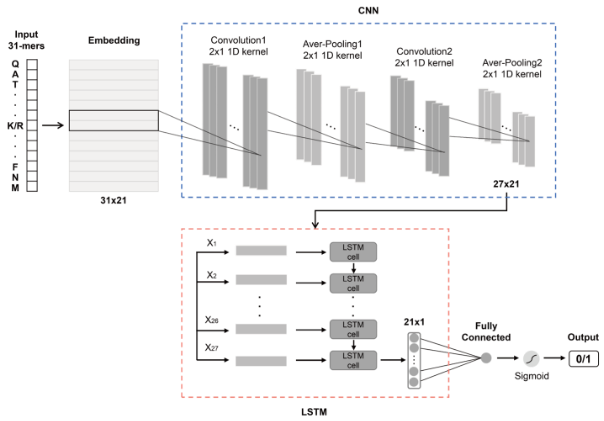
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式
输出对应8个蛋白酶的csv文件,每个csv文件包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein id | 蛋白名称 |
| Peptide sequence | 蛋白的理论酶切肽段 |
| Digestibility of the N-terminal site | N端肽键的裂解概率预测值 |
| Digestibility of the C-terminal site | C端肽键的裂解概率预测值 |
| Digestibility of the missed site(s) | 理论酶切肽段所有漏切(非N/C端)位点的酶切概率预测值 |
*注:概率值区间为0-1,越接近1表示发生概率越大。
Proteotypic Cleavage Site Predictor module is based on deep learning. Used to predict the protein-type cleavage sites of eight common proteases (trypsin, ArgC, chymotrypsin, GluC, LysC, AspN, LysN, and LysargiNase). It integrates convolutional neural network and short - and long-term memory network to achieve high accuracy and robustness. Compared with traditional machine learning algorithms (logistic regression, random forest and support vector machine), the prediction accuracy of all eight proteases was more accurate.
The following are protein-type cleavage site predictions for eight common proteases:
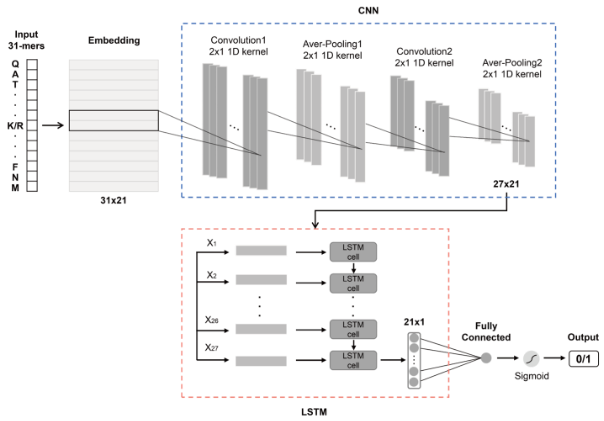
Protein sequence file in FASTA format
The output csv file is corresponding to the 8 proteases. Each csv file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein id | The identity of the protein from which the peptide is digested. |
| Peptide sequence | The sequence of the theoretical digested peptide. |
| Digestibility of the N-terminal site | The predicted cleavage probability of the cleavage site on the N-terminal of the peptide. |
| Digestibility of the C-terminal site | The predicted cleavage probability of the cleavage site on the C-terminal of the peptide. |
| Digestibility of the missed site(s) | The predicted cleavage probabilities of the missed cleavage sites in the peptide. |

通过基于扩散概率模型,在蛋白质结构去噪任务上对RoseTTAFold结构预测网络进行微调,得到该蛋白质骨架生成模型,在无条件和拓扑约束的蛋白质单体设计、蛋白质结合物设计、对称低聚物设计、酶活性位点支架以及治疗性和金属结合蛋白设计的对称主题支架上取得了出色的性能。RFdiffusion能够从简单的分子规格中设计出多样的、复合的、功能性的蛋白质。
模块功能为多场景蛋白设计,如:Motif Scaffolding,Unconditional protein generation,Symmetric unconditional generation (cyclic, dihedral and tetrahedral symmetries),Symmetric motif scaffolding,Binder design,Design diversification (“partial diffusion”)
设计时的参考蛋白。
设计类型,支持2种类型:‘Motif_Scaffold’与’Binder’,分别说明如下:
‘Motif_Scaffold’ 表示基于参考蛋白的骨架结构(由后续参数定义),进行设计。
‘Binder’ 表示基于受体结构进行其Binder蛋白设计。
定义蛋白的设计策略,指定蛋白中的哪部分被随机设计、保留等。
如:该参数设置为 ‘5-15/A10-25/30-40/0 B1-100’ 时,
●’5-15’表示先设计长度为5到15之间(具体多长是随机的,如果要固定长度为10,可以设置为10-10)的motif
●‘/A10-25’表示紧接着从参考蛋白中取A链中编号为10至25的氨基酸,其N端连接到上一段’5-15’设计的motif的C端
●’/30-40’表示紧接着设计长度为30到40之间(具体多长是随机的)的motif,其N端连接到前面已经设计的motif的C端
●‘/0 ’表示链断开,前一条链结束,后续设计会是新的链,注意0后有一个空格!
●‘B1-100’表示从参考蛋白中取B链中编号为1至100的氨基酸,作为新的一条链
注意:
指定设计的结构数量。
在binder模式下可以指定受体中的热点残基,格式为"链名称",“氨基酸残基”,如:‘A59,A83,A91’。
设计对称蛋白,参数值为C_N或D_N,其中C表示循环对称(Cyclic symmetry),D表示二面体对称(Dihedral symmetry),N表示单体的数量。如:C2表示设计包含2个单体的循环对称蛋白。
注意:在进行对称蛋白设计时,Contigs参数的设置要与之匹配,如:Symmetry为C2时,Contigs参数的设置应该符合两条链。
设计时的参考蛋白。
为后续参数(Receptor, Initial Binder, Hotspot)中定义的氨基酸残基的索引设置类别。
有两种选择:UID或者POS,UID表示PDB文件中自带的残基编号,该编号可能存在间断不连续,不从1开始等情况;POS表示位置编号或自然顺序编号,从1开始按顺序进行编号。
该参数的默认值为UID。
定义受体蛋白,从参考蛋白中选定哪部分作为受体蛋白,格式为“链名称+残基编号或范围”,多段残基用逗号分隔。例如:参数设置为A1-50,A70-100,A105,A108,B1-108时,表示:
选取参考蛋白的A链中残基编号为1至50、70至100、105与108的残基,以及B链位置编号1至108的残基作为受体。
注意:这里输入的残基编号应与参数Index Type中的编号类别一致。
定义Binder蛋白的长度,可以是确定的长度,或长度范围,例如:设置为20或20-50时,
20表示Binder蛋白的长度为20个残基;
20-50表示Binder蛋白的长度范围为20至50个残基,具体长度视最终设计结果为准。
指定设计的结构数量(当前支持最大100)。
指定结构中初始的Binder,从参考蛋白中选定哪部分是初始的Binder蛋白,模型会在不改变初始Binder的前提下,进一步延长Binder。例如:参数设置为B1-10时,表示:
指定参考蛋白中的B链残基编号为1至10的残基为初始Binder蛋白,模型会以此为基础进行延长设计。
指定受体中的热点残基作为binder蛋白的结合位置,格式为“链名称+残基编号或范围”,多段残基用逗号分隔,例如:A59-61,A83,A91,表示:
指定A链编号为59至61、83及91的残基为binder蛋白的结合位置。
设计时的参考蛋白。
为后续参数(Design Range)中定义的氨基酸残基的索引设置类别。
有两种选择:UID或者POS,UID表示PDB文件中自带的残基编号,该编号可能存在间断不连续,不从1开始等情况;POS表示位置编号或自然顺序编号,从1开始按顺序进行编号。
该参数的默认值为UID。
定义需要设计的蛋白骨架范围,从参考蛋白中选定哪部分进行设计,格式为“链名称+残基编号或范围”,多段残基用逗号分隔。例如:参数设置为A1-50,A70-100,A105,A108,B1-108时,表示:
选取参考蛋白的A链中残基编号为1至50、70至100、105与108的残基,以及B链编号1至108的残基进行骨架优化设计。
注意:这里输入的残基编号应与参数Index Type中的编号类别一致。
指定设计的结构数量(当前支持最大100)。
为参数Design Range中的每段残基,定义其设计的长度,多个长度用逗号分隔。如不设置该参数,表示按Design Range中的原始长度进行设计。
注意:长度的数量要与上述Range参数中残基段的数量一致,且顺序对应。长度可以有多种不同的取值:
N,表示该段残基区域设计时,长度不变。5-10,表示该段残基设计时,长度在5-10个残基的范围内变化,具体长度看最终设计结果。N,5-10,15表示定义了3个长度(对应的Design Range参数中的残基段应该也是3个),第1段残基设计时保持长度不变,第2段残基设计时的长度范围为5-10,第3段残基设计时的长度为15。其他设计模式,可选为Fix,表示固定上述定义的Design Range不变,对结构中的所有其他区域进行设计。
当其他设计模式设置为Fix时,会对其他区域进行设计,设计时会在其他区域的原长度基础上做长度变动,该参数即为长度变动的大小,默认为5,即在原长度的基础上减少或增加5个残基。
不同设计模式的输出pdb文件。
注意:
By fine-tuning the RoseTTAFold structure prediction network on protein structure denoising tasks using diffusion probability models, this protein backbone generation model achieves excellent performance in unconditional and topology-constrained protein monomer design, protein binder design, symmetric oligomer design, enzyme active site scaffolding, and therapeutic and metal-binding protein symmetric theme scaffolding. RFdiffusion can design diverse, complex, and functional proteins from simple molecular specifications. The module functions for multi-scenario protein design include: Motif Scaffolding, Unconditional protein generation, Symmetric unconditional generation (cyclic, dihedral, and tetrahedral symmetries), Symmetric motif scaffolding, Binder design, and Design diversification (“partial diffusion”).
The reference protein for design.
Design type, supporting two types: ‘Motif_Scaffold’ and ‘Binder’, explained as follows:
Defines the protein design strategy, specifying which parts of the protein are randomly designed, retained, etc.
For example, if this parameter is set to ‘5-15/A10-25/30-40/0 B1-100’:
Note:
Specifies the number of structures to design.
In binder mode, hotspot residues in the receptor can be specified, formatted as “chain name,” “amino acid residue,” e.g., ‘A59,A83,A91’.
Design symmetric proteins with parameter values C_N or D_N, where C indicates cyclic symmetry, D indicates dihedral symmetry, and N indicates the number of monomers. For example, C2 designs a cyclic symmetric protein with 2 monomers.
Note: When designing symmetric proteins, the Contigs parameter settings should match, e.g., if Symmetry is C2, the Contigs parameter should correspond to two chains.
The reference protein for design.
Sets the index type for amino acid residues defined in subsequent parameters (Receptor, Initial Binder, Hotspot). Two options are available: UID or POS. UID refers to the residue numbers provided in the PDB file, which may be discontinuous or not start from 1. POS refers to position numbering or natural sequential numbering starting from 1. The default value is UID.
Defines the receptor protein, selecting which parts from the reference protein serve as the receptor, formatted as “chain name + residue number or range,” separated by commas for multiple segments. For example, if the parameter is set to A1-50,A70-100,A105,A108,B1-108, it means:
Select residues numbered 1 to 50, 70 to 100, 105, and 108 from chain A, and residues numbered 1 to 108 from chain B of the reference protein as the receptor.
Note: The residue numbers entered here should match the index type specified in Index Type.
Defines the length of the Binder protein, which can be a specific length or a range. For example, setting it to 20 or 20-50 means:
20 specifies the Binder protein length as 20 residues;
20-50 specifies the Binder protein length range as 20 to 50 residues, with the exact length determined by the final design.
Specifies the number of structures to design (currently supports up to 100).
Specifies the initial Binder structure, selecting which parts from the reference protein are the initial Binder protein, with the model extending the Binder without changing the initial Binder. For example, if the parameter is set to B1-10, it means:
Specify residues numbered 1 to 10 from chain B of the reference protein as the initial Binder protein, and the model will extend the design based on this.
Specify hotspot residues in the receptor as binder protein binding sites, formatted as “chain name + residue number or range,” separated by commas for multiple segments. For example, A59-61,A83,A91 means:
Specify residues numbered 59 to 61, 83, and 91 in chain A as binder protein binding sites.
The reference protein for design.
Sets the index type for amino acid residues defined in subsequent parameters (Design Range). Two options are available: UID or POS. UID refers to the residue numbers provided in the PDB file, which may be discontinuous or not start from 1. POS refers to position numbering or natural sequential numbering starting from 1. The default value is UID.
Defines the protein backbone range to design, selecting which parts from the reference protein to optimize, formatted as “chain name + residue number or range,” separated by commas for multiple segments. For example, if the parameter is set to A1-50,A70-100,A105,A108,B1-108, it means:
Select residues numbered 1 to 50, 70 to 100, 105, and 108 from chain A, and residues numbered 1 to 108 from chain B of the reference protein for backbone optimization design.
Note: The residue numbers entered here should match the index type specified in Index Type.
Specifies the number of structures to design (currently supports up to 100).
Defines the design length for each segment in the Design Range parameter, with multiple lengths separated by commas. If this parameter is not set, the design length will follow the original length in the Design Range. Note: The number of lengths must match the number of residue segments in the Range parameter, and the order must correspond. Length can have various values:
N, indicating the segment length remains unchanged during design.5-10, indicating the segment design length varies between 5 and 10 residues, with the exact length determined by the final design.N,5-10,15 defines three lengths (the corresponding Design Range parameter should also have three segments), with the first segment design length unchanged, the second segment design length ranging from 5 to 10, and the third segment design length as 15.Other design modes, with an option for Fix, indicating the defined Design Range remains unchanged, while all other areas are designed.
When the other design mode is set to Fix, other areas will be designed, with length changes based on the original length. This parameter specifies the magnitude of length change, defaulting to 5, meaning the length is increased or decreased by 5 residues based on the original length.
Output PDB files for different design modes.
Note:

对上传的蛋白Fasta序列分析其蛋白的理化性质,包括分子质量、等电点、消光系数、不稳定系数、蛋白质的芳香值、总平均亲水性以及二级结构占比。
输入的蛋白FASTA文件,格式:FASTA。
输出文件名称,必须为CSV后缀。
是否合并来自同一蛋白质链的信息。
仅当merge_chain=True时可用。默认值:merged.csv。
并行任务数,默认为1。
指定计算净电荷(net charge)的pH值
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| result.csv | 序列名称和蛋白质的信息一一对应的CSV文件 |
| merged.csv | 合并来自同一蛋白质链的信息的CSV文件 |
其中result.csv和merged.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Sequence ID | 蛋白序列名称 |
| Molecular Weight | 蛋白序列分子量 |
| Isoelectric Point | 蛋白序列等电点 |
| Molar Extinction Coefficient (without disulfide bond) | 假设半胱氨酸被还原时的摩尔消光系数,单位为M-1·cm-1。 |
| Extinction Coefficient (without disulfide bond) | 假设半胱氨酸被还原时的消光系数,单位为g·L-1。 |
| Molar Extinction Coefficient (with disulfide bond) | 假设成对半胱氨酸形成的二硫键的摩尔消光系数,单位为M-1·cm-1。 |
| Extinction Coefficient (with disulfide bond) | 假设成对半胱氨酸形成的二硫键的消光系数,单位为g·L-1。 |
| Instability Index | 蛋白的不稳定指数,当该数值高于40时都表示蛋白质不稳定(半衰期很短)。 |
| Aromaticity | 蛋白质的芳香值,即为Phe+Trp+Tyr的相对频率。 |
| Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) | 总平均亲水性,若此数值为负值则说明该蛋白为亲水性蛋白,反之为疏水性蛋白。 |
| Helix Fraction | 计算Helix结构在蛋白上所占比例。Helix中的氨基酸:V,I,Y,F,W,L。 |
| Turn Fraction | 计算Trun结构在蛋白上所占比例。Trun中氨基酸顺序为:N,P,G,S。 |
| Sheet Fraction | 计算Sheet结构在蛋白上所占比例。Sheet中氨基酸:E,M,A,L。 |
| Net Charge | 蛋白序列在特定pH值下的净电荷,采用Biopython中的电荷计算功能函数进行计算 |
This module analyzes the physicochemical properties of a protein based on the uploaded protein FASTA sequence. The properties include molecular weight, isoelectric point, molar extinction coefficient, instability index, aromaticity, total average hydrophobicity, and secondary structure composition.
Input protein FASTA file in FASTA format.
Name of the output file, must have a CSV extension.
Whether to merge information from the same protein chain.
Only available when merge_chain=True. Default value: merged.csv.
Number of parallel tasks, default is 1.
Specifies the pH value for calculating the net charge
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result.csv | CSV file mapping sequence names to protein information |
| merged.csv | CSV file containing merged information from the same protein chain |
Both result.csv and merged.csv contain the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Sequence ID | Protein sequence name |
| Molecular Weight | Molecular weight of the protein sequence |
| Isoelectric Point | Isoelectric point of the protein sequence |
| Molar Extinction Coefficient (without disulfide bond) | Molar extinction coefficient assuming cysteine is reduced, in M-1·cm-1 |
| Extinction Coefficient (without disulfide bond) | Extinction coefficient assuming cysteine is reduced, in g·L-1 |
| Molar Extinction Coefficient (with disulfide bond) | Molar extinction coefficient assuming disulfide bonds of paired cysteines, in M-1·cm-1 |
| Extinction Coefficient (with disulfide bond) | Extinction coefficient assuming disulfide bonds of paired cysteines, in g·L-1 |
| Instability Index | Instability index of the protein, values above 40 indicate protein instability (short half-life) |
| Aromaticity | Aromaticity of the protein, relative frequency of Phe+Trp+Tyr |
| Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY) | GRAVY value indicating the overall hydrophobicity of the protein, negative values indicate hydrophilic proteins |
| Helix Fraction | Fraction of helical structure in the protein, amino acids considered: V, I, Y, F, W, L |
| Turn Fraction | Fraction of turn structure in the protein, amino acids considered: N, P, G, S |
| Sheet Fraction | Fraction of sheet structure in the protein, amino acids considered: E, M, A, L |
| Net Charge | The net charge of a protein sequence at a specific pH, calculated by functions in Biopython |

Receptor-based Peptide Design模块是进行基于受体结构(目前支持单链)的结合多肽设计。该模块算法是基于AlphaFold2与Colabdesign实现。
PDB格式的受体结构。
设定肽binder的长度,如:10。
指定PDB文件中作为受体的链,如:“B”,如果结构中只有一条链,可以不用指定。
注意:目前仅支持单链模式,且链的长度不超过500个氨基酸。
指定受体中的热点残基,如:‘1-10,12,15’
指定多肽binder的起始序列,如设定,则会在此序列的基础上继续设计。
如果已有多肽binder在参数1的PDB文件中,指定该多肽为哪条链,可以此为基础进行多肽binder的优化设计。
默认False,是否使用Alphafold-Multimer进行设计
是否设定受体的骨架为柔性。
指定输出的结构评分文件名称,默认为“design_scores.csv”
输出5个肽binder设计的PDB文件:result_0~4.pdb,为受体中选择的链结构与设计肽的复合物。5个设计结果为5次平行设计的不同结果。
输出结构的评分指标:design_scores.csv,包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Name | 预测结构的文件名 |
| pLDDT | 局部结构的可信度指标,值范围是0-1.0,该值越大说明预测的结构越可靠。低于0.7被认为可靠性较低,低于0.5基本认为是可信度非常低,为无序预测 |
| pTM | 预测的TM分数(the predicted template modeling score),衡量预测结构整体准确性,越大表示越准确,该分数大于0.5时,表示结构整体折叠可能与真实结构相似 |
| ipTM | 预测的亚基接触面的TM分数(the interface predicted template modeling score),当预测结构为复合物时才有该评价指标,衡量复合物中各个亚基之间相对位置的预测准确性,越大表示越准确,大于0.8表示高质量预测,小于0.6表示预测可能失败,0.6-0.8为灰色地带,预测正确与否不确定 |
The Receptor-Based Peptide Design module is used for designing binding peptides based on receptor structures (currently supporting single-chain structures). The algorithm of this module is implemented based on AlphaFold2 and Colabdesign.
The receptor structure in PDB format.
Specifies the length of the peptide binder, e.g., 10.
Specifies the chain in the PDB file to be used as the receptor, e.g., “B”. If the structure contains only one chain, this parameter may not need to be specified. Note: Currently, only single-chain mode is supported, and the chain length should not exceed 500 amino acids.
Specifies the hotspot residues in the receptor, e.g., ‘1-10,12,15’.
Specifies the starting sequence of the peptide binder. If provided, the design will be based on this sequence.
If a peptide binder already exists in the PDB file specified in parameter 1, this parameter specifies which chain the peptide belongs to, allowing optimization and design based on this peptide.
Default is False. Specifies whether to use AlphaFold-Multimer for design.
Specifies whether to set the receptor backbone as flexible.
the output scoring file, default is “design_scores.csv”
The output file is result.pdb, which contains the structure of the designed peptide binder. The resultpdb is a complex of the selected chain structure from the receptor and the designed peptide.
The design_scores.csv file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | The file name of the predicted structure. |
| pLDDT | The confidence score for local structure, with a range of 0-100. A higher value indicates a more reliable prediction. Values below 70 are considered low reliability, below 50 are generally regarded as very low confidence, indicating disordered predictions. |
| pTM | The predicted template modeling score, which measures the overall accuracy of the predicted structure. A higher score indicates greater accuracy. If the score is greater than 0.5, it suggests that the overall folding of the structure may be similar to the true structure. |
| ipTM | The interface predicted template modeling score, which measures the accuracy of the predicted relative positions of the subunits in the complex. A higher score indicates greater accuracy. Scores above 0.8 indicate high-quality predictions, while scores below 0.6 suggest potential failure of the prediction. Scores between 0.6 and 0.8 are in a gray area, where the accuracy of the prediction is uncertain. |

Antibody Paratope Predictor模块的功能是预测抗体上与抗原结合的氨基酸位点,称为Paratope。其算法是基于等变图神经网络的深度学习模型,使用抗体结构进行训练和预测,预测精度在现有方法中最佳。

需要预测的抗体结构,链名称必须为H, L, H/L才能判断为抗体结构。
输出文件为result.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| pdb | 文件名 |
| chain_type | 抗体链类型 |
| chain_id | 抗体链标识 |
| IMGT | 抗体氨基酸对应的IMGT编号 |
| AA | 抗体氨基酸名称 |
| atom_num | 抗体氨基酸的Alpha碳原子的原子编号(PDB文件中)。 |
| x,y,z | 抗体氨基酸的Alpha碳原子的坐标。 |
| pred | 该氨基酸为Paratope的预测概率(取值范围0-1),参考值为0.734,大于参考值时,为Paratope的可能性高,值越大可能性越高。 |
The Antibody Paratope Predictor module aims to predict the amino acid residues on an antibody that bind to antigens, known as the Paratope. The algorithm is based on a deep learning model using a variant of graph neural networks, trained and tested on antibody structures. It achieves the highest prediction accuracy among existing methods.

The antibody structure for which the paratope needs to be predicted. The chain names must be H, L, or H/L to be recognized as an antibody structure.
The output file is result.csv, containing the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| pdb | File name |
| chain_type | Antibody chain type |
| chain_id | Antibody chain identifier |
| IMGT | IMGT number corresponding to the antibody amino acid |
| AA | Antibody amino acid name |
| atom_num | Atom number of the alpha carbon of the antibody amino acid in the PDB file |
| x, y, z | Coordinates of the alpha carbon of the antibody amino acid |
| pred | Predicted probability that the amino acid is part of the Paratope (range 0-1). A reference value of 0.734 is provided; a value greater than this indicates a high likelihood of being part of the Paratope, with higher values indicating higher likelihood. |
Lewis Chinery, Newton Wahome, Iain Moal, Charlotte M. Deane. Paragraph - Antibody Paratope prediction using Graph Neural Networks with minimal feature vectors. bioRxiv 2022.06.10.495640. Link

基于扩散概率模型和等价神经网络,进行抗体设计,可针对特定抗原结构生成抗体,也可基于抗体-抗原复合物结构进行抗体结构和序列的优化。
抗体是免疫系统的蛋白质,通过与特定的抗原(如病毒和细菌)结合来保护宿主。抗体和抗原之间的结合主要是由抗体的互补性决定区域(CDR)决定的。该模块是基于扩散概率模型和等价神经网络的深度生成模型,对CDR的序列和结构共同建模。该方法可明确针对特定抗原结构生成抗体,是最早的蛋白质结构扩散概率模型之一。能进行序列-结构协同设计、给定骨架结构的序列设计和抗体优化。
抗体-抗原复合物结构文件,PDB格式
设计模式选择,对于抗原-抗体复合物有4种设计模式可选:
只有在指定Optimize设计模式后,才需要选择改参数,默认值为H_CDR3,一共有6个选项:H_CDR1、H_CDR2、H_CDR3、L_CDR1、L_CDR2、L_CDR3。
1.输出一个结构优化后或构建后的压缩包result.tar.gz。
2.展示不同设计模式的第一个结构优化结果,输出结果分别如下:
(1) 'Optimize’模式,输出输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| H_CDR1-O1_0000.pdb | O1表示优化次数为1,对应的优化程度很低,序列变化很小 |
| H_CDR1-O2_0000.pdb | O2表示优化次数为2,优化程度低,序列变化小 |
| H_CDR1-O4_0000.pdb | 优化次数为4,优化程度较低,序列变化较小 |
| H_CDR1-O8_0000.pdb | 优化次数为8,优化程度一般,序列变化一般 |
| H_CDR1-O16_0000.pdb | 优化次数为16,优化程度较高,序列变化较大 |
| H_CDR1-O32_0000.pdb | 优化次数为32,优化程度高,序列变化大 |
| H_CDR1-O64_0000.pdb | 优化次数为64,优化程度很高,序列变化很大 |
(2) ‘Fixbb’ 模式,输出输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| H_CDR1_0000.pdb | 重链CDR1区优化的结构文件 |
| H_CDR2_0000.pdb | 重链CDR2区优化的结构文件 |
| H_CDR3_0000.pdb | 重链CDR3区优化的结构文件 |
| L_CDR1_0000.pdb | 轻链CDR1区优化的结构文件 |
| L_CDR2_0000.pdb | 轻链CDR2区优化的结构文件 |
| L_CDR3_0000.pdb | 轻链CDR3区优化的结构文件 |
(3) ‘Sample_one_CDR’模式,输出文件名称与’Fixbb’ 模式相同。
(4) 'Sample_multi_CDRs’模式,输出CDR区进行优化后的结构文件"MultipleCDRs_0000.pdb"。
Antibody design is conducted based on diffusion probability models and equivalent neural networks, allowing for the generation of antibodies targeting specific antigen structures and optimization of antibody structures and sequences based on antibody-antigen complex structures.
Antibodies are proteins of the immune system that protect the host by binding to specific antigens such as viruses and bacteria. The binding between antibodies and antigens is primarily determined by the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) of the antibodies. This module is a deep generative model based on diffusion probability models and equivalent neural networks, jointly modeling the sequences and structures of CDRs. This method can explicitly generate antibodies targeting specific antigen structures and is one of the earliest protein structure diffusion probability models. It enables sequence-structure co-design, sequence design with given scaffold structures, and antibody optimization.

Structure file of the antibody-antigen complex in PDB format.
Design mode selection for the antigen-antibody complex with four available options:
This parameter is only required when selecting the Optimize design mode, with a default value of H_CDR3. There are a total of six options: H_CDR1, H_CDR2, H_CDR3, L_CDR1, L_CDR2, L_CDR3.
Outputs a compressed file, result.tar.gz, containing the optimized or constructed structure.
Displays the first structure optimization results for different design modes as follows:
(1)For the Optimize mode, the output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| H_CDR1-O1_0000.pdb | O1 indicates optimization at 1, with low optimization level and minimal sequence changes |
| H_CDR1-O2_0000.pdb | O2 indicates optimization at 2, with low optimization level and small sequence changes |
| H_CDR1-O4_0000.pdb | Optimization at 4, with relatively low optimization level and moderate sequence changes |
| H_CDR1-O8_0000.pdb | Optimization at 8, with moderate optimization level and average sequence changes |
| H_CDR1-O16_0000.pdb | Optimization at 16, with relatively high optimization level and significant sequence changes |
| H_CDR1-O32_0000.pdb | Optimization at 32, with high optimization level and substantial sequence changes |
| H_CDR1-O64_0000.pdb | Optimization at 64, with very high optimization level and extensive sequence changes |
(2)For the Fixbb mode, the output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| H_CDR1_0000.pdb | Structure file optimized for the heavy chain CDR1 region |
| H_CDR2_0000.pdb | Structure file optimized for the heavy chain CDR2 region |
| H_CDR3_0000.pdb | Structure file optimized for the heavy chain CDR3 region |
| L_CDR1_0000.pdb | Structure file optimized for the light chain CDR1 region |
| L_CDR2_0000.pdb | Structure file optimized for the light chain CDR2 region |
| L_CDR3_0000.pdb | Structure file optimized for the light chain CDR3 region |
(3)For the Sample_one_CDR mode, the output file names are the same as the Fixbb mode.
(4)For the Sample_multi_CDRs mode, the output is the structure file “MultipleCDRs_0000.pdb” after optimizing the CDR regions.

提交GROMACS对应文件,从而进行分子动力学模拟,得到平衡模拟后得到的轨迹文件。
提交模拟体系的gro文件。该文件可以从MD Solvation或者Membrane Solvation模块获取。
提交模拟体系的top文件。该文件可以从MD Solvation或者Membrane Solvation模块获取。
提交模拟体系的itp文件。该文件可以从MD Solvation或者Membrane Solvation模块获取。
提交进行最小化的参数化文件,文件格式为mdp。可以根据GMX MDP Generation模块的Minimization方法或者**GMX MDP Generation (Auto)**生成。
提交进行等压等温的参数化文件,文件格式为mdp。可以根据GMX MDP Generation模块的NPT方法或者**GMX MDP Generation (Auto)**生成。
提交进行平衡模拟的参数化文件,文件格式为mdp。可以根据GMX MDP Generation模块的MD方法或者**GMX MDP Generation (Auto)**生成。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| md.cpt | md模拟断点文件 |
| md.gro | md的分子坐标文件 |
| md.log | md记录文件 |
| md.tpr | md模拟所需的所有初始化数据(分子拓扑、初始结构等) |
| mini.gro | mini运行的分子坐标文件 |
| mini.log | mini运行记录文件 |
| mini.tpr | mini模拟运行所需的所有初始化数据(分子拓扑、初始结构等) |
| npt.gro | npt的分子坐标文件 |
| npt.log | npt记录文件 |
| npt.tpr | npt模拟所需的所有初始化数据(分子拓扑、初始结构等) |
| path.txt | 模拟轨迹文件存储路径,可用于后续分析模块的Path File输入。 |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
Submit corresponding files to GROMACS to perform molecular dynamics simulations and obtain trajectory files after equilibrium simulations.
Submit the gro file of the simulated system. This file can be obtained from the MD Solvation or Membrane Solvation modules.
Submit the top file of the simulated system. This file can be obtained from the MD Solvation or Membrane Solvation modules.
Submit the itp file of the simulated system. This file can be obtained from the MD Solvation or Membrane Solvation modules.
Submit the script file for minimization, in mdp format. This file can be generated using the GMX MDP Generation module with the Minimization method or GMX MDP Generation (Auto).
Submit the script file for NPT (isothermal-isobaric) simulation, in mdp format. This file can be generated using the GMX MDP Generation module with the NPT method or GMX MDP Generation (Auto).
Submit the script file for equilibrium simulation, in mdp format. This file can be generated using the GMX MDP Generation module with the MD method or GMX MDP Generation (Auto).
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| md.cpt | Checkpoint file for the MD simulation |
| md.gro | Molecular coordinate file for the MD simulation |
| md.log | Log file for the MD simulation |
| md.tpr | All initial data required for the MD simulation (molecular topology, initial structure, etc.) |
| mini.gro | Molecular coordinate file for the minimization run |
| mini.log | Log file for the minimization run |
| mini.tpr | All initial data required for the minimization run (molecular topology, initial structure, etc.) |
| npt.gro | Molecular coordinate file for the NPT simulation |
| npt.log | Log file for the NPT simulation |
| npt.tpr | All initial data required for the NPT simulation (molecular topology, initial structure, etc.) |
| path.txt | Path to store the simulation trajectory files, which can be used as input for the Path File in subsequent analysis modules. |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.

SDF File Split是个化合物库文件分割模块,可以将一个大的SDF文件分割为多个SDF文件,支持按文件个数或者分子数目分割,使得分割后的每个SD文件分子数目接近。
小分子库结构文件,SDF格式
生成文件的数目
新生成SDF文件的前缀,默认subset,生成的文件名为:subset1.sdf,subset2.sdf,以此类推。
小分子库结构文件,SDF格式
每个新生成的SD文件包含的分子数目
新生成SDF文件的前缀,默认subset,生成的文件名为:subset1.sdf,subset2.sdf,以此类推。
拆分后的SDF文件列表文件。
SDF File Split is a compound library file splitting module that can divide a large SDF file into multiple SDF files. It supports splitting based on the number of files or the number of compounds, ensuring that the number of molecules in each split SDF file is similar.
Structure file of the small molecule library, in SDF format.
Number of files to generate.
Prefix for the newly generated SDF files, default is “subset”. The generated files will be named as: subset1.sdf, subset2.sdf, and so on.
Structure file of the small molecule library, in SDF format.
Number of compounds to include in each newly generated SDF file.
Prefix for the newly generated SDF files, default is “subset”. The generated files will be named as: subset1.sdf, subset2.sdf, and so on.
List of split SDF files.

Enumerate Stereoisomers是枚举小分子立体异构体的工具,支持顺反异构体和对映异构体两种形式的枚举。立体异构(stereoisomerism)是在有相同分子式的化合物分子中,原子或原子团互相连接的次序相同,但在空间的排列方式不同,与构造异构同属有机化学范畴中的同分异构现象。对所有或未分配的手性原子和键周围的分子进行立体异构体的组合枚举。
小分子结构文件,支持SMILES、MOL、SDF格式。
指定输出文件的名称,支持SDF(.sd)和SMILES格式(.smi)。
枚举模式,包括如下:
UnassignedOnly:只枚举未分配手性原子和键的分子的构型异构体。所有原子和键都分配手性时,选择该选项得到该分子本身。
All:枚举所有立体异构体,包括构型异构和构象异构。
每个分子产生异构体的最大数目。
小分子的smiles字符串,一行一个分子
得到小分子构型异构体的组合SDF文件generated_isomers.sdf。
Enumerate Stereoisomers is a tool for enumerating stereoisomers of small molecules, supporting both cis-trans isomers and enantiomers. Stereoisomerism refers to the phenomenon in organic chemistry where compounds with the same molecular formula have atoms or groups connected in the same order but arranged differently in space, belonging to the category of structural isomerism. It enumerates stereoisomeric combinations for all or unassigned chiral atoms and bonds in a molecule.
The small molecule structure file, supporting SMILES, MOL, and SDF formats.
Specify the name of the output file, supporting SDF (.sd) and SMILES (.smi) formats.
Enumeration modes include:
Maximum number of isomers to generate for each molecule.
SMILES string of the small molecule, one molecule per line.
Obtain a combined SDF file (generated_isomers.sdf) of conformational isomers of small molecules.

SDF Viewer是小分子化合物库的可视化模块,可以针对一个SDF文件生成一个结构和属性可视、可交互、可检索的HTML页面,方便浏览化合物的结构和属性信息。
小分子结构文件,SDF格式
输出HTML文件名,默认为library.html
针对SDF文件生成一个结构和属性可视、可交互、可检索的HTML页面library.html。
The SDF Viewer is a visualization module for small molecule compound libraries. It generates an HTML page that visualizes and makes the structures and properties of compounds in an SDF file interactive and searchable, facilitating the browsing of compound structure and property information.
The small molecule structure file in SDF format.
The output HTML file name, defaulting to library.html.
Generates an interactive and searchable HTML page (library.html) that visualizes the structures and properties of compounds in the SDF file.

HADDOCK v3.0 是一个自下而上的对长期以来被证实的HADDOCK的重新构想,用于生物分子复合物的综合建模。旨在对HADDOCK的核心功能进行模块化和扩展。它能够充分利用模糊的相互作用约束(AIRs)来驱动对接过程。使用蛋白质-蛋白质对接基准5对它进行了评估,并与实时版本(v2.4)进行了比较。该评估是使用每个复合物的真实界面(3.9 Å)进行的,并以成功率表示;在按HADDOCK-score排名的特定解决方案子集中,至少有一个对接解决方案低于指定阈值的BM5目标数量。
用于进行对接的抗体PDB文件,当前仅支持普通双链抗体(需要含有重、轻链)
用于进行对接的抗原PDB文件
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| score.csv | 复合物构象的对接能量打分文件 |
| result.tar.gz | 所有复合物构象PDB文件压缩包 |
| cluster_01_model.pdb-cluster_10_model.pdb | 打分前十的复合物构象 |
其中score.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| RANK | 打分排序 |
| Score | 对接能量打分,其中打分值越低,结合能力越强。 |
HADDOCK v3.0 is a bottom-up reimagining of the well-established HADDOCK for comprehensive modeling of biomolecular complexes. It aims to modularize and extend the core functionalities of HADDOCK, leveraging ambiguous interaction restraints (AIRs) to drive the docking process. It has been evaluated against five protein-protein docking benchmarks and compared to the real-time version (v2.4). The evaluation was conducted using the true interfaces (3.9 Å) of each complex and represented in terms of success rates; in a specific subset of solutions ranked by HADDOCK-score, a minimum number of BM5 targets have at least one docking solution below a specified threshold.
PDB file of the antibody used for docking. Currently, only normal antibodies (which must contain both heavy and light chains) are supported.
PDB file of the antigen used for docking.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| score.csv | Docking energy scoring file for complex conformations. |
| result.tar.gz | Compressed archive of all complex conformation PDB files. |
| cluster_01_model.pdb-cluster_10_model.pdb | Top ten complex conformation models before scoring. |
In score.csv, the information is as follows:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| RANK | Ranking based on scoring. |
| Score | Docking energy score, where lower scores indicate stronger binding capability. |

基于AfCycDesign算法,利用ColabDesign与AlphaFold2等技术,基于模板分子结构骨架的环肽设计,或进行全新环肽设计。测试表明,这种方法能够准确地预测来自单一序列的原生环状肽的结构,在49个案例中,有36个被预测为高置信度的环状肽,pLDDT>0.85,与原生结构相匹配,均方根偏差(RMSD)小于1.5 Å。

本模块存在两种模式FixBB与Hallucination,其中前者表示进行基于模板蛋白(环肽)结构骨架的环肽设计;后者表示进行全新的环肽设计,不参考模板骨架,可设置环肽长度。
。
上传模板蛋白(环肽)结构。注意,环肽长度不能超过100个氨基酸。
指定模板蛋白中用于参考设计的蛋白链标识,如:“B”,如果结构中只有一条链,可以不用指定。
指定设计时固定模板蛋白中的某些位置的氨基酸不变化,如:‘1,5-10’ 将固定模板蛋白中的第1和5至10的氨基酸不变。
指定全新设计的环肽长度,如:20.
指定设计时需要去除的氨基酸类型,如:“C,W”表示设计的环肽不会出现cysteine和Tryptophan。
设计的环肽的三维结构文件result.pdb。
The Cyclic Peptide Design module utilizes the AfCycDesign algorithm in conjunction with technologies such as ColabDesign and AlphaFold2 to design cyclic peptides based on the structural backbone of template molecules or to create entirely new cyclic peptide designs. Tests have shown that this method can accurately predict the structures of native cyclic peptides from a single sequence. Out of 49 cases, 36 were predicted as high-confidence cyclic peptides with pLDDT > 0.85, matching the native structures with a root mean square deviation (RMSD) of less than 1.5 Å.

This module has two modes: FixBB and Hallucination. The former involves designing cyclic peptides based on the template protein (cyclic peptide) structure, while the latter involves designing entirely new cyclic peptides without reference to a template backbone and allows for setting the length of the cyclic peptide.
Upload the template protein (cyclic peptide) structure. Note that the length of the cyclic peptide cannot exceed 100 amino acids.
Specify the protein chain identifier used for reference design in the template protein, e.g., “B”. If there is only one chain in the structure, this can be left unspecified.
Specify the amino acids in the template protein that should remain fixed during design, e.g., ‘1,5-10’ will fix amino acids at positions 1 and 5 to 10 in the template protein.
Specify the length of the newly designed cyclic peptide, e.g., 20.
Specify the types of amino acids to be removed during design, e.g., “C,W” indicates that the designed cyclic peptide will not contain cysteine and tryptophan.
The three-dimensional structure file of the designed cyclic peptide is stored in result.pdb.

基于深度学习技术预测氨基酸突变对蛋白质-蛋白质相互作用的影响。该模块是基于开源的GeoPPI方法开发的,使用蛋白质复合物的深度几何表征来模拟突变对结合亲和力的影响。为了实现几何结构的强大表达能力和预测的稳健性,模块依次采用了两个组件,即一个几何编码器(擅长提取图形特征)和一个梯度增强树(GBT,擅长避免过度拟合)。几何编码器是一个图形神经网络,在相邻的原子上执行神经信息传递,以更新中心原子的表征。它通过一个新的自我监督学习方案进行训练,以产生蛋白质结构的深度几何表示。基于这些对复合物及其突变体的学习表征,GBT从突变数据中学习,以预测相应的结合亲和力变化。
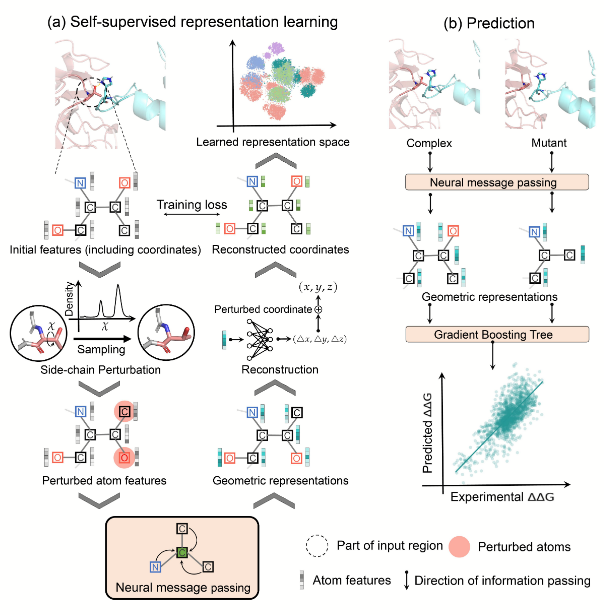
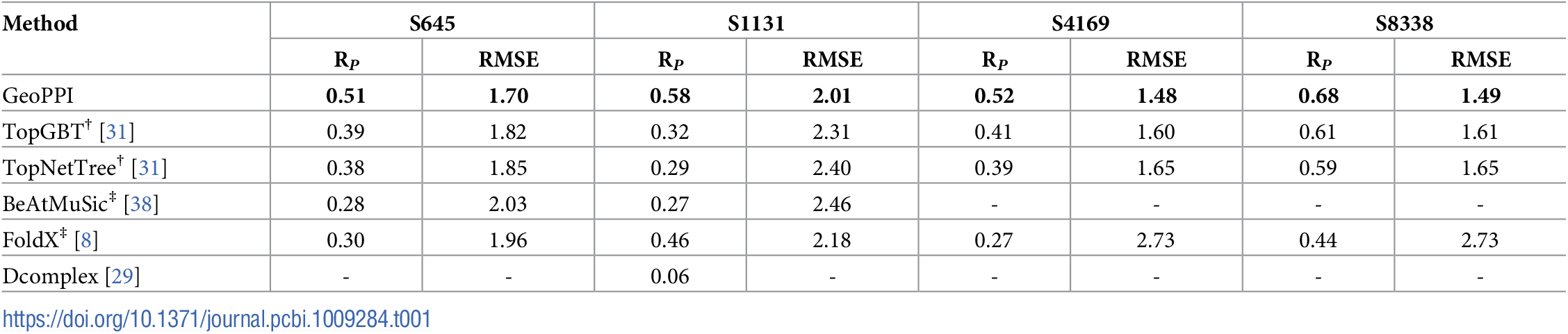
野生型的复合物结构,PDB格式。
突变列表文件,TXT格式,每行包含突变信息,格式如下:
TI17R,EI19R;E_I
AI15R;E_I
每行突变信息及一个相互作用链信息,用分号“;”分隔,其中:
TI17R中的T表示野生型的氨基酸,I表示该氨基酸所在的链,17表示结构文件中该氨基酸的序号,R表示突变后的氨基酸。当存在多点突变时,突变信息用逗号(“,”)隔开,如TI17R,EI19R。E_I表示复合物中产生相互作用的蛋白链是E链与I链;相应的,如果是多条链与多条链产生相互作用,如:HL_WV,表示H、L链与W、V链产生相互作用。
需要注意的时突变信息可以时多点或者单点,但是每一行的相互作用链信息只能是一个。
输出结果文件为score.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Mutation | 突变位点 |
| Chain | 突变点所在的链 |
| Interaction_Chains | 相互作用之间的链名称 |
| deltaEnergy | 该突变引起的结合能量的变化(wildtype-mutant),值越小说明突变后结合越弱,该突变位点对受配体之间结合越重要,单位为kcal/mol。 |
Copyright © 2021 LiuXianggen
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
The Mutation Energy of Binding (GeoPPI) module predicts the effect of amino acid mutations on protein-protein interactions using deep learning techniques. Developed based on the open-source GeoPPI method, this module utilizes deep geometric representations of protein complexes to simulate the impact of mutations on binding affinity. To achieve robust prediction capabilities and powerful geometric structure representations, the module sequentially employs two components: a geometric encoder (proficient at extracting graphical features) and a Gradient Boosting Tree (GBT, adept at preventing overfitting). The geometric encoder is a graph neural network that performs neural message passing on neighboring atoms to update the representation of central atoms. It is trained using a novel self-supervised learning scheme to generate deep geometric representations of protein structures. Based on these learned representations of complexes and their mutants, the GBT learns from mutation data to predict corresponding changes in binding affinity.


The structure of the wild-type complex in PDB format.
A file listing mutations in TXT format, with each line containing mutation information in the following format:
TI17R,EI19R;E_I
AI15R;E_I
Each line contains mutation information and interaction chain information separated by a semicolon “;”. In the mutation information:
It is important to note that mutation information can be single-point or multi-point mutations, but the interaction chain information per line should be only one.
The output result file is score.csv, which includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Mutation | The mutation site |
| Chain | The chain where the mutation occurs |
| Interaction_Chains | Names of the interacting chains |
| deltaEnergy | The change in binding energy caused by the mutation (wildtype-mutant). A smaller value indicates weaker binding after the mutation, highlighting the importance of the mutation site for the binding between the ligand and receptor, in kcal/mol. |
Copyright © 2021 LiuXianggen
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the “Software”), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED “AS IS”, WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.

ProGen是一种语言模型,可以在大型蛋白质家族中生成具有可预测功能的蛋白质序列,类似于在不同主题上生成语法和语义正确的自然语言句子。该模型基于来自> 19,000个家族的2.8亿个蛋白质序列进行训练,并增加了指定蛋白质属性的控制标签。基于Progen2模型实现,ProGen2模型可扩展到64亿个参数,并在不同的序列数据集上进行训练,这些数据集来自基因组、元基因组和免疫剧目数据库的10亿多个蛋白质。ProGen2模型在捕捉观察到的进化序列的分布、产生新的可行的序列,并预测蛋白质的适应性等方面显示出最先进的性能。
Protein Sequence Generation (ProGen)目前主要功能是基于Reference序列,进行序列的增长(从Reference序列末端开始增长),后续开放其他场景的序列生成功能。
模型类型有2种可选(progen2-large,progen2-xlarge)。
模型信息:
progen2-large,参数数量2.7 Billion,神经网络层数32。
progen2-xlarge,模型参数数量6.4 Billion,神经网络层数32。
作为参考的序列(填序列信息)
注意:不支持多条序列,多条序列会被合并为一条序列。
生成序列的数目。
注意:序列长度不超过1024个氨基酸。
生成的蛋白序列文件result.fasta。
ProGen is a language model designed to generate protein sequences with predictable functions within large protein families, similar to generating syntactically and semantically correct natural language sentences on different topics. The model is trained on 280 million protein sequences from over 19,000 families and incorporates control labels specifying protein attributes. Built upon the Progen2 model, ProGen2 can scale up to 6.4 billion parameters and is trained on over a billion proteins from various sequence datasets sourced from genomes, metagenomes, and immune repertoire databases. ProGen2 demonstrates state-of-the-art performance in capturing the distribution of observed evolutionary sequences, generating novel feasible sequences, and predicting protein adaptability.
Currently, the main function of Protein Sequence Generation (ProGen) is to extend sequences based on a reference sequence (growing from the end of the reference sequence). Additional sequence generation functionalities for other scenarios will be made available in the future.
There are two model options available: progen2-large and progen2-xlarge.
Model details:
The reference sequence for sequence extension (provide sequence information).
Note: Multiple sequences are not supported; multiple sequences will be merged into one sequence.
The number of sequences to generate.
Note: The sequence length should not exceed 1024 amino acids.
The generated protein sequence file is named result.fasta.

Peptide Structure Generation模块只需要输入多肽序列字符或者文件,就能生成多肽的三维或者二维结构的SDF文件。
输入氨基酸序列,每行表示一条多肽,支持同时生成多条多肽。
输出文件名称。
输出多肽结构类型:3d或者2d。
输入氨基酸序列txt文件,与“Peptide Sequence”相同。
其他参数与Peptide Sequence模式相同。
得到多肽三维结构的SDF文件output.sdf。
Sud M. MayaChemTools: An Open Source Package for Computational Drug Discovery. J Chem Inf Model. 2016 Dec 27;56(12):2292-2297.
O’Boyle NM, Banck M, James CA, Morley C, Vandermeersch T, Hutchison GR. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J Cheminform. 2011 Oct 7;3:33.
The Peptide Structure Generation module can generate three-dimensional or two-dimensional structures of peptides in SDF format based on input peptide sequences.
Input amino acid sequences, with each line representing a peptide. Multiple peptides can be generated simultaneously.
Output file name.
Specify the type of peptide structure to generate: 3D or 2D.
Input a text file containing amino acid sequences, similar to the “Peptide Sequence” mode.
Other parameters are the same as in the Peptide Sequence mode.
The output is an SDF file named output.sdf containing the three-dimensional structure of the peptide.
Sud M. MayaChemTools: An Open Source Package for Computational Drug Discovery. J Chem Inf Model. 2016 Dec 27;56(12):2292-2297.
O’Boyle NM, Banck M, James CA, Morley C, Vandermeersch T, Hutchison GR. Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox. J Cheminform. 2011 Oct 7;3:33.

根据OAS数据库中的抗体序列训练的语言模型,可预测抗体序列中指定位点可能的氨基酸,或者修复抗体序列数据中缺失残基,在抗体序列预测中优于通用蛋白质语言模型如Meta开发的ESM-1b模型。
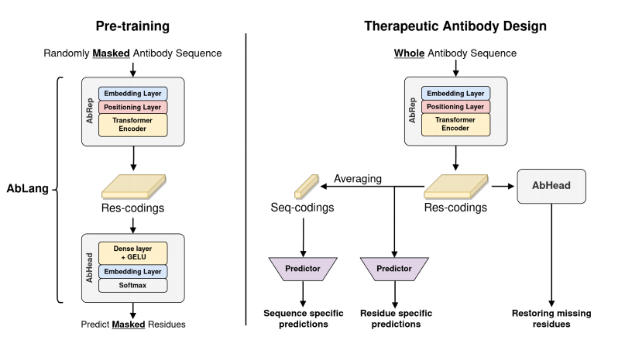
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式。使用*表示需要修复区域,支持多条序列。抗体序列文件如下所示:
>H
EV*LVESG*GLVQPGKSLRLSCVASGFTFSGYGMH
指定抗体序列是重链还是轻链,值为"H" 或 “L”。
预测概率最高的一条抗体序列,其文件为result.fasta。
The Antibody Sequence Prediction module utilizes a language model trained on antibody sequences from the OAS database to predict the likely amino acids at specified positions in antibody sequences or to fill in missing residues in antibody sequence data. This model outperforms general protein language models like the ESM-1b model developed by Meta in antibody sequence prediction.

Antibody sequence file in FASTA format. Use “*” to indicate regions that need to be filled in, and multiple sequences are supported. An example of an antibody sequence file is shown below:
>H
EV*LVESG*GLVQPGKSLRLSCVASGFTFSGYGMH
Specify whether the antibody sequence is heavy chain (“H”) or light chain (“L”).
The predicted antibody sequence with the highest probability is saved in the file result.fasta.
Structure Clustering是基于分子指纹的小分子结构聚类模块,其采用的聚类方法有Butina或任何其他可用的分层聚类方法。
小分子的结构文件,支持SDF、SMILES格式。
输出文件名称。
在分层聚类过程中生成的聚类的数目。
Butina聚类算法中使用的相似度截断值。
聚类算法,包括如下:
用于计算相似度或者距离的分子指纹类型,包括如下:
分子指纹方式,包括如下:
相似度计算指标,包括如下:
在原有SDF文件中加入聚类编号,得到新的SDF文件output.sdf。
Structure Clustering is a module for clustering small molecule structures based on molecular fingerprints. It employs clustering methods such as Butina or any other available hierarchical clustering method.
The structure file of the small molecule, supported formats include SDF and SMILES.
Name of the output file.
Number of clusters generated during the hierarchical clustering process.
Similarity cutoff value used in the Butina clustering algorithm.
Clustering algorithms available include:
Types of molecular fingerprints used for similarity or distance calculation include:
Types of molecular fingerprint representations include:
Similarity metrics for calculation include:
The original SDF file will be updated with cluster numbers, resulting in a new SDF file named output.sdf.

Sequence Clustering使用DBSCAN算法对多序列比对(MSA)后的结果进行聚类分析,将多序列分为多个cluster类别,并通过可视化模块UMAP进行序列的embedding,并获取二维可视化信息。
需要聚类序列的多序列比对结果文件(fasta格式),可以由Multiple Sequence Alignmnet模块产生的alignmnet.fasta。
输出结果文件为res_clustering_assignments.tsv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SequenceName | 序列名称 |
| sequence | 序列 |
| frac_gaps | 后续序列与参考序列(第一条序列)氨基酸差异(填充‘-’)的比例 |
| dbscan_label | 聚类后的类别标签(如果值为-1表示未分配类别) |
| UMAP 1,UMAP 2 | 二维可视化坐标信息(UMAP 1,UMAP 2对应X,Y坐标) |
Sequence Clustering uses the DBSCAN algorithm to perform cluster analysis on the results of multiple sequence alignment (MSA), dividing multiple sequences into different cluster categories. It utilizes the UMAP visualization module to embed sequences and obtain two-dimensional visualization information.

The file containing the results of multiple sequence alignment (in FASTA format) that need to be clustered. This file can be generated by the Multiple Sequence Alignment module as alignmnet.fasta.
The output result file is res_clustering_assignments.tsv, which includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SequenceName | Name of the sequence |
| sequence | The sequence itself |
| frac_gaps | Proportion of gaps (‘-’) in the sequence compared to the reference sequence (the first sequence) |
| dbscan_label | Cluster label after clustering (if the value is -1, it means the sequence is unassigned to any cluster) |
| UMAP 1, UMAP 2 | Two-dimensional visualization coordinate information (UMAP 1 corresponds to the X-coordinate and UMAP 2 corresponds to the Y-coordinate) |

Extract Sequence from Structure (PDB2FASTA)模块是从蛋白的PDB文件中将序列提取出来保存为FASTA文件。常规氨基酸序列用单字母表示,其他类型都标注为X。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式。
将指定链的序列转存为fasta格式,默认all代表将所有链的序列输出。
输出序列文件名称,FASTA格式。
得到蛋白的序列文件,默认为seq.fasta。
The Extract Sequence from Structure (PDB2FASTA) module extracts sequences from a protein’s PDB file and saves them as a FASTA file. Conventional amino acid sequences are represented by single letters, while other types are labeled as X.
The protein’s structure file in PDB format.
Specify the chain whose sequence will be saved in FASTA format. Use “all” to output sequences from all chains by default.
Name of the output sequence file in FASTA format.
Obtain the protein sequence file, default name is seq.fasta.

把三字母表示的氨基酸转换为单字母表示。"ASP ILE VAL ASN"转换为 “DIVQ”.
包含三字符氨基酸序列的文本文件
指定输出序列文件的名称,FASTA格式
三字符代表的氨基酸序列,例如:
ASP ILE VAL ASN
指定输出序列文件的名称,FASTA格式
三字母表示的氨基酸转换为单字母,并以序列FASTA格式输出sequence.fasta。
Converts three-letter amino acid representations to single-letter representations. For example, “ASP ILE VAL ASN” is converted to “DIVQ”.
Text file containing sequences of three-character amino acids.
Specify the name of the output sequence file in FASTA format.
Sequence of three-character amino acids, for example:
ASP ILE VAL ASN
Specify the name of the output sequence file in FASTA format.
Converts three-letter amino acid representations to single-letter representations and outputs the sequence in FASTA format as sequence.fasta.

Sequence Translation是DNA序列转换成RNA序列和蛋白序列的工具。
DNA序列文件,FASTA格式
DNA序列,例如:
TTATGACGTTATTCTACTTTGATTGTGCGAGACAATGCTACCTTACCGGTCGGAACTCGATCGGTTGAACTCTATCACGCCTGGTCTTCGAAGTTAGCAC
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| prepared_dna.fasta | 转换成DNA的FASTA文件 |
| protein.fasta | 转换成蛋白的FASTA文件 |
| mrna.fasta | 转换成mRNA的FASTA文件 |
Sequence Translation is a tool for converting DNA sequences into RNA sequences and protein sequences.
DNA sequence file in FASTA format.
DNA sequence, for example:
TTATGACGTTATTCTACTTTGATTGTGCGAGACAATGCTACCTTACCGGTCGGAACTCGATCGGTTGAACTCTATCACGCCTGGTCTTCGAAGTTAGCAC
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| prepared_dna.fasta | FASTA file converted to DNA |
| protein.fasta | FASTA file converted to protein |
| mrna.fasta | FASTA file converted to mRNA |

ESMFold使用大型语言模型从主序列直接推断结构,预测的速度比最先进的方法快60倍,同时能够保持分辨率和准确性。AlphaFold2和其他替代方法使用多序列比对(MSA)和类似蛋白质的模板来实现原子分辨率结构预测的最佳性能获突破性成功;而ESMFold通过利用语言模型的内部表征,只用一个序列作为输入就能生成结构预测。ESMFold与AlphaFold2和RoseTTAFold具有相似的准确性,但ESMFold在探索宏基因组蛋白质的结构空间方面速度更快。
蛋白序列文件,FASTA格式,支持多条序列。
预测复合物,多条链通过英文冒号(:)相连,举例:
>complex
MGITQTPYKVSISGLYLRARV:QVQLQQSGAELARPGASVKMSCKASGYTFTRYTMHWVKQR
每个GPU前向传递中的最大令牌数。这将使较短的序列分组进行批量预测。如果在短序列上发生内存不足问题,降低此值可以有所帮助。
较低的值将导致更低的内存使用,但会降低速度。推荐值:128、64、32。
蛋白序列文件,FASTA格式,多条序列时默认为复合物预测。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| seq1.pdb | 默认输出第一条序列的预测结构。 |
| result.tar.gz | 针对含有多条序列的fasta文件,压缩包中含所有的序列的预测结构。 |
| score.csv | 预测结构的打分,包含结构可靠性指标pLDDT与pTM,pLDDT数值范围在0-100,数值越大表示结构可靠性越高,pTM数值范围在0-1,数值越大表示结构可靠性越高 |
| stdout.txt | 模块的标准输出信息。 |
ESMFold uses a large language model to directly infer structure from primary sequences, with prediction speeds 60 times faster than state-of-the-art methods, while maintaining resolution and accuracy. While AlphaFold2 and other alternative methods achieve breakthrough success in atomic-resolution structure prediction using multiple sequence alignments (MSA) and protein-like templates, ESMFold leverages the internal representation of a language model to generate structure predictions using just one sequence as input. ESMFold exhibits similar accuracy to AlphaFold2 and RoseTTAFold, but is faster in exploring the structural space of macrogenomic proteins.

Protein sequence file in FASTA format, supporting multiple sequences.
For predicting complexes, multiple chains are connected by a colon (:) as shown below:
>complex
MGITQTPYKVSISGLYLRARV:QVQLQQSGAELARPGASVKMSCKASGYTFTRYTMHWVKQR
Maximum number of tokens in each GPU forward pass. This allows grouping of shorter sequences for batch prediction. Lowering this value can help if memory issues occur with short sequences.
A lower value leads to lower memory usage but decreases speed. Recommended values: 128, 64, 32.
Protein sequence file in FASTA format, defaulting to complex prediction for multiple sequences.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| seq1.pdb | Default output of the predicted structure for the first sequence. |
| result.tar.gz | For fasta files containing multiple sequences, the compressed file includes predicted structures for all sequences. |
| score.csv | The score of the predicted structure includes the structural reliability indicators pLDDT and pTM. The pLDDT value range is 0-100, and the larger the value, the higher the structural quality. The pTM value range is 0-1, and the larger the value, the higher the structural quality. |
| stdout.txt | Standard output. |
.png)
Retrosynthetic Prediction (AiZynthFinder)是阿斯利康开发的针对小分子的逆反应合成路线预测算法。AiZynthFinder算法基于蒙特卡罗树搜索最终得到可被购买的小分子,用于合成输出分子。树搜索策略采用神经网络方法对已知的反应库进行训练得到。
目标小分子的结构文件,SMILES格式,如:
Cc1cccc(c1N(CC(=O)Nc2ccc(cc2)c3ncon3)C(=O)C4CCS(=O)(=O)CC4)C
得到逆合成分析的路线图route000.png-route010.png。
Genheden S, Thakkar A, Chadimová V, et al. AiZynthFinder: a fast, robust and flexible open-source software for retrosynthetic planning. J Cheminform. 2020 Nov 17;12(1):70.
http://www.github.com/MolecularAI/aizynthfinder
AiZynthFinder is a tool for retrosynthetic planning. The algorithm is based on a Monte Carlo tree search that recursively breaks down a molecule to purchasable precursors. The tree search is guided by a policy that suggests possible precursors by utilizing a neural network trained on a library of known reaction templates.
Product molecule structure file in SMILES format. Example:
Cc1cccc(c1N(CC(=O)Nc2ccc(cc2)c3ncon3)C(=O)C4CCS(=O)(=O)CC4)C
The road map of inverse synthesis analysis is obtained. route000.png-route010.png
Genheden S, Thakkar A, Chadimová V, et al. AiZynthFinder: a fast, robust and flexible open-source software for retrosynthetic planning. J Cheminform. 2020 Nov 17;12(1):70.
http://www.github.com/MolecularAI/aizynthfinder

IgFold是一种基于深度学习的快速预测抗体Fv结构的方法。IgFold由一个预先训练的语言模型和直接预测骨架原子坐标的图网络组成,该语言模型训练了558M个天然抗体序列。IgFold在显著更短的时间内(不到一分钟)预测出与其他方法(包括AlphaFold)相似或更好质量的结构。注:该模块只适合预测可变区构象,如果是全长抗体或者包含多个可变区的抗体等情况,需要使用Protein Structure Prediction (AlphaFold2.3.2)或者Protein Structure Prediction (ESMFold)进行结构预测。
输入抗体Fv区重链和或轻链序列,其中抗体序列名称中必须包含重链标识符:H,Heavy,.H;轻链标识符:L,Light,.L。例如:
>antibody.H
XXXXXX
>antibody.L
XXXXXX
输出文件为预测抗体的结构文件antibody_pred.pdb。
【已知问题】部分预测结构会比输入序列缺失个别氨基酸,请留意!
IgFold, a fast deep learning method for antibody structure prediction. IgFold consists of a pre-trained language model trained on 558M natural antibody sequences followed by graph networks that directly predict backbone atom coordinates. IgFold predicts structures of similar or better quality than alternative methods (including AlphaFold) in significantly less time (under one minute).
Antibody Fv sequence file in FASTA format. The heavy chain sequence name should contain :H, Heavy, or .H. The light chain sequence name should contain :L, Light, or .L. Demo:
>antibody.H
XXXXXX
>antibody.L
XXXXXX
The output file is antibody_pred.pdb, which is a structure file for predicting antibodies.
Part of the predicted structure will be missing individual amino acids compared to the input sequence, please note!

基于神经网络的MHC-I型相互作用预测模型。模型训练是利用亲和力和质谱洗脱配体的数据,预测特定MHC分子结合肽段的亲和力值和肽段的长度,可用于肿瘤新抗原的预测。
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式。
输出结果文件为result.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Seq_ID | 蛋白序列名称 |
| Pos | 肽段在蛋白质序列中的残基编号(从0开始) |
| MHC | MHC分子/等位基因名称 |
| Peptide | 潜在配体的氨基酸序列 |
| Core | 直接与MHC接触的最小的9个氨基酸结合核心 |
| Of | 核心在肽段中的起始位置(如果>0,则该方法预测N-末端突出) |
| Gp | 如有删除,删除的位置 |
| Gl | 如有删除,删除的长度 |
| Ip | 如有插入,插入的位置 |
| Il | 如有插入,插入的长度 |
| Icore | 相互作用核心。这是包括插入和删除的结合核心序列 |
| Identity | 蛋白质标识符,即FASTA条目的名称 |
| Score | 原始预测得分。(EL:质谱洗脱配体,BA:亲和力) |
| %Rank | 预测结合得分与一组随机天然肽相比的排名。此测量不受某些分子固有偏向于更高或更低的预测亲和力的影响。强结合物被定义为具有%rank<0.5的物质,而弱结合物则具有%rank<2。我们建议基于%Rank而不是得分选择候选配体。(EL:质谱洗脱配体,BA:亲和力) |
| Aff(nM) | 亲和力大小 |
| BindLevel | 如果%Rank低于强结合物的指定阈值(默认为0.5%),则将识别肽段为强结合物。如果%Rank高于强结合物的阈值但低于弱结合物的指定阈值(默认为2%),则将识别肽段为弱结合物。(SB:强结合物,WB:弱结合物) |
A neural network-based model for predicting MHC-I interactions. The model is trained using affinity and mass spectrometry-eluted ligand data to forecast the affinity values and lengths of peptides binding to specific MHC molecules. This can be employed for predicting tumor neoantigens.
Protein sequence file in FASTA format.
The output file is result.csv and contains the following information:
| Seq_ID | Protein sequence name |
|---|---|
| Pos | Residue number (starting from 0) of the peptide in the protein sequence. |
| MHC | Specified MHC molecule / Allele name. |
| Peptide | Amino acid sequence of the potential ligand. |
| Core | The minimal 9 amino acid binding core directly in contact with the MHC. |
| Of | The starting position of the Core within the Peptide (if > 0, the method predicts a N-terminal protrusion). |
| Gp | Position of the deletion, if any. |
| Gl | Length of the deletion, if any. |
| Ip | Position of the insertion, if any |
| Il | Length of the insertion, if any |
| Icore | Interaction core. This is the sequence of the binding core including eventual insertions of deletions. |
| Identity | Protein identifier, i.e. the name of the FASTA entry. |
| Score | The raw prediction score. (EL: MS eluted ligand, BA: Binding Affinity) |
| %Rank | Rank of the predicted binding score compared to a set of random natural peptides. This measure is not affected by inherent bias of certain molecules towards higher or lower mean predicted affinities. Strong binders are defined as having %rank<0.5, and weak binders with %rank<2. We advise to select candidate binders based on %Rank rather than Score. (EL: MS eluted ligand, BA: Binding Affinity) |
| Aff(nM) | Affinity value |
| BindLevel | The peptide will be identified as a strong binder if the %Rank is below the specified threshold for the strong binders (by default, 0.5%). The peptide will be identified as a weak binder if the %Rank is above the threshold of the strong binders but below the specified threshold for the weak binders (by default, 2%). (SB: Strong Binder, WB: Weak Binder) |

NPT MDP Generation是生成等温等压(NPT)MDP文件的模块。
Define用于传递预处理器的定义,可以使用任何定义来控制自定义拓扑文件(.top)中的选项。可选择的定义包括以下选项:
模拟中积分方式的选择:md算法。
md是蛙跳法,对符合牛顿公式的运动进行积分。
时间步长,单位为ps。(默认为0.001)
模拟时长,单位为ns。
质心进行操作的组,可以是索引文件中的一个,或者多个组。默认为整个系统。
系统或者系统中各个组质心的操作。(默认为None)
在轨迹文件中写入坐标的频率。(默认为0)
在轨迹文件中写入速度(v)的频率。(默认为0)
在轨迹文件中写入力的频率。(默认为0)
在log文件中写入能量的频率。(默认为50)
在记录能量的文件中写入能量的频率。(默认为100)
输入压缩的轨迹文件的频率。(默认为50)
输入轨迹包含的结构。默认为整个系统。
周期化边界条件设置(默认为xyz)。
原子静电相互作用的计算方法,默认为PME。
库仑力截止距离,单位nm(默认为1.2)
范德华相互作用的计算方法,默认为Cut-off。
LJ或Buckingham截止距离,单位nm(默认为1.2)
能量和压力的长程色散校正方法(默认为EnerPres)。
温度耦合的方法(默认为V-rescale)。
耦合到单独的温度浴的组别,多个组别用空格间隔。
温度耦合时间常数,单位为ps。(默认为0.2)
耦合的参考温度,即动力学模拟的温度,单位为K。(默认为300)
压力耦合的方法(默认为Berendsen)。
压力耦合的各向同性类型。每种类型取一个或多个可压缩性(compressibility)和Coupling Reference Pressure。Time for Pressure Coupling仅允许一个值。(默认为isotropic)
压力耦合的时间常数(所有方向一个值),单位为ps。(默认为2)
耦合的参考压力,单位为bar。(默认为1)
可压缩性(注:这实际上是在bar^-1)对于水在1atm和300k的可压缩性是4.5e-5 bar^-1。所需值的数量由pcoupltype [bar^-1]暗示。
限制类型。(默认为none)
输出文件名称
得到一个计算NPT的MDP文件npt.mdp。
The NPT MDP Generation module is used to generate the MDP file for an isothermal-isobaric (NPT) simulation.
The Define section is used to pass preprocessor definitions that can control options in custom topology files (.top). Available options include:
Choice of integration method in the simulation: md algorithm.
md is the leap-frog algorithm used to integrate motions conforming to Newton’s equations.
Time step size in ps. (Default is 0.001)
Duration of the simulation in ns.
Group(s) for center of mass operations, can be one or multiple groups from the index file. Default is the entire system.
Operations for the system or center of mass of individual groups in the system. (Default is None)
Frequency of writing coordinates to the trajectory file. (Default is 0)
Frequency of writing velocities to the trajectory file. (Default is 0)
Frequency of writing forces to the trajectory file. (Default is 0)
Frequency of writing energy to the log file. (Default is 50)
Frequency of writing energy to the energy file. (Default is 100)
Frequency of inputting compressed trajectory files. (Default is 50)
Structures included in the input trajectory. Default is the entire system.
Setting for periodic boundary conditions (Default is xyz).
Method for calculating atomic electrostatic interactions, default is PME.
Coulomb force cut-off distance in nm. (Default is 1.2)
Method for calculating van der Waals interactions, default is Cut-off.
LJ or Buckingham cut-off distance in nm. (Default is 1.2)
Method for long-range dispersion correction for energy and pressure (Default is EnerPres).
Method for temperature coupling (Default is V-rescale).
Groups to which temperature baths are coupled, multiple groups separated by spaces.
Time constant for temperature coupling in ps. (Default is 0.2)
Reference temperature for coupling in K. (Default is 300)
Method for pressure coupling (Default is Berendsen).
Isotropic type of pressure coupling. Each type takes one or more compressibility and Coupling Reference Pressure values. Time for Pressure Coupling allows only one value. (Default is isotropic)
Time constant for pressure coupling (one value for all directions) in ps. (Default is 2)
Reference pressure for coupling in bar. (Default is 1)
Compressibility (actually in bar^-1). For water at 1 atm and 300K, the compressibility is 4.5e-5 bar^-1. The number of values required is implied by pcoupltype [bar^-1].
Type of constraints. (Default is none)
Output file name.
Generates an MDP file named npt.mdp for the NPT calculation.

Minimize MDP Generation是生成能量优化(Minimization)MDP文件的模块。
模拟中积分方式的选择:cg和steep算法。
cg用于能量最小化的共轭梯度算法,在能量下降最陡峭时,比steep更加高效。
steep用于能量最小化的最陡下降算法。一般在setup的能量最小化中使用。
最小化的最大时间,-1没有最大值。
最大容许力,单位为kJ/(mol·nm)。当最大作用力小于此值,认为最小化过程收敛。(默认为100)
起始步长,单位为nm。(默认为0.01)
在轨迹文件中写入坐标的频率。(默认为50)
在log文件中写入能量的频率。(默认为50)
在记录能量的文件中写入能量的频率。(默认为50)
周期化边界条件设置:
xyz: 在所有方向上使用周期性边界条件
no: 不使用周期性边界条件,忽略box。若要模拟无截止,请将所有Cutoff相关选项和nstlist设置为0。若要在单个MPlrank上实现无截止的最佳性能,请将nstlist设置为0,ns-type=simple.
xy: 仅在x和y方向使用周期性边界条件。这仅适用于 ns-type=grid,并可与墙(walls)结合使用。如果没有墙或只有一面墙,系统在z方向上的大小是无限的,因此不能使用压力糟合或 Ewald求和方法。当使用两个墙时,这些缺点不存在。
原子静电相互作用的计算方法,默认为PME。
指定库仑力阈值,单位为nm。(默认为1.2)
范德华相互作用的计算方法,默认为Cut-off。
LJ或Buckingham截止距离,单位nm。(默认为1.2)
控制拓扑中被转换为刚性完整约束的键类型。典型的刚性水模型没有键,因此不受此关键字的影响。
none:不将键转化为约束.
h-bonds:将与氢原子的键合转换为约束
all-bonds:将所有键转换为约束
h-angles:将所有键转换为约束,并将涉及氢原子的角度转换为键约束
al-angles:将所有结合转换为约束,将所有角度转换为结合约束
输出文件名称
得到一个计算最小化的MDP文件mini.mdp。
The Minimize MDP Generation module is used to generate the MDP file for energy minimization.
Choice of integration method in the simulation: cg and steep algorithms.
cg is the conjugate gradient algorithm used for energy minimization, more efficient than steep when the energy decreases steeply.
steep is the steepest descent algorithm used for energy minimization. Generally used in setting up energy minimization.
Maximum time for minimization, -1 means no maximum.
Maximum allowable force in kJ/(mol·nm). Minimization is considered converged when the maximum force is below this value. (Default is 100)
Initial step size in nm. (Default is 0.01)
Frequency of writing coordinates in the trajectory file. (Default is 50)
Frequency of writing energy to the log file. (Default is 50)
Frequency of writing energy to the energy file. (Default is 50)
Setting for periodic boundary conditions:
Method for calculating atomic electrostatic interactions, default is PME.
Specifies the Coulomb force threshold in nm. (Default is 1.2)
Method for calculating van der Waals interactions, default is Cut-off.
LJ or Buckingham cut-off distance in nm. (Default is 1.2)
Controls which types of bonds in the topology are converted to rigid constraints. Typical rigid water models have no bonds, so they are not affected by this keyword.
Output file name.
Generates an MDP file named mini.mdp for the energy minimization calculation.

MD PDB Prepare是一个在分子动力学模拟前PDB结构处理模块,结合PDBFixer工具对输入PDB文件中的蛋白结果进行修复,再分离出PDB文件中的蛋白结构、小分子结构以及核酸结构。
结构文件,PDB格式。
需要注意体系中若存在配体,其名称不能为*号且必须以HETATM开头。如下所示为正确的小分子结构文件:
HETATM 3767 C1 GOL A 302 -4.671 -11.067 -0.429 1.00 43.56 C
HETATM 3768 O1 GOL A 302 -5.324 -9.793 -0.300 1.00 41.43 O
若体系中有特殊金属原子,只能选AMBER力场。离子需要按照特定书写格式,以下为一些常见原子书写格式:
# Mg2+离子
HETATM 1431 MG MG A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 MG
# Mn2+离子
HETATM 1431 MN MN A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 MN
# Zn2+离子
HETATM 1431 ZN ZN A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 ZN
# Fe2+离子
HETATM 1431 FE2 FE2 A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 FE
# Fe3+离子
HETATM 1431 FE3 FE3 A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 FE
# Ca2+离子
HETATM 1431 CA CA A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 C0
# Cu2+离子
HETATM 1431 CU CU A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 CU
其中atom type,residue需要是大写,atom name只需是标准金属离子(可以通过文本编辑器查看书写格式是否相同)。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| protein.pdb | 分离得到体系中蛋白文件 |
| ligand.pdb/ligand_pdb.tar.gz | 分离得到体系中小分子文件或者压缩文件 |
| nucleic_acid.pdb | 分离得到体系中核酸文件 |
| membrane.pdb/lipid_membrane.pdb | 分离得到体系中膜结构 |
MD PDB Prepare is a module for pre-processing PDB structures before molecular dynamics simulations. It uses the PDBFixer tool to repair protein structures in the input PDB file and separates the protein structure, small molecule structure, and nucleic acid structure from the PDB file.
Structure file in PDB format.
It is important to note that if there is a ligand in the system, its name cannot be an asterisk (*) and must start with HETATM. Below is an example of a correct small molecule structure in a file:
HETATM 3767 C1 GOL A 302 -4.671 -11.067 -0.429 1.00 43.56 C
HETATM 3768 O1 GOL A 302 -5.324 -9.793 -0.300 1.00 41.43 O
If the system contains special metal atoms, only the AMBER force field can be selected. Ions need to be written in a specific format. Here are some common atomic writing formats:
# Mg2+ ion
HETATM 1431 MG MG A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 MG
# Mn2+ ion
HETATM 1431 MN MN A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 MN
# Zn2+ ion
HETATM 1431 ZN ZN A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 ZN
# Fe2+ ion
HETATM 1431 FE2 FE2 A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 FE
# Fe3+ ion
HETATM 1431 FE3 FE3 A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 FE
# Ca2+ ion
HETATM 1431 CA CA A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 C0
# Cu2+ ion
HETATM 1431 CU CU A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 CU
Where atom type and residue should be in uppercase, and atom name should be the standard metal ion name (you can check the writing format using a text editor).
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| protein.pdb | Separated protein file from the system |
| ligand.pdb/ligand_pdb.tar.gz | Separated small molecule file or compressed file from the system |
| nucleic_acid.pdb | Separated nucleic acid file from the system |
| membrane.pdb/lipid_membrane.pdb | Separated membrane structure from the system |

可根据起始帧数、结束帧数以及间隔帧数对平衡模拟进行轨迹提取,从而将其转换为GRO或者PDB轨迹文件。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在GMX MD Run模块或者AlphaAutoMD模块中获取。
文件输出类型:GRO或者PDB。
输出文件是否保留水盒子。
起始位置(单位ps)。
结束位置(单位ps)。
间隔时间,单位ps。
索引文件,ndx格式。对于膜体系的轨迹提取是必填项。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| md_finally.pdb | 最后一帧结构文件 |
| md_center.pdb | PDB格式轨迹文件 |
| md_center.gro | GRO格式轨迹文件 |
The MD Trajectory module allows for the extraction of trajectories from equilibrium simulations based on the starting frame number, ending frame number, and frame interval, converting them into GRO or PDB trajectory files.
Path file obtained after MD simulation, can be obtained from the GMX MD Run module or the AlphaAutoMD module.
File output type: GRO or PDB.
Whether to retain the water box in the output files.
Starting time (in ps).
Ending time (in ps).
Time interval, in ps.
Index file in ndx format. This is a required parameter for extracting trajectories in membrane systems.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| md_finally.pdb | Structure file of the final frame |
| md_center.pdb | PDB format trajectory file |
| md_center.gro | GRO format trajectory file |

Protein Protonation是蛋白质子化模块主要是预测每个蛋白残基的pKa并根据指定的pH值判断每个残基的质子化状态。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式,该文件可以MD PDB Prepare模块提取得到。
pH值,默认为7。
N端残基质子化状态,只有charge和neutral两个选项,默认charge。
C端残基质子化状态,只有charge和neutral两个选项,默认charge。
自定义残基质子化状态。
预测的含质子化状态的结构文件。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| protein_protonation.pdb | 质子化状态的结构文件 |
| predict_pKa.txt | 含pKa值输出文件 |
The Protein Protonation module is primarily used to predict the pKa of each protein residue and determine the protonation state of each residue based on the specified pH value.
The structure file of the protein in PDB format, which can be obtained from the MD PDB Prepare module.
pH value, default is 7.
Protonation state of the N-terminal residue, with options of charge and neutral, default is charge.
Protonation state of the C-terminal residue, with options of charge and neutral, default is charge.
Customize the protonation state of residues.
Structure file with predicted protonation states.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| protein_protonation.pdb | Structure file with protonation states |
| predict_pKa.txt | Output file containing pKa values |

GMX Receptor Parameterization模块根据Gromacs生成受体(包括蛋白或者核酸)的GRO,ITP以及TOP文件。
蛋白结构文件。提交的蛋白质文件最好经过Protein Protonation模块的处理。
若体系中有特殊金属原子,只能选AMBER力场。离子需要按照特定书写格式,以下为一些常见原子书写格式:
# Mg2+离子
HETATM 1431 MG MG A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 MG
# Mn2+离子
HETATM 1431 MN MN A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 MN
# Zn2+离子
HETATM 1431 ZN ZN A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 ZN
# Fe2+离子
HETATM 1431 FE2 FE2 A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 FE
# Fe3+离子
HETATM 1431 FE3 FE3 A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 FE
# Ca2+离子
HETATM 1431 CA CA A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 C0
# Cu2+离子
HETATM 1431 CU CU A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 CU
其中atom type,residue需要是大写,atom name只需是标准金属离子(可以通过文本编辑器查看书写格式是否相同)。
核酸结构文件。
力场,默认amber03。以下是各个力场适用于那些情况:
amber03,amber14sb_parmbsc1适合蛋白和核酸的凝聚相模拟,也支持小分子。
charmm27,charmm36-jul2020适用于核酸和脂(膜)。
gromos54a7适合烷烃、蛋白、核酸凝聚相的模拟。
oplsaa适合高分子模拟。
注意:根据提交的pdb结构选取力场。
水模型,默认spc。
spc:最好用于GROMOS力场。
spce:对纯水体系比SPC、TIP3P都好。
tip3p:最好用于amber。
tip4p:最好用于opls。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| receptor.gro | 受体的分子坐标文件 |
| receptor_itp.tar.gz | 受体平衡模拟时固定原子位置所施加的力 |
| receptor.top | 受体的拓扑文件 |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
The GMX Receptor Parameterization module generates GRO, ITP, and TOP files for receptors (including proteins or nucleic acids) based on Gromacs.
Protein structure file. The submitted protein file is preferably processed through the Protein Protonation module.
If the system contains special metal atoms, only the AMBER force field can be selected. Ions need to be written in specific formats. Below are some common atomic writing formats:
# Mg2+ ion
HETATM 1431 MG MG A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 MG
# Mn2+ ion
HETATM 1431 MN MN A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 MN
# Zn2+ ion
HETATM 1431 ZN ZN A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 ZN
# Fe2+ ion
HETATM 1431 FE2 FE2 A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 FE
# Fe3+ ion
HETATM 1431 FE3 FE3 A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 FE
# Ca2+ ion
HETATM 1431 CA CA A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 C0
# Cu2+ ion
HETATM 1431 CU CU A 301 -23.030 15.955 -4.315 1.00 47.40 CU
Where atom type and residue should be in uppercase, and atom name should match the standard metal ion format (check in a text editor if the writing format is the same).
Nucleic acid structure file.
Force field, default is amber03. The following are the scenarios for each force field:
amber03, amber14sb_parmbsc1 are suitable for protein and nucleic acid condensed phase simulations, and also support small molecules.
charmm27, charmm36-jul2020 are suitable for nucleic acids and lipids (membranes).
gromos54a7 is suitable for simulations of alkanes, proteins, and nucleic acids in the condensed phase.
oplsaa is suitable for polymer simulations.
Note: Select the force field based on the submitted pdb structure.
Water model, default is spc.
spc: Best used for the GROMOS force field.
spce: Better for pure water systems compared to SPC and TIP3P.
tip3p: Best used for amber.
tip4p: Best used for opls.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| receptor.gro | Molecular coordinate file of the receptor |
| receptor_itp.tar.gz | Force applied to fix atomic positions during receptor equilibrium simulations |
| receptor.top | Topology file of the receptor |
GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. M. J. Abraham, T. Murtola, R. Schulz, S. Páll, J. C. Smith, B. Hess, E. Lindahl, SoftwareX, 1, (2015), 19-25.
基于obabel,Antechamber(Ambertool),ACPYPE以及ORCA对小分子进行处理。将小分子的PDB文件根据所需电荷,电荷类型和自旋多重度进行处理,从而生成Gromacs分子动力学模拟所需的GRO和ITP文件。
支持pdb和tar.gz的文件格式。当单个配体时提交pdb文件,多个配体时提交含有pdb的tar.gz文件。该文件最好经过MD PDB Prepare模块处理。
配体分子不能用*号,最好是重新命名成英文名称。
选取计算的电荷类型,默认为bcc电荷。
如设置则配体在该pH环境下加氢;如不设置,按全氢加氢。注意:设置pH后,如果配体电荷不为0,自旋多重度不为1,则需要在Charge Multiplicity设置。
指明要计算的配体文件的电荷和自旋多重度,默认为电荷为0,自旋多重度为1。格式要求:配体文件名称(不包含后缀) 电荷值 自旋多重度,例如提交文件为ligand.pdb、电荷为0、自旋多重度为1,则该栏输入为“ligand 0 1”。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ligand.gro | 受体的分子坐标文件 |
| ligand_itp.tar.gz | 受体平衡模拟时固定原子位置所施加的力 |
| ligand.mol2/ligand_mol2.tar.gz | 分子结构的mol2文件,多个配体时为tar.gz文件 |
Processing of small molecules is performed based on obabel, Antechamber (Ambertool), ACPYPE, and ORCA. The PDB file of the small molecule is processed according to the desired charge, charge type, and spin multiplicity to generate the GRO and ITP files required for Gromacs molecular dynamics simulations.
Supports file formats of pdb and tar.gz. Submit a pdb file when a single ligand is present, and submit a tar.gz file containing pdb when multiple ligands are present. It is recommended that the file has been processed through the MD PDB Prepare module.
Ligand molecules should not contain asterisks (*), and it is preferable to rename them with English names.
Select the type of charge calculation, with the default being the bcc charge.
If set, hydrogenation of the ligand will occur at the specified pH environment; if not set, full hydrogenation will be applied. Note: when pH is set, if the ligand charge is not 0 and the spin multiplicity is not 1, it needs to be specified in Charge Multiplicity.
Specifies the charge and spin multiplicity of the ligand file to be calculated, with the default charge being 0 and spin multiplicity being 1. Format requirement: ligand file name (excluding the extension) charge value spin multiplicity. For example, if the submitted file is ligand.pdb with a charge of 0 and a spin multiplicity of 1, the input in this field should be “ligand 0 1”.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ligand.gro | Molecular coordinate file of the ligand |
| ligand_itp.tar.gz | Force applied to fix atomic positions during ligand equilibrium simulations |
| ligand.mol2/ligand_mol2.tar.gz | Mol2 file of the molecular structure, a tar.gz file for multiple ligands |

MD MDP Generation是生成平衡模拟(MD)MDP文件的模块。
Define用于传递预处理器的定义,可以使用任何定义来控制自定义拓扑文件(.top)中的选项。可选择的定义包括以下选项:
模拟中积分方式的选择:md算法。
md是蛙跳法,对符合牛顿公式的运动进行积分。
时间步长,单位为ps。(默认为0.001)
模拟时长,单位为ns。
质心进行操作的组,可以是索引文件中的一个,或者多个组。默认为整个系统。
系统或者系统中各个组质心的操作。(默认为None)
在轨迹文件中写入坐标的频率。(默认为0)
在轨迹文件中写入速度(v)的频率。(默认为0)
在轨迹文件中写入力的频率。(默认为0)
在log文件中写入能量的频率。(默认为5000)
在记录能量的文件中写入能量的频率。(默认为1000)
输入压缩的轨迹文件的频率。(默认为1000)
输入轨迹包含的结构。默认为整个系统。
周期化边界条件设置(默认为xyz)。
原子静电相互作用的计算方法,默认为PME。
库仑力截止距离,单位nm。(默认为1.2)
范德华相互作用的计算方法,默认为Cut-off。
LJ势或Buckingham的阈值,单位为nm。(默认为1.2)
能量和压力的长程色散校正方法(默认为EnerPres)。
温度耦合的方法(默认为V-rescale)。
耦合到单独的温度浴的组别,多个组别用空格间隔。
耦合时间常数,每个组别都需要定义温度,-1表示无温度耦合,单位为ps。(默认为0.2)
耦合的参考温度,即动力学模拟的温度,单位为K。(默认为300)
压力耦合的方法(默认为Berendsen)。
压力耦合的各向同性类型。每种类型取一个或多个可压缩性(compressibility)和Coupling Reference Pressure。Time for Pressure Coupling仅允许一个值。(默认为isotropic)
压力耦合的时间常数(所有方向一个值),单位为ps。(默认为2)
耦合的参考压力,单位为bar。(默认为1)
可压缩性(注:这实际上是在bar^-1)对于水在1atm和300k的可压缩性是4.5e-5 bar^-1。所需值的数量由pcoupltype [bar^-1]暗示。
限制类型。(默认为none)
xyz方向的位置限制的力常数,三个数值之间用逗号分隔开,单位为kJ/(mol·nm^2)。例如:500,500,500。
MD运行中距离、角度、二面角限制是否生效:
no表示忽略拓扑文件中的约束信息;
simple表示简单的(每分子)的距离约束;
ensemble表示一个模拟盒中分子系综的距离约束。
约束力权重类型:
equal表示将约束力平分到约束中的所有原子对上;
conservative表示约束力为约束势的导数, 将导致原子对的权重为r^-7.,当Time Constant for Restraints=0时,约束力为保守力。
Dirse mixed采用的方法:
no表示计算约束力时使用时间平均的违反;
yes表示计算约束力时使用时间平均违反与瞬时违反乘积的平方根。
约束的力常数,乘以拓扑文件中相互作用约束给出的Factor即为最终的约束力大小。
限制约束的时间,设置为0时表示MD过程中一直进行约束,单位为ps。
将约束中所有原子对的运行距离和瞬时距离写入能量文件的间隔步数。间隔越小该文件越大。
输出文件名称
生成跑MD的MDP文件md.mdp。
MD MDP Generation is a module for generating the MDP file for equilibrium simulations (MD).
Used to pass definitions to the preprocessor, which can be used to control options in custom topology files (.top). Available options include:
Choice of integration method in the simulation: md algorithm.
md is the leap-frog algorithm for integrating motion conforming to Newton’s equations.
Time step, in ps. (Default is 0.001)
Simulation duration, in ns.
Groups for which center of mass operations will be performed, can be one or multiple groups from an index file. Default is the entire system.
Operations for the system or center of mass of groups in the system. (Default is None)
Frequency of writing coordinates to the trajectory file. (Default is 0)
Frequency of writing velocities to the trajectory file. (Default is 0)
Frequency of writing forces to the trajectory file. (Default is 0)
Frequency of writing energies to the log file. (Default is 5000)
Frequency of writing energies to the energy file. (Default is 1000)
Frequency of inputting compressed trajectory files. (Default is 1000)
Structures included in the input trajectory. Default is the entire system.
Periodic boundary conditions setting. (Default is xyz)
Method for calculating atomic electrostatic interactions, default is PME.
Coulomb force cut-off distance, in nm. (Default is 1.2)
Method for calculating van der Waals interactions, default is Cut-off.
Threshold for LJ potential or Buckingham, in nm. (Default is 1.2)
Method for long-range dispersion correction for energy and pressure. (Default is EnerPres)
Method for temperature coupling. (Default is V-rescale)
Groups to which temperature baths are coupled, multiple groups separated by spaces.
Time constant for temperature coupling, each group defining a temperature needs to be defined, -1 indicates no temperature coupling, in ps. (Default is 0.2)
Reference temperature for coupling, the temperature of the dynamic simulation, in K. (Default is 300)
Method for pressure coupling. (Default is Berendsen)
Isotropic type for pressure coupling. Each type takes one or more compressibility values and a Coupling Reference Pressure. Time for Pressure Coupling allows only one value. (Default is isotropic)
Time constant for pressure coupling (one value for all directions), in ps. (Default is 2)
Reference pressure for coupling, in bar. (Default is 1)
Compressibility (note: this is actually in bar^-1). For water at 1 atm and 300 K, the compressibility is 4.5e-5 bar^-1. The number of values required is indicated by pcoupltype [bar^-1].
Type of constraints. (Default is none)
Force constant for position restraints in the xyz directions, separated by commas, in units of kJ/(mol·nm^2). For example: 500,500,500.
Whether distance, angle, and dihedral restraints are active during MD runs:
no means ignore constraint information in the topology file;
simple means simple (per-molecule) distance constraints;
ensemble means distance constraints for a molecule ensemble in a simulation box.
Type of constraint force weighting:
equal distributes the constraint force equally among all atom pairs in the constraint;
conservative gives the derivative of the constraint potential, leading to a weight of r^-7 for atom pairs, and if Time Constant for Restraints=0, the constraint force is conservative.
Method used by Dirse mixed:
no uses time-averaged violations in computing the constraint force;
yes uses the square root of the time-averaged violation times the instantaneous violation in computing the constraint force.
Force constant for constraints, multiplied by the Factor given by the interaction constraints in the topology file to determine the final constraint force magnitude.
Time for constraints, set to 0 to maintain constraints throughout the MD process, in ps.
Interval steps for writing the running and instantaneous distances of all atom pairs in the constraint to the energy file. Smaller intervals lead to larger files.
Output file name.
Generates the MDP file md.mdp for running MD.

MD Solvation将原有的受配体结构中加入水分子和离子。
输入的受体拓扑文件,可由GMX Receptor Parameterization模块生成。
输入的受体结构文件,可由GMX Receptor Parameterization模块生成。
输入的受体参数(压缩)文件,可由GMX Receptor Parameterization模块生成。
输入的配体结构(压缩)文件,可由GMX Ligand Parameterization模块生成。
输入的配体参数(压缩)文件,可由GMX Ligand Parameterization模块生成。
输出的体系总的拓扑文件
输出的体系总的结构文件
输出的体系参数的(压缩)文件
距离限制,仅当Disre不为no时生效,格式如下所示:
[AtomIndex1] [AtomIndex2] [Type] [Index] [Type] [Low] [Up1] [Up2] [Factor]
其中,AtomIndex1和AtomIndex2为在system.gro的原子编号;Type为施加约束类型,通常设置为1,Type类型见表1;Index是计算顺序;Low、Up1、Up2为原子间限制距离,Low到Up1区间的原子距离是不受限制的,但是不能超过Up2,单位为nm;Factor为因子,将Factor乘以“Disre Force Constant”即为限制力的大小,单位为kJ/mol/nm2。
例如:
10 16 1 0 1 0.0 0.3 0.4 1.0
10 46 1 1 1 0.0 0.3 0.4 1.0
16 22 1 2 1 0.0 0.3 0.4 2.5
表1:GROMACS中三种约束类型对原子对进行限制
| Type Code | 约束类型 | 作用情况 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Complex NMR distance restraints | 当Disre Type为ensemble时,即非键相互作用设置为1 |
| 6 | Simple harmonic restraints | 当Disre Type为simple时,即分子内成键相互作用设定,可设为6或者10. |
| 10 | Piecewise linear/harmonic restraints | 当Disre Type为simple时,即分子内成键相互作用设定,可设为6或者10 |
角度限制是两对原子间角度的限制,仅当Disre不为no时生效,格式如下所示:
[AtomIndex1] [AtomIndex2] [AtomIndex3] [AtomIndex4] [Type] [Theta0] [Force Constant] [Multiplicity]
其中,AtomIndex1-AtomIndex2是第一对原子编号;AtomIndex3-AtomIndex4为第二对原子编号;Type在这里无用,定义为1即可;Theta0为约束的角度,单位为deg;Force Constant为约束力常数,单位为kJ/mol;Multiplicity为多重度。
例如
2642 2643 2635 2652 1 67.0 1500 1
二面角限制,仅当Disre不为no时生效,格式如下所示:
[AtomIndex1] [AtomIndex2] [AtomIndex3] [AtomIndex4] [Type] [Label] [Phi] [dPhi] [KFactor] [Power]
其中,AtomIndex1-AtomIndex4为组成二面角的原子编号;Type为约束类型函数,总是为1;Label无效;Phi为参考角,dPhi为超出参考角的角度值,单位为deg;KFactor为因子,将KFactor乘以“Disre Force Constant”即为限制力的大小,单位为 kJ/mol/rad2;Power无效。
例如:
2642 2643 2635 2652 1 67.0 1500 1
约束势函数如下所示:
其中,Φ’为参考角Phi,ΔΦ为超出参考角的值dPhi,K_dihr为限制力的大小KFactor。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| system.gro | 体系的分子坐标文件 |
| system_itp.tar.gz | 体系平衡模拟时固定原子位置所施加的力 |
| system.top | 体系的拓扑文件 |
MD Solvation adds water molecules and ions to the original ligand-bound structure.
Input receptor topology file, can be generated by the GMX Receptor Parameterization module.
Input receptor structure file, can be generated by the GMX Receptor Parameterization module.
Input receptor parameter (compressed) file, can be generated by the GMX Receptor Parameterization module.
Input ligand structure (compressed) file, can be generated by the GMX Ligand Parameterization module.
Input ligand parameter (compressed) file, can be generated by the GMX Ligand Parameterization module.
Output total system topology file.
Output total system structure file.
Output system parameter (compressed) file.
Distance restraints, effective only when Disre is not “no”, formatted as follows:
[AtomIndex1] [AtomIndex2] [Type] [Index] [Type] [Low] [Up1] [Up2] [Factor]
Where AtomIndex1 and AtomIndex2 are atomic indices in system.gro; Type is the type of constraint applied, typically set to 1, see Table 1 for Type codes; Index is the calculation order; Low, Up1, Up2 are the distance limits between atoms, the distance between atoms in the Low to Up1 range is unrestricted but cannot exceed Up2, in nm; Factor is a multiplier, multiplying Factor by the “Disre Force Constant” gives the size of the restraint force, in kJ/mol/nm2.
For example:
10 16 1 0 1 0.0 0.3 0.4 1.0
10 46 1 1 1 0.0 0.3 0.4 1.0
16 22 1 2 1 0.0 0.3 0.4 2.5
Table 1: Three constraint types in GROMACS for atom pairs
| Type Code | Constraint Type | Application |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Complex NMR distance restraints | Set to 1 for non-bonded interactions when Disre Type is ensemble |
| 6 | Simple harmonic restraints | Set to 6 or 10 for intramolecular bonded interactions when Disre Type is simple |
| 10 | Piecewise linear/harmonic restraints | Set to 6 or 10 for intramolecular bonded interactions when Disre Type is simple |
Angle restraints limit the angle between two pairs of atoms, effective only when Disre is not “no”, formatted as follows:
[AtomIndex1] [AtomIndex2] [AtomIndex3] [AtomIndex4] [Type] [Theta0] [Force Constant] [Multiplicity]
Where AtomIndex1-AtomIndex2 is the first pair of atom indices; AtomIndex3-AtomIndex4 is the second pair of atom indices; Type is not used here, defined as 1; Theta0 is the constrained angle in degrees; Force Constant is the constraint force constant in kJ/mol; Multiplicity is the multiplicity.
For example:
2642 2643 2635 2652 1 67.0 1500 1
Dihedral restraints, effective only when Disre is not “no”, formatted as follows:
[AtomIndex1] [AtomIndex2] [AtomIndex3] [AtomIndex4] [Type] [Label] [Phi] [dPhi] [KFactor] [Power]
Where AtomIndex1-AtomIndex4 are the atomic indices composing the dihedral; Type is always 1; Label is not used; Phi is the reference angle, dPhi is the angle value beyond the reference angle in degrees; KFactor is a factor, multiplying KFactor by the “Disre Force Constant” gives the size of the restraint force in kJ/mol/rad2; Power is not used.
For example:
2642 2643 2635 2652 1 67.0 1500 1
The constraint potential functions are as follows:
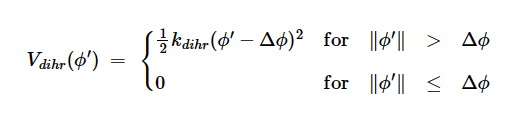
Where Φ’ is the reference angle Phi, ΔΦ is the value beyond the reference angle dPhi, and K_dihr is the size of the restraint force KFactor.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| system.gro | Molecular coordinate file of the system |
| system_itp.tar.gz | Force applied to fix atomic positions during system equilibrium simulation |
| system.top | Topology file of the system |

通过计算平衡模拟轨迹的均方根偏差(RMSD,Root Mean Square Deviation)和均方根波动(RMSF,Root Mean Square Fluctuation),从而分析结构的稳定性和结构变化情况。
MD模拟后得到的路径文件,可以在**GMX MD Run (GMX2023)模块或者AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023)**模块中获取。
选择分析类型:RMSD或者RMSF(可多选)。
选择需要计算的组别。
自定义需要计算的残基编号,连续参数可用“-”表示,不连续残基用逗号隔开,例如:1-10,15。
自定义需要计算的原子编号,用逗号隔开,例如:CA,O,H。与Custom Resid是交集关系。
索引文件,可由Membrane Solvation模块得到。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| rmsd_result.csv | 所选组别的RMSD的CSV文件 |
| rmsd_result.png | 所选组别的RMSD的PNG文件 |
| rmsd_result.xvg | 所选组别的RMSD的XVG文件 |
| rmsf_*.csv | 所选组别的RMSF的CSV文件 |
| rmsf_*.png | 所选组别的RMSF的PNG文件 |
| rmsf_*xvg. | 所选组别的RMSF的XVG文件 |
| bfac.pdb | PDB中的B-Factor一列为原子RMSF值通过公式<Δr²> = 3B/(8π²)转换得到。 |
By calculating the Root Mean Square Deviation (RMSD) and Root Mean Square Fluctuation (RMSF) of equilibrium simulation trajectories, the stability and structural changes of the system can be analyzed.
The path file obtained after MD simulation, which can be obtained from the GMX MD Run (GMX2023) module or the AlphaAutoMD (GMX2023) module.
Select the type of analysis: RMSD or RMSF (multiple selections possible).
Select the group to be calculated.
Custom residue numbers to be calculated, continuous parameters can be represented by “-”, non-continuous residues are separated by commas, for example: 1-10,15.
Custom atom numbers to be calculated, separated by commas, for example: CA, O, H. This intersects with Custom Resid.
Index file obtained from the Membrane Solvation module.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| rmsd_result.csv | CSV file of RMSD for the selected group |
| rmsd_result.png | PNG file of RMSD for the selected group |
| rmsd_result.xvg | XVG file of RMSD for the selected group |
| rmsf_*.csv | CSV file of RMSF for the selected group |
| rmsf_*.png | PNG file of RMSF for the selected group |
| rmsf_*xvg. | XVG file of RMSF for the selected group |
| bfac.pdb | The RMSF values are converted to B-factor values by the formula<Δr^2>=3B/(8π^2). |
传统分子生成模型无法限制特定骨架,限制了分子生成在结构优化中的应用,Scaffold Constrained Generation是一种骨架限制的生成模型,可以限制骨架,指定优化部位,特异性的生成全新分子库。
小分子骨架结构文件,SDF格式。结构中用星号*表示骨架结构上需要连接新结构片段的位置,如下图所示(可使用WeDraw进行结构编辑):
使用WeDraw生成小分子结构文件,SDF格式。
输入小分子SMILES格式字段:
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CN3CCN(CC3)C)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CC=C5
期望生成的分子数目。
最终输出文件的文件名称,默认为scg_results.sdf。
生成优化后的分子库的sdf文件scg_results.sdf。
Traditional molecular generation models cannot restrict specific scaffolds, limiting the application of molecular generation in structure optimization. Scaffold Constrained Generation is a scaffold-constrained generation model that can restrict scaffolds, specify optimization sites, and generate a new molecular library with specificity.
Small molecule scaffold structure file in SDF format. The structure uses an asterisk ‘*’ to indicate the positions on the scaffold structure where new structure fragments need to be connected, as shown in the following figure (WeDraw can be used for structure editing).
Generate small molecule structure file using WeDraw, in SDF format.
Input small molecule in SMILES format:
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CN3CCN(CC3)C)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CC=C5
The desired number of molecules to generate.
The file name for the final output file, default is scg_results.sdf.
The optimized molecular library is saved in an SDF file named scg_results.sdf.
De novo Generation (Moses)是基于深度学习的分子生成模块,实现了多种主流的分子生成模型,包括字符级循环神经网络,变分自编码器,以及对抗自编码器。
分子生成模型,目前包含以下几种:
char_rnn:Character-level Recurrent Neural Network(CharRNN)字符级循环神经网络。
vae:Variational Autoencoder(VAE)变分自编码器。
aae:Adversarial Autoencoder(AAE)对抗自编码器。
期望生成的分子数目。
采样随机数。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| result.sdf | 生成sdf格式分子库。 |
| result.csv | 生成smiles格式分子库,写入csv文件中,首行列名smiles。 |
De novo Generation (Moses) is a deep learning-based molecular generation module that implements various mainstream molecular generation models, including character-level recurrent neural networks, variational autoencoders, and adversarial autoencoders.
Molecular generation model, currently includes the following:
The desired number of molecules to generate.
The sampling random number.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result.sdf | Generated molecular library in SDF format. |
| result.csv | Generated molecular library in SMILES format, written to a CSV file with the column name “smiles”. |

ProteinMPNN是一种基于深度学习的蛋白质序列设计方法,在天然蛋白质骨架上,ProteinMPNN的序列恢复率为52.4%,而Rosetta为32.9%。在训练过程中加入噪声可以提高蛋白质结构模型的序列恢复率,并且产生的序列可以更稳健地编码它们的结构。X射线晶体学、低温电镜和功能研究也证明了ProteinMPNN的广泛实用性和高准确性,它成功挽救了以前用Rosetta或AlphaFold设计失败的蛋白质单体、环状同源多聚体、四面体纳米颗粒和目标结合蛋白等。
在ProteinMPNN的基础上,Exscientia提出了一种针对抗体结构进行优化的微调逆折叠模型AbMPNN,该模型在抗体序列恢复和结构稳健性方面优于通用蛋白质模型,尤其在超可变区CDR-H3环上有显著改进。
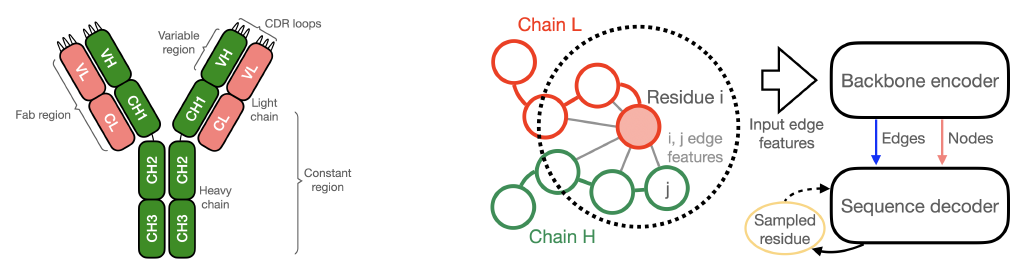
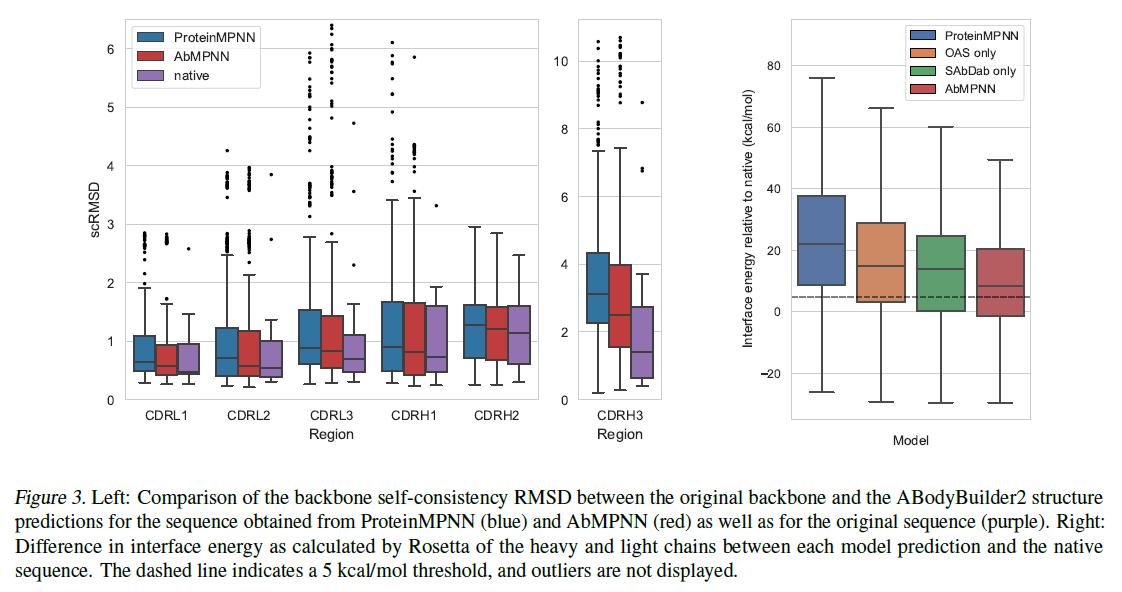
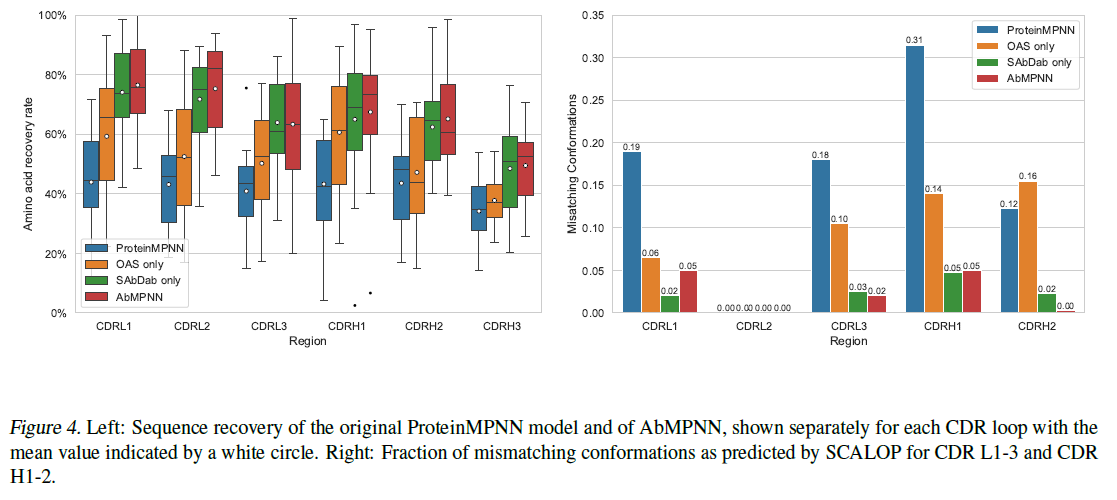
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式。
指定需要设计的链,多条链用空格分割,例如:‘A,B’。
输出设计的序列数目。
氨基酸采样温度,T=0.0表示取argmax,T>>1.0表示随机采样。建议的取值为0.1、0.15、0.2、0.25、0.3。较高的值会导致更多的多样性。
设计残基模式:固定(Fix,指定下一步Position中的残基在设计时保持不变)或者设计(Design,指定下一步Position中的残基可进行设计而其他未指定残基在设计时保持不变)。默认:Fix。
可选参数,设置氨基酸序号,对设置的氨基酸根据’Position Type’选项进行固定或设计。当参数Chain设置为’A,C’ 时,此参数如果设置为 ‘1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 23 25, 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 40’ 意味着对A中的残基1 2 3…25和链C中的残基10 11 12…40进行固定或设计。
注意:这里的氨基酸序号是从1开始,而不是PDB文件中带有的氨基酸序号。同一条链的氨基酸序号用空格分隔,不同链的氨基酸用逗号分隔。
可选参数,指定在生成的结果序列中不许出现的氨基酸种类。
可选参数,可指定设计时参考的模式。具体含义如下:
Homomer:基于同源多聚体进行序列设计;
soluble:基于可溶蛋白模型进行序列设计,即SolMPNN,仅使用可溶蛋白数据进行训练的MPNN模型。
antibody:基于抗体优化模型AbMPNN进行序列设计,AbMPNN是使用抗体结构数据对ProteinMPNN模型进行微调得到的模型。
以上模式都不选择时,会使用默认的ProteinMPNN模型,即使用PDB数据库的全部蛋白结构训练的模型。
MPNN预测的每个位置的概率:0为不进行预测,1为是进行预测。
输出结果文件为seqs/result.fasta,里面包含最终设计的序列。
其中序列名称:
Score:设计残基的概率评分,通常分值越小越好。概率评分是设计残基平均概率的负对数(-logP),因此评分越小意味着平均概率值越大。
Global Score:序列中所有残基的整体概率评分,通常分值越小越好。概率评分是设计残基平均概率的负对数(-logP),因此评分越小意味着平均概率值越大。
seq_recovery:序列恢复率(与原序列的相似程度),0-1之间,越高表示与原序列越相似
ProteinMPNN is a deep learning-based protein sequence design method that achieves a sequence recovery rate of 52.4% on natural protein scaffolds, compared to 32.9% for Rosetta. Adding noise during the training process can improve the sequence recovery rate of the protein structural model, and the resulting sequences can more robustly encode their structures. X-ray crystallography, cryo-electron microscopy, and functional studies have also demonstrated the wide applicability and high accuracy of ProteinMPNN, which has successfully rescued previously failed protein monomers, cyclic homooligomers, tetrahedral nanoparticles, and target-binding proteins designed using Rosetta or AlphaFold.
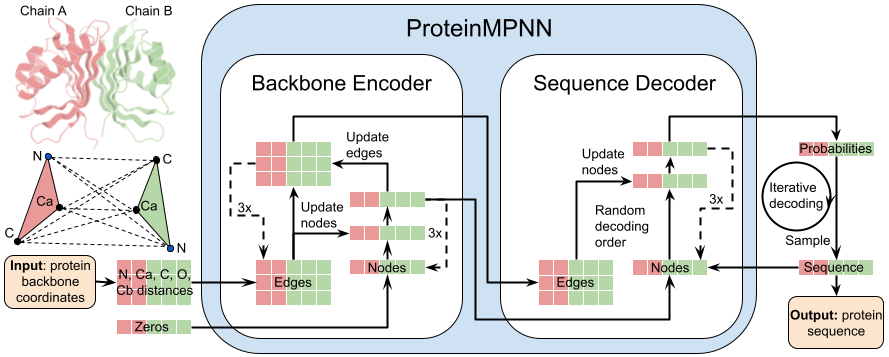
On top of ProteinMPNN, Exscientia has introduced a fine-tuning inverse folding model called AbMPNN specifically tailored for optimizing antibody structures. This model outperforms general protein models in antibody sequence recovery and structural robustness, particularly showing significant improvements in the highly variable CDR-H3 loop region.



Protein structure file in PDB format.
Specify the chain to be designed, multiple chains are separated by spaces, for example: ‘A,B’.
Output the number of sequences designed.
Amino acid sampling temperature, T=0.0 means argmax, T>>1.0 means random sampling. The suggested values are 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, 0.3. Higher values result in more diversity.
Residue Design Mode: Fixed (Fix, specifying that the residues in the next Position step remain unchanged during design) or Design (Design, specifying that the residues in the next Position step can be designed while other unspecified residues remain unchanged during design). Default: Fix.
Optional parameter to set the amino acid sequence number for fixing or designing amino acids based on the ‘Position Type’ option. When the parameter Chain is set to ‘A C’, if this parameter is set to ‘1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 23 25, 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 40’, it means that residues 1 2 3…25 in chain A and residues 10 11 12…40 in chain C are fixed or designed.
Note: The amino acid sequence numbers here start from 1, not the amino acid numbers in the PDB file. Amino acid sequence numbers of the same chain are separated by spaces, while amino acids from different chains are separated by commas.
Optional parameter specifying the types of amino acids that are not allowed to appear in the generated sequence.
Optional parameter specifying the reference mode for design. Specific meanings are as follows:
Homomer: Sequence design based on homologous oligomers;
use_soluble_mode: Sequence design based on soluble protein models, namely SolMPNN, the MPNN model trained exclusively on soluble protein data.
antibody_design: Sequence design based on the antibody optimization model AbMPNN, the model obtained by fine-tuning the ProteinMPNN model using antibody structure data.
When none of the above options are selected, the default ProteinMPNN model will be used, which is trained on all protein structures from the PDB database.
Probability of each position predicted by MPNN: 0 for no prediction, 1 for prediction.
The output file is seqs/result.fasta and contains the final design sequence.
Where the sequence name:
Score: This is the probability score for designed residues, where a lower score is generally better. The probability score is the negative logarithm (-logP) of the average probability of the designed residues, so a lower score indicates a higher average probability value.
Global Score: This is the overall probability score for all residues in the sequence, where a lower score is generally better. The probability score is the negative logarithm (-logP) of the average probability of the designed residues, so a lower score indicates a higher average probability value.
seq_recovery: the sequence recovery rate (the degree of similarity to the original sequence) is between 0 and 1, the higher the higher the similarity to the original sequence

FASTA File是一个指定FASTA文件的模块,可以用于其他模块的输入。会对FASTA文件的有效性进行判断。
上传FASTA文件
输出一个对应的FASTA文件,会对文件的有效性进行判断。
FASTA File is a module for specifying fasta file which could used for other modules input.
input FASTA file
Generate a corresponding FASTA file and validate its effectiveness.
AlphaShape(简称AlphaS)是一种构象表征与识别算法,可以基于分子的三维空间形状和药效团等药学特征比较进行高通量的虚拟筛选,可以最大化区分海量化合物中与已知活性分子相似的活性化合物(筛选的化合物库分子可使用AlphaConf进行构象生成)。也可用于蛋白质结构域匹配以指导蛋白质设计。
通过创造性地在高斯函数表征方式之上融合深度学习技术,AlphaShape虚拟筛选的计算精度已经领先同超越主流商业算法(例如Schrodinger的Phase,OpenEye的ROCS),在DUD-E标准数据集的测试中,虚拟筛选的AUC值达到了0.837(对比Phase与ROCS的0.663及0.696)。
通过采用高性能计算(HPC)技术,特别是NVIDIA的GPU加速技术,目前在搜索或筛选速度上都领先同领域商业软件。以小分子化合物筛选为例,使用一块GPU卡,数小时即可筛完全世界所有的现货商业化合物库的数千万分子,一天可高通量虚拟筛选上亿个化合物分子。
目前已被多家合作药企用于虚拟筛选并成功发现生物活性分子。目前已被合作药企用于虚拟筛选并成功发现生物活性分子。
除了高精度之外,AlphaShape 还充分利用了GPU的能力。 一张GPU卡每天可以筛选大约 5000万种化合物。
输入查询分子文件,SDF格式
小分子的构象库文件,由AlphaConf模块产生,AC.GZ格式
小分子的片段库文件,由AlphaConf模块产生,AUX.GZ格式
输出和每个查询分子相似度排名前n个分子,默认100。
是否对输入的查询分子产生3D构象,True 表示生成,当输入分子是2D结构时可用,False表示不生成,直接使用输入分子的3D结构。
输出最终相似度命中化合物的文件名称,SDF格式,默认文件名为hits.sdf
输入查询分子文件,SDF格式
系统内置的小分子化合物数据库,可多选。
输出和每个查询分子相似度排名前n个分子,默认100。
是否对输入的查询分子产生3D构象,True 表示生成,当输入分子是2D结构时可用,False表示不生成,直接使用输入分子的3D结构。
输出最终相似度命中化合物的文件名称,SDF格式,默认文件名为hits.sdf
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| result.csv | 相似度值信息,包含查询分子名称与库中分子名称。 |
| hits.sdf | 筛选相似度最高的n个化合物。多个查询分子时,这个文件是多个查询分子命中化合物合并去重后的结果。 |
| result/AA-173-40757587.sdf | 查询分子对应的命中化合物。每个查询分子都会生成一个对应的包含top n个命中化合物的文件 |
其中result.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| querymol | 查询分子化合物名称 |
| confdb | 化合物库名称 |
| molname | 命中化合物名称 |
| Total Similarity | 3D相似度值 |
AlphaShape (AlphaS for short) is a conformation representation and recognition algorithm that enables high-throughput virtual screening based on the three-dimensional spatial shape and pharmacophoric features of molecules. It maximizes the differentiation of active compounds similar to known active molecules from a large number of compounds (the molecules in the compound library for screening can be generated using AlphaConf). It can also be used for protein domain matching to guide protein design.
By creatively integrating deep learning technology on top of Gaussian function representation, AlphaShape’s virtual screening computational accuracy has surpassed and outperformed mainstream commercial algorithms (such as Schrodinger’s Phase, OpenEye’s ROCS). In testing on the DUD-E standard dataset, the AUC value of virtual screening reached 0.837 (compared to Phase and ROCS at 0.663 and 0.696).

By employing high-performance computing (HPC) technology, especially NVIDIA’s GPU acceleration technology, AlphaShape currently leads in search or screening speed compared to commercial software in the field. For example, in small molecule compound screening, using a single GPU card, it is possible to screen tens of millions of molecules in commercial compound libraries worldwide in a few hours, and conduct high-throughput virtual screening of billions of compound molecules in a day.
It has been used by several collaborative pharmaceutical companies for virtual screening and successful discovery of bioactive molecules. In addition to high accuracy, AlphaShape fully leverages the capabilities of GPUs. A single GPU card can screen approximately 50 million compounds per day.
Input file of query molecules in SDF format.
File of conformation libraries for small molecules, generated by the AlphaConf module, in AC.GZ format.
File of fragment libraries for small molecules, generated by the AlphaConf module, in AUX.GZ format.
Output the top N molecules ranked by similarity to each query molecule, default is 100.
Whether to generate 3D conformations for the input query molecules. True for generation, useful when the input molecules are in 2D structure; False for direct use of the input molecules’ 3D structures.
File name for the final hit compounds based on similarity, in SDF format, default file name is hits.sdf.
Input file of query molecules in SDF format.
System’s built-in small molecule compound database, multiple selections allowed.
Output the top N molecules ranked by similarity to each query molecule, default is 100.
Whether to generate 3D conformations for the input query molecules. True for generation, useful when the input molecules are in 2D structure; False for direct use of the input molecules’ 3D structures.
File name for the final hit compounds based on similarity, in SDF format, default file name is hits.sdf.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result.csv | Information on similarity values, including query molecule names and library molecule names. |
| hits.sdf | Top N screened compounds based on similarity. For multiple query molecules, this file is the merged and deduplicated result of top N hit compounds for each query molecule. |
| result/AA-173-40757587.sdf | Hit compounds corresponding to the query molecule. A file containing the top N hit compounds is generated for each query molecule. |
In result.csv, the information includes:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| querymol | Query molecule name |
| confdb | Compound library name |
| molname | Hit compound name |
| Total Similarity | 3D similarity value |

File Convert是基于RDKit对分子文件格式之间进行转换的模块。支持的输入文件格式为:SD(.sdf、.sd)、SMILES(.smi、.csv、.tsv、.txt)、PDB(.pdb)、mol2。支持的输出文件格式为:SD(.sdf、.sd)、SMILES(.smi)、PDB(.pdb)。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。
输出文件名。更改文件扩展名。
输入SDF文件转换成SMILES格式output.smi文件。
The File Convert module is designed to convert molecular file formats using RDKit. Supported input file formats include: SD (.sdf, .sd), SMILES (.smi, .csv, .tsv, .txt),PDB(.pdb), mol2. Supported output file formats include: SD (.sdf, .sd), SMILES (.smi), PDB (.pdb).
Input file containing the molecular structure in SDF or SMILES format.
Name of the output file. Change the file extension as needed.
Convert the input SDF file to SMILES format and save it as output.smi.

Molecular Docking (AutoDock-GPU) 是一种用于分子对接模拟的工具,主要用于预测分子之间的结合模式和相互作用,评估对接的能量和结合亲和力等信息。同时,它还可用于计算和比较多个分子之间的结合能力,广泛应用于药物分子的筛选、设计和优化。AutoDock-GPU 是 AutoDock 4.2.6 的 OpenCL 和 CUDA 加速版本。它利用可并行的遗传算法(LGA),通过在多个计算单元上并行处理配体-受体的结合构象,大幅提升计算效率。
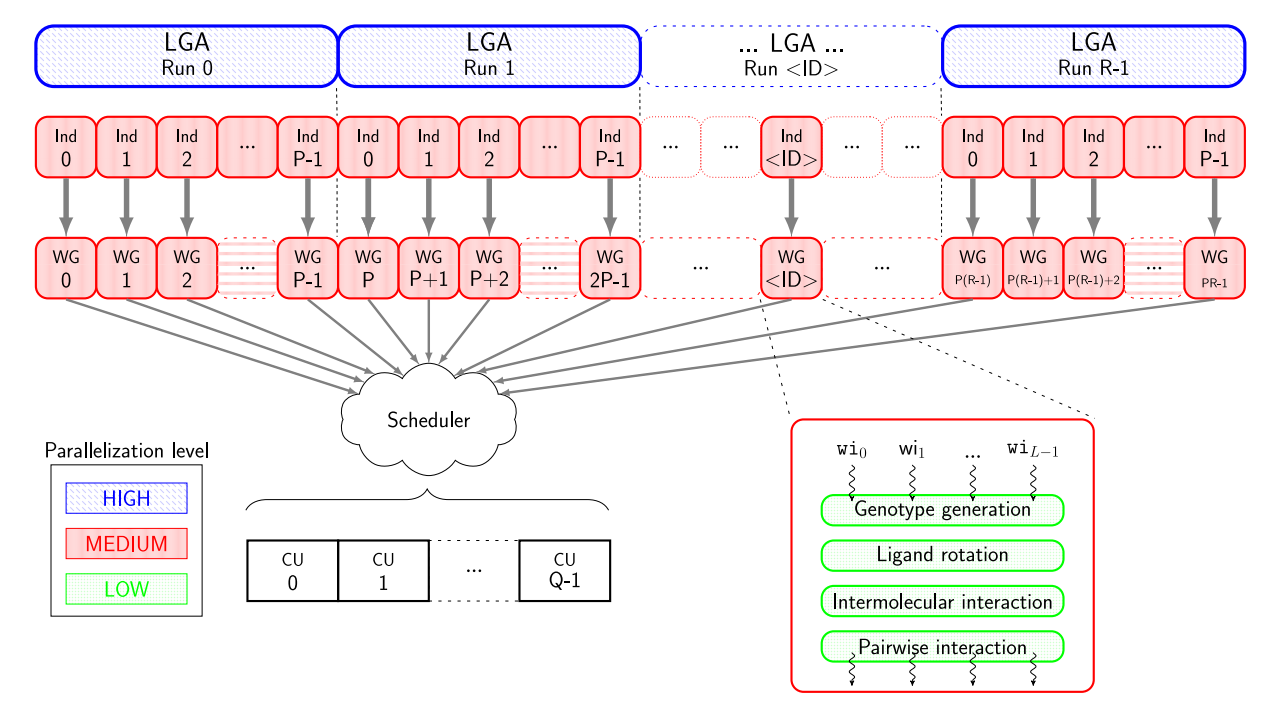
AutoDock 使用一种半经验的自由能力场来评估对接模拟中的构象。该力场基于大量具有已知结构和抑制常数(Ki)的蛋白质-抑制剂复合物进行参数化,评分过程分为两步:
AutoDock的自由能评分函数(ΔG)包含六种成对能量项(V),以及结合时构象熵的损失(ΔSconf):
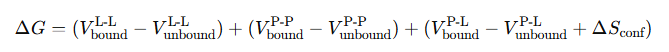
其中,L 表示“配体”,P 表示“蛋白质”。
AutoDock力场中的成对能量项V包括以下四种主要相互作用,每种相互作用的组成和贡献如下:
成对能量的计算公式如下:
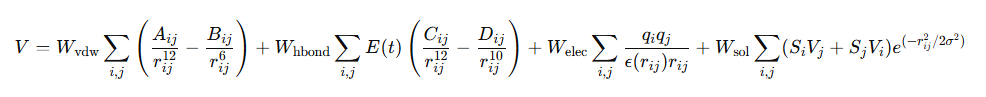
其中,第一项为范德华相互作用,第二项为方向性氢键作用,第三项为静电作用,第四项为溶剂化效应。
该模块存在两种对接方法Rigid Docking和Flexible Docking。
上传受体蛋白文件,格式为PDB。受体蛋白被定义为刚性。
上传配体文件,当配体为一个时允许上传SDF,PDB和MOL格式,当配体为多个时(≤2000)只允许上传SDF格式。注:配体需要是三维结构,可用Small Molecule Minimization模块转换。
配体结合口袋中心xyz坐标,用空格分开,例如 10.734 2.033 -11.537。
配体结合口袋大小,用空格分开,例如 24 22 32。
指定打分前TopN小分子作为输出文件,默认为100。
每个配体与受体对接时得到的总构象数,默认为50。
每个配体与蛋白对接后输出的构象数目,默认为10。该数值应当≤“Run Pose”。
配体可旋转键大于该值时被剔除,默认为50。
配体分子量大于该值时被剔除,默认为1000。
上传受体蛋白文件,格式为PDB。受体蛋白被设置为局部柔性,柔性残基由Flexible Residues定义。
定义柔性残基其格式为"链名称":“氨基酸名称”“氨基酸编号”,每个氨基酸用逗号隔开,例如:“A:ALA1221,A:MET1211,A:LEU1140”。柔性氨基酸必须在口袋附近。
其他参数相同
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Scores.csv | 提交所有配体(≤2000)与受体的打分文件。 |
| output_complex_topn.tar.gz | TopN小分子中每个配体与受体打分最高的复合物构象PDB文件压缩包。 |
| output_complex_top10.pdb | 展示每个配体与受体打分最高的前十复合物构象文件(仅展示作用,不适用于后续计算)。 |
| output_ligand_topn.sdf | 对接打分topN的配体SDF文件。 |
| TopNScores.csv | 按照每个配体与受体对接打分最高的排序得到打分文件。 |
| output_complex_topn_pdbqt.tar.gz | TopN小分子中每个配体与受体打分最高的复合物构象PDBQT文件压缩包。 |
其中TopNScores.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Ligand | 对接配体名称。 |
| Mol Index | 对接配体在原始SDF文件的编号。 |
| Score(kcal/mol) | 对接打分,该值越低说明结合亲和力越高。 |
| Complex File Name | 复合物文件名称。 |
Molecular Docking (AutoDock-GPU) is a tool used for molecular docking simulations, primarily aimed at predicting the binding modes and interactions between molecules, as well as evaluating docking energies and binding affinities. It can also be used to calculate and compare the binding capabilities of multiple molecules, making it widely applicable in the screening, design, and optimization of drug molecules. AutoDock-GPU is an OpenCL and CUDA accelerated version of AutoDock 4.2.6. It significantly enhances computational efficiency by utilizing a parallelized genetic algorithm (LGA) to process ligand-receptor binding conformations across multiple computing units.

AutoDock employs a semi-empirical free energy force field to evaluate conformations in docking simulations. This force field is parameterized based on a large number of protein-inhibitor complexes with known structures and inhibition constants (Ki). The scoring process is divided into two steps:
The free energy scoring function (ΔG) in AutoDock includes six pairwise energy terms (V), as well as the loss of conformational entropy upon binding (ΔSconf):
Here, L represents “ligand” and P represents “protein.”
The pairwise energy terms V in the AutoDock force field include four main types of interactions, each with its composition and contribution as follows:
The formula for calculating pairwise energy is as follows:
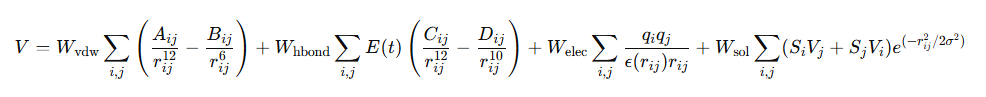
Where the first term represents the Van der Waals interactions, the second term represents the directional hydrogen bonding, the third term represents electrostatic interactions, and the fourth term represents solvation effects.
Upload the receptor protein file in PDB format. The receptor is set to be rigid.
Upload the ligand file. When there is only one ligand, SDF, PDB, and MOL formats are allowed. When there are multiple ligands (≤2000), only SDF format is allowed. Note: The ligand needs to be in a three-dimensional structure, which can be converted using the Small Molecule Minimization module.
The xyz coordinates of the center of the binding pocket, separated by spaces. For example, 10.734 2.033 -11.537.
The size of the binding pocket, separated by spaces. For example, 24 22 32.
Specify the topN ligands to be output as the scoring file, with the default being 100.
The total number of poses obtained for each ligand-receptor docking, with the default being 50.
The number of output poses obtained for each ligand-receptor docking, with the default being 50.(The number of output poses is less than the number of running poses.)
Molecules with rotatable bonds greater than this value will be ignored,with the default being 50.
Molecules with molecular weight greater than this value will be ignored,with the default being 1000.
Upload the receptor protein file in PDB format. The receptor is set to be locally flexible and the flexible residues are defined by Flexible Residues.
The flexible residues are defined in the format of "Chain:“Residue name”“Residue ID”, with each amino acid separated by a comma. For example, “A:ALA1221,A:MET1211,A:LEU1140”. Flexible amino acids must be located near the docking pocket.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Scores.csv | Scores.csv with all ligand (≤2000) docking with receptor. |
| output_complex_topn.tar.gz | output_complex_topn.tar.gz containing the top-scoring complex conformation (PDB format) for each ligand and receptor in TopN small molecules. |
| output_complex_top10.pdb | Show the top 10 complex conformation files output_complex_top10.pdb for each ligand-receptor with the highest score (The function is shown only and is not applicable to subsequent calculations). |
| output_ligand_topn.sdf | Each ligand docked with the top 100 scoring complexes. |
| TopNScores.csv | Sort the scoring file according to the highest score for each ligand-receptor docking. |
| output_complex_topn_pdbqt.tar.gz | output_complex_topn_pdbqt.tar.gz containing the top-scoring complex conformation (PDBQT format) for each ligand and receptor in TopN small molecules. |
其中TopNScores.csv包括信息如下:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Ligand | Ligand Name |
| Mol Index | Number of the ligand in the original SDF file. |
| Score(kcal/mol) | In the docking score, the lower the value, the higher the binding affinity. |
| Complex File Name | Complex file name |
Metabolism Site Prediction模块为预测小分子被CYP450代谢的代谢位点。模型对小分子的每个原子进行评估被代谢的可能性,并通过打分排序。支持的小分子输入文件格式为:SD(.sdf、.sd)、SMILES(.smi)。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| molecule_1_atomNumbers.png | 原子编号图片 |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms.png | P450代谢酶(CYP3A4)预测结果图 |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms1A2.png | P450代谢酶(CYP1A2)预测结果图 |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms2C19.png | P450代谢酶(CYP2C19)预测结果图 |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms2C9.png | P450代谢酶(CYP2C9)预测结果图 |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms2D6.png | P450代谢酶(CYP2D6)预测结果图 |
| results.csv | 评估被代谢可能性的csv文件 |
| results.html | 评估被代谢可能性的html文件 |
其中results.html,包含如下信息:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Rank | 排序 |
| Atom | 原子类型和序号 |
| Score | 最终的打分,也是排序的标准,打分越低,排名越前,被代谢的可能性越高。 |
| Energy | 能量值,基于DFT计算以及原子匹配得到的原子激活的能量值。是打分Score的重要参考项。 |
| Accessibility | 原子到分子中心的相对拓扑距离。 |
The Metabolism Site Prediction module is used to predict the metabolism sites of small molecules by P450 enzymes. The model evaluates the likelihood of each atom in the small molecule being metabolized and ranks them based on scores. Supported input file formats for small molecules include: SD (.sdf, .sd) and SMILES (.smi).
Input file containing the small molecule structure in SDF or SMILES format.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| molecule_1_atomNumbers.png | Image showing atom numbering |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms.png | Prediction results for P450 enzyme (CYP3A4) |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms1A2.png | Prediction results for P450 enzyme (CYP1A2) |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms2C19.png | Prediction results for P450 enzyme (CYP2C19) |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms2C9.png | Prediction results for P450 enzyme (CYP2C9) |
| molecule_1_heteroAtoms2D6.png | Prediction results for P450 enzyme (CYP2D6) |
| results.csv | CSV file evaluating the likelihood of metabolism |
| results.html | HTML file evaluating the likelihood of metabolism |
The results in results.html include the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Rank | Ranking |
| Atom | Atom type and number |
| Score | Final score, also the sorting criterion. The lower the score, the higher the ranking, indicating a higher likelihood of metabolism. |
| Energy | Energy value based on DFT calculations and atomic activation energy obtained from atomic matching. An important reference for the score. |
| Accessibility | Relative topological distance of the atom to the molecular center. |

Toxic Fragment Identification模块用于识别小分子的毒效片段,从文献中收集了大量的毒效片段构成毒效片段库,利用子结构匹配方法,实现对化合物库中每个分子进行毒效片段匹配,并通过不同颜色区分。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。
得到化合物库中与小分子毒效片段匹配的output.xlsx文件,并通过不同颜色区分毒性片段。
output.xlsx包括如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Smiles | 分子的smiles |
| Image | 分子的化学结构图片,包括毒效片段的匹配。 |
| MolName | 分子名称 |
| Smarts | 毒效片段的Smarts |
| Bad_type | 毒性类型 |
| BadNum | 毒性数量 |
| Literature | 参考文献 |
| Colors | 毒效片段匹配颜色 |
Bad_type毒性类型,包括如下:
Potential_electrophilic_agents,Inpharmatica,Idiosyncratic_toxicity_(RM_formation),Non-genotoxic_carcinogenicity,Endocrine_disruption,MLSMR,AlphaScreen-HIS-FHs,AlphaScreen-FHs,Nonbiodegradable_compounds,Acute_Aquatic_Toxicity,AlphaScreen-GST-FHs,LINT,Promiscuity,LD50_mo_oral,Reactive,_unstable,_toxic,Skin_sensitization,Chelating_agents,Genotoxic_carcinogenicity,_mutagenicity,Developmental_and_mitochondrial_toxicity,PAINS,Hepatotoxicity_Nephrotoxicity,SMARTSfilter,Hepatotoxicity,Toxtree,Myelotoxicity
The Toxic Fragment Identification module is used to identify toxic fragments of small molecules. A large library of toxic fragments has been collected from the literature. Using a substructure matching method, this module matches toxic fragments in each molecule of the compound library and distinguishes them with different colors.
Small molecule structure file in SDF or SMILES format.
Obtain the output.xlsx file that matches toxic fragments in the compound library with the small molecule, color-coding the toxic fragments.
The output.xlsx includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Smiles | Molecular SMILES |
| Image | Chemical structure image of the molecule, including the matched toxic fragments. |
| MolName | Molecule name |
| Smarts | Toxic fragment SMARTS |
| Bad_type | Type of toxicity |
| BadNum | Number of toxicities |
| Literature | Literature reference |
| Colors | Colors for toxic fragment matches |
The Bad_type toxicity types include:
Potential_electrophilic_agents, Inpharmatica, Idiosyncratic_toxicity_(RM_formation), Non-genotoxic_carcinogenicity, Endocrine_disruption, MLSMR, AlphaScreen-HIS-FHs, AlphaScreen-FHs, Nonbiodegradable_compounds, Acute_Aquatic_Toxicity, AlphaScreen-GST-FHs, LINT, Promiscuity, LD50_mo_oral, Reactive,_unstable,_toxic, Skin_sensitization, Chelating_agents, Genotoxic_carcinogenicity,_mutagenicity, Developmental_and_mitochondrial_toxicity, PAINS, Hepatotoxicity_Nephrotoxicity, SMARTSfilter, Hepatotoxicity, Toxtree, Myelotoxicity

AlphaRNA是Wecomput开发的程序,可以有效地共同优化CAI(Codon Adaption Index)和MFE(Minimum free energy)/AUP(Average unpaired probability)。AlphaRNA提供了一种基于DFA图进行Motif约束的方法,该方法在不明显增加计算量的同时,隐式地将约束加入到密码子优化地过程中以获得更好的密码子偏好性和更稳定的二级结构,以优化其表达量和半衰期、抗体滴度等。可以支持任意数量和长度的序列。

所需要优化的编码区氨基酸序列,例如:
MDIDPYKEFGATVELLSFLPSDFFPSVRDLLDTASALYREALESPEHCSPHHTALRQAIL
要限制(避免出现在优化后序列中)的酶切位点,可多选。
需要限制的Motif序列,可指定多个,可手动输入不在列表中的新序列,使用空白符分隔。
CAI的lambda系数,正值越大能够调大结果中的CAI, 可设置多个,可为负值,负值越大表示越降低CAI。
GC碱基比例(GCR)的lambda系数,正值越大能够调大结果中的GCR, 可设置多个,可为负值,负值越大表示越降低GCR。
输出结果文件为result.csv,包含信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| lambda_cai | CAI的lambda系数 |
| lambda_gcr | GCR的lambda系数 |
| full_sequence | 优化后的序列 |
| CAI | 密码子适应指数 |
| AUP | 平均未配对率 |
| GCR | GC碱基比例 |
| MFE Structure | 最小自由能二级结构 |
| dG(MFE)[kcal/mol] | 最小自由能 |
AlphaRNA is a Wecomput-developed program that efficiently co-optimize both Codon Adaption Index (CAI) and Minimum free energy (MFE)/Average unpaired probability (AUP).It provides a method for motif-constrained codon optimization based on DFA graphs, which implicitly incorporates constraints into the codon optimization process to achieve better codon preferences and more stable secondary structures, optimizing expression levels, half-life, antibody titers, etc., without significantly increasing computational complexity. This method supports sequences of arbitrary numbers and lengths.

The amino acid sequence of the coding region that needs to be optimized, for example:
MDIDPYKEFGATVELLSFLPSDFFPSVRDLLDTASALYREALESPEHCSPHHTALRQAIL
The restriction enzyme cleavage sites to be limited (avoided in the optimized sequence) can be selected multiple times.
Motif sequences that need to be restricted, multiple can be specified, and new sequences that are not in the list can be manually entered, separated by blanks.
The lambda coefficient of CAI, the larger the positive value, the larger the CAI in the result, you can choose multiple. It can be negative, and the more negative the value is, the greater the reduction in CAI.
The lambda coefficient of GCR, the larger the positive value, the larger the GCR in the result, you can choose multiple. It can be negative, and the more negative the value is, the greater the reduction in GCR.
The output file is result.csv and contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| lambda_cai | Lambda coefficients of CAI |
| lambda_gcr | Lambda coefficients of GCR |
| full_sequence | The optimized sequence |
| CAI | Codon adaption index |
| AUP | Average unpaired probability |
| GCR | The proportion of GC bases |
| MFE Structure | The minimum free energy structure |
| dG(MFE)[kcal/mol] | The value of the minimum free energy |

Extract Fv Sequence是从抗体全长序列中提取Fv区序列的工具。
抗体全长序列文件,FASTA格式
指定输出抗体Fv序列文件的名称,FASTA格式
得到仅含Fv区域的序列FASTA文件Fv.fasta。
Extract Fv Sequence is a tool used to extract the Fv region sequence from the full-length antibody sequence.
The full-length antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
Specify the name of the output file for the antibody Fv sequence in FASTA format.
Obtain a FASTA file, Fv.fasta, containing only the Fv region sequence.

使用动态编程算法预测单链RNA或DNA序列的二级结构,返回单一的RNA最佳结构和最低自由能。
长度为n的序列上的结构由相等长度的括号和点组成的字符串表示。i和j之间的碱基对用“(”在i和“)”在在j位置表示,未配对的碱基用“.”表示。如下为RNA二级结构表示方式。
(((..((((...)))).)))
与之对应的RNA二级结构图为:
RNA序列文件,FASTA格式。
输出文件名称。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| output.txt | RNA序列二级结构的文本文件,其中包括序列、最佳二级结构以及与其对应的最小自由能(kcal/mol)。 |
| SeqN_2D.png | 第N条RNA序列对应的二级结构图 |
The dynamic programming algorithm is used to predict the secondary structure of a single-stranded RNA or DNA sequence, returning the best RNA structure and its minimum free energy.
The structure on a sequence of length n is represented by a string consisting of equal-length parentheses and dots. Base pairs between i and j are represented by “(” at position i and “)” at position j, while unpaired bases are represented by “.”. Below is an example of an RNA secondary structure representation.
(((..((((...)))).)))
The corresponding RNA secondary structure diagram is shown in the image above.

RNA sequence file in FASTA format.
Name of the output file.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| output.txt | Text file of the RNA sequence’s secondary structure, including the sequence, best secondary structure, and the corresponding minimum free energy (kcal/mol). |
| SeqN_2D.png | Secondary structure diagram for the Nth RNA sequence |
RNA 3D Structure Prediction是基于Rosetta中的RNA结构建模算法是基于现有RNA晶体结构的短片段(1到3个核苷酸)的组装,其序列与目标RNA的子序列相匹配。RNA片段组装(Fragment Assembly of RNA, FARNA)算法是一个蒙特卡洛过程,由一个低分辨率的基于知识的能量函数指导。然后,这些模型可以在全原子力场下进一步完善,以产生更真实的结构。由此产生的能量也能更好地区分原生构象和非原生构象。该计算方法被称为FARFAR(RNA片段组装与全原子细化)。
从5’到3’的序列。通常用小写字母,但大写字母是可以接受的,并且会被转换。支持多条序列同时生成3D结构。
点括号表示RNA二级结构文件。可以通过模块“RNA Secondary Structure Prediction”获取。
RNA二级结构文件,文本格式,例如:
>a
auauccccauauaucccauauauccccgcgcgucccgcgc
........((((((...))))))....(((((...))))) ( -6.60)
>b
aaauccccauauaucccauauauccccgcgcgucccgcgc
........((((((...))))))....(((((...))))) ( -6.60)
得到RNA结构的PDB文件S_000001.pdb。
RNA 3D Structure Prediction utilizes the RNA structure modeling algorithm in Rosetta, which assembles short fragments (1 to 3 nucleotides) based on existing RNA crystal structures, matching the sequence to a subsequence of the target RNA. The Fragment Assembly of RNA (FARNA) algorithm is a Monte Carlo process guided by a low-resolution, knowledge-based energy function. These models can then be further refined under a full-atom force field to produce more realistic structures. The resulting energy can better distinguish native conformations from non-native conformations. This computational method is known as FARFAR (Fragment Assembly of RNA with Full Atom Refinement).
Sequence(s) from 5’ to 3’. Typically in lowercase letters, but uppercase letters are acceptable and will be converted. Supports generating 3D structures for multiple sequences simultaneously.
RNA secondary structure file in dot-bracket notation. This can be obtained using the “RNA Secondary Structure Prediction” module.
Example RNA secondary structure file in text format:
>a
auauccccauauaucccauauauccccgcgcgucccgcgc
........((((((...))))))....(((((...))))) ( -6.60)
>b
aaauccccauauaucccauauauccccgcgcgucccgcgc
........((((((...))))))....(((((...))))) ( -6.60)
Obtain the PDB file for the RNA structure as S_000001.pdb.

AlphaMHC是唯信计算为解决现有预测方法的已知问题而开发的下一代免疫原性预测算法,采用流行的NLP自然语言处理技术,全新的多模融合深度神经网络架构,整合了近10亿条公开及私有的与免疫原性相关的湿实验数据(包括亲和力数据、NGS数据、质谱数据等)进行训练,成功实现了从序列到临床免疫原性风险的端到端的预测,并通过上百条来自FDA、EMA的临床真实免疫原性数据(包括单/多特异性抗体和重组蛋白等)进行验证,AlphaMHC能够准确区分免疫原性的高低,ROC-AUC达0.87,准确性超过80%(部分测试集高达91%),表现出比现有方法显著更优的预测性能,是已知唯一一个可以得到临床数据验证的算法。
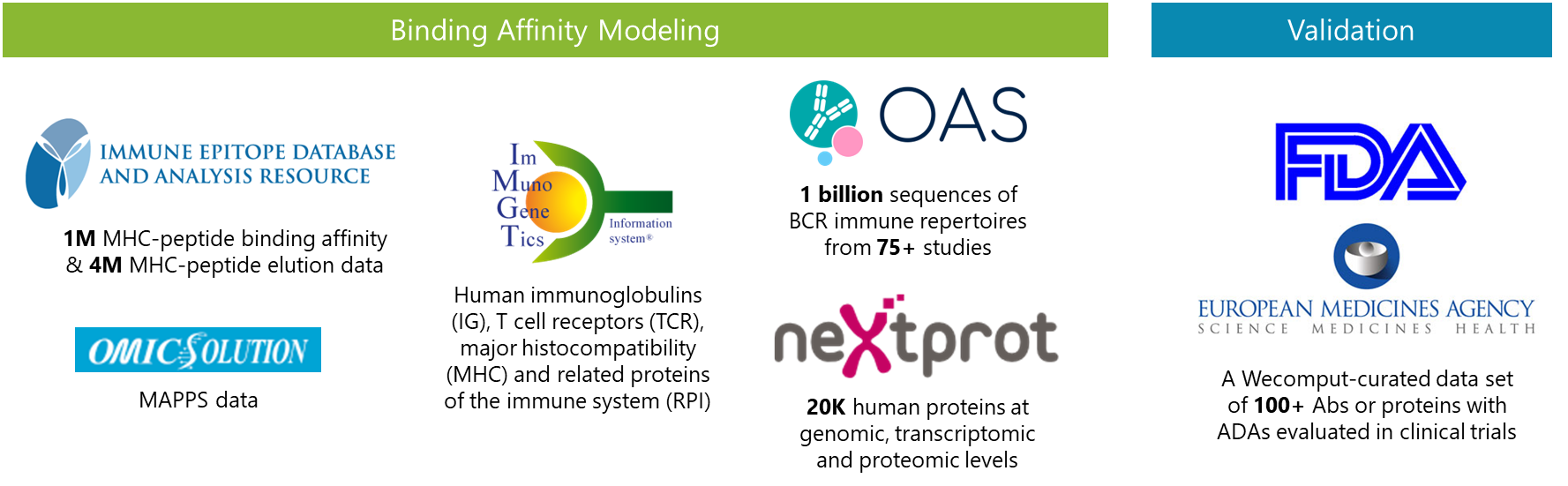
蛋白序列文件,FASTA格式。支持多条链以及多分子模式。
请注意按下面的规则来书写序列名,因为目前免疫原性风险的评分是以整个分子为单位的,链名会影响到程序区分同个分子的多条链,并影响对于分子总的风险评级(risk per molecule),但不影响对链的TCE的识别。
对于多条链的分子,序列名称应写为:分子名.链名,".“之前是分子名,”.“之后是链名,同个分子的不同链,只要”."之前的分子名保持一致就可以了,链名随意,顺序不限。
例如,下面mol1是常见的单抗,mol2是多抗:
>mol1.A
XXXXXXX
>mol1.B
XXXXXXX
>mol2.L1
XXXXXXX
>mol2.H1
XXXXXXX
>mol2.L2
XXXXXXX
>mol2.H2
XXXXXXX
预测HLA等位基因型。
rep:32个代表性等位基因型,适用于一般人群。
all:用于训练的所有非冗余人类等位基因型(1166个)。
一般推荐使用默认的"rep",因为免疫原性的风险评分(risk)是基于rep的代表性HLA来确定的。
导出每个 HLA 等位基因的结合亲和力曲线图,展示了与每条蛋白质链的 N 端到 C 端的所有15肽的结合亲和力。注意:即使“HLA Allotypes”选项设置为全部,也只会绘制代表性 HLA的曲线。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| score_immunogenicity_risk.csv | 该结果展示了预测的每个分子的免疫原性风险(自动将同个分子的多条链的预测的潜在T细胞表位的结果进行汇总后综合评估所得)。 |
| detail_tce_of_chains.csv | 该结果评估可以进行定向改造的HLA呈递表位,以降低免疫原性。 |
| BAProfile_of_mol.chain.png | 不同HLA亚型与每条链的不同位置的亲和力的分布情况,更精细的展示了不同HLA的亲和力的差异。 从左到右的分布图表示从其中一条蛋白质链的N末端移动到C末端的15聚肽窗口的结合亲和力。 即使“HLA同种异型”选项设置为“全部”,也只会包括代表性的HLA等位基因。 |
| Heatmap_of_mol.chain.png | 每个肽与代表性HLA之间结合亲和力的热图。Z-score是pAffinity,值越大(浅色)意味着预测结合越强。 |
其中score_immunogenicity_risk.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein_Id | 蛋白序列名称 |
| Risk | 预测的分子整体风险评估,高风险的分子为high,否则为low。 |
| Score | 表位总长度,是整体风险评估的重要依据。 |
| TCE_Sequences | 表位序列 |
其中detail_tce_of_chains.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Sequences | 蛋白序列名称 |
| TCE | 每条链的相对的高风险的T细胞表位 |
| Alleles_Number | 递呈的HLA亚型数 |
| Alleles | 递呈的HLA亚型 |
| Min_Affinity | 亲和力最小值 |
| Median_Affinity | 亲和力中位数 |
| Max_Affinity | 亲和力最大值 |
AlphaMHC is the next-generation immunogenicity prediction algorithm developed by Wecomput using popular NLP natural language processing technology to address known issues with existing prediction methods. It employs a new multi-modal fusion deep neural network architecture and is trained on nearly one billion publicly available and private wet-lab experimental data related to immunogenicity, including affinity data, NGS data, mass spectrometry data, etc. It successfully achieves end-to-end prediction of immunogenicity risk from sequence to clinical application and is validated using hundreds of clinical real-world immunogenicity data from FDA and EMA, including mono/multi-specific antibodies and recombinant proteins. AlphaMHC accurately distinguishes high and low immunogenicity with an ROC-AUC of 0.87 and an accuracy of over 80% (up to 91% on some test sets), demonstrating significantly better predictive performance than existing methods. It is the only known algorithm that has been validated with clinical data.

Protein sequence file in FASTA format.Multiple chains and multi-molecule modes are supported. For multi-molecule mode, the sequence name rule is: molecule name. chain name, for example:
>mol1.A
XXXXXXX
>mol1.B
XXXXXXX
>mol2.A
XXXXXXX
>mol2.B
XXXXXXX
Prediction of HLA allelic types. “rep” is recommended, which is faster.
rep: 32 representative allelic types, applicable to the general population.
all: all non-redundant human allele types used for training (1166).
Export binding affinity curve graphs for each HLA allele, showing the binding affinity of all 15 peptides from the N- to C-terminus for each protein chain. Note: Even if the “HLA Allotypes” option is set to all, curves will only be plotted for representative HLAs.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| score_immunogenicity_risk.csv | The result displays the immunogenicity risk for each predicted molecule (which is obtained by aggregating the predicted potential T cell epitopes from multiple chains of the same molecule and evaluating the overall risk). |
| detail_tce_of_chains.csv | The results evaluated HLA presentation epitopes that could be targeted for engineering to reduce immunogenicity. |
| BAProfile_of_mol.chain.png | The distribution profile of the binding affinity between each chain and the 32 representative HLAs. The profile from left to right represents the binding affinity of a 15-mer pepetide window moving from the N terminus to C terminus of one of the protein chain. PS. only representative HLA alleles will be included even if the “HLA allotypes” option is set to “all”. |
| Heatmap_of_mol.chain.png | The heat map of the binding affinity between each peptide and the representative HLAs. The Z-score is pAffinity, greater value (light color) means stronger binding by prediction. |
score_immunogenicity_risk.csv contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein_Id | Protein sequence name |
| Risk | The overall risk assessment for the predicted molecule, with “high” indicating high-risk molecules and “low” indicating low-risk molecules. |
| Score | The total length of the epitopes, which is an important basis for overall risk assessment. |
| TCE_Sequences | The epitope sequences |
detail_tce_of_chains.csv contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Sequences | Protein sequence name |
| TCE | The relative high risk T cell epitope of each strand. |
| Alleles_Number | Number of HLA subtypes presented |
| Alleles | The HLA subtypes presented |
| Min_Affinity | Affinity minimum |
| Median_Affinity | Median affinity |
| Max_Affinity | Affinity maximum |

基于知名的DNAWorks算法对氨基酸或DNA序列进行密码子优化(基于PCR的基因合成的自动寡核苷酸设计)。
整个基因组序列的可用性极大地增加了蛋白质靶标的数量,其中许多需要在原始DNA来源以外的细胞中过度表达。合成基因可以针对表达进行优化,并构建为易于突变操作而无需考虑亲本基因组。然而,合成基因的设计和构建,尤其是那些编码大蛋白质的基因,可能是一个缓慢、困难和令人困惑的过程。该模块通过基于PCR的方法自动设计用于基因合成的寡核苷酸。

蛋白或者核酸的序列文件,FASTA格式。
序列类型,蛋白或者核酸。
几种常用生物的密码子频率基于每个密码子在相应生物基因组的蛋白质编码区中出现的次数。大肠杆菌有两种选项:基于所有基因的标准频率(E. coli),或在指数增长期间以高水平表达的 II 类基因频率(ecoli2),通常建议用后者。
退火温度参数为一组合成寡核苷酸设定了理想的退火温度。 可接受的退火温度范围在 58 至 70°C 之间。
寡核苷酸长度参数限制了一组合成寡核苷酸中的任何一个可以达到的核苷酸长度。可接受的寡核苷酸长度范围在 30 到 999 nt 之间。
密码子频率阈值参数设置:密码子用于反向翻译蛋白质序列到DNA的截断值。
寡核苷酸的浓度。寡核苷酸必须在100 uM (1E-4 M)和1 nM (1E-9 M)之间。
一价阳离子(Na+,K+)的浓度。单价阳离子必须在10到1000mM之间。
镁离子的浓度。镁离子浓度必须在0到200mM之间。
执行中生成的寡核苷酸的数量,每个作业的最大运行次数为999次。
检查是否为热力学平衡由内而外合成法 (thermodynamically balanced inside-out, TBIO)输出模式。
要求被排除在合成基因的蛋白质编码区之外的位点,每个位点之间用逗号隔开,例如Aatll,Acc65I。
支持非简并位点共117种:
AatII,Acc65I,AclI,AcuI,AfeI,AflII,AgeI,AlwI,ApaI,ApaLI,AscI,AseI,AsiSI,AvrII,BamHI,BbsI,BbvCI,BbvI,BccI,BceAI,BciVI,BclI,BfrBI,BfuAI,BglII,BmgBI,BmrI,BmtI,BpmI,BpuEI,BsaI,BseRI,BseYI,BsgI,BsiWI,BsmAI,BsmBI,BsmFI,BsmI,BspCNI,BspDI,BspEI,BspHI,BspMI,BsrBI,BsrDI,BsrGI,BsrI,BssHII,BssSI,BstBI,BstZ17I,BtgZI,BtsI,ClaI,DraI,EagI,EarI,EciI,EcoRI,EcoRV,FauI,FokI,FseI,FspI,HgaI,HindIII,HpaI,HphI,KasI,KpnI,MboII,MfeI,MluI,MlyI,MscI,NaeI,NarI,NcoI,NdeI,NgoMIV,NheI,NotI,NruI,NsiI,PacI,PaeR7I,PciI,PleI,PmeI,PmlI,PsiI,PspOMI,PstI,PvuI,PvuII,SacI,SacII,SalI,SapI,SbfI,ScaI,SfaNI,SfoI,SmaI,SnaBI,SpeI,SphI,SspI,StuI,SwaI,TliI,TspRI,XbaI,XhoI,XmaI,ZraI
支持简并位点共62种:
AccI,AflIII,AhdI,AleI,AlwNI,ApoI,AvaI,BanI,BanII,BcgI,BglI,BlpI,Bme1580I,Bpu10I,BsaAI,BsaBI,BsaHI,BsaJI,BsaWI,BsaXI,BsiEI,BsiHKAI,BslI,BsoBI,Bsp1286I,BsrFI,BstAPI,BstEII,BstF5I,BstXI,BstYI,Bsu36I,BtgI,Cac8I,DraIII,DrdI,EaeI,EcoNI,EcoO109I,HaeII,HincII,Hpy188III,MmeI,MslI,MspA1I,MwoI,NlaIV,NspI,PflFI,PflMI,PpuMI,PshAI,RsrII,SexAI,SfcI,SfiI,SgrAI,SmlI,StyI,Tth111I,XcmI,XmnI
自定义被排除在合成基因的蛋白质编码区之外的位点,自定义位点格式必须包含名称和序列,名称和序列之间用空格隔开,多个位点时用逗号隔开,例如:Aatll GACGTC,Acc65I GGTACC。
输出结果文件的名称。
输出结果文件为result.txt,包含优化后的密码子序列以及序列相关信息。
Codon optimization can be used for optimizing codons (i.e., the genetic code) for the automated oligonucleotide design of gene synthesis based on PCR. The availability of whole genome sequences has greatly increased the number of protein targets, many of which need to be overexpressed in cells outside of their native DNA source. Synthetic genes can be optimized for expression and constructed to be easily mutagenized without consideration for the parental genome. However, designing and constructing synthetic genes, particularly those encoding large proteins, can be a slow, difficult, and confusing process. This module automatically designs oligonucleotides for gene synthesis using a PCR-based approach.
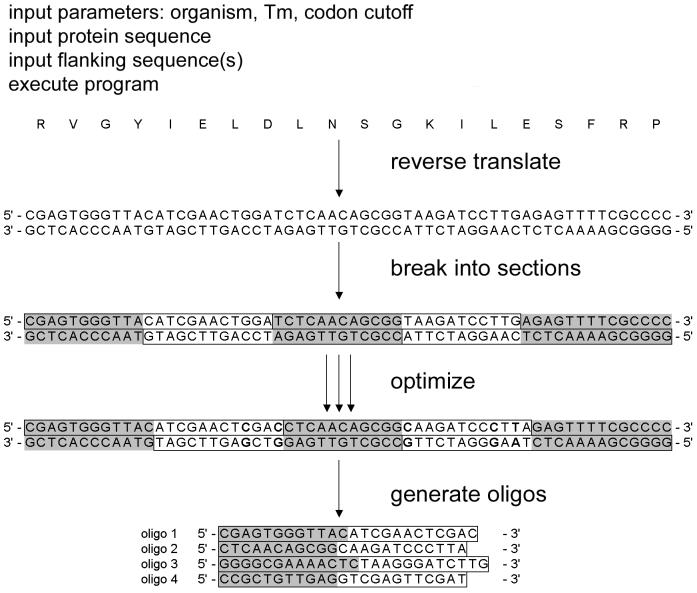
Protein or nucleotide sequences in FASTA format
Sequence files of proteins or nucleic acids
The codon frequencies of several commonly used organisms are based on the number of times each codon appears in the protein-coding regions of the respective organism’s genome. For Escherichia coli, there are two options: the standard frequency based on all genes (E. coli), or the frequency of Class II genes expressed at high levels during exponential growth (ecoli2), which is usually recommended to be used.
The annealing temperature parameter sets the ideal annealing temperature for a set of synthetic oligonucleotides. Acceptable annealing temperatures range from 58 to 70°C.
The oligonucleotide length parameter limits the achievable nucleotide length of any one of a set of synthetic oligonucleotides. Acceptable oligonucleotide lengths range from 30 to 999 nt.
Codon Frequency Threshold Parameter Settings: Codon cutoff value for backtranslation of protein sequences to DNA.
Concentration of oligonucleotides. Oligonucleotides must be between 100 uM (1E-4 M) and 1 nM (1E-9 M).
Concentration of monovalent cations (Na+, K+). Monovalent cations must be between 10 and 1000 mM.
concentration of magnesium ions. Magnesium ion concentration must be between 0 and 200mM.
The number of oligos generated in an execution, with a maximum of 999 runs per job.
Check if it is thermodynamically balanced inside-out (TBIO) output mode.
Sites required to be excluded from the protein coding region of the synthetic gene, separated by commas between each site, example: Aatll,Acc65I.
Support a total of 117 non-degenerate sites:
AatII,Acc65I,AclI,AcuI,AfeI,AflII,AgeI,AlwI,ApaI,ApaLI,AscI,AseI,AsiSI,AvrII,BamHI,BbsI,BbvCI,BbvI,BccI,BceAI,BciVI,BclI,BfrBI,BfuAI,BglII,BmgBI,BmrI,BmtI,BpmI,BpuEI,BsaI,BseRI,BseYI,BsgI,BsiWI,BsmAI,BsmBI,BsmFI,BsmI,BspCNI,BspDI,BspEI,BspHI,BspMI,BsrBI,BsrDI,BsrGI,BsrI,BssHII,BssSI,BstBI,BstZ17I,BtgZI,BtsI,ClaI,DraI,EagI,EarI,EciI,EcoRI,EcoRV,FauI,FokI,FseI,FspI,HgaI,HindIII,HpaI,HphI,KasI,KpnI,MboII,MfeI,MluI,MlyI,MscI,NaeI,NarI,NcoI,NdeI,NgoMIV,NheI,NotI,NruI,NsiI,PacI,PaeR7I,PciI,PleI,PmeI,PmlI,PsiI,PspOMI,PstI,PvuI,PvuII,SacI,SacII,SalI,SapI,SbfI,ScaI,SfaNI,SfoI,SmaI,SnaBI,SpeI,SphI,SspI,StuI,SwaI,TliI,TspRI,XbaI,XhoI,XmaI,ZraI
Support a total of 62 degenerate sites:
AccI,AflIII,AhdI,AleI,AlwNI,ApoI,AvaI,BanI,BanII,BcgI,BglI,BlpI,Bme1580I,Bpu10I,BsaAI,BsaBI,BsaHI,BsaJI,BsaWI,BsaXI,BsiEI,BsiHKAI,BslI,BsoBI,Bsp1286I,BsrFI,BstAPI,BstEII,BstF5I,BstXI,BstYI,Bsu36I,BtgI,Cac8I,DraIII,DrdI,EaeI,EcoNI,EcoO109I,HaeII,HincII,Hpy188III,MmeI,MslI,MspA1I,MwoI,NlaIV,NspI,PflFI,PflMI,PpuMI,PshAI,RsrII,SexAI,SfcI,SfiI,SgrAI,SmlI,StyI,Tth111I,XcmI,XmnI
Custom sites that to be excluded from the protein coding region(s) of the synthetic gene. The custom site format must contain the name and sequence, separated by a space between the name and sequence, and separated by a comma when there are multiple sites. Example: Aatll GACGTC,Acc65I GGTACC.
Specify output file name
The output file is result.txt, which contains the optimized codon sequence and sequence-related information.

PDB Mutation是用于突变PDB格式的蛋白质结构并返回突变后的结构。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式
突变文本文件,包含突变信息,格式如下:
KA100N;KA101T;
KA100T;
第一字母代表的是原始残基,第二个字母代表PDB文件中待突变残基所在的链名,后面的数字代表残基位置编号,最后一个字母代表突变后的残基。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| mutation_result.tar.gz | 所有突变体PDB结构的压缩包文件 |
| mutation_001.pdb | 每个突变体的结构PDB文件 |
PDB Mutation is a tool used to mutate protein structures in PDB format and return the mutated structures.
Structure file of the protein in PDB format.
Mutation text file containing mutation information in the following format:
KA100N;KA101T;
KA100T;
The first letter represents the original residue, the second letter represents the chain name of the residue to be mutated in the PDB file, the following number represents the residue position number, and the last letter represents the mutated residue.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| mutation_result.tar.gz | Compressed file containing all mutated PDB structures |
| mutation_001.pdb | PDB file for each mutated structure |

通过解析美国(https://patentcenter.uspto.gov/)和国际(https://patentscope2.wipo.int/search/en/search.jsf)专利附带的序列清单(Sequence Listing)文件,里面存储了专利权利要求的序列,但是人工很难读取,该模块可以从中一次性批量提取专利中所有具有正式编号(SEQ ID NO.)的序列。
1. Sequence Listing文件下载
序列清单(Sequence Listing)文件内容示例:

用法:
(1)从专利网站搜索专利:
2. Image(OCR)
Image(OCR)是基于图像的蛋白质序列转换为3个字母编码或1个字母编码的序列。
注意:截图时请务必省略标题,类似下图。
专利文件,TXT或者XML格式。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| seq_list.csv | 记录所有序列信息的csv文件 |
| seq_list.fasta | 记录所有序列信息的fasta文件 |
其中seq_list.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| idx | 序列编号 |
| type | 序列类型,DNA/蛋白 |
| sequence | 序列信息 |
专利图片文件,PNG或者JPG格式
输出文件名称,默认为result.fasta
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| result.fasta | 专利图片转换成一个字母序列的FASTA文件 |
| result.txt | 包含图片文件的字符,转换成一个字母和三个字母的序列 |
By parsing the sequence listing files attached to U.S. (https://patentcenter.uspto.gov/) and international (https://patentscope2.wipo.int/search/en/search.jsf) patents, which store the sequences claimed in patents, it is difficult for humans to read them. This module can extract all sequences with official numbers (SEQ ID NO.) from the patents in bulk.
1. Sequence Listing File Download
Example content of a Sequence Listing file:

Usage:
(1) Search for patents on patent websites:


2. Image(OCR)
Image(OCR) is for converting protein sequences from images into three-letter or one-letter coded sequences.
Note: When taking screenshots, please be sure to omit the headers, similar to the image below.

Patent file in TXT or XML format.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| seq_list.csv | CSV file recording all sequence information |
| seq_list.fasta | FASTA file recording all sequence information |
The seq_list.csv includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| idx | Sequence number |
| type | Sequence type, DNA/protein |
| sequence | Sequence information |
Patent image file in PNG or JPG format
Output file name, default is result.fasta
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result.fasta | FASTA file of one-letter sequences converted from patent images |
| result.txt | Characters from image files converted into one-letter and three-letter sequences |

基于TCGA和GTEx等数据,检索指定基因在肿瘤和正常组织的表达情况,统计并绘制肿瘤细胞、肿瘤组织、正常组织等的基因表达差异,帮助药物靶点选择、研发立项和决策。
基因名称,输入的基因名须对应HGNC(https://www.genenames.org/)的"Approved Symbol"。例如:在HGNC搜索“PD-1”,得知“approved symbol”为“PDCD1”,后者“PDCD1”是该程序需要的输入。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| tcga_expression.jpeg | 不同疾病中该基因分别在肿瘤、正常、癌旁组织的表达量分布。 |
| tcga_tissue_expression.jpeg | 不同组织中该基因分别在肿瘤、正常、癌旁组织的表达量分布。 |
Plot gene expression in normal and tumor tissues, based on databases TCGA and GTEx. It retrieves the expression of specified genes in tumors and normal tissues, counts and maps the gene expression differences of tumor cells, tumor tissues, and normal tissues, etc., to help drug target selection and decision-making.
The entered gene name must correspond to the “Approved Symbol” of HGNC (https://www.genenames.org/). For example: search for “PD-1” in HGNC, and know that “approved symbol” is “PDCD1”, and the latter “PDCD1” is the input required by the program.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| tcga_expression.jpeg | The program will return the expression distribution of the gene in tumor, normal, and adjacent tissues in different disease. |
| tcga_tissue_expression.jpeg | The program will return the expression distribution of the gene in tumor, normal, and adjacent tissues in different tissues. |

Multiple Sequence Alignment 是多重序列比对模块,用于进化分析,绘制进化树,帮助对候选序列进行聚类、分析多样性等。
蛋白序列文件,FASTA格式。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| alignment.fasta | 多重序列进行比对后的FASTA文件 |
| alignment.png | 多重序列进行比对后的PNG文件 |
| newick.txt | 多重序列进行多样性分析的结果文件 |
| tree.png | 多重序列进化树图片 |
Multiple Sequence Alignment is a module for aligning multiple sequences, used for evolutionary analysis, drawing evolutionary trees, and aiding in clustering and analyzing diversity of candidate sequences.
Protein sequence file in FASTA format.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| alignment.fasta | FASTA file after aligning multiple sequences |
| alignment.png | PNG file after aligning multiple sequences |
| newick.txt | Evolutionary analysis result of multiple sequence |
| tree.png | Evolutionary trees picture of multiple sequence |

Structural Alignment是对两个蛋白质的三维结构进行叠合的工具。使用BLOSUM62矩阵和Needleman-Wunsch算法在两个序列之间执行全局配对比对,返回叠合后的蛋白结构,同时输出RMSD值。
参考蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式
需要叠合蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式
指定参考蛋白的链名,默认是A链
指定需要叠合蛋白的链名,默认是A链
指定输出叠合后的结构文件,PDB格式
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| result.csv | 参考蛋白与样本蛋白之间的RMSD值记录文件 |
| alignment_renumbering_pred.pdb | 叠合后的结构文件 |
其中result.csv包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Reference | 参考蛋白构象 |
| Sample | 需要叠合的蛋白构象 |
| RMSD | 叠合后的RMSD值 |
Structural Alignment is a tool for overlaying the 3D structures of two proteins. It performs a global pairwise alignment between two sequences using the BLOSUM62 matrix and the Needleman-Wunsch algorithm, returning the aligned protein structures and outputting the RMSD value.
Structure file of the reference protein in PDB format.
Structure file of the protein to be aligned in PDB format.
Specify the chain name of the reference protein, default is chain A.
Specify the chain name of the protein to be aligned, default is chain A.
Specify the output structure file after alignment in PDB format.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| result.csv | RMSD value record file between the reference protein and the sample protein |
| alignment_renumbering_pred.pdb | Aligned structure file |
The result.csv file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Reference | Conformation of the reference protein |
| Sample | Conformation of the protein to be aligned |
| RMSD | RMSD value after alignment |

PDB Insertion Removal模块用于去掉抗体PDB文件中的插入序列,因为某些计算工具不支持PDB中的插入序列。比如,20A改成20。
抗体结构文件,PDB格式。
得到去掉抗体中的插入序列的PDB文件prepared_insert.pdb。
The PDB Insertion Removal module is used to remove insertion sequences from antibody PDB files because some computational tools do not support insertion sequences in PDB files. For example, changing 20A to 20.
Antibody structure file in PDB format.
Obtain the PDB file prepared_insert.pdb with the insertion sequences removed from the antibody.

该模块用于预测蛋白质结构中的聚集倾向和蛋白质溶解度,通过考虑序列和结构来预测蛋白质中易聚集的位点,这对于球状蛋白质特别有用,其中容易聚集的位点可能埋藏在天然结构内并且序列不连续。通过考虑天然氨基酸的实验聚集倾向尺度,该方法可以准确预测蛋白质聚集倾向,也可用于预测构象紊乱中家族性突变的致病作用。任何已知或预测的蛋白质结构都是适用的,它具备其他基于序列的算法未考虑的特性,例如蛋白质动态波动和蛋白质序列中距离较远的残基的空间聚类,这对于从初始折叠状态准确预测蛋白质聚集非常重要。
底层算法Aggrescan3D(A3D)旨在预测蛋白质在其折叠状态下的聚集倾向。为了实现这个目标,A3D使用蛋白质的三维结构作为输入,这些结构可以通过X射线衍射、溶液NMR或建模方法得到,并以pdb格式表示。在分析之前,这些结构会经过能量最小化处理。该方法利用了实验得出的天然氨基酸内在聚集倾向尺度,并将这个尺度应用于蛋白质的三维结构中。在A3D方法中,结构中每个特定氨基酸的内在聚集倾向会受到其特定的结构环境的调节。聚集倾向是通过以每个残基Cα碳为中心的球形区域计算得出的。这为结构中每个氨基酸提供了一个独特的经过结构修正的聚集值(A3D分数),其公式如下:

其中:Aggi是球心处残基的内在聚集倾向;RSAi是其相对于溶剂暴露的表面积;Agge是包括在球体中的每个额外残基的内在聚集倾向,RSAe是其相对于溶剂暴露的表面积,dist是到中心残基i的距离。
蛋白的结构文件,PDB格式。如果没有已知结构,可以用结构预测模块预测。
输出结果包括:
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Aggregation Score (result_A3D.csv) | 蛋白结构中每个氨基酸聚集倾向和蛋白质溶解度的打分文件 |
| Structure (output.pdb) | 根据聚集倾向和蛋白质溶解度得到的结构文件,在PDB文件温度因子一栏填入计算得到的聚集度和溶解度数值 |
| result_A.png | A链中每个氨基酸对应的聚集度和溶解度打分值的png格式图片 |
| result_A.svg | A链中每个氨基酸对应的聚集度和溶解度打分值的svg格式图片 |
其中result_A3D.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| protein | 氨基酸残基折叠 |
| chain | 蛋白链名称 |
| residue | 氨基酸索引(PDB文件中) |
| residue_name | 氨基酸名称缩写(PDB文件中) |
| score | 聚集度和溶解度打分值,该数值为正代表氨基酸促进聚集,为负代表氨基酸促进溶解。 |
This module is used to predict the aggregation propensity and protein solubility in protein structures. By considering both sequence and structure, it predicts sites in proteins that are prone to aggregation, which is particularly useful for globular proteins where aggregation-prone sites may be buried within the native structure and not contiguous in sequence. By considering experimentally derived aggregation propensity scales of natural amino acids, this method accurately predicts protein aggregation propensity and can be used to predict the pathogenic effects of familial mutations in conformational disorders. Any known or predicted protein structure is applicable. It incorporates features not considered by other sequence-based algorithms, such as protein dynamic fluctuations and spatial clustering of residues that are distant in the protein sequence, which is crucial for accurately predicting protein aggregation from the initial folding state.
The underlying algorithm, Aggrescan3D (A3D), aims to predict the aggregation propensity of proteins in their folded states. To achieve this, A3D uses the protein’s 3D structure as input, which can be obtained through X-ray crystallography, solution NMR, or modeling methods, and is represented in PDB format. These structures undergo energy minimization before analysis. The method utilizes experimentally determined intrinsic aggregation propensity scales of natural amino acids and applies this scale to the protein’s 3D structure. In the A3D method, the intrinsic aggregation propensity of each specific amino acid in the structure is modulated by its specific structural environment. The aggregation propensity is calculated within a spherical region centered on the Cα carbon of each residue. This provides a unique, structurally corrected aggregation value (A3D score) for each amino acid in the structure.The calculation formula is as follows:

Where:
The structure file of the protein in PDB format. If the structure is not known, it can be predicted using the structure prediction module.
The output results include:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Aggregation Score (result_A3D.csv) | A scoring file for the aggregation propensity and protein solubility of each amino acid in the protein structure. |
| Structure (output.pdb) | Structure file obtained based on the aggregation propensity and protein solubility, with the calculated aggregation and solubility values filled in the temperature factor column of the PDB file. |
| result_A.png | A PNG format image showing the aggregation and solubility scores for each amino acid in chain A. |
| result_A.svg | An SVG format image showing the aggregation and solubility scores for each amino acid in chain A. |
The result_A3D.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| protein | Fold of the amino acid residue. |
| chain | Protein chain name. |
| residue | Amino acid index in the PDB file. |
| residue_name | Amino acid name abbreviation in the PDB file. |
| score | Aggregation and solubility score, where a positive value indicates promotion of aggregation and a negative value indicates promotion of solubility. |

Sequence Mutagenesis (Saturated)是用于枚举蛋白质序列指定位置饱和突变的所有可能性,生成所有对应突变的文本文件和突变体序列文件。
蛋白序列文件,FASTA格式。
突变位置,多个位置可以用逗号(,)隔开。
指定输出突变后的序列文件的名称,FASTA格式。
包含突变信息的文本文件的名称。
指定链名,生成带有链名的突变信息。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| mutated_seqs.fasta | 突变后的序列文件 |
| individual.txt | 突变文件信息,包含链信息 |
| mutated_polict.txt | 突变文件信息,不包含链信息 |
Sequence Mutagenesis (Saturated) is used to enumerate all possibilities of saturated mutations at specified positions in a protein sequence, generating text files with all corresponding mutations and mutated sequence files.
Protein sequence file in FASTA format.
Mutation locations, multiple positions can be separated by commas (,).
Specify the name of the output file containing the mutated sequence in FASTA format.
Name of the text file containing mutation information.
Specify the chain name to generate mutation information with chain names.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| mutated_seqs.fasta | Mutated sequence file after mutation. |
| individual.txt | Mutation file information with chain information. |
| mutated_polict.txt | Mutation file information without chain information. |

Mutation Format Conversion将突变文件中的突变信息加上链名,转换为适用于结构的格式。如将C20S改为CA20S。
突变文件,TXT格式
指定链名
将原本不带链名的转换为带有链名的突变文件individual.txt。
Mutation Format Conversion adds chain names to the mutation information in the mutation file, converting it into a format suitable for structures. For example, converting C20S to CA20S.
Mutation file in TXT format.
Specify the chain name.
Converts the original mutation file without chain names to a mutation file with chain names, named individual.txt.

对复合物界面区域进行单点或者多点的虚拟饱和突变,从而获得不同格式的突变文件以及突变后的Fasta文件。这为后续复合物之间的亲和力以及对突变体之间的结合自由能计算提供基础。
蛋白结构文件,PDB格式。
突变位点文件,JSON格式,一般由Complex Interface Analysis模块生成的json文件。
指定链名。
指定输出突变后的序列文件的名称。
指定输出突变文件的名称,不包含链信息。
指定输出突变文件的名称,包含指定链信息。
突变模式:
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| mutated_policy.txt | 突变文件信息,不包含链信息 |
| mutated_policy_with_chain.txt | 突变文件信息,包含链信息 |
| output_mutated_seqs.fasta | 突变后的序列文件 |
Virtual saturation mutagenesis is performed on single or multiple points in the interface region of a complex to generate mutation files in different formats and mutated Fasta files. This provides a basis for calculating the affinity between complexes and the binding free energy between mutants.
Protein structure file in PDB format.
Mutation site file in JSON format, typically generated by the Complex Interface Analysis module.
Specify the chain name.
Specify the name of the output file containing the mutated sequence.
Specify the name of the output mutation file without chain information.
Specify the name of the output mutation file with specified chain information.
Mutation mode:
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| mutated_policy.txt | Mutation file information without chain information. |
| mutated_policy_with_chain.txt | Mutation file information with chain information. |
| output_mutated_seqs.fasta | Mutated sequence file after mutation. |

Complex Interface Analysis模块是基于结构的分析蛋白质复合物相互作用界面的关键残基。
蛋白复合物结构文件,PDB格式
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| interaction_score.csv | 记录复合物不同链之间相互作用的能量的文件 |
| interface_residues.csv | 记录相互作用界面关键氨基酸的csv文件 |
| interface_residues.json | 记录相互作用界面关键氨基酸的json文件 |
其中interaction_score.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| PDB | 蛋白质复合物结构名称 |
| Group1 | 链名称 |
| Group2 | 链名称 |
| Interaction Energy | 相互作用能(kcal/mol) |
其中interface_residues.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Chain1_and_Chain2 | Chain1链和Chain2链之间相互作用的关键氨基酸,此处Chain1和Chain2为蛋白结构文件中的链名称。 |
The Complex Interface Analysis module is a structure-based analysis of key residues involved in the protein complex interaction interface.
Protein complex structure file in PDB format.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| interaction_score.csv | File recording the energy of interactions between different chains of the complex. |
| interface_residues.csv | CSV file recording key amino acids at the interaction interface. |
| interface_residues.json | JSON file recording key amino acids at the interaction interface. |
The interaction_score.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| PDB | Name of the protein complex structure. |
| Group1 | Chain name. |
| Group2 | Chain name. |
| Interaction Energy | Interaction energy (kcal/mol). |
The interface_residues.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Chain1_and_Chain2 | Key amino acids involved in the interaction between Chain1 and Chain2, where Chain1 and Chain2 are chain names in the protein structure file. |

Protein BLAST是蛋白Blast数据库,该数据库序列整合了GenPept、Swissprot、PIR、PDF、PDB、RefSeq等序列数据库。
蛋白序列文件,FASTA格式。
指定序列比对数据库类型:蛋白,抗体,或者CDR区域。
nr:蛋白Blast数据库。
oas:Observed Antibody Space,抗体Blast数据库。
cdr:CDR区域数据库,专利保护抗体数据库 。
输出结果文件为alignment.fasta,是系列对齐后的FASTA文件,可在WeSeq中查看。
Protein BLAST is a protein Blast database that integrates sequences from databases such as GenPept, Swissprot, PIR, PDF, PDB, RefSeq, and others.
Protein sequence file in FASTA format.
Specifies the sequence alignment database type: protein, antibody, or CDR region.
nr: Protein BLAST database.
oas: Observed Antibody Space, an antibody BLAST database.
cdr: CDR region database, a patent-protected antibody database.
The output result file is alignment.fasta, which is a FASTA file of the aligned sequences that can be viewed in WeSeq.

Sequence Mutagenesis (Directed) for Ab是根据模板抗体序列和描述突变的突变文件(json)批量生成突变抗体序列,通常突变文件由BLAST和MSA自动生成。这对于高通量抗体工程设计很有用。
抗体的序列文件,FASTA格式
突变文件,JSON格式
突变频率截断值,默认10,只针对突变频率超过截断值的氨基酸生成对应的突变信息。用于过滤掉低频率的突变氨基酸。
抗体编号类型:kabat,chothia,imgt以及none
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| gen.fr.fasta | 骨架区(frameworkregion,FR)FASTA文件 |
| gen.fr.mutations.txt | 骨架区(frameworkregion,FR)突变文件信息 |
| gen.cdr.fasta | 互补决定区(complementarity-determining region, CDR)FASTA文件 |
| gen.cdr.mutations.txt | 互补决定区(complementarity-determining region, CDR)突变文件信息 |
Sequence Mutagenesis (Directed) for Ab is a process that batch generates mutated antibody sequences based on a template antibody sequence and a mutation file (in JSON format) describing the mutations. The mutation file is typically generated automatically by BLAST and MSA. This is particularly useful for high-throughput antibody engineering design.
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
Mutation file in JSON format.
Mutation frequency cutoff value, default is 10. Only mutations with frequencies exceeding the cutoff value will generate corresponding mutation information. This is used to filter out low-frequency mutated amino acids.
Antibody numbering type: kabat, chothia, imgt, or none.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| gen.fr.fasta | FASTA file for the Framework Region (FR) |
| gen.fr.mutations.txt | Mutation file information for the Framework Region (FR) |
| gen.cdr.fasta | FASTA file for the Complementarity-Determining Region (CDR) |
| gen.cdr.mutations.txt | Mutation file information for the Complementarity-Determining Region (CDR) |

Mutation List Generation是基于一个原始序列,从经过序列比对后得到的序列(例如BLAST得到的同源序列)中提取每个位点出现过的所有突变(同源突变/共识突变),生成一个突变列表,并按位点统计突变的频率。
参考蛋白序列,FASTA格式
同源序列文件,一般由参考序列BLAST数据库后得到,FASTA格式
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| mutations.csv | 突变统计文件,包含每个位点的突变的类型及其百分比,CSV格式 |
| output.json | 突变统计文件,包含每个位点的突变类型及其频率,JSON格式 |
| mutations.txt | 突变文件,根据前面的突变统计信息生成,包含了野生型氨基酸、位置以及突变后氨基酸 |
其中mutations.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| WT | 野生型氨基酸 |
| Position | 突变位置 |
| Mutations and frequency | 突变氨基酸及其频率 |
Mutation List Generation is a process that extracts all mutations (homologous mutations/consensus mutations) occurring at each position from a sequence obtained through sequence alignment (e.g., homologous sequences obtained from BLAST), based on an original sequence. It generates a mutation list and calculates the frequency of mutations at each position.
Reference protein sequence in FASTA format.
Homologous sequence file typically obtained by BLASTing the reference sequence against a database, in FASTA format.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| mutations.csv | Mutation statistics file containing the type and percentage of mutations at each position, in CSV format |
| output.json | Mutation statistics file containing the type and frequency of mutations at each position, in JSON format |
| mutations.txt | Mutation file generated based on the mutation statistics information, containing the wild-type amino acid, position, and mutated amino acid |
The mutations.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| WT | Wild-type amino acid |
| Position | Mutation position |
| Mutations and frequency | Mutated amino acid and its frequency |

蛋白质溶解度不良阻碍了许多治疗和工业上有用的蛋白质的生产。通过实验手段增加溶解度的努力往往成功率低,并且通常会降低生物活性。使用序列信息来计算预测蛋白的溶解度,可以大大降低实验研究的成本。
本模块使用CamSol、SoluProt和Protein-Sol算法进行溶解度预测。其中:
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| protein-sol_score_show.png | Protein–Sol方法下,针对Folding Propensity和Charge两个指标的分布图。横坐标Windows为每21个氨基酸为一个片段组别。 |
| result_per_chain.csv | 三种方法下,每条链的预测溶解度结果。 |
| result_per_residue.csv | Protein–Sol方法下,不同蛋白区域对应的溶解度情况(该结果仅针对第一条链)。 |
其中result_per_chain.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein ID | 蛋白序列名称 |
| Solubility (CamSol) | CamSol方法预测的溶解度。越大表示溶解性越好,大于1时,表示溶解性很好;当分数小于-1时,溶解性很差。 |
| Solubility (Soluprot) | Soluprot方法预测的溶解度,值越大表示溶解性越好 |
| Solubility (Protein-Sol) | Protein-Sol方法预测的溶解度,值越大表示溶解性越好 |
| pI | 蛋白等电点 |
其中result_per_residue.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ID | 蛋白序列名称 |
| Kyte-Doolittle Hydropathy | 氨基酸亲水指数是一个描述其支链的亲水性或疏水性程度大小的值。亲水指数越小代表该氨基酸段的亲水性越强。 |
| Folding Propensity | 该数值描述蛋白折叠程度,该数值越大,越不利于蛋白溶解。 |
| Entropy | 熵是在某种分子折叠构象下能保证该分子最稳定(熵最大)。熵越大越不利于蛋白溶解。 |
| Charge | 蛋白质表面带有的电荷值,带电蛋白均有利于溶解度,无论正负。 |
| Sequence | 所分析的序列段。 |
Poor protein solubility hinders the production of many therapeutically and industrially useful proteins. Efforts to increase solubility through experimental means often have low success rates and can compromise biological activity. Calculating protein solubility based on sequence information can significantly reduce the cost of experimental research.
This module uses the CamSol, SoluProt, and Protein-Sol algorithms for solubility prediction. Specifically:
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| protein-sol_score_show.png | Distribution of Folding Propensity and Charge under the Protein-Sol method. The horizontal coordinate Windows for each 21 amino acids is a fragment group. |
| result_per_chain.csv | Predicted solubility results for each chain under the three methods. |
| result_per_residue.csv | Solubility status corresponding to different protein regions under the Protein-Sol method (this result is only for the first chain). |
The result_per_chain.csv includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein ID | Protein sequence name |
| Solubility (CamSol) | Predicted solubility by CamSol. A higher score indicates better solubility, with scores greater than 1 indicating good solubility and scores less than -1 indicating poor solubility. |
| Solubility (SoluProt) | Predicted solubility by SoluProt, a higher score indicates better solubility |
| Solubility (Protein-Sol) | Predicted solubility by Protein-Sol,a higher score indicates better solubility |
| pI | Isoelectric point of the protein |
The result_per_residue.csv includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Protein sequence name |
| Kyte-Doolittle Hydropathy | Hydropathy index of amino acids, describing the hydrophilicity or hydrophobicity of their side chains. A smaller hydropathy index indicates higher hydrophilicity of the amino acid segment. |
| Folding Propensity | This value describes the folding degree of the protein, with higher values being less favorable for protein solubility. |
| Entropy | Entropy ensures the most stable molecular conformation under certain folding configurations. Higher entropy is less favorable for protein solubility. |
| Charge | The charge value on the protein surface, with charged proteins being favorable for solubility regardless of positive or negative charge. |
| Sequence | The analyzed sequence segment. |

Humanization Report是抗体人源化设计报告生成模块,用于生成最终的抗体人源化设计报告以及相应的专利实施例段落。
Grafting模块生成的Graft Policy文件。
Back Mutation Grouping模块生成的Policy文件。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| BM.pptx | 回复突变位点汇总文件 |
| batch_registration_template.xlsx | 批量注册模板文件 |
| hotspot_summary.xlsx | 风险位点总结 |
| patent_example_template.docx | 人源化设计序列在相应的专利实施例段落 |
| humanized_variants.fasta | 抗体人源化设计序列文件,FASTA格式 |
| Report.docx | 抗体人源化设计报告,包括整个人源化设计过程涉及的序列、分组等信息 |
其中batch_registration_template.xlsx包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Protein Sequence | 蛋白序列 |
| Molecule Name | 分子名称 |
其中hotspot_summary.xlsx包含如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ID | 抗体序列名称 |
| Sequence-CDR | CDR序列区域 |
| Deamidation | 脱酰胺位点 |
| Isomerization | 异构化位点 |
| Cleavage | 酶切位点 |
| Hydrolysis | 水解位点 |
| Glycosylation | 糖基化位点 |
| Cys | 半胱氨酸数量 |
| Oxidation | 氧化位点 |
| High risk | 高风险率 |
| High risk sites | 高风险位点 |
The Humanization Report is a module for generating reports on antibody humanization design, including the final antibody humanization design report and corresponding paragraphs for patent implementation examples.
The Graft Policy file generated by the Grafting module.
The Policy file generated by the Back Mutation Grouping module.
The output results include:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| BM.pptx | Summary file of back mutation sites |
| batch_registration_template.xlsx | Batch registration template file |
| hotspot_summary.xlsx | Summary of hotspot sites |
| patent_example_template.docx | Humanization design sequences in corresponding patent implementation example paragraphs |
| humanized_variants.fasta | Antibody humanization design sequence file in FASTA format |
| Report.docx | Antibody humanization design report, including information on sequences, grouping, etc., involved in the entire humanization design process |
The batch_registration_template.xlsx file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Protein Sequence | Protein sequence |
| Molecule Name | Molecule name |
The hotspot_summary.xlsx file contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ID | Antibody sequence name |
| Sequence-CDR | CDR sequence region |
| Deamidation | Deamidation site |
| Isomerization | Isomerization site |
| Cleavage | Cleavage site |
| Hydrolysis | Hydrolysis site |
| Glycosylation | Glycosylation site |
| Cys | Number of cysteines |
| Oxidation | Oxidation site |
| High risk | High-risk rate |
| High risk sites | High-risk sites |

ADMET Prediction模块基于通信消息传递神经网络(Compositional Message Passing Neural Network,CMPNN)对化合物的在体内的吸收、分布、代谢、排泄和毒性特性进行预测并且评估其潜在药效,从而筛选出更有前途的化合物,缩短新药研发周期。
早期的图神经网络(GNN),尤其是消息传递神经网络(MPNN)及其变体,在分子图建模方面取得了显著成效。然而,这些模型主要关注节点(原子)或边(键)的信息,可能导致对分子图的表示不够充分。CMPNN模型通过增强节点和边之间的消息交互,改进了分子图的嵌入。该模型引入了消息增强器(Message Booster)模块,丰富了消息生成过程。同时,设计了节点-边消息通信函数,以更好地利用节点和边的信息。
CMPNN的核心原理在于将分子表示为图结构,通过消息传递机制在不同节点之间传递信息。通过迭代优化多个局部属性和全局特征的计算,CMPNN最终生成整个分子的特征表示。该模型能够在不同级别的分子特征之间进行有效的信息传递和整合,使其在分子预测、反应预测和药物发现等领域表现优异。
图1. CMPNN 嵌入生成过程。
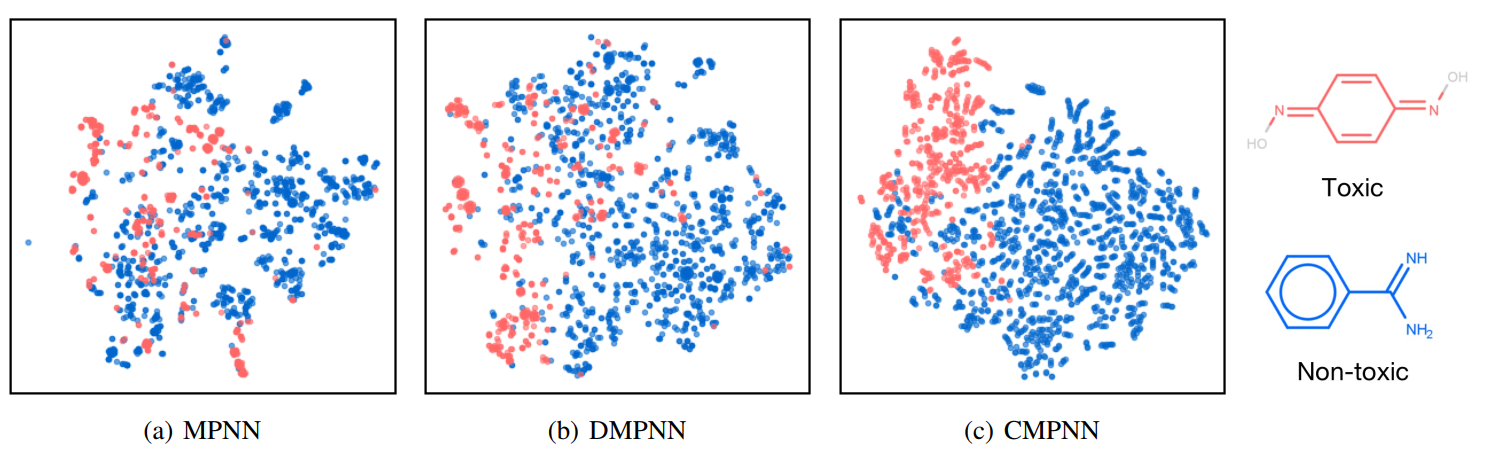
图2. MPNN、DMPNN和CMPNN三种模型在区分毒性和非毒性原子方面的能力。CMPNN能够更精细地区分毒性原子和非毒性原子,红色点(有毒原子)和蓝色点(非毒性原子)之间的分离更为明显。
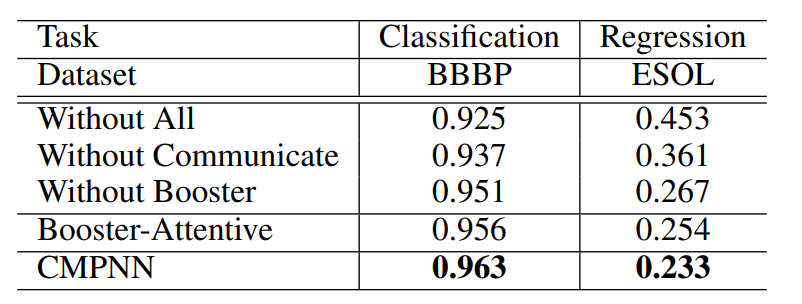
图3. CMPNN模型在BBBP和ESOL数据集上的消融研究结果。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。对SMILES文件上传格式要求如下所示,第一行必须为smiles字段:
smiles
CCCC(C)C
CCOC(=O)c1cncn1C(C)c2ccccc2
选择需要预测的ADMET性质,包括如下:
选择不同ADMET性质,输出不同结果的result.csv文件,包含信息如下:
Ying Song, Shuangjia Zheng, Zhangming Niu, et al., Communicative Representation Learning on Attributed Molecular Graphs. International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2020. 29:2831-2838.
The ADMET Prediction module uses the Compositional Message Passing Neural Network (CMPNN) to predict the absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, and toxicity properties of compounds in vivo. It evaluates their potential efficacy, thereby identifying more promising compounds and shortening the drug development cycle.
Early Graph Neural Networks (GNNs), especially Message Passing Neural Networks (MPNNs) and their variants, achieved significant success in molecular graph modeling. However, these models mainly focus on the information of nodes (atoms) or edges (bonds), which may lead to insufficient representation of the molecular graph. The CMPNN model improves the embedding of molecular graphs by enhancing message interactions between nodes and edges. This model introduces a Message Booster module to enrich the message generation process. Additionally, a node-edge message communication function is designed to better utilize the information from nodes and edges.
The core principle of CMPNN is to represent molecules as graph structures and transmit information between different nodes through a message passing mechanism. By iteratively optimizing the computation of multiple local properties and global features, CMPNN ultimately generates a feature representation of the entire molecule. This model can effectively transmit and integrate information between different levels of molecular features, making it excel in areas such as molecular prediction, reaction prediction, and drug discovery.

Figure 1.CMPNN embedding generation algorithm.

Figure 2. The ability of the MPNN, DMPNN, and CMPNN models to distinguish between toxic and non-toxic atoms. The CMPNN is able to differentiate toxic atoms from non-toxic atoms more precisely, with a more pronounced separation between red dots (toxic atoms) and blue dots (non-toxic atoms).

Figure 3. Ablation results on BBBP and ESOL datasets.
Small molecule structure file in SDF or SMILES format. For SMILES file upload, the format should follow as shown below, where the first line must be the smiles field:
smiles
CCCC(C)C
CCOC(=O)c1cncn1C(C)c2ccccc2
Select the ADMET properties to predict, including:
Selecting different ADMET properties will output different result.csv files, containing the following information:
Ying Song, Shuangjia Zheng, Zhangming Niu, et al., Communicative Representation Learning on Attributed Molecular Graphs. International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. 2020. 29:2831-2838.

FRODOCK是由西班牙Pablo Chacón教授开发的蛋白-蛋白对接软件。FRODOCK使用球谐函数(spherical harmonics)的旋转搜索提高对接效率。全局能量优化采用 6D(3D 旋转 + 3D平移)刚体详尽搜索(rigid-body exhaustive search)固定配体的构象。复合物的结合能考虑范德华力、静电和去溶剂化三个能量项。在抗原-抗体复合物、酶-底物、其他蛋白复合物的基准测试集中效果表现很好。具有以下技术特点:
受体结构文件,PDB格式。
配体结构文件,PDB格式。
相互作用类型。
限制文件,文本格式如下:
# RECEPT_____ LIGAND_____ D__
# -------------------------------
GLY A 269 SER A 81 5
GLY A 269 LEU A 84 10
其中"GLY A 269"代表受体部分的残基名称"GLY"、链名称"A"、残基编号"269";“SER A 81"代表配体部分的残基"SER”,链名称"A",残基编号"81";"5"代表受配体残基之间的距离在5Å。
生成构象聚类最大数目。
保存的得分最高分子的PDB文件。
参考结合配体分子(用于比较),格式:PDB。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| complex_01.pdb-complex_10.pdb | 输出打分前十的复合物构象 |
| output_complex_TopN.tar.gz | 输出所有复合物结构的压缩包文件 |
| TopN_score.csv | 提供复合物构象的对接打分,其中打分值越大,结合能力越强。 |
| output_ligand_TopN.tar.gz | 输出所有配体结构的压缩包文件 |
其中TopN_score.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| NO | 打分排序 |
| Euler1 | 配体旋转α角度(ZYZ顺序旋转的欧拉角) |
| Euler2 | 配体旋转β角度(ZYZ顺序旋转的欧拉角) |
| Euler3 | 配体旋转γ角度(ZYZ顺序旋转的欧拉角) |
| posX | 配体质心所在位置的X坐标 |
| posY | 配体质心所在位置的Y坐标 |
| posZ | 配体质心所在位置的Z坐标 |
| Absolute_Energy_Score | 绝对能量分数用来评估复合物结合能力强弱。 |
| Ligand_File | 配体文件名称 |
| complex_pdb | 复合物文件名称 |
FRODOCK is a protein-protein docking software developed by Professor Pablo Chacón from Spain. FRODOCK utilizes spherical harmonics for rotation search to enhance docking efficiency. Global energy optimization is achieved through a 6D (3D rotation + 3D translation) rigid-body exhaustive search with fixed ligand conformation. The binding energy of the complex considers van der Waals forces, electrostatic interactions, and desolvation energy. It has shown good performance in benchmark tests with antigen-antibody complexes, enzyme-substrate interactions, and other protein complexes. It features the following technical aspects:
Structure file of the receptor in PDB format.
Structure file of the ligand in PDB format.
Type of interaction.
Text file specifying constraints, with the format:
# RECEPT_____ LIGAND_____ D__
# -------------------------------
GLY A 269 SER A 81 5
GLY A 269 LEU A 84 10
Where “GLY A 269” represents the residue name “GLY”, chain “A”, residue number “269” in the receptor part; “SER A 81” represents the residue “SER”, chain “A”, residue number “81” in the ligand part; and “5” represents a distance of 5Å between the receptor and ligand residues.
Maximum number of conformation clusters to generate.
Number of top-scoring molecules to save as PDB files.
Reference ligand molecule for comparison, in PDB format.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| complex_01.pdb-complex_10.pdb | Output of the top ten scored complex conformations |
| output_complex_TopN.tar.gz | Compressed file containing all complex structures |
| TopN_score.csv | Provides docking scores for complex conformations, where higher scores indicate stronger binding affinity |
| output_ligand_TopN.tar.gz | Compressed file containing all ligand structures |
The TopN_score.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| NO | Ranking based on scores |
| Euler1 | Euler angles for ligand rotation (in ZYZ order) |
| Euler2 | Euler angles for ligand rotation (in ZYZ order) |
| Euler3 | Euler angles for ligand rotation (in ZYZ order) |
| posX | X-coordinate of the ligand center of mass |
| posY | Y-coordinate of the ligand center of mass |
| posZ | Z-coordinate of the ligand center of mass |
| Absolute_Energy_Score | Absolute energy score for evaluating binding strength |
| Ligand_File | Ligand file name |
| complex_pdb | Complex file name |

Observed Antibody Space 数据库 (OAS) 是一个收集和注释免疫组库以用于大规模分析的项目。它目前包含来自超过75项不同研究的超过10亿个真实抗体序列。这些库涵盖了不同的免疫状态、生物体(主要是人类和小鼠)和个体。本功能从OAS库中搜索同源的人源抗体序列,通过序列比对,可以得到不同位点的进化信息,常用于对亲和力成熟或是对人源化过程中突变位点的选择提供参考依据,指导抗体设计。
抗体序列文件,FASTA格式。
通过序列比对,可以得到不同位点的进化信息文件alignment.fasta。
The Observed Antibody Space (OAS) database is a project that collects and annotates immune repertoires for large-scale analysis. It currently contains over 1 billion real antibody sequences from more than 75 different studies. These libraries cover different immune states, organisms (primarily humans and mice), and individuals. This feature searches for homologous human antibody sequences from the OAS database. By aligning sequences, evolutionary information at different sites can be obtained. This is commonly used to provide reference for the selection of mutation sites during affinity maturation or humanization processes, guiding antibody design.
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
The evolutionary information file for different sites can be obtained through sequence alignment, saved as alignment.fasta.

HDOCK是由华中科技大学物理学院黄胜友教授团队开发的一个集成了同源搜索、基于模板建模、结构预测、大分子对接、生物信息整合的快速蛋白质-蛋白质对接程序。HDOCK使用基于快速傅里叶变换 (FFT) 的对接算法对所有结合模式进行全局采样,然后通过迭代导出的基于知识的评分函数对结合模式进行打分。在多个基准测试中显示很好的预测效果。具有以下技术特点:
受体的结构文件,PDB格式
配体的结构文件,PDB格式
输出打分最高的复合物PDB文件个数
平动网格间距
转动角间距
受体的结合位点残基。
结合位点残基可以作为一个文件(.txt)提交,格式如下:
195:A
203-206:A
108:B
表示A链的195号、203-206号残基以及B链的108号残基。请注意,文件中的残基应该放在不同的行上。
配体的结合位点残基。
结合位点残基可以作为一个文件(.txt)提交,格式如下:
195:A
203-206:A
108:B
表示A链的195号、203-206号残基以及B链的108号残基。请注意,文件中的残基应该放在不同的行上。
相互作用氨基酸之间的距离约束。
距离约束可以作为一个文件(.txt)提供,格式如下:
195:A 236:B 8
215-218:A 306:B 6
其中,受体上的A链195号残基和配体上的B链236号残基的距离将在8埃之内。受体上的A链215-218号残基和配体上的B链306号残基的距离将在6埃之内。
注意:对于每个约束,第一个字段是受体,第二个字段是配体,第三个字段是约束距离。残基表示必须采用num:chainID或num1-num2:chainID格式,其中残基编号和链ID指的是输入结构(如果输入是结构)或模型结构(如果输入是序列)。
聚类RMSD截断值
是否保留受体中非标准氨基酸:都保留(all),只保留水(water),指定保留非标准氨基酸(specify),去除所有非标准氨基酸(none)。
多个残基用逗号(,)分隔开。例如:“X:UNL-1”,其中X为链名,UNL为非标准氨基酸残基名称,1为残基编号。
是否保留配体中非标准氨基酸:都保留(all),只保留水(water),指定保留非标准氨基酸(specify),去除所有非标准氨基酸(none)。
指定配体中需要保留非标准氨基酸,多个残基用逗号(,)分隔开。例如:“X:UNL-1”,其中X为链名,UNL为非标准氨基酸残基名称,1为残基编号。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| complex_01.pdb-complex_10.pdb | 打分前十的复合物构象 |
| score.csv | 提供复合物构象的对接打分,其中打分值越低,结合能力越强。 |
| TopNComplex.tar.gz | 输出所有复合物结构的压缩包文件 |
其中score.csv包括如下信息:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Number | 打分排序 |
| RMSD | 复合物构象的RMSD |
| Score | 对接能量打分,其中打分值越低,结合能力越强。 |
Yan Y, Tao H, He J, Huang S-Y.* The HDOCK server for integrated protein-protein docking. Nature Protocols, 2020.
Yan Y, Zhang D, Zhou P, Li B, Huang S-Y. HDOCK: a web server for protein-protein and protein-DNA/RNA docking based on a hybrid strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017;45(W1):W365-W373.
HDOCK is a fast protein-protein docking program developed by the team of Professor Shengyou Huang at the School of Physics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology. It integrates homology search, template-based modeling, structure prediction, macromolecular docking, and bioinformatics integration. HDOCK uses a docking algorithm based on Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) to globally sample all binding modes and then scores the binding modes using an iteratively derived knowledge-based scoring function. It has shown good predictive performance in multiple benchmark tests. Its technical features include:
Structure file of the receptor in PDB format.
Structure file of the ligand in PDB format.
Number of top-scoring complex PDB files to output.
Translation grid spacing.
Rotation angle interval.
Residues of the receptor’s binding site.
Binding site residues can be submitted as a file (.txt) with the following format:
195:A
203-206:A
108:B
This indicates residue 195 of chain A, residues 203-206 of chain A, and residue 108 of chain B. Note that residues in the file should be on separate lines.
Residues of the ligand’s binding site.
Binding site residues can be submitted as a file (.txt) with the same format as above.
195:A
203-206:A
108:B
Distance constraints between interacting amino acids.
Distance constraints can be provided as a file (.txt) with the following format:
195:A 236:B 8
215-218:A 306:B 6
Here, the distance between residue 195 of chain A in the receptor and residue 236 of chain B in the ligand is within 8 angstroms. The distance between residues 215-218 of chain A in the receptor and residue 306 of chain B in the ligand is within 6 angstroms.
Note: For each constraint, the first field is the receptor, the second field is the ligand, and the third field is the constraint distance. Residues should be in the format num:chainID or num1-num2:chainID, where residue number and chain ID refer to the input structure (if the input is a structure) or model structure (if the input is a sequence).
RMSD cutoff value for clustering.
Whether to retain non-standard amino acids in the receptor: retain all (all), retain only water (water), specify which non-standard amino acids to retain (specify), remove all non-standard amino acids (none).
Multiple residues should be separated by commas (,). For example: “X:UNL-1”, where X is the chain name, UNL is the name of the non-standard amino acid residue, and 1 is the residue number.
Whether to retain non-standard amino acids in the ligand: retain all (all), retain only water (water), specify which non-standard amino acids to retain (specify), remove all non-standard amino acids (none).
Specify which non-standard amino acids in the ligand need to be retained, with multiple residues separated by commas (,). For example: “X:UNL-1”, where X is the chain name, UNL is the name of the non-standard amino acid residue, and 1 is the residue number.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| complex_01.pdb-complex_10.pdb | Top ten scoring complex conformations |
| score.csv | Provides docking scores for complex conformations, where lower scores indicate stronger binding |
| TopNComplex.tar.gz | Compressed file containing all complex structures |
The score.csv file includes the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Number | Score ranking |
| RMSD | RMSD of complex conformations |
| Score | Docking energy score, where lower scores indicate stronger binding |

Seqkit是一款专门处理fsata/q序列文件的软件,由go语言编写,功能比较完善,软件使用也很稳定。
该模块主要提供的功能有:
序列文件,FASTA格式。
指定序列中需要清理掉的间隔字符。
指定输出序列文件名称,FASTA格式。
序列文件,FASTA格式。
指定输出序列文件名称,FASTA格式。
对FASTA文件进行单独突变:在给定位置改变碱基。例如:“2:C”为将第二位碱基变为胞嘧啶(C);“-1:A”为将最后一位碱基变为腺嘌呤(A)。
删除突变:删除指定范围内的子序列,例如,“1:2”表示删除前两个碱基,“-3:-1”表示删除最后三个碱基。
插入突变:在给定位置后插入碱基,例如,“0:ACGT”表示在开头插入ACGT,“-1:”表示在末尾添加。
CPUs数目。
序列文件,FASTA格式。
指定输出序列文件名称,FASTA格式。
按name (-n)或按seq (-s)删除重复序列。
保存重复序列数和列表的文件(-D)或保存重复序列的文件(-d)。
CPUs数目。
序列文件,FASTA格式。
指定输出序列文件名称,FASTA格式。
转换类型,包括如下几种:
–complement:互补序列
–dna2rna:DNA转RNA
–rna2dna:RNA转DNA
–lower-case:以小写形式打印序列
–upper-case:以大写形式打印序列
CPUs数目。
序列文件,FASTA格式。
指定输出序列文件名称,FASTA格式。
按照指定要求得到FASTA文件。
SeqKit is a software specifically designed for processing fasta/q sequence files. It is written in Go language, offering comprehensive functionality and stable performance. The module provides the following main features:
Sequence file in FASTA format.
Specify the gap characters to be cleaned from the sequence.
Specify the output sequence file name in FASTA format.
Sequence file in FASTA format.
Specify the output sequence file name in FASTA format.
Perform individual mutations on the FASTA file: change bases at specified positions. For example, “2:C” changes the base at the second position to cytosine ©; “-1:A” changes the last base to adenine (A).
Deletion mutation: delete a subsequence within a specified range. For example, “1:2” deletes the first two bases, “-3:-1” deletes the last three bases.
Insertion mutation: insert bases after the specified position. For example, “0:ACGT” inserts ACGT at the beginning, “-1:*” appends * at the end.
Number of CPUs.
Sequence file in FASTA format.
Specify the output sequence file name in FASTA format.
Delete duplicate sequences by name (-n) or by sequence (-s).
Save a file with the count and list of duplicate sequences (-D) or save a file with duplicate sequences (-d).
Number of CPUs.
Sequence file in FASTA format.
Specify the output sequence file name in FASTA format.
Transformation types include:
–complement: Complementary sequences
–dna2rna: DNA to RNA conversion
–rna2dna: RNA to DNA conversion
–lower-case: Print sequences in lowercase
–upper-case: Print sequences in uppercase
Number of CPUs.
Sequence file in FASTA format.
Specify the output sequence file name in FASTA format.
Obtain a FASTA file according to the specified requirements.

Property Filter模块可以基于导入的分子属性(例如从SDF文件导入)或在运行时对分子进行计算来选择分子的子集。支持的输入文件格式为:SD(.sdf,.sd)。支持的输出文件格式为:SD(.sdf,.sd)。
小分子结构文件,SDF格式。
过滤属性,相关的描述符含义分别如下:
L5 (Lipinski rule of five):类药物五原则,指的是一组用于评估化合物作为口服药物潜力的规则,包括的规则为HBD<5、HBA1<10、MW<500以及logP<5。
HBA1 (Number of hydrogen bond acceptors 1 [JoelLib]):用于识别化合物中符合此模式的氢键受体,其匹配的SMARTS格式为[$([!#6;+0]);!$([F,Cl,Br,I]);!$([o,s,nX3]);!$([Nv5,Pv5,Sv4,Sv6])]
HBA2 (Number of hydrogen bond acceptors 2 [JoelLib]):用于识别另一种模式的氢键受体,其匹配的SMARTS格式为[$([$([#8,#16]);!$(*=N~O);!$(*~N=O);X1,X2]),$([#7;v3;!$([nH]);!$(*(-a)-a)])]
HBD (Number of hydrogen bond donors [JoelLib]):其匹配的SMARTS格式为[!#6;!H0],用于识别化合物中符合此模式的氢键供体。
logP (Octanol/water partition coefficient):辛醇/水分配系数,是衡量化合物在辛醇与水之间分配的比例,通常用于预测化合物的疏水性。
MW (Molecular weight):分子量。
abonds (Number of aromatic bonds):芳香键的数量,SMARTS格式为*:*。
atoms (Number of atoms):原子数量,通过添加或去除氢原子来计算总原子或重原子数量,SMARTS格式为*。
bonds (Number of bonds):键的数量,通过添加或去除氢原子来计算总键或重原子之间的键,SMARTS格式为*~*。
cansmi (Canonical SMILES):规范化的SMILES(简化分子线性输入规范),用于唯一表示化合物的线性结构。
cansmiNS (Canonical SMILES without isotopes or stereo):不含同位素或立体化学信息的规范化SMILES。
dbonds (Number of double bonds):双键的数量,SMARTS格式为*=*。
formula (Chemical formula):化学式。
InChI (IUPAC InChI identifier):国际化学标识符。
InChIKey (InChIKey):InChI的简化版,固定长度的字符串,用于快速查找和识别化合物。
MP (Melting point):熔点,是由Andy Lang开发的熔点描述符,用于预测化合物的熔点。
MR (Molar refractivity):摩尔折射率,是化合物体积和极化率的量度,通常用于评估分子间相互作用。
nF (Number of fluorine atoms):氟原子的数量,SMARTS格式为F,用于识别化合物中的氟原子数量。
s/smarts (SMARTS filter):SMARTS过滤器,用于根据特定模式筛选化合物。
sbonds (Number of single bonds):单键的数量,SMARTS格式为*-*。
tbonds (Number of triple bonds):三键的数量,SMARTS格式为*#*。
title (For comparing a molecule's title):用于比较分子标题的信息。
TPSA (Topological polar surface area):拓扑极性表面积,是分子中极性区域的表面积总和,通常用于预测药物的吸收性和透过性。
选择属性的名称和所需的关系(如>、<、=、>=、<=、!=),多个符号用逗号(,)分隔。当筛选性质为L5时,该栏填None。
属性过滤器的截止值。当筛选性质为L5时,该栏填None。
前后条件的逻辑关系连接符(&&或者||),多个用逗号分隔
输出文件名称。
得到筛选后的SDF结构文件output.sdf。
The Property Filter module allows for the selection of a subset of molecules based on imported molecular properties (e.g., imported from an SDF file) or calculated at runtime. Supported input file formats include: SD (.sdf, .sd). Supported output file formats include: SD (.sdf, .sd).
Small molecule structure file in SDF format.
Filter properties, with the meanings of related descriptors as follows:
L5 (Lipinski rule of five): A set of rules used to evaluate the potential of compounds as oral drugs, including the following criteria: HBD<5, HBA1<10, MW<500, and logP<5.
HBA1 (Number of hydrogen bond acceptors 1 [JoelLib]): Used to identify hydrogen bond acceptors in compounds that match this pattern, with the SMARTS format: [$([!#6;+0]);!$([F,Cl,Br,I]);!$([o,s,nX3]);!$([Nv5,Pv5,Sv4,Sv6])]
HBA2 (Number of hydrogen bond acceptors 2 [JoelLib]): Used to identify another pattern of hydrogen bond acceptors, with the SMARTS format: [$([$([#8,#16]);!$(*=N~O);!$(*~N=O);X1,X2]),$([#7;v3;!$([nH]);!$(*(-a)-a)])]
HBD (Number of hydrogen bond donors [JoelLib]): Matches the SMARTS format [!#6;!H0], used to identify hydrogen bond donors in compounds that match this pattern.
logP (Octanol/water partition coefficient): The octanol/water partition coefficient, which measures the ratio of a compound's distribution between octanol and water, typically used to predict compound hydrophobicity.
MW (Molecular weight): The molecular weight.
abonds (Number of aromatic bonds): The number of aromatic bonds, SMARTS format: *:*.
atoms (Number of atoms): The number of atoms, calculated by adding or removing hydrogen atoms to count total or heavy atoms, SMARTS format: *.
bonds (Number of bonds): The number of bonds, calculated by adding or removing hydrogen atoms to count total bonds or bonds between heavy atoms, SMARTS format: *~*.
cansmi (Canonical SMILES): Canonical SMILES (Simplified Molecular Input Line Entry System), used to uniquely represent the linear structure of a compound.
cansmiNS (Canonical SMILES without isotopes or stereo): Canonical SMILES without isotope or stereochemistry information.
dbonds (Number of double bonds): The number of double bonds, SMARTS format: *=*.
formula (Chemical formula): The chemical formula.
InChI (IUPAC InChI identifier): The International Chemical Identifier, a standardized text string to represent the structure of a compound.
InChIKey (InChIKey): A simplified version of InChI, a fixed-length string used for quick lookup and identification of compounds.
MP (Melting point): The melting point, a descriptor developed by Andy Lang, used to predict the melting point of compounds.
MR (Molar refractivity): Molar refractivity, a measure of the compound's volume and polarizability, typically used to assess intermolecular interactions.
nF (Number of fluorine atoms): The number of fluorine atoms, SMARTS format: F, used to identify the number of fluorine atoms in a compound.
s/smarts (SMARTS filter): A SMARTS filter used to filter compounds based on specific patterns.
sbonds (Number of single bonds): The number of single bonds, SMARTS format: *-*.
tbonds (Number of triple bonds): The number of triple bonds, SMARTS format: *#*.
title (For comparing a molecule's title): Used for comparing the titles of molecules.
TPSA (Topological polar surface area): The topological polar surface area, the total surface area of polar regions in a molecule, typically used to predict drug absorption and permeability.
Select the name of the property and the desired relation (such as >, <, =, >=, <=, !=), separated by commas. When filtering by L5, fill in None for this field.
The cutoff value for the property filter. When filtering by L5, fill in None for this field.
Logical operators (&& or ||) connecting the conditions, separated by commas.
Obtain the filtered SDF structure file, output.sdf.
The name of the output file.
The filtered SDF structure file output.sdf is obtained.

Homology Modeling (Protein)采用老牌蛋白质同源模建算法Modeller,可以对蛋白质三维结构的同源性或比较建模。用户提供一个待建模的序列与已知相关结构的比对。通过满足空间约束条件进行比较蛋白质结构建模,以及许多其他任务,包括蛋白质结构中循环的全新建模、针对灵活定义的目标函数优化各种蛋白质结构模型、蛋白质序列和/或结构的多重比对、聚类、搜索序列数据库、比较蛋白质结构等。
蛋白的序列文件,FASTA格式。
输出预测结构数目。
构建PDB结构的模板文件。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| output.log | 输出记录文件 |
| score.csv | 预测结构对应的打分文件 |
| Top0001.pdb-Top0005.pdb | 打分前五的结构文件 |
其中score.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| name | 预测结构名称 |
| molpdf | 评估预测结构与模板结构的一致性,其值越大越好。 |
| DOPE score | 评估预测结构与真实结构相似的可能性,其值越低越好。 |
| Template | 构建结构所使用的模板PDB ID和链名称。 |
Webb B, Sali A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun 20;54:5.6.1-5.6.37.
Martí-Renom MA, Stuart AC, Fiser A, Sánchez R, Melo F, Sali A. Comparative protein structure modeling of genes and genomes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2000;29:291-325.
Sali A, Blundell TL. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 5;234(3):779-815.
Fiser A, Do RK, Sali A. Modeling of loops in protein structures. Protein Sci. 2000 Sep;9(9):1753-73.
Homology Modeling (Protein) uses the established protein homology modeling algorithm Modeller to model protein three-dimensional structures based on homology or comparative modeling. Users provide a sequence to be modeled and perform a comparison with known related structures. The modeling of protein structures is achieved by satisfying spatial constraints, as well as many other tasks, including novel modeling of loops in protein structures, optimizing various protein structure models for flexible-defined target functions, multiple sequence and/or structure alignments, clustering, searching sequence databases, and comparing protein structures.
Protein sequence file in FASTA format.
Number of predicted structures.
Build a template file for the PDB structure.
Name of log file
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| output.log | Output record file |
| score.csv | Predict the structure of the corresponding scoring file |
| Top0001.pdb-Top0005.pdb | Score the top five structure files |
score.csv contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| name | Prediction structures name |
| molpdf | The molpdf score informs about the agreement of the model with the restraints derived from the alignment, the larger the value, the better. |
| DOPE score | The DOPE score tries to inform on the likelihood of the model resembling a real structure, the lower the value, the better. |
| Template | The template PDB ID and chain name used to build the structure. |
Webb B, Sali A. Comparative Protein Structure Modeling Using MODELLER. Curr Protoc Bioinformatics. 2016 Jun 20;54:5.6.1-5.6.37.
Martí-Renom MA, Stuart AC, Fiser A, Sánchez R, Melo F, Sali A. Comparative protein structure modeling of genes and genomes. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 2000;29:291-325.
Sali A, Blundell TL. Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 5;234(3):779-815.
Fiser A, Do RK, Sali A. Modeling of loops in protein structures. Protein Sci. 2000 Sep;9(9):1753-73.

扫描抗体序列发现潜在的翻译后修饰(PTM)风险位点,PTM位点是生物制剂开发的常见风险。主要包括:氧化位点Oxidation、糖基化位点Glycosylation、水解位点Hydrolysis、脱酰胺基位点Deamidation、裂解位点Cleavage、天冬氨酸异构化位点Isomerization、半胱氨酸位点Cysteine。
抗体的序列文件,FASTA格式
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hotspots.md | 风险位点信息,Mardown格式 |
| Hotspots.json | 风险位点信息,JSON格式 |
针对抗体序列,会自动识别CDR区域,并输出CDR区和全部序列区域的风险位点。
风险位点说明:
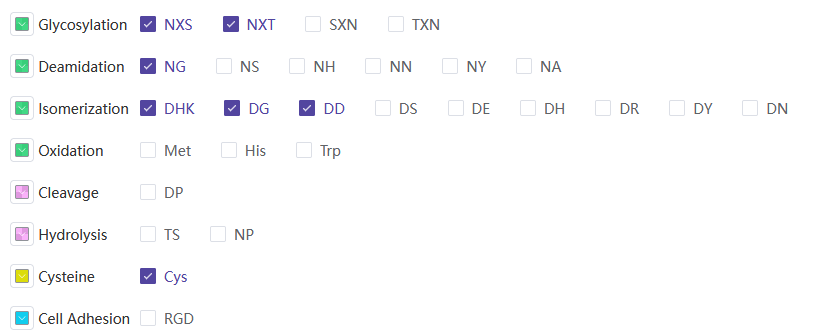
其中打勾的位点默认视为高风险位点(NXS, NXT, NG, DG, DHK, DD, Cys),修饰发生率相对较高,通常需要重点关注。也可基于经验自行判断。
这两个位点是非典型的N糖基化位点,可见于Amgen发表的文献:
Glutamine-linked and Non-consensus Asparagine-linked Oligosaccharides Present in Human Recombinant Antibodies Define Novel Protein Glycosylation Motifs, Journal of Biological Chemistry, Volume 285, Issue 21, 16012 - 16022
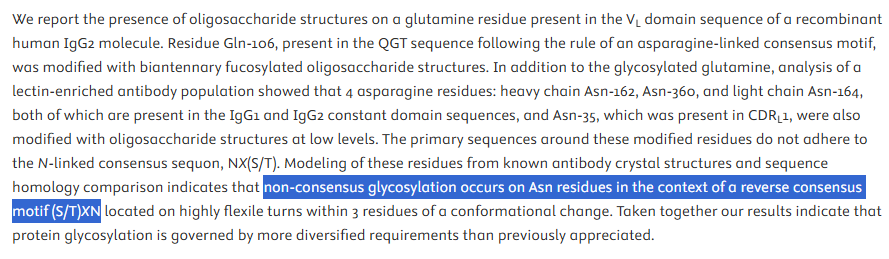
This module scans antibody sequences to identify potential post-translational modification (PTM) hotspot sites. PTM sites are common risks in biologics development and include Oxidation, Glycosylation, Hydrolysis, Deamidation, Cleavage, Isomerization, and Cysteine sites.
Antibody sequence file in FASTA format.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| hotspots.md | Information on hotspot sites in Markdown format |
| Hotspots.json | Information on hotspot sites in JSON format |
For antibody sequences, the module automatically identifies the CDR regions and outputs hotspot sites for both the CDR and the entire sequence regions.
Explanation of Hotspot Sites:

Among the marked sites, the six sites NXS, NXT, NG, DHK, DG, DD, and Cys are potential high-risk PTM hotspots that require special attention.
They are non-classic N-glycosylation PTM hotspots as reported in:
Glutamine-linked and Non-consensus Asparagine-linked Oligosaccharides Present in Human Recombinant Antibodies Define Novel Protein Glycosylation Motifs, Journal of Biological Chemistry, Volume 285, Issue 21, 16012 - 16022


Sequence Mutagenesis (Directed)是根据模板序列批量生成突变体的模块。 用户可以在文本文件中定义所有突变位置和突变氨基酸。
输入序列字符,如:
QAVVTQESALTTSPGETVTL
生成满足突变要求的FASTA文件mutations.fasta。
Sequence Mutagenesis (Directed) is a module for generating mutant variants in bulk based on a template sequence. Users can define all mutation positions and mutant amino acids in a text file.
Input sequence characters, for example:
QAVVTQESALTTSPGETVTL
Generate a FASTA file mutations.fasta that meets the mutation requirements.

2D Similarity Search模块是基于分子指纹进行二维相似度搜索的工具。根据不同指纹类型(Maccs Key、pharmacophore fingerprints、extended connectivity fingerprints)计算得到的指纹向量或者向量字符串进行相似性搜索,从分子数据库中筛选出与模板分子相似(不相似)的化合物。相似性评估方法采用的是常用的Tanimoto系数,用于比较两个化合物之间的相似性。它是基于化合物指纹或描述符的重叠程度计算得出的,数值范围从0到1,值越大表示两个化合物越相似。其主要功能如下所示:
小分子结构文件,SDF格式。
小分子结构,SMILES格式,支持多个小分子,一行一个SMILES,例如:
CSC1=C(c2ccc(C)s2)/C(=N/C(C)(C)C)C1
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CN3CCN(CC3)C)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CC=C5
选择用于相似性搜索的分子库,该模块提供17个公共分子数据库用于进行相似性搜索:
Public Library与Private Library选填其中一个。
上传用于进行相似度搜索的个人分子数据库,格式为SDF。
Public Library与Private Library选填其中一个。
分子指纹类型:maccskey、phar、ecfp
当搜索模式为SimilaritySearch时,表示搜索相似度≥截断值的分子;当搜索模式为DissimilaritySearch时,表示搜索相似度≤截断值的分子。计算值取值范围是0~1。Cutoff默认为0.75。
指定搜索模式:SimilaritySearch是查找相似分子,DissimilaritySearch是查找不相似分子。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| hits_values.csv | 添加数据库与模板分子相似度值。 |
| hits.sdf | 数据库中筛选出与模板分子相似在截断值以内的化合物。 |
其中hits_values.csv包括信息如下:
| 字段名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ReferenceCompoundID | 模板分子库中分子的名称,无名称则别表示为“Cmpd”前缀+“分子编号”。 |
| DatabaseCompoundID | 搜索库中符合条件的分子的名称,无名称同上。 |
| ComparisonValue | 模板分子与分子库的相似度值。 |
其余参数为所提供的分子数据库包含的描述。
Kier LB, Hall LH, The E-State as the basis for molecular structure space definition and structure similarity. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2000, 40, 784-791.
Filimonov D, Poroikov V, Borodina Y, Gloriozova T, Chemical similarity assessment through multilevel neighborhoods of atoms: Definition and comparison with the other Descriptors. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 1999, 39, 666-670
Venkatraman V, Prez-Nueno VI, Mavridis L, Ritchie DW, Comprehensive comparison of ligand-based virtual screening tools against the DUD data set reveals limitations of current 3D methods. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2010, 50, 2079-2093.
Durant, J.L.; Leland, B.A.; Henry, D.H.; Nourse, J.G. Reoptimization of MDL Keys for Use in Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2002, 42, 1273-1280.
Willett, P.; Similarity searching using 2D structural fingerprints. Chemoinformatics and Computational Chemical Biology. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2011, 672, 133-58.
The 2D Similarity Search module is a tool based on molecular fingerprint for 2D similarity search. The fingerprint bit-vector or vector string obtained by calculating the fingerprint types (Maccs Key, pharmacophore fingerprints, extended connectivity fingerprints) are used for similarity search, and compounds similar (or dissimilar) to the template molecule are selected from the small molecular database. The similarity assessment method used is the commonly used Tanimoto coefficient, which is used to compare the similarity between two compounds. It is based on the overlap of molecular fingerprints or descriptors, and the numerical range is from 0 to 1. The larger the value, the more similar the two compounds are considered to be. Its main functions are as follows:
Small molecule structure file in format.
Small molecule SMILES string. Example:
CSC1=C(c2ccc(C)s2)/C(=N/C(C)(C)C)C1
CC1=C(C=C(C=C1)NC(=O)C2=CC=C(C=C2)CN3CCN(CC3)C)NC4=NC=CC(=N4)C5=CN=CC=C5
Select the molecular database for similarity search. This module provides 17 public molecular databases for conducting similarity search:
Public Library and Private Library are optional, choose one of them.
Upload a personal molecular database in SDF format for similarity search.
Public Library and Private Library are optional, choose one of them.
Types of Molecular Fingerprints: maccskey, phar, ecfp.
When the search mode is set to SimilaritySearch, it means that molecules with a similarity ≥ the cutoff value will be searched. When the search mode is set to DissimilaritySearch, it means that molecules with a similarity ≤ the cutoff value will be searched. The calculated values range from 0 to 1, with a default cutoff value of 0.75.
Specify the search mode: SimilaritySearch or DissimilaritySearch.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| hits_values.csv | Add database and template molecular similarity values. |
| hits.sdf | Compounds similar to template molecules within the truncation value were screened from the database. |
The hits_values.csv contains the following information:
| Field Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ReferenceCompoundID | The name of the molecule in the template library, or denoted as “Cmpd” prefix + “molecule number” if it has no name. |
| DatabaseCompoundID | The name of the compound in the search library that meets the conditions, or denoted as above if it has no name. |
| ComparisonValue | The similarity value between the template molecule and the compound in the database. |
The remaining parameters are the descriptors contained in the provided molecular database.
Kier LB, Hall LH, The E-State as the basis for molecular structure space definition and structure similarity. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2000, 40, 784-791.
Filimonov D, Poroikov V, Borodina Y, Gloriozova T, Chemical similarity assessment through multilevel neighborhoods of atoms: Definition and comparison with the other Descriptors. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci., 1999, 39, 666-670
Venkatraman V, Prez-Nueno VI, Mavridis L, Ritchie DW, Comprehensive comparison of ligand-based virtual screening tools against the DUD data set reveals limitations of current 3D methods. J. Chem. Inf. Model., 2010, 50, 2079-2093.
Durant, J.L.; Leland, B.A.; Henry, D.H.; Nourse, J.G. Reoptimization of MDL Keys for Use in Drug Discovery. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2002, 42, 1273-1280.
Willett, P.; Similarity searching using 2D structural fingerprints. Chemoinformatics and Computational Chemical Biology. Methods in Molecular Biology. 2011, 672, 133-58.

Batch Renaming模块设计用于化学库的分子重命名。用户可以使用前缀和定义的长度来规范分子名称。例如,将一个从WCP0001开始的库重命名为WCP9999,用户可以输入WCP前缀,长度为4。用户还可以使用——keeptitle参数保存以前的名称,以保存名称之间的关系。该模块可用于大型从头库或用户私有化学库中的自定义分子命名。支持的输入文件格式为:SD(.sdf,.sd)。支持的输出文件格式为:SD(.sdf,.sd)。
小分子结构文件,SDF格式。
输出SDF文件名称。
自定义前缀,如C表示从C001生成名称,并结合长度为3。
固定名称长度,如4表示生成名C0001, 1表示生成C1, C2……。
新生成名称的位置:
字段名作为新生成的名称,仅当Location为filed或all时有效。
保留以前的分子标题名称。
得到重命名后的sdf文件output.sdf。
The Batch Renaming module is designed for renaming molecules in chemical libraries. Users can standardize molecule names using a prefix and a defined length. For example, to rename a library starting from WCP0001 to WCP9999, users can input the prefix WCP and a length of 4. Users can also use the --keeptitle parameter to preserve previous names, maintaining relationships between names. This module can be used for custom molecule naming in large de novo libraries or user-private chemical libraries. Supported input file formats: SD (.sdf, .sd). Supported output file formats: SD (.sdf, .sd).
Small molecule structure file in SDF format.
Name of the output SDF file.
Custom prefix, e.g., C indicating names generated from C001, combined with a length of 3.
Fixed name length, e.g., 4 generates names like C0001, 1 generates C1, C2, and so on.
Position for the newly generated names:
Field name to be used as the newly generated name, only valid when Location is field or all.
Keep the previous molecule title name.
Obtain the renamed SDF file named output.sdf.

3D Conf Generation (AlphaConf)采用唯信计算自研的分子三维构象生成算法,超快速生成分子三维构象库,比Open Eyes的Omega至少快一个数量级,后者被认为是目前最高效的商业产品。它也比薛定谔的ConfGenX快一个数量级以上。其优异的构象多样性和质量已被下游应用证明。AlphaConf非常适合用于药物分子发现的超高通量虚拟筛选。其技术特点如下:
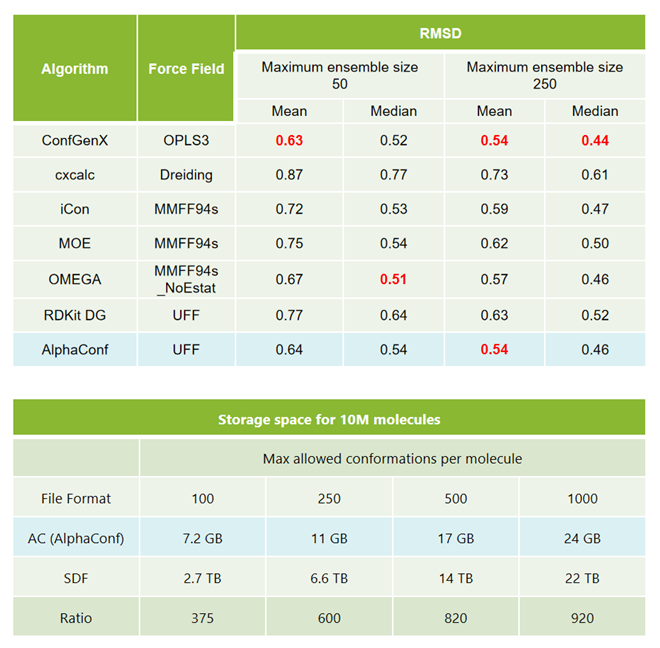
小分子结构文件,SDF格式或者压缩的SDF格式(.gz文件)。
每个分子的最大构象数,默认100。
构象能量截断值(单位:kcal/mol),默认20kcal/mol。
指定输出文件名称,后缀是.sd,.ac,.ac.gz或者.aux.gz。除了构象文件外,当输出文件后缀为.ac.gz或者.aux.gz还会输出片段库文件(文件后缀为.aux,其文件名根据构象文件名称自动命名,如:构象文件名设置为conf.ac.gz,片段文件名自动命名为conf.aux.gz)。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| SelfConf.ac.gz | 构象压缩文件,AC格式,用于AlphaShape模块的构象库输入 |
| SelfConf.aux.gz | 片段库文件(其文件名根据构象文件名称自动命名,如:构象文件名设置为conf.ac.gz或者conf.aux.gz,片段文件名自动命名为conf.aux),AUX格式,用于AlphaShape模块的片段库输入 |
3D Conf Generation (AlphaConf) uses a proprietary molecular conformation generation algorithm developed by Wecompute to rapidly generate a library of molecular conformations. It is at least an order of magnitude faster than Open Eye’s Omega, which is considered the most efficient commercial product, and more than an order of magnitude faster than Schrodinger’s ConfGenX. Its excellent conformational diversity and quality have been proven in downstream applications, making AlphaConf particularly suitable for high-throughput virtual screening in drug discovery. Its technical features are as follows:

Small molecule structure file in SDF format or gzip format with .gz file extension for SDF file.
The maximum number of conformations per molecule, the default value is 100.
Specify energy cutoff for confs.(kcal/mol), the default value is 20 kcal/mol.
Specify output conformation file in SD format(.sd) or AC format(.ac)
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SelfConf.ac.gz | Conformation compressed file in AC format, used as input for the conformation library in the AlphaShape module. |
| SelfConf.aux.gz | Fragment library file in AUX format, used as input for the fragment library in the AlphaShape module. |

该模块可以去除或者统计分子含有的盐,从而获得去盐后分子结构或者分子结构含有的盐数量。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。
输出文件名称。
选择去除(remove)或者统计(count)盐离子。
得到无盐离子的分子结构文件oufile.sdf。
The Salts Removal module can remove or count the salts present in molecules, providing the option to obtain the molecular structures without salts or the count of salts in the molecular structures.
Small molecule structure file in SDF or SMILES format.
Name of the output file.
Select whether to remove (remove) or count (count) salt ions.
Obtain a molecular structure file without salt ions named outfile.sdf.

基于规范SMILES字符串识别和删除重复分子,或者仅统计重复分子数量。支持的输入文件格式为:MOL(.mol)、SD(.sdf、.sd)、SMILES(.smi、.csv、.tsv、.txt)。支持的输出文件格式为:SD(.sdf、.sd)、SMILES(.smi、.csv、.tsv、.txt)。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。
输出文件名称。
选择是去除重复分子(remove)还是对重复分子进行计数(count),默认为remove。
得到删除重复分子的sdf文件outfile.sdf。
The Duplicates Removal module identifies and removes duplicate molecules based on canonical SMILES strings, or it can simply count the number of duplicate molecules. Supported input file formats are: MOL (.mol), SD (.sdf, .sd), SMILES (.smi, .csv, .tsv, .txt). Supported output file formats are: SD (.sdf, .sd), SMILES (.smi, .csv, .tsv, .txt).
Small molecule structure file in SDF or SMILES format.
Name of the output file.
Select whether to remove duplicate molecules (remove) or count duplicate molecules (count), default is remove.
Obtain an SDF file named outfile.sdf after removing duplicate molecules.

基于多种2D指纹选择分子子集,使用MaxMin或可用的分层聚类方法,并将它们写入文件。RDKit中可用的Dice和Tanimoto相似性函数能够处理对应于IntVect和BitVect的指纹。然而,所有其他相似性函数都期望使用BitVect指纹来计算成对相似性。因此,对于AtomPairs、Morgan、MorganFeatures和TopologicalTorsions的相似性计算,使用ExplicitBitVect指纹代替默认的IntVect指纹。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。
输出文件名称。
指定划分数量。
利用最大最小距离(MaxMin)或分层聚类方法(Hierarchical Clustering)进行聚类,从而选择不同的分子子集类型。
用于计算分子间相似性的方法,有Tanimoto、Cosine以及Dice。
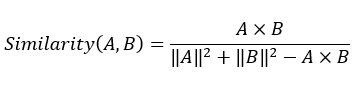
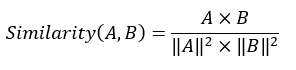
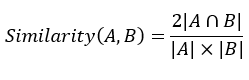
用于计算分子间相似性/距离的指纹。
按划分数量得到聚类结果,输出每个聚类中的第一个分子文件diverse_set.sdf。
The Diverse Subset module selects a subset of molecules based on multiple 2D fingerprints, using MaxMin or available hierarchical clustering methods, and writes them to a file. The Dice and Tanimoto similarity functions available in RDKit can handle fingerprints corresponding to IntVect and BitVect. However, all other similarity functions expect to use BitVect fingerprints to compute pairwise similarities. Therefore, for similarity calculations of AtomPairs, Morgan, MorganFeatures, and TopologicalTorsions, ExplicitBitVect fingerprints are used instead of the default IntVect fingerprints.
Small molecule structure file in SDF or SMILES format.
Name of the output file.
Specify the number of partitions.
Use MaxMin distance or hierarchical clustering to select different types of molecular subsets.
Methods used to calculate molecular similarity, including Tanimoto, Cosine, and Dice.
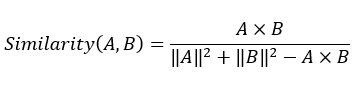
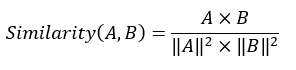
Fingerprints used to calculate molecular similarity/distance.
Cluster results are obtained based on the specified number of partitions, and the first molecule in each cluster is written to the file diverse_set.sdf.
Descriptors (RDKit)模块是计算分子的2D/3D描述符并将其写入SD或CSV/TSV文本文件中。2D描述符:Autocorr2D、MolWt、Ipc、NumRotatableBonds、qed等;3D描述符:Autocorr3D、RadiusOfGyration、Eccentricity等;以及FragmentCountOnly描述符:fr_Al_COO、fr_Al_OH、fr_Al_OH_noTert等。支持的输入文件格式为:Mol(.mol)、SD(.sdf、.sd)、SMILES(.smi、.txt、.csv、.tsv)。支持的输出文件格式为:SD文件(.sdf、.sd)、CSV/TSV(.csv、.tsv、.txt)。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。
输出文件以保存计算的描述符。
使用多进程处理(默认:yes)。
计算分子描述符的类型,可选值有2D、3D、FragmentCountOnly和Specify。
2D描述符包括以下:
Autocorr2D, BalabanJ, BertzCT, Chi0, Chi1, Chi0n - Chi4n, Chi0v - Chi4v, EState_VSA1 - EState_VSA11, ExactMolWt, FpDensityMorgan1, FpDensityMorgan2, FpDensityMorgan3, FractionCSP3, HallKierAlpha, HeavyAtomCount, HeavyAtomMolWt, Ipc, Kappa1 - Kappa3, LabuteASA, MaxAbsEStateIndex, MaxAbsPartialCharge, MaxEStateIndex, MaxPartialCharge, MinAbsEStateIndex, MinAbsPartialCharge, MinEStateIndex, MinPartialCharge, MolLogP, MolMR, MolWt, NHOHCount, NOCount, NumAliphaticCarbocycles, NumAliphaticHeterocycles, NumAliphaticRings, NumAromaticCarbocycles, NumAromaticHeterocycles, NumAromaticRings, NumHAcceptors, NumHDonors, NumHeteroatoms, NumRadicalElectrons, NumRotatableBonds, NumSaturatedCarbocycles, NumSaturatedHeterocycles, NumSaturatedRings, NumValenceElectrons, PEOE_VSA1 - PEOE_VSA14, RingCount, SMR_VSA1 - SMR_VSA10, SlogP_VSA1 - SlogP_VSA12, TPSA, VSA_EState1 - VSA_EState10, qed
FragmentCountOnly描述符包括以下:
fr_Al_COO, fr_Al_OH, fr_Al_OH_noTert, fr_ArN, fr_Ar_COO, fr_Ar_N, fr_Ar_NH, fr_Ar_OH, fr_COO, fr_COO2, fr_C_O, fr_C_O_noCOO, fr_C_S, fr_HOCCN, fr_Imine, fr_NH0, fr_NH1, fr_NH2, fr_N_O, fr_Ndealkylation1, fr_Ndealkylation2, fr_Nhpyrrole, fr_SH, fr_aldehyde, fr_alkyl_carbamate, fr_alkyl_halide, fr_allylic_oxid, fr_amide, fr_amidine, fr_aniline, fr_aryl_methyl, fr_azide, fr_azo, fr_barbitur, fr_benzene, fr_benzodiazepine, fr_bicyclic, fr_diazo, fr_dihydropyridine, fr_epoxide, fr_ester, fr_ether, fr_furan, fr_guanido, fr_halogen, fr_hdrzine, fr_hdrzone, fr_imidazole, fr_imide, fr_isocyan, fr_isothiocyan, fr_ketone, fr_ketone_Topliss, fr_lactam, fr_lactone, fr_methoxy, fr_morpholine, fr_nitrile, fr_nitro, fr_nitro_arom, fr_nitro_arom_nonortho, fr_nitroso, fr_oxazole, fr_oxime, fr_para_hydroxylation, fr_phenol, fr_phenol_noOrthoHbond, fr_phos_acid, fr_phos_ester, fr_piperdine, fr_piperzine, fr_priamide, fr_prisulfonamd, fr_pyridine, fr_quatN, fr_sulfide, fr_sulfonamd, fr_sulfone, fr_term_acetylene, fr_tetrazole, fr_thiazole, fr_thiocyan, fr_thiophene, fr_unbrch_alkane, fr_urea
3D描述符包括以下:
Asphericity, Autocorr3D, Eccentricity, GETAWAY, InertialShapeFactor, MORSE, NPR1, NPR2, PMI1, PMI2, PMI3, RDF, RadiusOfGyration, SpherocityIndex, WHIM
此选项仅在Type为“Specify”时使用。当应用多个描述符时,由逗号分隔描述符,如MolWt, qed。
得到各个分子指定描述符的数值在descriptors.csv文件中。
The Descriptors (RDKit) module calculates 2D/3D descriptors of molecules and writes them to an SD or CSV/TSV text file. 2D descriptors include Autocorr2D, MolWt, Ipc, NumRotatableBonds, qed, etc.; 3D descriptors include Autocorr3D, RadiusOfGyration, Eccentricity, etc.; and FragmentCountOnly descriptors include fr_Al_COO, fr_Al_OH, fr_Al_OH_noTert, etc. Supported input file formats are: Mol (.mol), SD (.sdf, .sd), SMILES (.smi, .txt, .csv, .tsv). Supported output file formats are: SD files (.sdf, .sd), CSV/TSV (.csv, .tsv, .txt).
Small molecule structure file in SDF or SMILES format.
File to save the calculated descriptors.
Use multiprocessing for computation (default: yes).
Type of molecular descriptors to compute, options are 2D, 3D, FragmentCountOnly, and Specify.
2D descriptors include the following:
Autocorr2D, BalabanJ, BertzCT, Chi0, Chi1, Chi0n - Chi4n, Chi0v - Chi4v, EState_VSA1 - EState_VSA11, ExactMolWt, FpDensityMorgan1, FpDensityMorgan2, FpDensityMorgan3, FractionCSP3, HallKierAlpha, HeavyAtomCount, HeavyAtomMolWt, Ipc, Kappa1 - Kappa3, LabuteASA, MaxAbsEStateIndex, MaxAbsPartialCharge, MaxEStateIndex, MaxPartialCharge, MinAbsEStateIndex, MinAbsPartialCharge, MinEStateIndex, MinPartialCharge, MolLogP, MolMR, MolWt, NHOHCount, NOCount, NumAliphaticCarbocycles, NumAliphaticHeterocycles, NumAliphaticRings, NumAromaticCarbocycles, NumAromaticHeterocycles, NumAromaticRings, NumHAcceptors, NumHDonors, NumHeteroatoms, NumRadicalElectrons, NumRotatableBonds, NumSaturatedCarbocycles, NumSaturatedHeterocycles, NumSaturatedRings, NumValenceElectrons, PEOE_VSA1 - PEOE_VSA14, RingCount, SMR_VSA1 - SMR_VSA10, SlogP_VSA1 - SlogP_VSA12, TPSA, VSA_EState1 - VSA_EState10, qed
FragmentCountOnly descriptors include the following:
fr_Al_COO, fr_Al_OH, fr_Al_OH_noTert, fr_ArN, fr_Ar_COO, fr_Ar_N, fr_Ar_NH, fr_Ar_OH, fr_COO, fr_COO2, fr_C_O, fr_C_O_noCOO, fr_C_S, fr_HOCCN, fr_Imine, fr_NH0, fr_NH1, fr_NH2, fr_N_O, fr_Ndealkylation1, fr_Ndealkylation2, fr_Nhpyrrole, fr_SH, fr_aldehyde, fr_alkyl_carbamate, fr_alkyl_halide, fr_allylic_oxid, fr_amide, fr_amidine, fr_aniline, fr_aryl_methyl, fr_azide, fr_azo, fr_barbitur, fr_benzene, fr_benzodiazepine, fr_bicyclic, fr_diazo, fr_dihydropyridine, fr_epoxide, fr_ester, fr_ether, fr_furan, fr_guanido, fr_halogen, fr_hdrzine, fr_hdrzone, fr_imidazole, fr_imide, fr_isocyan, fr_isothiocyan, fr_ketone, fr_ketone_Topliss, fr_lactam, fr_lactone, fr_methoxy, fr_morpholine, fr_nitrile, fr_nitro, fr_nitro_arom, fr_nitro_arom_nonortho, fr_nitroso, fr_oxazole, fr_oxime, fr_para_hydroxylation, fr_phenol, fr_phenol_noOrthoHbond, fr_phos_acid, fr_phos_ester, fr_piperdine, fr_piperzine, fr_priamide, fr_prisulfonamd, fr_pyridine, fr_quatN, fr_sulfide, fr_sulfonamd, fr_sulfone, fr_term_acetylene, fr_tetrazole, fr_thiazole, fr_thiocyan, fr_thiophene, fr_unbrch_alkane, fr_urea
3D descriptors include the following:
Asphericity, Autocorr3D, Eccentricity, GETAWAY, InertialShapeFactor, MORSE, NPR1, NPR2, PMI1, PMI2, PMI3, RDF, RadiusOfGyration, SpherocityIndex, WHIM
This option is only used when Type is “Specify.” When applying multiple descriptors, separate them by commas, e.g., MolWt, qed.
The numerical values of the specified descriptors for each molecule are stored in the descriptors.csv file.

PAINS Filter模块通过SMARTS子结构规则来搜索输入文件中假阳性化合物(Pan-assay Interference molecules,PAINS),并将符合条件的分子输出或者统计过滤分子的数量。
小分子结构文件,SDF或者SMILES格式。
输出文件名称。
是否使用多进程进行计算,可选:yes或者no,默认为yes。
输出文件包含与PAINS匹配的分子,可选:yes或者no,默认为no。
输出结果包括:
| 输出文件名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| output.sdf | 筛选出不匹配PAINS规则的化合物 |
| output_Filtered.sdf | 筛选出匹配PAINS规则的化合物 |
The PAINS Filter module searches for false positive compounds (Pan-assay Interference molecules, PAINS) in the input file using SMARTS substructure rules and either outputs or counts the molecules that meet the criteria.
Small molecule structure file in SDF or SMILES format.
Name of the output file.
Whether to use multiprocessing for computation, options: yes or no, default is yes.
Whether the output file includes molecules that match PAINS, options: yes or no, default is no.
The output includes:
| Output File Name | Description |
|---|---|
| output.sdf | Compounds that do not match the PAINS rules |
| output_Filtered.sdf | Compounds that match the PAINS rules |

File是用于指定输入文件的模块,可用于多个模块的统一输入。
上传小分子结构文件(SDF格式)或者蛋白的结构文件(PDB格式)
输出重命名后的文件。
The File module is used to specify input files and can be used for unified input across multiple modules.
Upload a small molecule structure file (SDF format) or a protein structure file (PDB format).
Output the file after renaming.

SDF File是一个用于指定SDF文件的模块,可用于其他模块的输入。
小分子结构文件,SDF
得到一个与原文件相同的SDF文件
The SDF File module is used to specify an SDF file that can be used as input for other modules.
Small molecule structure file in SDF format.
Obtain an SDF file identical to the original file.

PDB文件是一个用于指定PDB文件的模块,可用于其他模块的输入。
Protein structure file in PDB format
得到PDB文件
The PDB File module is used to specify a PDB file that can be used as input for other modules.
Protein structure file in PDB format.
Obtain a PDB file.